Abstract
Background and Objectives
Valuing children’s health states for use in economic evaluations is globally relevant and is of particular relevance in jurisdictions where a cost-utility analysis is the preferred form of analysis for decision making. Despite this, the challenges with valuing child health mean that there are many remaining questions for debate about the approach to elicitation of values. The aim of this paper was to identify and describe the methods used to value children’s health states and the specific issues that arise in the use of these methods.
Methods
We conducted a systematic search of electronic databases to identify studies published in English since 1990 that used preference elicitation methods to value child and adolescent (under 18 years of age) health states. Eligibility criteria comprised valuation studies concerning both child-specific patient-reported outcome measures and child health states defined in other ways, and methodological studies of valuation approaches that may or may not have yielded a value set algorithm.
Results
A total of 77 eligible studies were identified from which data on country setting, aims, condition (general population or clinically specific), sample size, age of respondents, the perspective that participants were asked to adopt, source of values (respondents who completed the preference elicitation tasks) and methods questions asked were extracted. Extracted data were classified and evaluated using narrative synthesis methods. The studies were classified into three groups: (1) studies comparing elicitation methods (n = 30); (2) studies comparing perspectives (n = 23); and (3) studies where no comparisons were presented (n = 26); selected studies could fall into more than one group. Overall, the studies varied considerably both in methods used and in reporting. The preference elicitation tasks included time trade-off, standard gamble, visual analogue scaling, rating/ranking, discrete choice experiments, best-worst scaling and willingness to pay elicited through a contingent valuation. Perspectives included adults’ considering the health states from their own perspective, adults taking the perspective of a child (own, other, hypothetical) and a child/adolescent taking their own or the perspective of another child. There was some evidence that children gave lower values for comparable health states than did adults that adopted their own perspective or adult/parents that adopted the perspective of children.
Conclusions
Differences in reporting limited the conclusions that can be formed about which methods are most suitable for eliciting preferences for children’s health and the influence of differing perspectives and values. Difficulties encountered in drawing conclusions from the data (such as lack of consensus and poor reporting making it difficult for users to choose and interpret available values) suggest that reporting guidelines are required to improve the consistency and quality of reporting of studies that value children’s health using preference-based techniques.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
We investigated methods used to value children’s health states and the specific considerations required in the use of these methods through a systematic review of the literature. |
Studies included in the review used a range of preference elicitation methods such as standard gamble, time-trade off, discrete choice modelling, best-worst scaling and visual analogue scales, with and without modification, for different sources of values (who was asked, children or adults or both) and perspectives (point of view that participants were asked to consider). |
Deficiencies in reporting made it difficult to compare studies; we recommend the development of guidelines for the design, conduct and reporting of studies in this area. |
1 Introduction
There is worldwide interest in how resource allocation decisions can be made around interventions that affect children, and the need to assess the value of the health outcomes they provide in a way that allows for a robust economic evaluation using a cost-utility analysis [1]. Patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) are widely accepted and used in adult populations for directly measuring health status, quality of life and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) [2]. There are specific challenges, though, in valuing HRQoL for children and adolescents, an important requirement for an economic evaluation using a cost-utility analysis [1, 3]. There are ethical challenges in asking children to engage in valuation tasks, particularly tasks that allow for anchoring of values on a full health to dead scale, as is required for estimation of quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). Preference elicitation methods need to accommodate the different ages and stages of children’s development, and take account of differences in the ways that children perceive their health and health outcomes compared with adults [1].
Elicitation techniques are defined here as the use of stated preference tasks to obtain weights (often referred to as utilities, values or QALY weights) for health states, where health states might be defined by bespoke health state descriptions or vignettes or by the items (dimensions and levels) measured in HRQoL instruments [2]. The term ‘values’ will be used throughout to encapsulate preference weights (often referred to as utilities, values or QALY weights). The ways in which values can be derived varies and may include time trade-off (TTO), standard gamble (SG), visual analogue scale (VAS), rating/ranking, discrete choice experiments (DCEs), best-worst scaling (BWS) and willingness to pay (WTP) elicited through contingent valuation methods (referred simply as WTP from here) [2]. Time trade-off and SG can be modified to take quite different forms, and DCEs can be designed to provide only latent scale values or, with the addition of duration as an attribute or by including comparisons with ‘dead’, to allow the weights to be anchored on a full health to dead scale (where full health has a value of 1 and dead has a value of 0). The techniques of TTO and SG ask participants to value health states by observing their willingness to trade quality of life with duration or risk, respectively; whereas, DCE and BWS techniques ask participants to choose between two or more multi-attribute scenarios, each describing a health state and to make a judgement between them based on preferences. When valuing adult health states, adults are typically asked to value based on their own perspective (i.e. how they would perceive the trade-offs for themselves in that health state, even if it is a hypothetical health state). The additional complexity with valuing children’s health is that the respondent not only has to imagine the health state, but may also need to imagine experiencing that health state at a different age and then undertake the valuation [4]. Thus, there are both practical and normative judgements involved in asking adults or children/adolescents to value child/adolescent health. Perspectives may include adults imagining themselves as a child experiencing the health state, imagining their own child (as a parent) or imagining a hypothetical child. Additionally, the age of the imagined child may vary if not specified (which can affect perceptions and preferences). We do not know how valuation differs across the spectrum of a hypothetical child’s age or how values change with variation in childhood age.
A range of PROMs has been developed for use in children and adolescents, and value sets have been produced for some of these from which utility values can be derived [5]. Patient-reported outcome measures with value sets for children include the 16D [6], the 17D [7], the Adolescent Health Utility Measure (AHUM) [8], the adolescent version of the Assessment of Quality of Life (AQoL-6D Adolescent) [9], the Child Health Utility instrument (CHU9D) [10], the youth version of the EQ-5D (EQ-5D-Y) [11], the Health Utilities Index Mark 2 (HUI2) [12] and Mark 3 (HUI3) [13], the Quality of Well Being Self-Administered (QWB-SA) scale [14] and the Infant health-related Quality of life Instrument (IQI) [15], each of which covers different age groups and domains. For health technology assessment guidelines internationally, there are a wide range of recommendations about which PROMs to use in economic evaluations of paediatric interventions [16, 17]. In part, the lack of consensus about which PROMs are preferred is due to the lack of good comparative psychometric evidence on the performance of the available instruments across disease areas and paediatric populations, and this is an area of ongoing research [18].
Previous reviews have described the measurement characteristics of children’s generic multidimensional PROMs accompanied by preference-based value sets [5, 19, 20]; however, information on the elicitation methods and perspectives used to obtain these values is lacking. In addition to these value sets for childhood PROMs, other valuation research includes methodological studies, and studies aimed at valuing specific vignettes or scenarios concerning child health. To date, there has been no review of the valuation methods used across these various study types. The aim of the current review, therefore, was to: (i) identify what elicitation techniques have been used to value children’s health states (including the valuation task, the sample, the perspective taken for the task and, where relevant, the age of the child whose health is being valued) and (ii) describe the methodological issues specific to valuing child health states (e.g. due to perspective) that have been explored empirically.
