Abstract
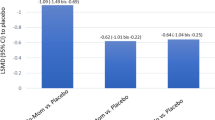
Olopatadine/mometasone furoate combination nasal spray (Ryaltris®; referred to hereafter as olopatadine/mometasone), a convenient fixed-dose combination (FDC) of the antihistamine olopatadine and the corticosteroid mometasone furoate, is approved in Australia for the treatment of symptoms associated with allergic rhinitis (AR) and rhinoconjunctivitis in patients 12 years of age and older. Olopatadine/mometasone is an effective treatment for seasonal and perennial AR, providing statistically significant and clinically meaningful relief of nasal symptoms relative to monocomponents and/or placebo in clinical trials. Ocular symptoms of AR were also improved with olopatadine/mometasone. Benefits of olopatadine/mometasone were maintained over 52 weeks of treatment in adults and adolescents with perennial AR. Olopatadine/mometasone is generally well tolerated, with most treatment-emergent adverse events being of mild to moderate severity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy. ASCIA information for health professionals: allergic rhinitis clinical update. 2020. https://www.allergy.org.au. Accessed 9 Sep 2020.
Seidman MD, Gurgel RK, Lin SY, et al. Clinical practice guidelines: allergic rhinitis. Otolaryng Head Neck. 2015;152(Suppl 1):1–43.
Bousquet J, Van Cauwenberge P, Khaltaev N, et al. Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108(5 Suppl):S147–S334.
Brożek JL, Bousquet J, Agache I, et al. Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma (ARIA) guidelines—2016 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140(4):950–8.
Rotiroti G, Scadding GK. Allergic rhinitis—an overview of a common disease. Paediatr Child Health. 2016;26(7):298–303.
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Allergic rhinitis (‘hay fever’). 2019. https://www.aihw.gov.au/. Accessed 9 Sep 2020.
Yanez A, Rodrigo GJ. Intranasal corticosteroids versus topical H1 receptor antagonists for the treatment of allergic rhinitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Allerg Asthma Immunol. 2002;89(5):479–84.
Tahir E, Cingi C, Wise SK. Medical treatment of allergic rhinitis. In: Muluk NB, Cingi C, editors. All around the nose. Cham: Springer; 2019. p. 311–317.
Patel P, Salapatek AM, Tantry SK. Effect of olopatadine-mometasone combination nasal spray on seasonal allergic rhinitis symptoms in an environmental exposure chamber study. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019;122(2):160–6.e1.
Mullol J, De Borja CF, Asunción Martínez-Antón M, et al. Mometasone and desloratadine additive effect on eosinophil survival and cytokine secretion from epithelial cells. Respir Res. 2011;12:23.
Ryaltris® (olopatadine hydrochloride 665 mcg and mometasone furoate 25 mcg) nasal spray: Australian prescribing information. Parkville, VIC: Seqirus Pty. Ltd.; April 2020.
Sharif NA, Xu SX, Miller ST, et al. Characterization of the ocular antiallergic and antihistamine effects of olopatadine (AL-4943A), a novel drug for treating ocular allergic diseases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;278(3):1252–61.
Cook EB, Stahl JL, Barney NP, et al. Olopatadine inhibits TNFα release from human conjunctival cells. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2000;84(5):504–8.
Yanni JM, Stephens DJ, Miller ST, et al. The in vitro and in vivo ocular pharmacology of olopatadine (AL-4943A), an effective antiallergic, antihistamine agent. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2009;12(4):389–400.
Baldwin CM, Scott LJ. Mometasone furoate: a review of its intranasal use in allergic rhinitis. Drugs. 2008;68(12):1723–39.
Patel P, Salapatek AM, Talluri RS, et al. Pharmacokinetics of intranasal mometasone in the fixed-dose combination GSP301 versus two monotherapy intranasal mometasone formulations. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2018;39(3):232–9.
Patel P, Salapatek AM, Talluri RS, et al. Pharmacokinetics of intranasal olopatadine in the fixed-dose combination GSP301 versus two monotherapy intranasal olopatadine formulations. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2018;39(3):224–31.
Andrews CP, Mohar D, Salhi Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of twice-daily and once-daily olopatadine-mometasone combination nasal spray for seasonal allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124(2):171–8.e2.
Gross GN, Berman G, Amar NJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of olopatadine-mometasone combination nasal spray for the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019;122(6):630–8.e3.
