Abstract
Oral semaglutide (Rybelsus®) is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) with 94% homology to human GLP-1. It is the first GLP-1RA developed for oral administration, and it comprises a co-formulation of the peptide semaglutide with the absorption enhancer sodium N-(8-[2-hydroxybenzoyl] amino) caprylate, which overcomes the challenges of peptide absorption in the acidic conditions of the stomach. Oral semaglutide is indicated for use as an add-on combination therapy (with other glucose-lowering agents, including insulin) or as a monotherapy (in patients who are intolerant to metformin) for type 2 diabetes when diet and exercise do not provide adequate glycemic control. In an extensive phase III clinical program including patients from across the disease spectrum, treatment with oral semaglutide resulted in effective glycemic control, reductions in body weight, and decreases in systolic blood pressure when used as monotherapy or in combination with other glucose-lowering therapies. Studies showed that oral semaglutide was well tolerated, with a safety profile consistent with the GLP-1RA drug class. The risk of hypoglycemia was low, and the most common adverse events were gastrointestinal, with nausea and diarrhea generally being the most frequently reported manifestations. Cardiovascular (CV) safety was shown to be noninferior to placebo and observations suggest that the CV profile of oral semaglutide is likely to be similar to that of subcutaneous semaglutide. The evolution of the GLP-1RA class to include an oral agent could facilitate the use of these agents earlier in the diabetes treatment cascade owing to wider acceptance from patients and healthcare professionals.
Video abstract
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Digital Features for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.13653191 |
Oral semaglutide is a co-formulation of semaglutide with an absorption enhancer, sodium N-(8-[2-hydroxybenzoyl] amino) caprylate (SNAC). SNAC provides a local increase in pH that helps protect semaglutide from proteolytic degradation in the stomach and facilitates the absorption of semaglutide across the gastric epithelium in a concentration-dependent manner. |
Across a range of different patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) receiving different background medications, oral semaglutide provides more effective glycemic control than common oral glucose-lowering therapies, as well as providing reductions in body weight and systolic blood pressure, including in patients with more advanced T2D on insulin treatment. |
The tolerability profile for oral semaglutide was consistent with the wider glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist drug class, with the most frequent adverse events being gastrointestinal, for example, nausea and diarrhea. |
Cardiovascular (CV) safety for oral semaglutide was noninferior to placebo and, although the hazard ratio was of a magnitude consistent with that seen with subcutaneous semaglutide in SUSTAIN 6, superiority to placebo was not demonstrated. A nominal statistically significant reduction in deaths from CV causes was reported for oral semaglutide versus placebo. |
1 Introduction
The principal goal of disease management in type 2 diabetes (T2D) is the prevention or delay of both microvascular and macrovascular complications through the achievement of good glycemic control and, where necessary, weight loss and cardiovascular (CV) risk factor management [1]. For many individuals with T2D, treatment with multiple glucose-lowering therapies may be required to achieve good glycemic control. Metformin is commonly used as first-line therapy unless contraindicated or poorly tolerated, but the addition of glucose-lowering therapies with different mechanisms of action is usually needed to provide adequate glycemic control [1,2,3], with the choice of agent being dependent on multiple factors, such as cost and the presence of comorbidities [1].
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are a well-established treatment option for the treatment of T2D. These agents are peptide-based drugs that have been developed to activate the receptor of the gut-derived hormone GLP-1, which has an important role in glucose homeostasis [3, 4]. Within the drug class, GLP-1RAs have different origins and molecular characteristics. Four of the GLP-1RAs—albiglutide, dulaglutide, semaglutide, and liraglutide—are GLP-1 analogs, modified from the native structure of GLP-1, while exenatide and lixisenatide are based on the peptide exendin (a hormone derived from the saliva of the Gila monster), which has a similar structure to that of GLP-1 and retains GLP-1 activity [4]. GLP-1 receptor activation by native GLP-1 or GLP-1RAs leads to insulin secretion and lowers inappropriately high glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner, thereby improving glycemic control [3]. When plasma glucose levels are low, GLP-1RAs do not stimulate insulin secretion, which helps to maintain glycemic control while also reducing the risk of hypoglycemia [3, 4]. In addition to effective glycemic control, GLP-1RA treatment is also associated with body-weight reductions [3]. Patients also experience lipid and blood pressure reductions with GLP-1RAs [3], and several GLP-1RAs have been reported to reduce the risk of CV events [5,6,7,8].
For patients without established atherosclerotic CV disease (ASCVD) or chronic kidney disease (CKD) and for whom there is a compelling need to minimize weight gain or promote weight loss, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) guidelines recommend GLP-1RA and sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor (SGLT2i) drugs as the preferred second-line treatment option for patients with inadequate glycemic control despite use of metformin [1, 9]. The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/American College of Endocrinology consensus statement also recommends either a GLP-1RA or SGLT2i as a preferred treatment option (either as first-line or, more typically, second-line treatment after metformin) over alternative options such as a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, a thiazolidinedione (TZD), or a sulfonylurea (SU), for patients with T2D and ASCVD, stage 3 CKD, or heart failure with reduced ejection fraction [2]. These recommendations for treatment selection for individuals with high CV risk should be considered independent of baseline HbA1c [2, 10]. SGLT2is have the benefit of being oral agents, which may make them an attractive choice for prescribers and a convenient add-on treatment for patients [11]. Conversely, studies have shown that both patients and healthcare professionals are reluctant to initiate GLP-1RAs [11, 12], despite the guideline recommendations and the health benefits of these therapies, particularly for patients in need of weight loss and those with low estimated glomerular filtration rate [1]. This reluctance is likely to be at least partially attributable to the fact that, until recently, all GLP-1RAs were available as subcutaneous (s.c.) injections, given twice daily (exenatide [13]), once daily (lixisenatide [14] and liraglutide [15]), or once weekly (semaglutide [16], dulaglutide [17], and exenatide extended release [18]), a route that may be less preferable to some patients compared with oral administration [1, 19].
Oral semaglutide is the first GLP-1RA developed for oral administration. It was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in September 2019 for the treatment of adults with T2D and has since received approval from the European Medicines Agency. The evolution of the GLP-1RA class to include an oral agent could potentially aid initiation of these agents earlier in the diabetes treatment cascade owing to wider acceptance from patients and healthcare professionals. The simplicity and convenience of tablet administration could also lead to improved compliance [20]. To help provide insights into the potential role of oral semaglutide in current T2D management, this article aims to discuss the pharmacology of oral semaglutide, review the current clinical evidence on the efficacy and safety of this agent from the extensive phase III PIONEER clinical trial program in patients with T2D, and describe findings from initial cost-effectiveness studies.
A literature review was conducted in which PubMed and Embase databases were searched using the term “oral semaglutide.” Searches were conducted on 20 May 2020 for PubMed and 2 June 2020 for Embase, and were not limited by start date. Online searches were also conducted on 7 July 2020 for diabetes congress abstracts from ENDO 2019, ADA 2019 and 2020, and EASD 2019. A total of 352 publications were identified and 306 were excluded (as duplicates, not relevant, review articles, case reports, commentaries, letters, or conference abstracts for data that had subsequently been published). This review includes 46 cited articles for studies or analyses investigating oral semaglutide in T2D, of which 23 relate to its efficacy/tolerability. One publication was updated and a recent publication added during the peer-review process.