2 Methods
A systematic search strategy was used to identify suitable studies for the review. As sourcing methodological information was the main aim, a “systematic search and review” approach was used [21]. This approach is suitable for understanding what is known on a subject and making recommendations for practice and is combined with a comprehensive search strategy. A detailed protocol was developed and agreed on by the authors prior to the searches and adhered to throughout. PROSPERO registration was published on 19/03/2021 (Registration number: CRD42021236494). We define children and adolescents as persons aged under 18 years. For distinctions between the two terms, we relied on the definitions as stated individually by the included studies. The definition of under 18 years was used in this review as this is a commonly accepted age range in many countries worldwide for a child or adolescent; we acknowledge that this is not the case in some countries.
2.1 Information Sources
Five databases were searched: EMBASE, MEDLINE and PsychInfo via Ovid, Econlit and CINAHL via EBSCO. These databases have previously been recommended as suitable for systematic reviews of economic studies in health [22]. The search strategy was based on the following elements: (1) HRQoL studies and childhood PROMs (what was being valued); (2) elicitation techniques (how it was valued); and (3) a sample from which values were sought for childhood and adolescent health states (under 18 years of age) [who valued it]. The searches were performed on 15 March, 2021. Search terms are presented in Table S1 of the Electronic Supplementary Material (ESM). Additional records were identified by authors in the course of their everyday work.
2.2 Eligibility Criteria
Papers were included if they were published in English from 1 January, 1990 in a peer-reviewed journal, were experimental studies (quantitative or mixed methods) using preference elicitation methods for child health states (under 18 years of age), and concerned with the valuation of PROMs or addressed methodological questions about preference elicitation and valuation. Studies that included the perspective of a child, the perspective of an adult about a child, any preference-based valuation of a child-specific health-related quality-of-life instrument or vignettes for specific diseases were included. Exclusion criteria were studies not published in English, all studies published prior to 1990, publications not in peer-reviewed journals (such as theses/dissertations, conference presentations, abstract only and grey literature), valuation of adult health states and papers on the measurement but not valuation of PROMs.
2.3 Study Selection and Data Extraction
Studies were selected following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) reporting guidelines [23]. Publications were screened using the referencing program Rayyan [24]. Titles and abstracts were screened against the inclusion/exclusion criteria by CB, MH, RR and AS. Papers that potentially met the inclusion criteria were accessed in full text and discussed by at least two of the four reviewers against the inclusion/exclusion criteria. Differences in assessment were resolved through discussion and consensus by the four members of the screening team. Papers excluded at the full-text stage are presented in Table S2 of the ESM. Data extraction was performed for the following categories: study, country, title, aims, condition, sample size and age, whose perspective (the point of view that the participant was asked to consider), whose values (who completed the task), values obtained and methods questions asked. Ten percent of the papers were double extracted. When reported, the utility values (0 dead, 1 full health) were extracted and summarised. In some studies, results were expressed as QALYs without underlying utility values. In these cases, the QALY results were extracted as the basis for comparisons. Extraction of results focussed on data relevant to our stated aims, particularly highlighting methodological issues. Results in relation to a specific condition, instrument or comparison of instruments have not been reported. A formal quality assessment was not conducted, as the primary purpose was to investigate the features of the approaches and methods based on the methodological details reported in the studies. Whilst some outcome data were extracted and reported, given the heterogeneity of conditions and health states addressed these data do not provide a basis to support one method over another. Furthermore, there are no appropriate frameworks or guidelines that enable a meaningful assessment of the varied study types, designs and outcomes.
2.4 Analysis
Data were analysed through a narrative synthesis. Data were presented in separate tables for three groups of studies: (1) those comparing elicitation methods; (2) those comparing perspectives and (3) those with no comparisons presented. Groups 1 and 2 were not mutually exclusive. These categories were chosen so that we could compare methods (Group 1) and perspectives (Group 2). Within the studies included in Group 2, we compared perspectives in three categories: (a) child/adolescents’ own perspective, compared to adult/parent values taking the perspective of the child/adolescent, (b) child/adolescents’ own perspective, compared to adult/parents’ own perspective and (c) adult/parents’ own perspective, compared to adult/parent values taking the perspective of a child/adolescent. Tables were constructed for each group from the extracted data and are presented in Tables S3–S5 of the ESM.
3 Results
Including articles sourced through the databases and additional records identified by the authorship group, and after duplicates were removed, we double screened the titles, abstracts and keywords of 1311 papers (CB, MH, RR). Of these, 110 were retained for full-text screening and 77 were included for data extraction (CB, MH, RR, AS), as shown in Fig. 1. There were 30 studies included in Group 1 (comparisons between different elicitation methods), 23 studies in Group 2 (comparison between perspectives) and 26 studies in Group 3 (papers where a single method, measure or perspective was studied, and no comparisons were made). Two papers met the criteria for both groups 1 and 2 [25, 26]. The PROMs examined included variants of the HUI [12, 27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43], as well as the CHU9D [10, 44,45,46,47,48,49,50], the EQ-5D-Y [11, 51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61] and the AQoL-6D [9]. In one paper [46], young adults valued their own health; we included this study because its main aim was to obtain values for re-scaling (anchoring) the CHU9D value set for adolescents).
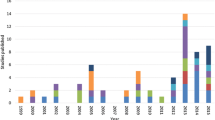
In terms of elicitation methods used across all 77 studies, the application of methods has changed over time as new methods have emerged. Standard gamble has been used regularly since 1996, but thefrequency of use has decreased since a peak in the mid-2000s, while TTO has been used regularly since 2003. Discrete choice experiments first appeared in published reports in this field in 2011 [49] and have become increasingly popular in recent years. Best-worst scaling was first reported in the same paper in 2011 [49], but there have been relatively few papers using BWS since then. Frequency of reporting of the elicitation methods over time is presented in Fig. 2.
3.1 Comparisons Between Different Elicitation Methods (Group 1)
There were 30 studies that compared alternative methods for eliciting preferences for child HRQoL. Table S3 of the ESM contains information on country, study title, aims, health conditions, sample size and age, perspective adopted (the point of view that the participant was asked to consider), source of values (who completed the task) and information on values. Three studies were from Australia [37, 38, 49], seven from Canada [27, 32, 34, 36, 42, 43, 62], one from Canada and Kenya [59], one from Canada and the USA [41], one from Iran [63], one from Singapore [64], three from the UK [10, 65, 66] and 13 from the USA [26, 28, 39, 67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76]. Elicitation methods used included TTO [26,27,28, 36, 38, 39, 46, 49, 52, 59, 62,63,64, 67,68,69,70,71,72, 74], SG [10, 27, 32, 36, 39, 41,42,43, 46, 49, 62,63,64, 67, 69, 72,73,74, 76], VAS, [26, 27, 32, 36, 38, 39, 41, 42, 52, 59, 62, 63, 67, 69, 73, 76] rating/ranking scale [59], DCEs [49, 52, 65, 68], BWS [49, 65] and WTP [68, 70, 71, 75]. Six (20%) studies [10, 46, 49, 52, 72, 74] were focused on elicitation of values for child health states defined by generic PROMs, with the remainder focused on a range of acute and chronic conditions. The perspective of the studies was highly variable, from consideration of very broad age groups to narrowly defined ages, such as ‘a 10-year-old’. Where available, values were extracted for each elicitation method and are presented in Table 1.