Hampel FC, Pedinoff AJ, Jacobs RL, et al. Olopatadine-mometasone combination nasal spray: evaluation of efficacy and safety in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019;40(4):261–72.
Barnes ML, Vaidyanathan S, Williamson PA, et al. The minimal clinically important difference in allergic rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010;40:242–50.
Gross GN, Amar NJ, Fernando N, et al. Olopatadine/mometasone combination nasal spray for the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis: a pooled analysis of efficacy and safety [abstract no. 189]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143(2 Suppl):AB63.
Prenner B, Hampel F, Fernando N, et al. Rapid nasal symptom onset of action and ocular symptom relief with olopatadine/mometasone combination nasal spray in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis: a pooled analysis [abstract no. 188]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143(2 Suppl):AB62.
Juniper EF, Guyatt GH, Griffith LE, et al. Interpretation of rhinoconjunctivitis quality of life questionnaire data. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996;98(4):843–5.
Mohar D, Andrews CP, Fernando N, et al. Quality of life improvements following treatment with olopatadine/mometasone combination nasal spray in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis: a pooled analysis [abstract no. 186]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143(2 Suppl):62.
Segall N, Prenner B, Lumry W, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of olopatadine-mometasone combination nasal spray in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019;40(5):301–10.
Bousquet J, Schünemann HJ, Togias A, et al. Next-generation allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma (ARIA) guidelines for allergic rhinitis based on grading of recommendations, assessment, development and evaluation (GRADE) and real-world evidence. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145(1):70–80.e3.
Blaiss MS, Hammerby E, Robinson S, et al. The burden of allergic rhinitis and allergic rhinoconjunctivitis on adolescents: a literature review. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;121:43–52.
Ozdoganoglu T, Songu M, Inancli HM. Quality of life in allergic rhinitis. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2012;6(1):25–39.
Dymista nasal spray. summary of product characteristics. Bishops Stortford: Meda Pharmaceuticals Ltd; 2015.
Dymista (azelastine hydrochloride and fluticasone propionate) nasal spray: US prescribing information. Somerset: Meda Pharmaceuticals Inc.; 2019.
Dymista® 125/50 (azelastine hydrochloride and fluticasone propionate nasal spray): Australian prescribing information. Millers Point: Mylan Health Pty. Ltd.; 2019.
Meltzer EO, Farrar JR, Sennett C. Findings from an online survey assessing the burden and management of seasonal allergic conjunctivitis in US patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017;5:779–89.
Menditto E, Costa E, Midão L, et al. Adherence to treatment in allergic rhinitis using mobile technology: the MASK study. Clin Exp Allergy. 2018;49(4):442–60.
Gani F, Lombardi C, Barrocu L, et al. The control of allergic rhinitis in real life: a multicenter cross-sectional Italian study. Clin Mol Allergy. 2018;16(4):1–6.
Acknowledgements
The manuscript was reviewed by: J. Mullol, Rhinology Unit & Smell Clinic, ENT Department, Hospital Clínic, Universitat de Barcelona; Clinical and Experimental Respiratory Immunoallergy (IRCE), Institut d’Investigacions Biomèdiques August Pi i Sunyer (IDIBAPS); CIBER of Respiratory Diseases (IDIBAPS), Carlos III Institute. Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain; B. Spoelhof, Department of Pharmacy, University of Virginia Health System, Charlottesville, VA, USA; A. Zandi, Pharmacology, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences School of Medicine, Tehran, Iran. During the peer review process, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd. (innovator/manufacturer of olopatadine/mometasone) and Seqirus (marketing-authorization holder in Australia) were also offered an opportunity to provide a scientific accuracy review of their data. Changes resulting from comments received were made on the basis of scientific and editorial merit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Authorship and Conflict of interest
Y. N. Lamb is an employee of Adis International Ltd./Springer Nature and declares no relevant conflicts of interest. All authors contributed to the review and are responsible for the article content.
Ethics approval, Consent to participate, Consent to publish, Availability of data and material, Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Enhanced material for this Adis Drug Q&A can be found at https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.12845843.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamb, Y.N. Olopatadine/mometasone combination nasal spray in allergic rhinitis: a profile of its use. Drugs Ther Perspect 36, 494–501 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-020-00778-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-020-00778-y