2 Pharmacological Properties
2.1 Pharmacology
Semaglutide was first identified as part of a series of studies that aimed to design a once-weekly s.c. GLP-1 analog with increased albumin affinity and security against metabolic degradation [21]. Its efficacy was first described in a dose-response study in db/db mice, which confirmed the potency and duration of action, with an ED50 below 2 nmol/kg [21, 22]. Semaglutide has 94% homology to human GLP-1, with two amino acid substitutions (Aib8 and Arg34), and is derivatized at lysine 26 (Fig. 1a) [21,22,23]. It is fully metabolized in the human body by the same processes as other peptides and fatty acids [22, 24]. Unlike liraglutide, semaglutide contains an amino acid (α-aminoisobutyric acid) described in nature but not in humans, and it appears that more metabolites of semaglutide are excreted in the feces [22].
For researchers developing oral formulations of GLP-1RAs, including oral semaglutide, the fact that absorption takes place in the stomach presents a challenge. Obtaining sufficient systemic exposure of peptide-based drugs following oral administration is difficult owing to the acidic environment and presence of proteolytic enzymes in the stomach, and the limited permeability of peptides and proteins through the gastrointestinal epithelium [20, 25]. An absorption enhancer may help mitigate these barriers [25]. Consequently, the tablet formulation of semaglutide has been developed with the peptide co-formulated with an absorption enhancer, sodium N-(8-[2-hydroxybenzoyl] amino) caprylate (SNAC) (Fig. 1a) [25, 26]. SNAC is a small fatty-acid derivative that has been shown to provide a local increase in pH, which helps protect semaglutide from proteolytic degradation in the stomach, and to facilitate the absorption of semaglutide across the gastric epithelium in a concentration-dependent manner, primarily through the transcellular route [25] (Fig. 1b). Research has shown that absorption of semaglutide in the stomach is confined to an area in close proximity to the tablet [27]. As part of the development process, it was important to determine the amount of SNAC needed for optimal semaglutide exposure. A single-dose study in healthy males (n = 135) found that oral semaglutide exposure levels were greatest with 300 mg SNAC, and thus this amount was selected for further clinical development [26].
2.2 Absorption and Pharmacokinetics of Oral Semaglutide
Oral semaglutide is absorbed from the stomach, and this process may be hindered by the presence of food. A food-effect study carried out in healthy volunteers (N = 78) reported that individuals receiving once-daily oral semaglutide in the fasting state (n = 26) had measurable exposure, whereas this was not the case in the fed state where exposure was either limited (11 of 25 individuals) or not observed (14 out of 25 individuals) [25, 28]. It is therefore recommended that administration of the oral formulation of semaglutide should be in the fasting state [27,28,29]. Studies have also evaluated the effects of water volume (when swallowing the tablet) on the pharmacokinetics of semaglutide. A study in 26 healthy male individuals found that tablet erosion of oral semaglutide was slower with 50 mL versus 240 mL of water [30]. This study also showed that delayed delivery of the drug to the small intestine was associated with higher plasma exposure [30]. Another study conducted in 158 healthy male volunteers assessed the impact of different water volumes and post-dosing fasting periods on semaglutide exposure, and the authors concluded that administration of oral semaglutide in the fasting state with up to 120 mL of water and a post-dose fasting period of at least 30 min resulted in clinically relevant semaglutide exposure [31]. Finally, co-administration of placebo tablets with oral semaglutide has been reported to reduce semaglutide exposure by 34% in a two-part, open-label, crossover trial in 45 healthy subjects [32]. Therefore, the dosing conditions used in the phase III clinical trial program were for oral semaglutide to be administered once daily on waking, in a fasting state, with up to 120 mL of water, and then waiting for 30 min before consumption of any food, drink, or other oral medications.
Plasma exposure for oral semaglutide was shown to be dose-dependent in a multiple-dose study (N = 84 healthy male individuals and 23 male individuals with T2D). Exposure was approximately twofold higher with a 40 mg versus a 20 mg dose, and there was no difference in exposure for the 40 mg dose between healthy individuals and those with T2D. The half-life (t½) of oral semaglutide was shown to be similar to that of s.c. semaglutide, being approximately 1 week [26]. This long t½ of semaglutide may help mitigate any day-to-day variability in exposure that may occur with oral administration. Indeed, a comparison of exposure–response relationships for oral and s.c. semaglutide from their respective phase III clinical trial programs in T2D revealed that, although there is a greater variability in semaglutide plasma concentrations following daily oral administration, this does not impact efficacy response. Indeed, considerable overlap was observed between the exposure-response seen with once-daily oral semaglutide (7 and 14 mg) and that seen with once-weekly s.c. semaglutide (0.5 and 1.0 mg) [33].
As the enhanced absorption of oral semaglutide from the stomach is facilitated by SNAC in a pH-dependent manner, the impact of agents that influence gastric pH on the pharmacokinetics of oral semaglutide required investigation. In healthy volunteers (N = 54), administration of a proton pump inhibitor, omeprazole (40 mg once daily), resulted in a slight non-statistically significant increase in exposure to semaglutide that was not considered to be clinically relevant and no dose adjustment is recommended with these agents [34]. Given the site of absorption of oral semaglutide, the impact of upper gastrointestinal disease on the pharmacokinetics of oral semaglutide would also be of interest. In a study of individuals with (N = 36) or without (N = 19) upper gastrointestinal disease (gastritis and/or gastroesophageal reflux disease), no significant difference in exposure to semaglutide was observed between individuals with or without gastrointestinal disease and the agent was well tolerated in these patients [35].
Many patients with T2D also have underlying comorbidities that may affect the pharmacokinetic profile of treatment, and of particular importance is the impact of renal or hepatic impairment. The effect of renal impairment on exposure to oral semaglutide was investigated in individuals (N = 71) with varying degrees of renal impairment [normal function, mild, moderate, severe, and end-stage renal disease (ESRD)] [36]. After 10 consecutive days of once-daily oral administration, no consistent or clinically relevant pattern of increase or decrease in semaglutide exposure was observed between individuals with varying degrees of renal function. Hemodialysis did not appear to affect the pharmacokinetics of oral semaglutide or SNAC [36]. The pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of oral semaglutide were also studied in patients (N = 56) with varying degrees of hepatic impairment (normal function, mild, moderate, and severe) over ten doses [37]. This study was important as there had been no previous reported data on the possible effects of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of SNAC, which is metabolized via β-oxidation and glucuronidation and is highly bound to albumin. Semaglutide exposure appeared to be similar across all four hepatic impairment groups, and no semaglutide was detected in any of the urine samples. SNAC exposure did increase with decreases in hepatic function, with the greatest increase seen in patients with severe hepatic impairment (3.64 times higher than patients with normal hepatic function). This increase in SNAC was not considered clinically relevant as it has no anticipated pharmacodynamic effects [37].
2.3 Pharmacodynamics
The effects of oral semaglutide on fasting and post-prandial glucose and on lipid metabolism were investigated in a double-blinded crossover trial of 15 individuals with T2D. Oral semaglutide significantly improved fasting and post-prandial glucose metabolism and lipid metabolism, and delayed gastric emptying during the first post-prandial hour, which is consistent with observations for s.c. semaglutide in subjects with obesity [38, 39]. The effect of oral semaglutide treatment on appetite and energy intake was also assessed, and the study incorporated the Control of Eating Questionnaire (CoEQ). After 12 weeks of treatment with oral semaglutide, energy intake was reduced, control of eating was improved, and patients experienced weight loss and fewer food cravings. There was no change in appetite in this study, a finding that is inconsistent with observations for the s.c. formulation [40, 41].