In terms of the reporting of the elicitation techniques over time across 30 studies from Group 1, TTO has been used regularly from 1996 to 2021, as have the SG and VAS. Best-worst scaling was used in studies in 2011 [49] and 2021 [65] and DCEs were reported in 2013 [68], 2020 [52] and 2021 [65]. Other than changes in the use of elicitation methods over time, there were no consistent patterns in the reported values between the different elicitation methods. Of note, there were also variations in approaches taken within each of the elicitation methods, which potentially limits our ability to compare results between methods. One example of this was in three studies in which a modified SG task was presented [27, 36, 73]. In the task, respondents were asked to consider a jar of black and white pills, which represented an instant cure (white pills), and instant painless death (black pills); parents were asked whether they would take a pill from a jar containing a mix of pills with varying proportions of black and white, i.e. changing the probability that selecting a pill will result in instant cure or instant death and give it to their child [36]. Another interesting example was the ‘parental TTO’, where the poor health state was experienced by the child, but the length of life in full health being traded off was that of the parent [77]. Methodological questions explored in studies included comparisons between elicitation methods [39, 41, 46], whether the order of the valuation technique matters [72], the extent of participant understanding of the technique [65] and comparing conventional SG to a modified SG [36]. There was substantial variation in the application of specific methods, in particular for SG and TTO, including modifications such as avoiding the use of death as an endpoint. In some cases, this reflected the non-fatal nature of the condition being assessed (e.g. tooth decay [65]), in others, it was to limit potential distress for the children participating. [36, 45]
3.2 Comparison Between Perspectives (Group 2)
Twenty-three studies compared values from different perspectives: one from Australia [47], one from Australia and Spain [78], four from Canada [27, 35, 40, 79], two from Europe [54, 55], one from the UK and Europe [80], three from the UK alone [52, 57, 58] and 11 from the USA [25, 26, 28, 31, 67, 77, 81,82,83,84,85]. Table S4 of the ESM contains detailed information on the country, title, aims, target condition, sample size and age, perspective and values for each study.
Thirteen studies included values from the adults’ own perspective [28, 47, 52, 54,55,56,57, 78, 80,81,82, 84, 85], nine studies included values from the adolescent’s own perspective [26, 31, 35, 47, 78, 81, 82, 84], six studies included values from the child’s own perspective [27, 28, 54, 67, 80, 85], and two studies included values from the parent’s own perspective [35, 77]. Eight studies included values from the perspective of an adult valuing for the child [25, 52, 55, 56, 58, 78, 83, 85, 86], and four studies included values from the parent valuing for the child, [28, 40, 57, 67]. No studies included values from the perspective of an adult valuing for an adolescent, seven studies included values from the parent valuing for the adolescent [26, 27, 31, 57, 79, 83, 84] and two studies included values from healthcare providers on behalf of children [35, 79]. Health conditions that were considered for valuation were highly varied, with some samples including participants with specific conditions and some covering health states described by a generic instrument; these differences may have influenced observed differences in values. The elicitation tasks used in the Group 2 studies were predominantly VAS, SG and TTO with only five studies (21%) [47, 52, 58, 78, 81] using a DCE or BWS.
Five studies compared child/adolescent own values with adult/parent values for children (Table 2a). In four of these studies, children/adolescents provided lower values than those provided by adults/parents valuing the child/adolescent health state (type 1 diabetes [28], type 2 diabetes or the risk thereof [31], pelvic inflammatory disease in adolescent girls [26] and generic health states [54]). In only one study in this group (children with cancer) were the child’s own values higher than those provided by adult/parent proxies [27].
Of the five studies comparing child/adolescent’s own to adult/parents’ own values, three studies displayed higher values for adult/parents’ own values compared with child/adolescent values (history of extremely low birth weight [35], allergic rhino-conjunctivitis [80] and vision loss [82]). In one study, children estimated their own values higher than adults rated their own values for type 1 diabetes [28], and in one study there was no clear difference between the values of adolescents and adults’ own values over a range of health states [47] (Table 2b).
When adult/parents’ own values were compared to adult/parent values for the child/adolescent, in three of six studies, adult/parents’ own values were higher than adult/parent values for the child/adolescent (type 1 diabetes [57], autism spectrum disorders [77] and congenital differences of sex development [25]). Another three studies found the opposite, with adults’ own values being lower than adult values for the child [52, 54, 55] (all three studies investigated a range of health states and were not condition specific). Differences noted in two studies [52, 55] may have been related to the anchoring of the lowest health state (in one of these studies, the differences were only small, and significance was unclear [55]). These two studies also allowed for health states to be considered to be worse than being dead (values less than zero), which may have impacted on the comparability of the values (Table 2c). We were unable to ascertain whether values less than zero were allowed in many of the studies, as shown in Table 2. Eight studies [40, 58, 67, 78, 79, 81, 83, 84] did not fall into any of the above comparison categories (Table 2d).
3.3 Single Elicitation Methods Used, No Comparisons Made (Group 3)
There were 27 papers where no comparisons between elicitation methods or perspectives were made. Of these, three were from Australia [45, 48, 87], three from Canada [12, 33, 88], one from China [44], one from Japan [53], three from the Netherlands [30, 50, 61], one from New Zealand [9], one from Slovenia [60], five from the UK [8, 29, 89,90,91], seven from the USA [11, 51, 92,93,94,95,96] and two multi-country studies [15, 97]. Elicitation techniques used in studies in the group included TTO [8, 9, 44, 48, 53, 60, 91,92,93], (note that in some studies TTO was used to anchor the DCEs or BWS and not for comparative purposes), SG, [12, 29, 33, 88,89,90, 94, 95], VAS [9, 12, 30, 61, 89, 91] WTP [92, 93], BWS [44, 45, 48] and DCEs [11, 15, 50, 53, 60, 87, 96, 97] (some studies used more than one technique). Table S5 of the ESM contains study, country, title, aims, condition, sample size and age, perspective and information on values.
Standard gamble was used extensively in earlier papers (1996–2005 [12, 33, 88,89,90, 94]) and only once after 2005 (in 2019) [95]. Time trade-off has been used regularly from 2005 to 2021 [8, 9, 11, 44, 47, 53, 60, 92, 93]. Visual analogue scale was also used regularly over time [9, 12, 30, 61, 89, 91]. Best-worst scaling was used in 2012 [45], 2016 [47] and 2019 [44]. Discrete choice experiments were used from 2016 onwards [15, 50, 51, 53, 60, 87, 96, 97]. Health states being valued were variable, with 14 (52%) being generic and the remainder covering a range of acute, chronic and behavioural conditions. Similarly, where adult preferences were being elicited, perspectives varied from wide age groups to a specific age and values included child, parents and adult representatives of the general public, with no clear patterns between the values obtained from different perspectives. Reported values or utility decrements (when possible) are included in Table 3 as these reflect variations in perspective, values and elicitation methods (comparison of values between conditions is not meaningful here).
