Abstract
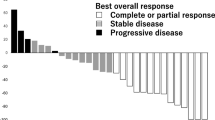
Eribulin mesylate (Halaven®), a synthetic analogue of halichondrin B, is a welcome addition to the therapeutic options for treatment-refractory liposarcoma. It acts as a microtubule dynamics inhibitor, disrupting mitosis and leading to apoptotic cell death in cancer cells. Eribulin mesylate significantly improved overall and progression-free survival compared with dacarbazine and has a manageable tolerability profile in patients with unresectable, advanced liposarcoma whose disease has progressed following prior treatment, including an anthracycline-based regimen.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schoffski P, Chawla S, Maki RG, et al. Eribulin versus dacarbazine in previously treated patients with advanced liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma: a randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016;387(10028):1629–37.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guideline®): soft tissue sarcoma (version 2.2016). Fort Washington (PA): National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc.; 2016.
The ESMO/European Sarcoma Network Working Group. Soft tissue and visceral sarcomas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2014;25 Suppl 3:iii102–12.
Fletcher CDM, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn PCW, et al. WHO classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone. 4th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer/World Health Organization; 2013.
Halaven 0.44 mg/ml solution for injection: summary of product characteristics. London: European Medicines Agency; 2016.
Halaven (eribulin mesylate) injection, for intravenous use: US prescribing information. Woodcliff Lake (NJ): Eisai Inc.: 2016.
Dybdal-Hargreaves NF, Risinger AL, Mooberry SL. Eribulin mesylate: mechanism of action of a unique microtubule-targeting agent. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(11):2445–52.
Kawano S, Asano M, Adachi Y, et al. Antimitotic and non-mitotic effects of eribulin mesilate in soft tissue sarcoma. Anticancer Res. 2016;36(4):1553–61.
Schoffski P, Ray-Coquard IL, Cioffi A, et al. Activity of eribulin mesylate in patients with soft-tissue sarcoma: a phase 2 study in four independent histological subtypes. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(11):1045–52.
Acknowledgements
The article was reviewed by: L. Bergmann, Medical Clinic II, University Hospital Frankfurt, Frankfurt/Main, Germany; S. V. Sakpal, Department of Surgery, Saint Barnabas Medical Center, Livingston, NJ, USA; R. J. Young, Academic Unit of Oncology, Weston Park Hospital, Sheffield, UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Conflict of interest
K. P. Garnock-Jones and K. A. Lyseng-Williamson are salaried employees of Adis/Springer, are responsible for the article content and declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garnock-Jones, K.P., Lyseng-Williamson, K.A. Eribulin mesylate in previously treated patients with advanced liposarcoma: a guide to its use. Drugs Ther Perspect 32, 510–514 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-016-0356-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-016-0356-8