2.4 Drug–Drug Interactions
The impact of concomitant administration of this new oral formulation of semaglutide with other drug classes that are commonly administered in patients with T2D has also been evaluated (Table 1). Two open-label, single-sequence, crossover trials of healthy volunteers (trial 1: N = 52; trial 2: N = 32) demonstrated that there were no clinically relevant effects of oral semaglutide (20 mg) on the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) and maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) for the antihypertensive drug lisinopril (20 mg single dose [trial 1]), the anticoagulant agent warfarin (25 mg single dose [trial 1]), or digoxin (500 μg [trial 2]) [42]. The AUC of metformin (administered at 850 mg twice daily for 4 days [trial 2]) was increased by 32% [90% confidence interval (CI) 1.23−1.43] in individuals receiving oral semaglutide and metformin versus those receiving metformin alone. Given the broad therapeutic window for metformin, it was concluded that the increase in exposure was not clinically relevant, and is likely due to the known effect of GLP-1RAs for delaying gastric emptying. Administration of SNAC (300 mg) alone did not affect exposure/absorption of any of the agents [42].
Statins and diuretics may be used in patients with T2D for the management of dyslipidemia and hypertension, respectively. A study of healthy volunteers (N = 41) investigated whether oral semaglutide could potentially influence exposure to furosemide or rosuvastatin. Single doses of furosemide (40 mg) and rosuvastatin (20 mg) alone were co-administered with SNAC (300 mg) or oral semaglutide [43]. Co-administration of single-dose furosemide with steady-state oral semaglutide resulted in a 28% increase in total furosemide exposure (AUC0––∞) and a 34% decrease in Cmax compared with patients not receiving oral semaglutide. When co-administered with SNAC alone, there was no effect on the AUC0–∞ of single-dose furosemide, while Cmax decreased by 10%. Administration of single-dose rosuvastatin with oral semaglutide at steady state resulted in a 41% increase in AUC0–∞ and a 10% increase in Cmax for rosuvastatin compared with patients not receiving oral semaglutide. Pharmacokinetic parameters for rosuvastatin were unchanged by co-administration of SNAC alone. Changes in exposure of furosemide and rosuvastatin when co-administered with semaglutide may also be related to the known effect of GLP-1RAs for delaying gastric emptying. The authors concluded that the changes in exposure observed for furosemide and rosuvastatin are unlikely to be clinically relevant [43]. It has been suggested that a delay in gastric emptying may also contribute to the changes in pharmacokinetics (33% increase in AUC0–48 h) observed for levothyroxine when coadministered with oral semaglutide in a study of 45 healthy volunteers. Although the pharmacokinetics of levothyroxine were influenced by oral semaglutide, no change in clinical practice is required as close monitoring of thyroxine is already part of medical guidance [32].
Female patients with T2D may also take concomitant birth control medication and, therefore, an open-label study of healthy postmenopausal women (N = 25) was conducted to assess the effect of oral semaglutide on the pharmacokinetics of the combined oral contraceptive ethinylestradiol (0.03 mg)/levonorgestrel (0.15 mg). Exposure to ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel was similar when administered alone or with oral semaglutide, indicating that their bioavailability is not affected by co-administration with oral semaglutide [44].
3 Oral Semaglutide Clinical Trial Program
A phase II dose-finding study paved the way for the large phase III clinical program for oral semaglutide [45]. This dose-finding study included 632 patients with T2D (mean diabetes duration 6.3 years and mean baseline HbA1c 7.9%) and assessed the dose–response relationship on glycemic control [mean change in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)] of once-daily oral semaglutide (2.5, 5, 10, 20, and 40 mg dose escalated over 4 weeks) versus placebo (double-blind) and s.c. semaglutide (open-label). Mean change in HbA1c from baseline to week 26 was − 0.7 to − 1.9% with increasing doses of oral semaglutide, − 1.9% with once-weekly s.c. semaglutide, and − 0.3% with placebo. Reductions with oral semaglutide were significant versus placebo [dose-dependent estimated treatment difference (ETD) range for oral semaglutide vs. placebo was − 0.4 to − 1.6% (p < 0.05 for 2.5 mg and p < 0.001 for all other doses)]. Fewer adverse events (AEs) were reported when patients initiated oral semaglutide at a low (2.5 mg) versus a higher dose (5 mg) [45].
Based on the findings of this phase II study, the efficacy and safety of three doses of oral semaglutide (3, 7, and 14 mg) were investigated in the Peptide InnOvatioN for Early diabEtes tReatment (PIONEER) phase III clinical trial program, which included eight multinational studies (PIONEER 1−8) [44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53] and two Japan-specific studies (PIONEER 9 and 10) [54, 55]. Individuals recruited for this program were patients with T2D from across a broad range of disease durations and background therapies, and representative of many patients typically encountered in clinical practice (Table 2). The comparators in the PIONEER program were placebo (PIONEER 1, 4, 5, 6, and 8), empagliflozin 25 mg (PIONEER 2), sitagliptin 100 mg (PIONEER 3 and 7), liraglutide 1.8 mg (PIONEER 4) and 0.9 mg (PIONEER 9), and dulaglutide 0.75 mg (PIONEER 10). It is important to note that the doses of liraglutide (0.9 mg) and dulaglutide (0.75 mg) used in the Japanese studies (PIONEER 9 and 10, respectively) were selected as these were the approved maintenance doses of these GLP-1RAs in Japan at the time of trial design, and they are not the maximum doses typically used in global populations. Common inclusion criteria for the trials were: adults (typically aged ≥ 18 years, although slightly older age criteria were used in some countries), a diagnosis of T2D at least 30−90 days prior to screening, and HbA1c within a prespecified range [this range differed slightly between trials (Table 2)] [46,47,48,49,50, 52,53,54,55]. The primary and confirmatory secondary endpoints in most of the trials were change from baseline in HbA1c and body weight, respectively, at week 26, with the exception of the PIONEER 6, 7, and 10 trials (Table 2). The treatment policy estimand (data assessed regardless of rescue medication use or premature trial product discontinuation) was the primary estimand in all trials except PIONEER 9 [46,47,48,49,50, 52,53,54,55], and data for this estimand are reported in our review.
4 Therapeutic Efficacy
4.1 Glycemic Control
The results for HbA1c changes from baseline in active-comparator trials, placebo and active-comparator trials, and placebo-controlled trials are shown in Fig. 2.
Reductions in HbA1c with oral semaglutide in the PIONEER program. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 favoring oral semaglutide vs. placebo. †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01, †††p < 0.001 favoring oral semaglutide vs. active comparator. §p < 0.05, §§p < 0.01, §§§p < 0.001 favoring active comparator vs. oral semaglutide. Data are for the treatment policy estimand (regardless of premature treatment discontinuation or rescue medication use). BL baseline, HbA1c glycated hemoglobin, ins insulin, met metformin, MRI moderate renal impairment, OAD oral antidiabetes drug, SGLT2i sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, SU sulfonylurea, T2D type 2 diabetes
4.1.1 Active-Comparator Trials
The effects of oral semaglutide were investigated versus both oral and s.c. comparators. Oral semaglutide 14 mg was found to be superior in reducing HbA1c versus empagliflozin (25 mg) (PIONEER 2) at 26 weeks (ETD − 0.4%; p < 0.001) when used as second-line treatment in patients uncontrolled on metformin. The glucose-lowering effects were sustained to week 52 [47]. Oral semaglutide (7 and 14 mg) also provided superior improvements in HbA1c versus sitagliptin (100 mg) at week 26 (ETD − 0.3% and − 0.5%, respectively; both p < 0.001) in patients with T2D uncontrolled on metformin with or without an SU (PIONEER 3) [48]. The glycemic effects of oral semaglutide versus sitagliptin were maintained at both week 52 [ETD − 0.3 (7 mg) and − 0.5 (14 mg), respectively; p < 0.001] and week 78 [ETD − 0.4% (14 mg); p < 0.001] [48]. The observations from both studies indicate that oral semaglutide is an effective strategy for intensification of glycemic therapy in patients with T2D uncontrolled on metformin in the context of other oral glucose-lowering agents.