4 Discussion
The valuation of child health is key to conducting economic evaluations to inform decisions on the reimbursement and pricing of health interventions for children. Previous reviews have investigated the measurement of child PROMs [5, 19]. In the current review, we have focused on valuation approaches. Whilst the processes of valuing health in adults are generally well established, there is little agreement on how children’s health should be valued. Despite there being several generic PROMS used for the valuation of child health interventions (such as the EQ-5D-Y and the CHU9D), this review shows that there are a range of fundamental uncertainties as to how the health states described by these instruments should be valued. These uncertainties include appropriate methods for preference elicitation, and the perspective and sources of values that should underpin the valuation of child health. The different approaches that have been used have led to diverse findings across methods.
Our review has shown a growing trend in the use of elicitation methods such as DCEs and BWS surveys, and this trend has also been noted in the adult literature [98]. The use of methods such as SG and TTO when valuing child health has been relatively consistent over time, with the use of SG decreasing since the mid-2000s. The current use of TTO is predominantly limited to anchoring DCE and BWS preferences to a utility scale (see Shah et al. [66]). There have, however, been a few studies that have undertaken comparative evaluations of elicitation methods (though we note that observing differences in outcomes between methods may not explain how consistent and valid these methods are). None of the 30 studies that compared elicitation methods included comparisons between valuations obtained from DCE/BWS-based methods and TTO/SG-based elicitation methods. The increasing use of DCE/BWS-type elicitation methods noted in our review may reflect a perception that these methods might be less challenging for children and adults than TTO and SG methods. Obtaining consent from ethics committees for DCE/BWS studies may be less problematic as there are no life/death trade-offs such as in TTO and SG. Furthermore, some methods may vary in applicability dependent on the complexity of the descriptive system. For instance, in a study on the CHU9D [49], researchers concluded that BWS was easier to manage than DCEs for larger descriptive systems, whereas for a more concise descriptive system such as the EQ-5D-Y, a DCE may be easier to present and complete. Given the heterogeneity of methods used between studies as well as the differing perspectives and values, a comparison of values between methods was not meaningful.
A wide range of perspectives (whose health state the participant is being asked to value) have been used. These include valuing one’s own health, others’ health including one’s own child or a hypothetical child of varying age. Likewise, there was variation in who was asked to value the health state including adults, adolescents and children representative of the general population or from selected groups. An example of the influence of perspective on values is shown in the study by Tejwani et al. [83] where utilities were lowest when caregivers made TTOs from their own lives, intermediate when time was traded from both the caregiver’s and child’s life, and highest when traded exclusively from the child’s life.
There was also evidence of the influence of condition on perspective from selected groups including children/adolescents with a particular condition, adults who had the condition as a child or parents of children where the condition was also relevant. Differences in utilities may be expected amongst those with and without a condition, whether from their own perspective or as a parent proxy given the different level of knowledge and experience of the condition [99]. Whilst the studies identified in this review include health states for generic and a range of chronic, acute, fatal and non-fatal conditions, it was not possible to discern the likely magnitude of the difference in utilities assigned by the general public and those with experience of the condition. Lloyd et al. [57] suggest that respondents’ perceptions of HRQoL impacts were not only influenced by the physical effects of a condition, but by external factors as well, such as patients with type 1 diabetes familiarity with needling and therefore reduced disutility for infusion therapy when compared with the general public. The influence of condition has also been shown in other contexts. [100]
Our review identified 23 studies where a comparison between perspectives (i.e. whose health state is being valued, own, other) can be made and these tended to suggest that children provide lower utilities than adults for the same health states (Group 2 studies, see Table 2). However, there was little discussion by study authors of the implications of this finding. Because of the mix of perspectives and values, it was not possible to evaluate possible bias in outcomes or the viability of the various methods for valuing child health. Furthermore, the preference elicitation tasks in these studies was dominated by TTO, SG and VAS. This limits the assessment of possible interactions between methods, particularly given the increasing use of DCEs and BWS. We were also unable to make any conclusions regarding feasibility (dropout rates, time taken to complete survey, difficulty of task) because of the very limited information presented in the included studies.
When adults are asked to value child health states, length of survival seems to be viewed as more important relative to quality of life than when adults are asked to value adult health states. This can be an issue for the comparability of these values and their use in economic evaluations [101], and it raises the question of whose values should be sought when valuing children’s health. An argument used in the valuation of adult health is that the adult general public, as taxpayers and potential beneficiaries from publicly funded healthcare, should be the source of valuations, and this argument is used by bodies such as the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence in England and Wales [102]. The same principle might be taken to suggest that the preferences of the adult general public should also determine values for child health states; however, children are also potential beneficiaries of healthcare services, and older children may contribute financially through the tax system. Generally, societies tend not view children as autonomous legal, social and economic agents. Legal distinctions are typically made between children and adults across a wide range of behaviours and responsibilities, for example in the areas of drinking, driving, voting and making contracts, with different age cut-offs often used for these different behaviours. However, given that older children (e.g., 16- to 17-year-olds) have been found to be able to provide reasonable responses to valuation exercises [78, 103], and, in many countries, a proportion of children in this age group have regular engagement in the workforce and may therefore also contribute to the public purse through income tax contributions, we raise the question about who should be considered the “general public”, and whether adolescents should be included in valuations for adults’ HRQoL? These normative issues impact on methods and need further exploration.
Another consideration arising from this review is that most of the PROMs available for measuring child HRQoL contain states that may or may not be considered to be worse than dead; however, whether and how the studies allowed for states worse than dead, and what the minimum value is that preference elicitation methods could in principle produce, was often absent or poorly described. Only ten of the 77 studies appeared to allow for values less than zero, with the majority anchoring values to 0 (death or worst health state relevant to non-fatal conditions) to 1 (full or best imaginable health). In only a few studies was it clearly stated how anchoring to dead was undertaken. As noted by Shah et al. [52], adults may value states that are perceived to be worse than dead (or very poor health states) differently for themselves than they do when acting as a proxy for children, reflecting an unwillingness to trade off length of life for children.
4.1 Strengths and Limitations
Interest from the research community, policy makers and practitioners in valuing child health states has grown rapidly in recent years and we are aware of several studies currently underway (particularly to value the EQ-5D-Y) and others currently being considered for publication that could be included in future reviews. Our review takes a snapshot of the current situation but this area is changing quickly, and the outcomes of these studies, and whether they provide any additional clarity to our research questions, will need to be tracked over time. The search strategy used was broadly based using subject headings (MESH) and text words aimed at identifying studies on quality of life in populations of children and young adults. Subject headings and text words were used to filter the broad search terms to identifying studies addressing methodological issues. Although the methods concepts and text words were broad, there remains a possibility that relevant published studies may have been missed if they were not indexed according to the subject headings and did not describe the methods used in the abstract and keywords that match the terms used in the methods filter. Papers were only included if published in English. We also note that we limited our data extraction to the information that was contained in the papers, and that no contact was made with authors.
