Abstract
Background
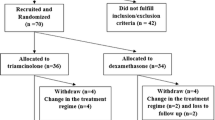
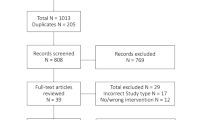
Intra-articular injection (IAI) with a glucocorticoid (GC) is often used in clinical practice, despite its controversial effectiveness. We performed a retrospective study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of IAI with the GC triamcinolone acetonide (TA) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) over the period of April 2014–March 2019.
Methods
Clinical indices 1 month and 1 year after the initial TA IAI were compared statistically. Changes in disease activity scores (DAS) and correlation between DAS and background factors were evaluated for each time period. Clinical indices, pain index, joint deformity index, bone mineral density (BMD), and changes in each parameter up to 1 month and 1 year after the initial IAI were compared between patient groups classified according to the number of IAIs per year. The DAS in patients who had received TA IAIs was compared with the DAS in patients who had received sodium hyaluronate (SH) IAIs.
Results
In total, 1010 IAIs were performed in 208 patients. All components of the simplified disease activity index, as well as pain scores, significantly decreased at 1 month and 1 year after the initial IAI (p < 0.01). The higher the frequency of IAIs, the greater the prevalence of adverse events (AEs), the most frequent of which were gastrointestinal disorders. The DAS improved to a greater extent with TA than with SH.
Conclusion
IAI is a useful therapeutic strategy in terms of controlling disease activity and managing pain; however, the frequency of IAI should be considered due to the increased risk of AEs with frequent administration.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sokka T, Pincus T. Rheumatoid arthritis: strategy more important than agent. Lancet. 2009;374:430–2.
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Bijlsma JW, et al. Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:631–7.
Smolen JS, Landewé R, Bijlsma J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:960–77.
Smolen JS, Landewé RBM, Bijlsma JWJ, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79:685–99.
Furtado RN, Oliveira LM, Natour J. Polyarticular corticosteroid injection versus systemic administration in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis patients: a randomized controlled study. J Rheumatol. 2005;32:1691–8.
Hetland ML, Ostergaard M, Ejbjerg B, et al. Short- and long-term efficacy of intra-articular injections with betamethasone as part of a treat-to-target strategy in early rheumatoid arthritis: impact of joint area, repeated injections, MRI findings, anti-CCP, IgM-RF and CRP. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:851–6.
Gvozdenovic E, Dirven L, van den Broek M, et al. Intra articular injection with corticosteroids in patients with recent onset rheumatoid arthritis: subanalyses from the BeSt study. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33:263–7.
Menon N, Kothari SY, Gogna A, et al. Comparison of intra-articular glucocorticoid injections with DMARDs versus DMARDs alone in rheumatoid arthritis. J Assoc Physicians India. 2014;62:673–6.
Kuusalo LA, Puolakka KT, Kautiainen H, et al. Intra-articular glucocorticoid injections should not be neglected in the remission targeted treatment of early rheumatoid arthritis: a post hoc analysis from the NEO-RACo trial. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016;34:1038–44.
Nordberg LB, Lillegraven S, Age A-B, et al. The impact of ultrasound on the use and efficacy of intraarticular glucocorticoid injections in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70:1192–9.
Hangody L, Szody R, Lukasik P, et al. Intraarticular injection of a cross-linked sodium hyaluronate combined with triamcinolone hexacetonide (Cingal) to provide symptomatic relief of osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter clinical trial. Cartilage. 2018;9:276–83.
Kraus VB, Conaghan PG, Aazami HA, et al. Synovial and systemic pharmacokinetics (PK) of triamcinolone acetonide (TA) following intra-articular (IA) injection of an extended-release microsphere-based formulation (FX006) or standard crystalline suspension in patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA). Osteoarthr Cartil. 2018;26:34–42.
Conaghan PG, Hunter DJ, Cohen SB, et al. Effects of a single intra-articular injection of a microsphere formulation of triamcinolone acetonide on knee osteoarthritis: a double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled, multinational study. J Bone Jt Surg Am. 2018;100:666–77.
Rudnik-Jansen I, Schrijver K, Woike N, et al. Intra-articular injection of triamcinolone acetonide releasing biomaterial microspheres inhibits pain and inflammation in an acute arthritis model. Drug Deliv. 2019;26:226–36.