A study investigating a flexible dose-adjustment approach for oral semaglutide (increasing or decreasing dose depending on efficacy and gastrointestinal tolerability) noted that oral semaglutide was more effective than sitagliptin (100 mg) in reducing HbA1c at week 52 (ETD − 0.5%; p < 0.001) [52]. This is of particular interest because a flexible dose-adjustment approach perhaps more closely replicates the individualized approach of adjusting treatment dose according to efficacy and tolerability that could be implemented in clinical practice [52].
Oral semaglutide was compared with the s.c. GLP-1RA dulaglutide (0.75 mg) in Japanese patients (PIONEER 10) [55]. Reductions in HbA1c with oral semaglutide 7 mg were similar to those seen with s.c. dulaglutide at weeks 26 and 52; however, oral semaglutide (14 mg) reduced HbA1c significantly more than dulaglutide at weeks 26 (ETD − 0.4; p < 0.001) and 52 (ETD − 0.3; p < 0.05).
4.1.2 Active- and Placebo-Controlled Trials
Oral semaglutide was compared with both placebo and liraglutide (0.9 mg) in a Japanese patient population (PIONEER 9) [54]. Oral semaglutide significantly reduced HbA1c versus placebo at all doses (ETD − 0.8 to − 1.4%; p < 0.001) at weeks 26 and 52. The change in HbA1c at week 26 was similar for the 7 mg dose of oral semaglutide versus liraglutide; however, a significantly greater reduction in HbA1c was observed for the 14 mg dose (ETD − 0.4; p < 0.01). At week 52, the difference between oral semaglutide 14 mg and liraglutide (ETD − 0.3) was no longer significant.
In another study (PIONEER 4), oral semaglutide (14 mg) was compared with both placebo and liraglutide (1.8 mg), with liraglutide used at a dose more commonly used globally in routine clinical practice [49]. Oral semaglutide was found to be superior to placebo in reducing HbA1c at week 26 in patients with T2D uncontrolled on metformin with or without an SGLT2i (ETD − 1.1%; p < 0.001) [49]. HbA1c reductions at week 26 were found to be similar with oral semaglutide (14 mg) versus s.c. liraglutide (1.8 mg) at 26 weeks (ETD − 0.1%; p = ns), but a significant improvement in HbA1c reduction was seen with oral semaglutide compared with liraglutide (ETD − 0.3; p < 0.001) and placebo (ETD − 1.0; p < 0.001) at week 52.
4.1.3 Placebo-Controlled Trials
In patients with T2D uncontrolled by diet and exercise (PIONEER 1), once-daily oral semaglutide monotherapy (3, 7, and 14 mg) demonstrated superior improvements in HbA1c versus placebo at week 26 [ETD − 0.6% (3 mg) to − 1.1% (14 mg); p < 0.001 for all] [46].
Benefits were also observed in patients with more advanced T2D receiving background insulin (PIONEER 8). Oral semaglutide reduced HbA1c significantly more than placebo at week 26 [ETD − 0.5% (3 mg), − 0.9% (7 mg), − 1.2% (14 mg); p < 0.001 for all] [53]. Significant reductions in HbA1c for all doses were also observed at week 52. These findings indicate that addition of oral semaglutide is an effective treatment intensification strategy for patients who are unable to reach, or maintain, HbA1c targets with insulin alone.
4.1.4 Special Populations
As mentioned previously, many patients with T2D have accompanying comorbidities, with CV and renal comorbidities being the most common [56, 57]. Oral semaglutide was therefore investigated in these patient populations. In the PIONEER 5 trial, which enrolled patients with moderate renal impairment (estimated glomerular filtration rate 30–59 mL/min/1.73 m2), oral semaglutide 14 mg was found to be significantly more effective than placebo in reducing HbA1c at week 26 (ETD − 0.8%; p < 0.001), highlighting that oral semaglutide is a suitable option for achieving glycemic control in this patient group [50]. In patients at high CV risk, HbA1c levels decreased by 1.0% with oral semaglutide and by 0.3% with placebo at the end of the trial; however, no statistical comparison of the HbA1c reductions was performed [51].
4.2 Body-Weight Reduction
In addition to the glycemic benefits described, oral semaglutide has also been shown to be effective in reducing body weight in patients with T2D on a variety of different background glucose-lowering therapies (Fig. 3).
Reductions in body weight with oral semaglutide in the PIONEER program. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 favoring oral semaglutide vs. placebo. †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01, †††p < 0.001 favoring oral semaglutide vs. active comparator. §p < 0.05, §§p < 0.01, §§§p < 0.001 favoring active comparator vs. oral semaglutide. Data are for the treatment policy estimand (regardless of premature treatment discontinuation or rescue medication use). BL baseline, ins insulin, met metformin, MRI moderate renal impairment, OAD oral antidiabetes drug, SGLT2i sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, SU sulfonylurea, T2D type 2 diabetes
4.2.1 Active-Comparator Trials
Body-weight reductions were found to be similar for oral semaglutide compared with empagliflozin [ETD − 0.1 kg (p = 0.76) and − 0.2 kg (p = 0.62) at weeks 26 and 52, respectively] (PIONEER 2; Fig. 3) [47]. All three doses of oral semaglutide were associated with significantly greater reductions in body weight compared with sitagliptin (100 mg) [ETD − 0.6 kg (3 mg) to − 2.5 kg (14 mg); p < 0.05 for all doses] at week 26, and these effects were sustained for the duration of the trial (PIONEER 3) [48]. When flexible dose-adjustment of oral semaglutide was used, body weight was also reduced significantly compared with sitagliptin (100 mg) (ETD − 1.9 kg at week 52; p < 0.001) [52]. Benefits on body weight were also observed in a Japanese patient population (PIONEER 10) in which treatment with oral semaglutide (7 and 14 mg) resulted in significantly reduced body weight compared with once-weekly dulaglutide at week 26 (ETD − 1.3 kg; p < 0.01 and − 2.5 kg; p < 0.001, respectively) and at week 52 (ETD − 1.9 kg; p < 0.001 and − 2.6; p < 0.001) [55].
4.2.2 Active- and Placebo-Controlled Trials
Significant reductions in body weight were observed in Japanese patients treated with oral semaglutide (14 mg) compared with both placebo (ETD − 1.2 kg; p < 0.01) and liraglutide (− 2.3 kg; p < 0.001) at week 26, and these benefits were maintained at week 52 (PIONEER 9) [54]. Oral semaglutide (14 mg) also provided a significantly greater body weight reduction compared with placebo (ETD − 3.8 kg; p < 0.001) and liraglutide (1.8 mg) at week 26 in a global population [ETD − 1.2 kg; p < 0.001 (PIONEER 4)], and again these effects were sustained at week 52 [49]. These observations suggest that oral semaglutide may provide some weight management benefits versus other commonly prescribed s.c. GLP-1RAs.
4.2.3 Placebo-Controlled Trials
In patients with T2D uncontrolled on lifestyle modifications, oral semaglutide (14 mg) monotherapy significantly reduced body weight versus placebo (ETD − 2.3 kg at week 26; p < 0.001). No significant changes versus placebo were observed for the oral semaglutide 3 and 7 mg doses (PIONEER 1) [46]. Weight management is particularly important for patients managed with insulin-based regimens, as insulin treatment is commonly associated with weight gain [1]. Oral semaglutide was shown to be a suitable treatment option in this patient population, with body weight being reduced versus placebo at week 26 [ETD − 0.9 kg (3 mg) to − 3.3 kg (14 mg); p < 0.05 for all], and the effects being sustained to week 52 (PIONEER 8) [53].