Whilst our review has identified over 70 studies published since 1996 that address elicitation methods for the valuation child health states, we were not able to draw clear conclusions on methodological issues because of the ad hoc nature of research in this field and inadequate reporting of key details of the studies. There are several key questions that require focused and well-designed research programmes to address. Fundamental aspects that remain unanswered include the influence on health state valuations of differing perspectives, values and elicitation methods as well as methods for anchoring scales (particularly relevant to DCEs and BWS). In respect of the latter two methods, the evidence does not support one method over another, and there are many issues still unresolved or unreported. We also found that measures of feasibility such as time to completion, participant dropout or qualitative approaches such as think-aloud assessments or interviews were not reported. When specifically addressed, feasibility was generally described as being demonstrated by achieving valid/sensible results with no feasibility testing. This shortcoming is a feature of research in this area more generally; for instance, in a recent systematic where out of 110 versions of 89 PROMs specifically developed for children, only two included feasibility testing [5]. As noted by Rowen et al. [1], some of these questions (e.g. perspectives and values) are essentially a matter of judgement (i.e. normative); however, judgements about differences between alternate normative positions need to be informed by evidence. A further question that requires more research is how to measure which elicitation method might work best and in which circumstances (such as ease, cognitive burden and evidence of feasibility), which could not be determined from the findings in this review. The authors acknowledge that there are challenges and issues related to evaluating valuation studies and that this can lead to philosophical differences between researchers. The authors have aimed to make these issues clear, and to come to reasonable conclusions given the limitations of the data.
A major challenge that emerged from this review was the significant variation in what information was reported in the papers, as well as the varying amount of detail provided on the methods used to generate utility values. There is a clear need for standards of reporting that reflect the specific requirements of child health valuations [104]. A recent review by Zoratti et al. [105] has highlighted the need for reporting standards for adult health valuation studies. However, as child health valuation presents a range of additional challenges, there is a strong need for child-specific reporting standards. Without such standards, it is not possible to summarise collective evidence to support normative positions or standardised requirements for health state valuations to support policy. Given the importance of understanding valuation for child HRQoL, guidelines for reporting of future studies would be likely to improve the overall quality of publications and enhance the comparability of research results.
5 Conclusions
This review summarises available evidence for a range of research questions relevant to valuations of child health, including whose values and perspectives are most relevant and how best to address the methodological challenges. The use of elicitation methods has changed over time, with recent studies favouring methods such as DCEs; however, the literature provides few meaningful data as to which methods are preferable for obtaining values for child HRQoL. Differences in reporting limited the conclusions that could be formed. Difficulties encountered in drawing conclusions from the data suggest that reporting guidelines are required to improve the consistency and quality of reporting of studies that value children’s health using preference-based techniques.
References
Rowen D, Rivero-Arias O, Devlin N, Ratcliffe J. Review of valuation methods of preference-based measures of health for economic evaluation in child and adolescent populations: where are we now and where are we going? Pharmacoeconomics. 2020;38(4):325–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-019-00873-7.
Brazier J, Ratcliffe J, Saloman J, Tsuchiya A. Measuring and valuing health benefits for economic evaluation. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2017.
Ungar WJ. Challenges in health state valuation in paediatric economic evaluation: are QALYs contraindicated? Pharmacoeconomics. 2011;29(8):641–52. https://doi.org/10.2165/11591570-000000000-00000.
Powell PA, Rowen D, Rivero-Arias O, Tsuchiya A, Brazier JE. Valuing child and adolescent health: a qualitative study on different perspectives and priorities taken by the adult general public. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021;19(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-021-01858-x.
Kwon J, Freijser L, Huynh E, et al. Systematic review of conceptual, age, measurement and valuation considerations for generic multidimensional childhood patient-reported outcome measures. Pharmacoeconomics. 2022;40(4):379–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-021-01128-0.
Apajasalo M, Sintonen H, Holmberg C, et al. Quality of life in early adolescence: a sixteen-dimensional health-related measure (16D). Qual Life Res. 1996;5(2):205–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00434742.
Apajasalo AM, Rautonen J, Holmberg C, et al. Quality of life in pre-adolescence: a 17-dimensional health-related measure (17D ). Qual Life Res. 1996;5(6):532–8.
Beusterien KM, Yeung JE, Pang F, Brazier J. Development of the multi-attribute adolescent health utility measure (AHUM). Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2012;10:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-10-102.
Moodie M, Richardson J, Rankin B, Iezzi A, Sinha K. Predicting time trade-off health state valuations of adolescents in four pacific countries using the assessment of quality-of-life (AQoL-6D) instrument. Value Health. 2010;13(8):1014–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4733.2010.00780.x.
Stevens K. Valuation of the child health utility 9D index. Pharmacoeconomics. 2012;30(8):729–47. https://doi.org/10.2165/11599120-000000000-00000.
Craig BM, Greiner W, Brown DS, Reeve BB. Valuation of child health-related quality of life in the United States. Health Econ. 2016;25:768–77. https://doi.org/10.1002/hec.3184.
Torrance GW, Feeny DH, Furlong WJ, Barr RD, Zhang Y, Wang Q. Multiattribute utility function for a comprehensive health status classification system: Health Utilities Index Mark 2. Med Care. 1996;34:702–22.
Feeny D, Furlong W, Torrance GW, et al. Multiattribute and single-attribute utility functions for the Health Utilities Index Mark 3 system. Med Care. 2002;40(2):113–28. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005650-200202000-00006.
Sieber W, Groessl E, David KM, Ganiats TG, Kaplan R. Quality of Well Being Self-Administered (QWB-SA) Scale: user ’s manual. 2008.
Krabbe PFM, Jabrayilov R, Detzel P, Dainelli L, Vermeulen KM, Van Asselt ADI. A two-step procedure to generate utilities for the infant health-related quality of life instrument (IQI). PLoS ONE. 2020;15(4):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0230852.
Kennedy-Martin M, Slaap B, Herdman M, et al. Which multi-attribute utility instruments are recommended for use in cost-utility analysis? A review of national health technology assessment (HTA) guidelines. Eur J Health Econ. 2020;21(8):1245–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-020-01195-8.
Hill H, Rowen D, Pennington B, Wong R, Wailoo A. A review of the methods used to generate utility values in NICE Technology Assessments for children and adolescents. Value Health. 2020;23(7):907–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2020.02.011.
Jones R, Mulhern B, McGregor K, et al. Psychometric performance of HRQoL measures: an Australian Paediatric Multi-Instrument Comparison Study Protocol (P-MIC). Children (Basel). 2021;8(8):714. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080714.
Janssens A, Thompson Coon J, Rogers M, et al. A systematic review of generic multidimensional patient-reported outcome measures for children, part I: descriptive characteristics. Value Health. 2015;18(2):315–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2014.12.006.
Khadka J, Kwon J, Petrou S, Lancsar E, Ratcliffe J. Mind the (inter-rater) gap. An investigation of self-reported versus proxy-reported assessments in the derivation of childhood utility values for economic evaluation: a systematic review. Soc Sci Med. 2019;240:112543. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2019.112543.
