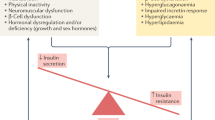
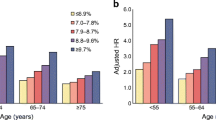
Abstract
The prevalence of diabetes in older adults is increasing worldwide and its management is complicated by the comorbidity, cognitive and psychosocial challenges associated with this population. An individualized and multipronged approach aiming to improve quality of life without intrusive and complicated interventions is recommended in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Medical complexity and functional status should be considered when introducing lifestyle modifications and selecting a pharmacological agent. Metformin remains the recommended first-line option (due to its efficacy, known cardioprotective effects, overall tolerance and affordability).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gandhi GY, Mooradian AD. Management of hyperglycemia in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Drugs Aging. 2022;39(1):39–58.
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th Edition. 2021. https://diabetesatlas.org/atlas/tenth-edition/. Accessed 30 Mar 2023.
Pham H, Marathe CS, Phillips LK, et al. Longitudinal changes in fasting and glucose-stimulated GLP-1 and GIP in healthy older subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104(12):6201–6.
Lee PG, Halter JB. The pathophysiology of hyperglycemia in older adults: clinical considerations. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(4):444–52.
DeFronzo RA. Insulin resistance, lipotoxicity, type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis: the missing links. The Claude Bernard Lecture 2009. Diabetologia. 2010;53(7):1270–87.
Sinclair A, Saeedi P, Kaundal A, et al. Diabetes and global ageing among 65–99-year-old adults: findings from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020;162:108078.
Weinger K, Beverly EA, Smaldone A. Diabetes self-care and the older adult. West J Nurs Res. 2014;36(9):1272–98.
Assar ME, Laosa O, Rodríguez ML. Diabetes and frailty. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2019;22(1):52–7.
Crandall J, Schade D, Ma Y, et al. The influence of age on the effects of lifestyle modification and metformin in prevention of diabetes. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2006;61(10):1075–8.
Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet. 1998;352(9131):854–65.
O’Hara DV, Parkhill TR, Badve SV, et al. The effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on kidney outcomes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021;23(3):763–73.
Bae JH, Kim S, Park EG, et al. Effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2019;34:1–80.
Kristensen SL, Rørth R, Jhund PS, et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(10):776–8.
Zannad F, Ferreira JP, Pocock SJ, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a meta-analysis of the EMPEROR-Reduced and DAPA-HF trials. Lancet. 2020;396(10254):819–29.
Shorr RI, Ray WA, Daugherty JR, et al. Individual sulfonylureas and serious hypoglycemia in older people. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996;44(7):751–5.
Oiknine R, Bernbaum M, Mooradian AD. A critical appraisal of the role of insulin analogues in the management of diabetes mellitus. Drugs. 2005;65(3):325–40.
Janka HU, Plewe G, Busch K. Combination of oral antidiabetic agents with basal insulin versus premixed insulin alone in randomized elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2007;55(2):182–8.
Hedrington MS, Davis SN. Considerations when using alpha-glucosidase inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2019;20(18):2229–35.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Authorship and conflict of interest
S. M. Hoy is a salaried employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature and declares no relevant conflicts of interest. All authors contributed to the review and are responsible for the article content.
Ethics approval, Consent to participate, Consent for publication, Availability of data and material, Code availability
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hoy, S.M. Take an individualized and multipronged approach when managing older adults with type 2 diabetes. Drugs Ther Perspect 39, 171–177 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-023-00991-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-023-00991-5