4.2.4 Special Populations
In patients with moderate renal impairment, body-weight reductions were observed with oral semaglutide (14 mg) compared with placebo (ETD − 2.5 kg at 26 weeks; p < 0.001) [50]. Although there was no statistical comparison of bodyweight changes with treatment in the CV safety trial, by the end of that study in patients at high CV risk, body weight had decreased by 4.2 kg with oral semaglutide and by 0.8 kg with placebo [51].
4.3 Additional Secondary Endpoints of Interest
Achieving a target HbA1c of < 7.0% (53 mmol/mol) is another established measure of glycemic control [58]. The proportion of patients achieving this target with oral semaglutide (14 mg or flexibly dosed) at the time point for the primary endpoint [i.e., week 26 except for PIONEER 7 (week 52)] was consistently greater than that seen with all the active comparators (except liraglutide in PIONEER 4) or placebo in each study (Table 3) [46,47,48,49,50, 53,54,55]. The proportion of patients achieving HbA1c < 7% at later time points (weeks 52 and 78) with oral semaglutide was maintained in some studies, while in others a slight decrease in the proportion of patients achieving this target was observed (Table 3) [47,48,49, 53,54,55], which is perhaps not surprising given the progressive nature of T2D.
The benefits of flexible dose-adjustment of oral semaglutide on glycemic control versus sitagliptin occurred despite greater use of rescue medication in patients receiving sitagliptin [52]. In general, across the PIONEER clinical trials, the use of rescue medication was low, occurring in less than 5% of patients who received oral semaglutide 7 or 14 mg after 26 weeks of treatment, and this was typically less than the prevalence of rescue medication use seen with placebo (5–15% at week 26) [46,47,48,49,50, 53,54,55].
For patients with T2D receiving insulin therapy (PIONEER 8), incorporation of oral semaglutide into the treatment regimen permitted reductions in insulin dosage for the majority of patients. Indeed, after 26 weeks on oral semaglutide 14 mg, patients were on average receiving 8 units/day less insulin than patients on placebo (p < 0.001), and by 52 weeks the disparity in insulin requirements was even greater (ETD –17 units/day; p < 0.001) [53].
The effects of oral semaglutide on a composite endpoint of HbA1c < 7% (53 nmol/mol) without severe or blood glucose-confirmed [<3.1 mmol/L (56 mg/dL)] hypoglycemia and with no weight gain were also examined. In general, a greater proportion of patients achieved this endpoint at week 26 when treated with the 7 and 14 mg doses versus oral active comparators (empagliflozin and sitagliptin) (Table 3) [47, 48]. In Japanese studies, a greater proportion of patients achieved the composite endpoint of HbA1c < 7% (53 nmol/mol) without hypoglycemia and no weight gain with oral semaglutide (14 mg) compared with the s.c. GLP-1RAs liraglutide (0.9 mg) (week 26: 70% vs. 33%; p < 0.001 for estimated odds ratio) and dulaglutide (0.75 mg) (week 26: 66% vs. 39%; p < 0.001 for estimated odds ratio) [54, 55]. It is, however, important to note that the GLP-1RA comparators in both these Japanese studies were investigated at doses that are lower than used in many other countries. Indeed, the odds of achieving this composite endpoint were not significantly different with oral semaglutide 14 mg versus liraglutide 1.8 mg [49], a dose more commonly used in routine clinical practice worldwide. As expected, more patients achieved the composite endpoint HbA1c < 7% (53 nmol/mol) without hypoglycemia and no weight gain for all investigated doses of oral semaglutide versus placebo, including in the study of patients with moderate renal impairment [46, 49, 50, 53, 54].
A post hoc analysis of the PIONEER 1−5 and 8 trials evaluated the response of any reduction in HbA1c (%) and/or body weight (%), and a clinically relevant composite endpoint of HbA1c reduction ≥ 1% and body-weight loss ≥ 5%, with oral semaglutide (14 mg) versus comparators at the end of treatment (26−78 weeks). Oral semaglutide was shown to be more effective than comparators in providing both an HbA1c reduction ≥ 1% and body-weight loss ≥ 5% [59].
Across most of the PIONEER studies, oral semaglutide reduced systolic blood pressure (SBP) by 1–6 mmHg, with many reductions achieving statistical significance for oral semaglutide (14 mg) versus placebo (Table 3) [46,47,48,49, 52,53,54,55]. In patients with T2D and renal impairment, for whom effective blood pressure regulation is particularly important, oral semaglutide (14 mg) reduced SBP by 7 mmHg versus 0 mmHg with placebo (p < 0.001) [51].
4.4 Patient-Reported Outcomes
While the effects of oral semaglutide on glycemic control and body weight are of prime importance, it is widely accepted that there is a need for healthcare professionals to consider other factors when managing T2D [1]. These factors include patient-reported outcomes (PROs), which can assess the impact of treatment on physical function and psychological aspects, such as treatment satisfaction, patient wellbeing, and quality of life (QoL) [60]. In the PIONEER clinical program, five PRO tools were used to measure patient satisfaction about treatment with semaglutide versus comparators, and the impact of treatment with semaglutide on wellbeing, QoL, physical functioning, and so forth.
Observations from the Diabetes Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire revealed that satisfaction with treatment, and convenience and flexibility of treatment were similar between patients receiving flexibly dosed oral semaglutide and a commonly used glucose-lowering agent, sitagliptin [52]. This may suggest that the dosing conditions of oral semaglutide are not a major factor in treatment satisfaction relative to another oral glucose-lowering agent. Patient perceptions about treatment and, more specifically, dosing conditions with oral semaglutide, were also investigated as part of a survey of study staff (N = 1,140) from the PIONEER trials. Of the study staff responders (n = 544) the oral semaglutide dosing conditions were perceived to be easy/very easy, neutral, or hard by 79.1%, 19.1%, and 1.8%, respectively [61].
The CoEQ is a validated PRO tool designed to assess the intensity and type of food cravings in addition to subjective sensations of appetite and mood [62]. Improvements in favor of oral semaglutide versus empagliflozin were observed for the “craving control” and “craving for savory” domains in the PIONEER 2 study [47]. This is an interesting finding given that body-weight changes reported in this study were similar for both treatments.
The Impact of Weight on Quality of Life questionnaire Clinical Trial Version (IWQOL-Lite-CT) was used to assess weight management in the PIONEER 3 and 8 studies. Rosenstock et al. reported that the ETDs significantly favored oral semaglutide (7 and 14 mg) over sitagliptin (100 mg) at week 52 for physical function domains. Moreover, oral semaglutide improved psychosocial (7 mg) and physical (14 mg) domains, and IWQOL-Lite-CT total scores (7 mg) at week 52 compared with sitagliptin [48]. However, these effects were not apparent at earlier or later time points. For patients receiving insulin in PIONEER 8, the ETD favored oral semaglutide (14 mg) over placebo for the psychosocial domain and for the IWQOL-Lite-CT total score at weeks 26 and 52 [53]. For these patients, it may be that reductions in body weight are associated with improvements in patient mood. Improvements were also observed in some health-related QoL domains and component summaries in patients with T2D and moderate renal impairment (PIONEER 5) and in those receiving insulin (PIONEER 8), as measured using the well-established Short Form (SF)-36v2™ questionnaire [50, 53].