Grant MJ, Booth A. A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Info Libr J. 2009;26(2):91–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Thielen FW, Van Mastrigt GAPG, Burgers LT, et al. How to prepare a systematic review of economic evaluations for clinical practice guidelines: database selection and search strategy development (part 2/3). Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2016;16(6):705–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737167.2016.1246962.
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339: b2700. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2700.
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, Elmagarmid A. Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4.
Alkazemi MH, Johnston AW, Meglin D, Adkins D, Routh JC. Community perspectives on difference of sex development (DSD) diagnoses: a crowdsourced survey. J Pediatr Urol. 2020;16(3):384.e1-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpurol.2020.03.023.
Trent M, Lehmann HP, Qian Q, Thompson CB, Ellen JM, Frick KD. Adolescent and parental utilities for the health states associated with pelvic inflammatory disease. Sex Transm Infect. 2011;87(7):583–7. https://doi.org/10.1136/sextrans-2011-050187.
Sung L, Young NL, Greenberg ML, et al. Health-related quality of life (HRQL) scores reported from parents and their children with chronic illness differed depending on utility elicitation method. J Clin Epidemiol. 2004;57(11):1161–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2004.05.003.
Lee JM, Rhee K, O’Grady MJ, et al. Health utilities for children and adults with type 1 diabetes. Med Care. 2011;49(10):924–31. https://doi.org/10.1097/MLR.0b013e318216592c.
McCabe C, Stevens K, Roberts J, Brazier J. Health state values for the HUI 2 descriptive system: results from a UK Survey. Discussion paper. 2003. http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/74892. Accessed 3 May 2022.
Raat H, Bonsel GJ, Hoogeveen WC, et al. Feasibility and reliability of a mailed questionnaire to obtain visual analogue scale valuations for health states defined by the Health Utilities Index Mark 3. Med Care. 2004;42(1):13–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mlr.0000102297.06535.e7.
Rhodes ET, Prosser LA, Lieu TA, Songer TJ, Ludwig DS, Laffel LM. Preferences for type 2 diabetes health states among adolescents with or at risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Diabetes. 2011;12(8):724–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-5448.2011.00772.x.
Saigal S, Feeny D, Rosenbaum P, Furlong W, Burrows E, Stoskopf B. Self-perceived health status and health-related quality of life of extremely low-birth-weight infants at adolescence. J Am Med Assoc. 1996;276(6):453–9. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.276.6.453.
Saigal S, Rosenbaum PL, Feeny D, et al. Parental perspectives of the health status and health-related quality of life of teen-aged children who were extremely low birth weight and term controls. Pediatrics. 2000;105(3):569–74. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.105.3.569.
Saigal S, Stoskopf BL, Burrows E, Streiner DL, Rosenbaum PL. Stability of maternal preferences for pediatric health states in the perinatal period and 1 year later. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2003;157(3):261–9. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.157.3.261.
Saigal S, Stoskopf BL, Feeny D, et al. Differences in preferences for neonatal outcomes among health care professionals, parents, and adolescents. J Am Med Assoc. 1999;281(21):1991–7. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.281.21.1991.
Sung L, Greenberg ML, Young NL, et al. Validity of a modified standard gamble elicited from parents of a hospital-based cohort of children. J Clin Epidemiol. 2003;56(9):848–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0895-4356(03)00160-4.
Tong A, Tjaden L, Howard K, Wong G, Morton R, Craig JC. Quality of life of adolescent kidney transplant recipients. J Pediatr. 2011;159(4):670-5.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2011.04.007.
Tong A, Wong G, McTaggart S, et al. Quality of life of young adults and adolescents with chronic kidney disease. J Pediatr. 2013;163(4):1179-85.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.04.066.
Yi MS, Britto MT, Wilmott RW, et al. Health values of adolescents with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 2003;142(2):133–40. https://doi.org/10.1067/mpd.2003.51.
Barr RD, Petrie C, Furlong W, Rothney M, Feeny D. Health-related quality of life during post-induction chemotherapy in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in remission: an influence of corticosteroid therapy. Int J Oncol. 1997;11(2):333–9. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.11.2.333.
Brunner HI, Maker D, Grundland B, et al. Preference-based measurement of health-related quality of life (HRQL) in children with chronic musculoskeletal disorders (MSKDs). Med Decis Mak. 2003;23(4):314–22. https://doi.org/10.1177/0272989X03256008.
Ebrahim S, Parshuram C. Comparison of utility scores from the Visual Analog Scale and Health Utilities Index 3 in children following pediatric intensive care unit admission. J Child Health Care. 2015;19(1):53–62. https://doi.org/10.1177/1367493513496909.
Feeny D, Furlong W, Saigal S, Sun J. Comparing directly measured standard gamble scores to HUI2 and HUI3 utility scores: group- and individual-level comparisons. Soc Sci Med. 2004;58(4):799–809. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0277-9536(03)00254-5.
Chen G, Xu F, Huynh E, Wang Z, Stevens K, Ratcliffe J. Scoring the Child Health Utility 9D instrument: estimation of a Chinese child and adolescent-specific tariff. Qual Life Res. 2019;28(1):163–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-018-2032-z.
Ratcliffe J, Flynn T, Terlich F, Stevens K, Brazier J, Sawyer M. Developing adolescent-specific health state values for economic evaluation. Pharmacoeconomics. 2012;30(8):713–27. https://doi.org/10.2165/11597900-000000000-00000.
Ratcliffe J, Chen G, Stevens K, et al. Valuing Child Health Utility 9D health states with young adults: insights from a time trade off study. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2015;13(5):485–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40258-015-0184-3.
Ratcliffe J, Huynh E, Stevens K, Brazier J, Sawyer M, Flynn T. Nothing about us without us? A comparison of adolescent and adult health-state values for the child health utility-9d using profile case best–worst scaling. Health Econ. 2016;25:486–96. https://doi.org/10.1002/hec.3165.
Ratcliffe J, Huynh E, Chen G, et al. Valuing the Child Health Utility 9D: using profile case best worst scaling methods to develop a new adolescent specific scoring algorithm. Soc Sci Med. 2016;157:48–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2016.03.042.
Ratcliffe J, Couzner L, Flynn T, et al. Valuing child health utility 9D health states with a young adolescent sample: a feasibility study to compare best-worst scaling discrete-choice experiment, standard gamble and time trade-off methods. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2011;9(1):15–27. https://doi.org/10.2165/11536960-000000000-00000.
Rowen D, Mulhern B, Stevens K, Vermaire JH. Estimating a Dutch value set for the pediatric preference-based CHU9D using a discrete choice experiment with duration. Value Health. 2018;21(10):1234–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2018.03.016.
Craig BM, Brown DS, Reeve BB. Valuation of child behavioral problems from the perspective of us adults. Med Decis Mak. 2016;36(2):199–209. https://doi.org/10.1177/0272989X15594370.
Shah KK, Ramos-Goñi JM, Kreimeier S, Devlin NJ. An exploration of methods for obtaining 0 = dead anchors for latent scale EQ-5D-Y values. Eur J Health Econ. 2020;21(7):1091–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-020-01205-9.