Paik J, Duggan ST, Keam SJ. Triamcinolone acetonide extended-release: a review in osteoarthritis pain of the knee. Drugs. 2019;79:455–62.
Shrestha R, Shrestha R, Thapa S, et al. Clinical outcome following intra-articular triamcinolone injection in osteoarthritis knee at the community: a randomized double blind placebo controlled trial. Kathmandu Univ Med J. 2018;62:175–80.
Chavez-Chiang NR, Sibbitt WL, Band PA, et al. The outcomes and cost-effectiveness of intraarticular injection of the rheumatoid knee. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32:513–8.
Aletaha D, Smolen J. The simplified disease activity index (SDAI) and the clinical disease activity index (CDAI): a review of their usefulness and validity in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005;23:S100–S108.
Kirwan JR, Reeback JS. Stanford health assessment questionnaire modified to assess disability in British patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1986;25:206–9.
van Der Heijde DM, van Riel PL, et al. Effects of hydroxychloroquine and sulphasalazine on progression of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1989;333:1036–8.
Yoshii I, Chijiwa T, Sawada N. The influence of pain score measured with a visual analog scale (PS-VAS) on the Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI) and 28-joint Disease Activity Index with C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018;21:1955–61.
Wang S, Wang X, Liu Y, et al. Ultrasound-guided intra-articular triamcinolone acetonide injection for treating refractory small joints arthritis of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98:e16714.
Hetland ML, Østergaard M, Ejbjerg B, et al. Short- and long-term efficacy of intra-articular injections with betamethasone as part of a treat-to-target strategy in early rheumatoid arthritis: impact of joint area, repeated injections, MRI findings, anti-CCP, IgM-RF, and CRP. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:851–6.
Furtado NV, Machado FS, da Luz KR, et al. Intra-articular injection with triamcinolone hexacetonide in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: prospective assessment of goniometry and joint inflammation parameters. Rev Bras Rheumatol Engl Ed. 2017;57:115–21.
Makrygiannakis D, Revu S, Engström M, et al. Local administration of glucocorticoids decreases synovial citrullination in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14:R20.
Weitoft T, Rönnelid J, Knight A, et al. Outcome predictors of intra-articular glucocorticoid treatment for knee synovitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis—a prospective cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16:R129.
Haugeberg G, Morton S, Emery P, et al. Effect of intra-articular corticosteroid injections and inflammation on periarticular and generalized bone loss in early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:184–7.
Berkoff DJ, Miller LE, Block JE. Clinical utility of ultrasound guidance for untra-articular knee injections: a review. Clin Interv Aging. 2012;7:89–95.
Pal B, Morris J. Perceived risks of joint infection following intra-articular corticosteroid injections: a survey of rheumatologists. Clin Rheumatol. 1999;18:264–5.
Pereira LC, Kerr J, Jolles BM. Intra-articular steroid injection for osteoarthritis of the hip prior to total hip arthroplasty: is it safe? A systematic review. Bone Jt J. 2016;98-B(8):1027–35.
Li H, Xing D, Ke Y, et al. Safety of intra-articular steroid injections prior to arthroplasty: best evidence selection and risk of bias considerations. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018;21:982–91.
Petersen SK, Hansen IMJ, Andreasen RA. Low frequency of septic arthritis after arthrocentesis and intra-articular glucocorticoid injection. Scand J Rheumatol. 2019;48:393–7.
Taliaferro K, Crawford A, Jabara J, et al. Intraocular pressure increases after intraarticular injection with triamcinolone but not hyaluronic acid. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476:1420–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
IY analyzed and interpreted the data used in this study, and NS checked the results and read the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The authors declare that no funding was received for this study.
Conflict of interest
Ichiro Yoshii and Naoya Sawada have no conflicts of interest to declare relevant to the contents of this article.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by our institution’s Ethics Committee (approval number Y-RA-2019-5) in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. In addition, anonymity was ensured for all patients and their families who participated in this study, and no names and/or addresses were issued that could help identify these individuals. Moreover, all patients were informed of the purpose and possible consequences of this study (i.e. that this was a retrospective study in clinical practice without any experimentation on subjects).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshii, I., Sawada, N. Efficacy and safety of intra-articular injection with triamcinolone acetonide for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs Ther Perspect 36, 404–412 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-020-00755-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-020-00755-5