In the Japanese patient population, total scores for the Diabetes Therapy-Related Quality of Life questionnaire for oral semaglutide (7 and 14 mg) were similar to those observed with liraglutide and slightly better than those seen with placebo (PIONEER 9), while improvements in Diabetes Therapy-Related Quality of Life scores for anxiety and dissatisfaction with treatment, and total score, were observed with oral semaglutide (7 and 14 mg) compared with dulaglutide at week 52 in PIONEER 10 [54, 55]. These observations may reflect the oral versus s.c. delivery.
5 Safety and Tolerability
Safety and tolerability findings for oral semaglutide in the PIONEER studies are summarized in Table 4, and are broadly consistent with the known safety and tolerability profile of a GLP-1RA. Overall, the doses of oral semaglutide investigated in the PIONEER trials were generally well tolerated, with AEs typically reported in similar proportions of patients in the oral semaglutide, placebo, and active-comparator groups across all of the studies [46,47,48,49,50, 52,53,54,55]. Serious AEs (SAEs) were generally reported in similar proportions of patients in the oral semaglutide, placebo, and active-comparator groups across studies [46,47,48,49,50, 52,53,54,55].
5.1 Adverse Events of Special Interest
5.1.1 Gastrointestinal Adverse Events
Consistent with what has been reported for other GLP-1RAs [63], the most common AEs encountered with oral semaglutide in the PIONEER trials tended to be gastrointestinal, with nausea and diarrhea generally the most common manifestations (Table 4) [46,47,48,49,50, 52,53,54,55]. In general, gastrointestinal AEs such as nausea mostly occurred earlier in the study during dose initiation and escalation (i.e., during the first 8−16 weeks) [46,47,48,49,50, 53,54,55]. Cases of nausea were typically mild to moderate in intensity, and transient [46,47,48,49,50, 52,53,54,55]. In PIONEER trials that studied oral semaglutide 3, 7, and 14 mg, the proportion of patients with gastrointestinal AEs and the proportion of patients who discontinued treatment due to gastrointestinal AEs appeared to increase with dose [46, 48, 53,54,55] (Table 4). As expected, gastrointestinal AEs also occurred on treatment with GLP-1RA comparators (Table 4). The peak occurrence of nausea was also reported to be earlier with liraglutide (approximately 2 weeks) compared with oral semaglutide (8 weeks) [49], potentially reflecting the quicker dose escalation that occurs with liraglutide. Constipation was also a common AE reported by patients in the Japan-specific PIONEER 9 and 10 trials, occurring in 9–15% of patients with oral semaglutide versus 9% with dulaglutide (0.75 mg) and 19% with liraglutide (0.9 mg) [54, 55].
Currently, the only clinical trial reporting an incidence of gastrointestinal AEs for both s.c. and oral formulations of semaglutide is the 26-week, phase II, dose-ranging study [45]. Gastrointestinal AEs were reported in similar proportions of patients in the s.c. semaglutide (1.0 mg) and oral semaglutide (10 and 20 mg) groups, which were the doses of oral semaglutide closest to the maximum approved oral semaglutide dose (14 mg) in the study [45]. An exposure-response analysis of data from the SUSTAIN and PIONEER programs for s.c. and oral semaglutide has demonstrated a consistent relationship between greater exposure to semaglutide and increases in the incidence of gastrointestinal AEs regardless of formulation [33], suggesting that exposure, rather than route of administration, is the determinant of such events.
In the PIONEER 1−8 studies, discontinuation due to gastrointestinal AEs was the most common cause of premature trial product discontinuations (Table 4), occurring in 1.7–12% of patients across oral semaglutide study groups [46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53].
5.1.2 Hypoglycemia
GLP-1RAs are considered to have a low inherent risk of hypoglycemia [3, 63], owing to their glucose-dependent mechanism of action [63]. Consistent with observations for the GLP-1RA class as a whole, severe hypoglycemic episodes were found to be rare in all the PIONEER studies (Table 4). For most PIONEER trials the combined incidence of severe or symptomatic blood glucose-confirmed [< 56 mg/dL (< 3.1 mmol/L)] hypoglycemia with oral semaglutide was similar to that seen with active comparators (liraglutide, empagliflozin, and sitagliptin) and placebo [46,47,48,49, 52, 54]. The proportion of patients with severe or blood glucose-confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia appeared to be greater in the PIONEER 3, 5, 7, and 8 trials [48, 50, 52, 53] relative to the other PIONEER trials (Table 4), but this may be attributed to the background therapies allowed in those trials, namely SUs (PIONEER 3, 5, and 7) and insulin (PIONEER 5 and 8). Nevertheless, in these studies, the rate of severe or blood glucose-confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia with oral semaglutide was found to be similar to that of sitagliptin or placebo [48, 52, 53].
5.1.3 Other Adverse Events of Special Interest
Post-marketing case reports and retrospective analyses of AEs have raised a possible association between pancreatitis and GLP-1RA therapy [63]. Cases of acute pancreatitis have been reported in the PIONEER clinical studies; however, the incidence of adjudication committee-confirmed pancreatitis with oral semaglutide was low, with no events observed in seven studies and the rate being generally similar to comparators in the other trials [46,47,48,49,50, 52,53,54,55]. In the CV outcomes trial, the frequency of acute pancreatitis was 0.1% for semaglutide and 0.2% for placebo [51].
The incidence of malignant neoplasms reported for oral semaglutide was also low and broadly similar to that of comparators [46,47,48,49,50, 52,53,54,55].
In a 2-year study of s.c. semaglutide in patients considered at high CV risk, a treatment difference was observed between groups with respect to diabetic retinopathy complications, i.e., 3.0% of patients in the s.c. semaglutide group experienced these complications compared with 1.8% of patients in the placebo group. This treatment difference appeared early and persisted throughout the trial [5]. In clinical trials of oral semaglutide of up to 18 months’ duration and involving 6352 patients with T2D, AEs related to diabetic retinopathy were reported in similar proportions in patients treated with oral semaglutide (4.2%) and comparators (3.8%) [29].
It should be noted, however, that patients with a history of pancreatitis, with proliferative retinopathy or maculopathy requiring acute treatment, or a history of malignant neoplasms in the previous 5 years were excluded from the phase III studies with oral semaglutide.
5.2 Cardiovascular Safety
As CV disease is the leading cause of death among patients with T2D, establishing the CV safety of new glucose-lowering therapies is of prime importance and required by regulatory authorities. PIONEER 6 was an event-driven CV outcomes trial conducted to establish the CV safety of oral semaglutide (14 mg) compared with placebo in patients considered at high CV risk [51]. Patients were followed up for a median of 15.9 months. Observations for key CV endpoints are summarized in Table 5. The primary composite endpoint of major adverse CV events (MACE) was reported in 3.8% of patients in the oral semaglutide group versus 4.8% in the placebo group [hazard ratio (HR) 0.79; 95% CI 0.57–1.11]. These data confirmed the noninferiority (p < 0.001), but not superiority (p = 0.17), of oral semaglutide to placebo in this study [51]. However, the study was not sufficiently powered to demonstrate superiority [64]. An analysis of individual MACE components revealed a nominally statistically significant reduction in the risk of death from CV causes with oral semaglutide treatment [HR 0.49 (95% CI 0.27–0.92)]; however, no significant differences were observed for other MACE components [51]. The authors of this study concluded that the CV risk profile of oral semaglutide was noninferior to that of placebo [51]. Interestingly, the observations from PIONEER 6 are also broadly consistent with those of the SUSTAIN 6 CV outcomes trial for s.c. semaglutide, including the HR for the primary MACE endpoint, which was 0.74 (95% CI 0.58–0.95) with s.c. semaglutide compared with placebo [5, 51]. A recent patient-level analysis of data from PIONEER 6 and SUSTAIN 6 combined showed consistent effects on MACE incidence across the two formulations, with an overall HR of 0.76 (95% CI 0.62–0.92) for combined semaglutide data (s.c. and oral) versus placebo [65]. These observations suggest that the CV profile of oral semaglutide is likely to be similar to that of s.c. semaglutide [51, 65].