Shiroiwa T, Ikeda S, Noto S, Fukuda T, Stolk E. Valuation survey of EQ-5D-Y based on the international common protocol: development of a value set in Japan. Med Decis Mak. 2021;41(5):597–606. https://doi.org/10.1177/0272989X211001859.
Kind P, Klose K, Gusi N, Olivares PR, Greiner W. Can adult weights be used to value child health states? Testing the influence of perspective in valuing EQ-5D-Y. Qual Life Res. 2015;24(10):2519–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-015-0971-1.
Kreimeier S, Oppe M, Ramos-Goñi JM, et al. Valuation of EuroQol Five-Dimensional Questionnaire, Youth Version (EQ-5D-Y) and EuroQol Five-Dimensional Questionnaire, Three-Level Version (EQ-5D-3L) health states: the impact of wording and perspective. Value Health. 2018;21(11):1291–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2018.05.002.
Lipman SA, Reckers-Droog V, Karimi M, Jakubczyk M, Attema A. Self vs. others, child vs. adult: an experimental comparison of valuation perspectives for valuation of EQ-5D-Y health states. Eur J Health Econ. 2021;22(9):1507–18.
Lloyd A, Swinburn P, Boye KS, et al. A valuation of infusion therapy to preserve islet function in type 1 diabetes. Value Health. 2010;13(5):636–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4733.2010.00705.x.
Mott DJ, Shah KK, Ramos-Goñi JM, Devlin NJ, Rivero-Arias O. Valuing EQ-5D-Y-3L health states using a discrete choice experiment: do adult and adolescent preferences differ? Med Decis Mak. 2021;41(5):584–96. https://doi.org/10.1177/0272989X21999607.
Poenaru D, Pemberton J, Frankfurter C, Cameron BH, Stolk E. Establishing disability weights for congenital pediatric surgical conditions: a multi-modal approach. Popul Health Metr. 2017;15(1):8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12963-017-0125-5.
Prevolnik Rupel V, Ogorevc M, Greiner W, Kreimeier S, Ludwig K, Ramos-Goni JM. EQ-5D-Y value set for Slovenia. Pharmacoeconomics. 2021;39(4):463–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-020-00994-4.
Retra JGA, Essers BAB, Joore MA, Evers SMAA, Dirksen CD. Age dependency of EQ-5D-Youth health states valuations on a visual analogue scale. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020;18(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-020-01638-z.
David C, Efanov JI, Borsuk DE. Utility outcome measures for the treatment of ameloblastomas during childhood. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021;9(1): e3311. https://doi.org/10.1097/gox.0000000000003311.
Shahjouei S, Vafaei Sadr A, Khorasani S, Nejat F, Habibi Z, Akbari SA. Utility measures in pediatric temporary health states: comparison of prone positioning valuation through 5 assessment tools. Value Health Reg Issues. 2019;18:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vhri.2019.01.003.
Saw SM, Gazzard G, Au Eong KG, Koh D. Utility values and myopia in teenage school students. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003;87(3):341–5. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.87.3.341.
Rogers HJ, Marshman Z, Rodd H, Rowen D. Discrete choice experiments or best-worst scaling? A qualitative study to determine the suitability of preference elicitation tasks in research with children and young people. J Patient Rep Outcomes. 2021;5(1):26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41687-021-00302-4.
Shah KL, Ramos-Goñi JM, Kreimeir S, Devlin NJ. Anchoring latent scale values for the EQ-5D-Y at 0 = Dead. 2020. https://www.ohe.org/publications/anchoring-latent-scale-values-eq-5d-y-0-dead#. Accessed 3 May 2022.
Dillman JR, Carlos RC, Smith EA, Davenport MS, De Matos MV, Adler J. Relationship of bowel MR imaging to health-related quality of life measures in newly diagnosed pediatric small bowel Crohn disease. Radiology. 2016;280(2):568–75. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2016151727.
Prosser LA, Payne K, Rusinak D, Shi P, Messonnier M. Using a discrete choice experiment to elicit time trade-off and willingness-to-pay amounts for influenza health-related quality of life at different ages. Pharmacoeconomics. 2013;31(4):305–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-013-0029-6.
Yi MS, Britto MT, Sherman SN, et al. Health values in adolescents with or without inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr. 2009;154(4):527–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2008.10.003.
Prosser L, Ray T, O’Brien M, Kleinman K, Santoli J, Lieu T. Preferences and willingness to pay for health states prevented by pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Pediatrics. 2004;113(2):283–90.
Chen CL, Kuppermann M, Caughey AB, Zane LT. A community-based study of acne-related health preferences in adolescents. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144(8):988–94. https://doi.org/10.1001/archderm.144.8.988.
Finnell SME, Carroll AE, Downs SM. The utility assessment method order influences measurement of parents’ risk attitude. Value Health. 2012;15(6):926–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2012.04.008.
Brunner HI, Klein-Gitelman MS, Miller MJ, et al. Health of children with chronic arthritis: relationship of different measures and the quality of parent proxy reporting. Arthritis Care Res. 2004;51(5):763–73. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.20689.
Carroll AE, Downs SM. Improving decision analyses: parent preferences (utility values) for pediatric health outcomes. J Pediatr. 2009;155(1):21-5.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.01.040.
Prosser LA, Bridges CB, Uyeki TM, et al. Values for preventing influenza-related morbidity and vaccine adverse events in children. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2005;3:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-3-18.
Chiou CF, Weaver MR, Bell MA, Lee TA, Krieger JW. Development of the multi-attribute Pediatric Asthma Health Outcome Measure (PAHOM). Int J Qual Health Care. 2005;17(1):23–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzh086.
Lavelle TA, Weinstein MC, Newhouse JP, Munir K, Kuhlthau KA, Prosser LA. Parent preferences for health outcomes associated with autism spectrum disorders. Pharmacoeconomics. 2019;37(4):541–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-019-00783-8.
Dalziel K, Catchpool M, García-Lorenzo B, Gorostiza I, Norman R, Rivero-Arias O. Feasibility, validity and differences in adolescent and adult EQ-5D-Y health state valuation in Australia and Spain: an application of best–worst scaling. Pharmacoeconomics. 2020;38(5):499–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-020-00884-9.
Ethier MC, Regier DA, Tomlinson D, et al. Perspectives toward oral mucositis prevention from parents and health care professionals in pediatric cancer. Support Care Cancer. 2012;20(8):1771–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-011-1274-x.
Retzler J, Grand TS, Domdey A, Smith A, Romano RM. Utility elicitation in adults and children for allergic rhinoconjunctivitis and associated health states. Qual Life Res. 2018;27(9):2383–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-018-1910-8.
Law EH, Pickard AL, Kaczynski A, Pickard AS. Choice blindness and health-state choices among adolescents and adults. Med Decis Mak. 2017;37(6):680–7. https://doi.org/10.1177/0272989X17700847.