5.3 Tolerability of Oral Semaglutide in Special Patient Populations
In patients with T2D and moderate renal impairment (PIONEER 5), no unexpected safety concerns were observed for oral semaglutide [50] (Table 4). Pharmacokinetic studies in patients with renal impairment (mild, moderate, or severe, or ESRD) and hepatic impairment (mild, moderate, or severe) indicated no impact of such impairment on either oral semaglutide pharmacokinetics or safety [36, 37].
6 Subgroup Analyses
Subgroup analyses have been conducted to examine whether the efficacy of oral semaglutide is consistent across different patient groups within the PIONEER 1−5, 7, and 8 trials (N = 5657 patients). An exploratory analysis of these PIONEER trials evaluated the efficacy of once-daily oral semaglutide (3, 7, and 14 mg) versus comparators by diabetes duration at baseline. Patients were grouped according to diabetes duration (< 5, 5 to < 10, and ≥10 years). The results showed that oral semaglutide (7 and 14 mg) improved glycemic control versus comparators in all groups, irrespective of disease duration subgroup [66].
The impact of age at baseline on the efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide was also examined in an exploratory analysis, and this showed that there were greater effects of oral semaglutide versus comparators on HbA1c and body weight in patients with T2D regardless of age group (< 45, ≥ 45–< 65, or ≥ 65 years). For the < 65 and ≥ 65 age groups, the safety profile of oral semaglutide was in line with that of other GLP-1RAs. In general, there was a higher discontinuation rate with oral semaglutide in older patients, although this was also true for many comparators [67].
The impact of race was also examined in a subgroup analysis of the same studies. This analysis revealed that there was a significant interaction between treatment and race in PIONEER 1, 4, and 8, with greater HbA1c reductions and ETDs in Asian patients than in other race subgroups. However, a treatment interaction by race was not observed in the PIONEER 2, 3, 5, and 7 studies [68], and the prescribing information notes that the efficacy of semaglutide is not impacted by race [29].
Meier et al. conducted an exploratory analysis to examine the effect of baseline HbA1c on overall HbA1c and body-weight reductions achieved during each trial [69]. Patients were grouped by trial and according to baseline HbA1c (≤ 8.0%, > 8.0–≤ 9.0%, and > 9.0%). HbA1c reductions were greater with higher baseline HbA1c, but there was no consistent relationship between change in body weight and baseline HbA1c. Reductions in HbA1c were greater with oral semaglutide (7 and 14 mg) versus placebo and versus active comparator in all HbA1c subgroups [69]. A subgroup analysis of the PIONEER 3 study explored the glycemic effects of oral semaglutide (3, 7, and 14 mg) versus sitagliptin (100 mg) by baseline HbA1c and also by background oral glucose-lowering therapy [70]. In this analysis, HbA1c was reduced across all baseline HbA1c and background oral glucose-lowering therapy groups in all treatment arms; reductions were greater with higher baseline HbA1c. HbA1c reductions were significantly greater with oral semaglutide (7 and 14 mg) compared with sitagliptin in all groups, except for oral semaglutide 7 mg in the HbA1c ≤ 8.0% group [70].
The potential impact of background therapy in the PIONEER trials is an important consideration. An exploratory subgroup analysis of five PIONEER trials (3−5, 7, and 8) assessed the potential impact of different background medications (metformin, SU, SGLT2i, insulin, or combinations) on the efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide and comparators [71]. Reductions in HbA1c and body weight were greater for oral semaglutide versus comparators (except liraglutide 1.8 mg, which gave similar reductions in HbA1c), regardless of background medication. In general, there were no statistically significant treatment interactions found between treatment and subgroups [71]. In PIONEER 4, the glycemic effects of oral semaglutide and comparators were investigated in patients with and without SGLT2i as background therapy. This subgroup analysis showed that both changes in HbA1c and body weight were similar in patients receiving oral semaglutide or s.c. liraglutide with or without SGLT2i background medication, as were the occurrence of gastrointestinal AEs [72]. An exploratory sub-analysis of the PIONEER 8 study evaluated the impact of background insulin (basal, premixed, or basal-bolus) with or without metformin on the efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide. Reductions in both HbA1c and body weight were similar across all background insulin groups. Most of the hypoglycemic episodes (six out of nine) were observed in the basal-bolus insulin subgroup. Fewer patients had severe or symptomatic blood glucose-confirmed hypoglycemia with oral semaglutide compared with placebo (basal: 10.4−15.8% vs. 20.0%; premix: 18.8−22.2% vs. 34.4%) except in the basal-bolus subgroup (39.7−50.7% vs. 37.5%) [73]. The findings from these analyses support the use of oral semaglutide across a broad population of patients with T2D in combination with other commonly used glucose-lowering agents.
7 Cost-Effectiveness
Several studies have evaluated the short- and long-term cost-effectiveness of oral semaglutide. A US cost-of-control analysis assessed the short-term cost-effectiveness of oral semaglutide (14 mg) versus s.c. GLP-1RAs, with results indicating that oral semaglutide (14 mg) is likely to be cost-effective versus dulaglutide, exenatide (once weekly and twice daily), liraglutide, and lixisenatide in terms of achieving glycemic control targets [74]. In another US analysis by Hunt et al., treatment with oral semaglutide was consistently associated with the lowest cost of control versus empagliflozin, sitagliptin, and liraglutide for HbA1c ≤ 6.5%, HbA1c < 7.0%, and a composite of HbA1c < 7.0% without hypoglycemia and without weight gain [75].
The long-term cost-effectiveness of oral semaglutide (14 mg) versus comparators [empagliflozin (25 mg), sitagliptin (100 mg), and liraglutide (1.8 mg)] has also been examined for the treatment of T2D from a healthcare-payer perspective in the UK, with findings showing that treatment with oral semaglutide was associated with improvements in quality-adjusted life expectancy and was projected to be a cost-effective treatment option versus all three comparators, even though direct costs were higher over the patient’s lifetime with oral semaglutide versus empagliflozin and sitagliptin [76]. The long-term cost-effectiveness of oral semaglutide versus empagliflozin was also estimated from a Canadian payer and a societal perspective using data from the PIONEER 2 study. It was suggested that, over 40 years, oral semaglutide would be associated with more quality-adjusted life years and be more cost-effective than empagliflozin in patients with T2D uncontrolled on metformin in Canada [77]. In contrast, a US study has examined the impact of utilizing oral semaglutide versus sitagliptin as a second-line agent, and found that over a 5-year time horizon, each 10% increase in the use of oral semaglutide instead of sitagliptin would result in an additional cost of $3.4 M for a US payer [78]. More studies are required in different healthcare systems to assess and further explore the cost-effectiveness of oral semaglutide.
8 Dosage and Administration
Oral semaglutide is indicated for the treatment of adults with insufficiently controlled T2D to improve glycemic control as an adjunct to diet and exercise, for use as monotherapy when metformin is considered inappropriate due to intolerance or contraindications, or in combination with other glucose-lowering therapies [29]. Oral semaglutide should be taken on an empty stomach and swallowed whole with up to 120 mL of water. Patients should then wait at least 30 min before consumption of food, drink, or other oral medications [29]. The starting dose of oral semaglutide is 3 mg once daily for 1 month, after which the dose should be increased to a maintenance dose of 7 mg once daily. If, after at least 1 month of treatment with oral semaglutide 7 mg once daily, further improvement in glycemic control is desired, then the dose can be increased to a maintenance dose of 14 mg once daily. The maximum single daily dose of oral semaglutide is 14 mg [29]. When oral semaglutide is used in combination with metformin, an SGLT2i, or a TZD, the current dosing of these medications can be continued as normal. When used in combination with an SU or insulin, a dose reduction of these agents may be required to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia [29]. No dose adjustment is required in patients with renal or hepatic impairment [29].