Stevens W, Brown GC, Brown MM, Stein JD, Sharma S. Vision-related quality-of-life estimates in adolescent youths. Can J Ophthalmol. 2021;56(6):385–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcjo.2021.01.012.
Tejwani R, Wang H-HS, Lloyd JC, Kokorowski PJ, Nelson CP, Routh JC. Utility estimation for pediatric vesicoureteral reflux: methodological considerations using an online survey platform. J Urol. 2017;197(3):805–10.
Wasserman J, Aday LA, Begley CE, Ahn C, Lairson DR. Measuring health state preferences for hemophilia: development of a disease-specific utility instrument. Haemophilia. 2005;11(1):49–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2516.2005.01054.x.
Lavelle TA, Meltzer MI, Gebremariam A, Lamarand K, Fiore AE, Prosser LA. Community-based values for 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1 illnesses and vaccination-related adverse events. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(12): e27777. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0027777.
Kramer MG. Sanctuary in a residential treatment center: creating a therapeutic community of hope countering violence. Int J Ther Communities. 2016;37(2):69–83. https://doi.org/10.1108/TC-01-2015-0005.
Bahrampour M, Norman R, Byrnes J, Downes M, Scuffham PA. Utility values for the CP-6D, a cerebral palsy-specific multi-attribute utility instrument, using a discrete choice experiment. Patient. 2021;14(1):129–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40271-020-00468-x.
Juniper EF, Guyatt GH, Feeny DH, Griffith LE, Ferrie PJ. Minimum skills required by children to complete health-related quality of life instruments for asthma: comparison of measurement properties. Eur Respir J. 1997;10(10):2285–94. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.97.10102285.
Secnik K, Matza LS, Cottrell S, Edgell E, Tilden D, Mannix S. Health state utilities for childhood attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder based on parent preferences in the United Kingdom. Med Decis Mak. 2005;25(1):56–70. https://doi.org/10.1177/0272989X04273140.
Stevens KJ, Brazier JE, McKenna SP, Doward LC, Cork MJ. The development of a preference-based measure of health in children with atopic dermatitis. Epidemiol Health Serv Res. 2005;153:372–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06736.x.
Summerfield AQ, Lovett RES, Bellenger H, Batten G. Estimates of the cost-effectiveness of pediatric bilateral cochlear implantation. Ear Hear. 2010;31(5):611–24. https://doi.org/10.1097/AUD.0b013e3181de40cd.
Lee GM, Salomon JA, Gay C, Hammitt JK. Preferences for health outcomes associated with Group A Streptococcal disease and vaccination. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2010;8:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-8-28.
Lee GM, Salomon JA, LeBaron CW, Lieu TA. Health-state valuations for pertussis: methods for valuing short-term health states. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2005;3:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-3-17.
Matza LS, Secnik K, Rentz AM, et al. Assessment of health state utilities for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children using parent proxy report. Qual Life Res. 2005;14(3):735–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/pl00022070.
McElderry BM, Mueller EL, Garcia A, Carroll AE, Bennett WE. Parents of healthy children assign lower quality of life measure to scenarios labeled as cancer than to identical scenarios not labeled as cancer. BMC Psychol. 2019;7(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-019-0280-5.
Craig BM, Brown DS, Reeve BB. The value adults place on child health and functional status. Value Health. 2015;18(4):449–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2015.02.012.
Jabrayilov R, Vermeulen KM, Detzel P, Dainelli L, van Asselt ADI, Krabbe PFM. Valuing health status in the first year of life: the infant health-related quality of life instrument. Value Health. 2019;22(6):721–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2018.12.009.
Rowen D, Brazier J, Van Hout B. A comparison of methods for converting DCE values onto the full health-dead QALY scale. Med Decis Making. 2015;35(3):328–40. https://doi.org/10.1177/0272989X14559542.
Goodwin E, Davey A, Green C, Hawton A. What drives differences in preferences for health states between patients and the public? A qualitative investigation of respondents’ thought processes. Soc Sci Med. 2021;282(January): 114150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.114150.
Knox SA, Viney RC, Gu Y, et al. The effect of adverse information and positive promotion on women’s preferences for prescribed contraceptive products. Soc Sci Med. 2013;83:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2012.12.025.
Devlin N, Pan T, Sculpher M, et al. Using values for pediatric HRQoL in cost effectiveness analysis: challenges and potential solutions. Paper presented to the EuroQol Scientific Plenary Meeting; 22 September 2021.
NICE. Developing NICE guidelines: the manual. 2014. http://www.nice.org.uk/article/pmg20. Accessed 3 May 2022.
Mott DJ, Shah, Koonal K, Ramos-Goñi JM, Devlin NJ, Rivero-Arias O. Valuing EQ-5D-Y health states using a discreet choice experiment. 2019. https://www.ohe.org/publications/valuing-eq-5d-yhealth-states-using-discrete-choice-experiment-do-adult-and-adolescent. Accessed 3 May 2022.
Hollin IL, Craig BM, Coast J, et al. Reporting formative qualitative research to support the development of quantitative preference study protocols and corresponding survey instruments: guidelines for authors and reviewers. Patient. 2020;13(1):121–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40271-019-00401-x.
Zoratti MJ, Pickard AS, Stalmeier PFM, et al. Evaluating the conduct and application of health utility studies: a review of critical appraisal tools and reporting checklists. Eur J Health Econ. 2021;22(5):723–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-021-01286-0.
Acknowledgements
QUOKKA: Professor Kim Dalziel – University of Melbourne. Professor Harriet Hiscock – Murdoch Children’s Research Institute. TORCH: Assoc. Prof Alison Hayes – School of Public Health, University of Sydney. Professor Germaine Wong – School of Public Health, University of Sydney. Professor Cam Donaldson – Glasgow Caledonian University. Professor Stacey Carter – University of Wollongong.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by CAUL and its Member Institutions. QUOKKA is funded through the Medical Future Research Fund (Grant number: APP1200816); TORCH is funded through the Medical Future Research Fund (Grant number: APP1199902).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. We note that ND, RV, DJS, RN and BM are members of the EuroQol Group and that ND, RV, DJS, RN, JR, BM, EL and CB have received funding through the EuroQol Group for related research. ND is the Chair of the Board of the EuroQol Research Foundation.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Authors’ contributions
Conceptualization: ND, KH, RV, EL, CB, MH. Methodology: CB, MH. Formal analysis and investigation: CB, MH, RR, AS. Writing, original draft preparation: CB, MH. Writing, review and editing: all authors. Funding acquisition: ND, EL, BM, RN, JR, DJS, RV, GC, MH, SP, JC, JCC, EH, KH. Resources: not applicable. Supervision: not applicable.
Additional information
Members of the Quality of Life in Kids: Key Evidence to Strengthen Decisions in Australia (QUOKKA), Tools for Outcomes Research to Measure, Value Child Health (TORCH) Project Teams are listed in the Acknowledgement section at the end of the article.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Bailey, C., Howell, M., Raghunandan, R. et al. Preference Elicitation Techniques Used in Valuing Children’s Health-Related Quality-of-Life: A Systematic Review. PharmacoEconomics 40, 663–698 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-022-01149-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-022-01149-3