9 Place for Oral Semaglutide in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes
Clinical trials have demonstrated clear benefits of the GLP-1RA drug class with respect to improvements in glycemic control (HbA1c), body-weight loss, and blood-pressure reduction, without the risk of hypoglycemia [3]. However, until recently, GLP-1RAs have only been available for s.c. administration, presenting a challenge for some healthcare professionals given that some patients express a preference for noninjectable therapy. Avoidance of injections has been reported in patients receiving injectable glucose-lowering agents such as insulin, with concerns about injection burden and pain contributing to this lack of adherence [79]. It has been noted that adherence with therapy seems to be better when the injection burden is reduced. For example, adherence seems to be better with weekly rather than daily injections of GLP-1RAs [80]. Knowledge of such trends could potentially impact the choice of treatments by the prescribers who are striving to achieve glycemic goals and facilitate patient adherence to therapy [81].
The observations from the PIONEER clinical program demonstrate that oral semaglutide can provide effective glycemic control and body weight reductions in T2D, across a range of patient populations receiving a wide spectrum of different background medications [47,48,49,50, 52, 53, 55], including diet and exercise [46, 54]. Moreover, oral semaglutide appears to offer advantages over some commonly used oral therapies in terms of glycemic efficacy and/or reductions in body weight, and therefore represents a valuable option for intensifying glycemic control when an oral therapy is preferred.
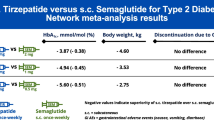
Oral semaglutide may also represent a useful option in patients without a preference for oral administration. Direct comparisons of oral semaglutide with s.c. GLP-1RAs are somewhat limited, as two of the studies were conducted in Japanese patients and consequently used maintenance doses of liraglutide and dulaglutide that are smaller than those commonly used elsewhere. When compared with the usual dose of s.c. liraglutide (1.8 mg), oral semaglutide appeared to provide greater body-weight loss and improved glycemic control in the longer term (52 weeks) [49]. Interestingly, a recent systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials with GLP-1RAs also suggested that oral semaglutide (14 mg) was associated with HbA1c and body-weight reductions that were at least as great, if not greater, than seen with most approved s.c. GLP-1RAs, with the exception of once-weekly s.c. semaglutide (1 mg) [82]. In this meta-analysis, the glycemic efficacy of once-weekly s.c. semaglutide 0.5 mg was similar to that seen with once-daily oral semaglutide 14 mg. The efficacy of once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide 1 mg appeared to be slightly greater than that seen with once-daily oral semaglutide 14 mg, although the differences in HbA1c [0.21% (95% credible intervals: − 0.03 to 0.46)] and body weight (0.63 kg [95% credible interval: − 0.28 to 1.52)] did not achieve statistical significance [82]. However, it should be noted that the meta-analysis is subject to various limitations, such as heterogeneity in populations between trials and differing time points used between trials, and therefore the comparative efficacy of once-daily oral semaglutide 14 mg versus once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide 1 mg needs to be confirmed in prospective clinical trials.
The safety and tolerability of the GLP-1RA class is well established [3, 63], with evidence available from a large number of clinical trials and from routine use in daily clinical practice. It is widely accepted that the most frequently encountered AEs with GLP-1RAs are gastrointestinal disorders, in particular nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea [3, 83]. In the PIONEER trials, oral semaglutide was shown to be well tolerated, including in patients with renal impairment or at high CV risk [50, 51], and the safety and tolerability profile was consistent with the GLP-1RA class [49, 54, 55]. As expected for a GLP-1RA, gastrointestinal disorders such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea were the most prevalent AEs seen with oral semaglutide [46,47,48,49,50, 52,53,54,55]. However, a systematic review and network meta-analysis suggested that the odds of experiencing gastrointestinal AEs with oral semaglutide (14 mg) are not significantly different compared with s.c. GLP-1RAs [82]. Studies in Japanese patients found that constipation was observed with oral semaglutide more frequently than nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea [54, 55]. Studies with other GLP-1RAs have also observed a propensity towards constipation as a gastrointestinal AE with these agents in Japanese patients [84,85,86], and this could be a result of differences in diet and patient behavior [86]. Although gastrointestinal AEs with GLP-1RAs can be troublesome, they are generally transient and decrease over a period of weeks or months. More gradual dose titration can help reduce their frequency and intensity for patients [3]. A potential risk to patients for gastrointestinal AEs is dehydration and, as such, patients taking oral semaglutide should take precautions to avoid fluid depletion [29].
Hypoglycemia is an important consideration for any glucose-lowering therapy, and severe hypoglycemic episodes were found to be rare with oral semaglutide. The incidence of other AEs of special interest, including acute pancreatitis, malignant neoplasms, and diabetic retinopathy, was also low and was broadly similar between oral semaglutide and comparators [46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55]. Perhaps most importantly, given the link between CV complications and T2D, the CV risk profile of oral semaglutide was also found to be noninferior to that of placebo [51]. However, unlike the observations for once-weekly s.c. semaglutide in the SUSTAIN 6 trial, a significant CV benefit was not observed with oral semaglutide [5, 51]. While the HR for the primary MACE endpoint in PIONEER 6 was similar in magnitude to that seen with once-weekly s.c. semaglutide in SUSTAIN 6 [5, 51], the PIONEER 6 trial was likely underpowered to demonstrate superiority versus placebo for oral semaglutide [64]. CV outcomes trials for GLP-1RAs were compared in a recent network meta-analysis using a binomial likelihood logit link model for outcomes including CV death, myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and death from any cause [87]. Seven GLP-1RA CV outcomes trials were included in this analysis after screening, and the results showed that oral semaglutide was statistically better than lixisenatide (HR 0.43; CI 0.19−0.92), albiglutide (HR 0.45; CI 0.19−0.97), dulaglutide (HR 0.46; CI 0.20−0.97), and exenatide (HR 0.47; CI 0.21−0.99) in reducing CV deaths. No significant differences were detected between most of the treatments regarding reducing all-cause death, MI, and stroke events. Ranking results showed that oral semaglutide had the highest probability to be ranked first (> 90%) in reducing CV death and death from any cause, while once-weekly s.c. semaglutide had the highest probability to be ranked first in reducing MI and stroke events [87]. Further clinical studies are required to confirm if the CV benefit seen with s.c. semaglutide will translate to oral semaglutide, and a phase III study (SOUL; clinicaltrials.gov NCT03914326 [88]) is underway to investigate the effect of oral semaglutide treatment on CV outcomes.
A potential limitation of oral semaglutide is the need to dose patients in a fasted state upon waking and 30 min before consuming food, drink, or other oral medications. For some patients this may not be practical, and currently there are no data regarding the efficacy of oral semaglutide with dosing conditions (e.g., different times or fasting periods) other than those used in the PIONEER trials. A recent online survey presented seven hypothetical, blinded drug profiles to 553 respondents in order to evaluate patient preferences towards various oral glucose-lowering therapies. In this survey, more patients said that they would prefer a treatment with a profile similar to empagliflozin (41%) or sitagliptin (31%) than to oral semaglutide (11%), with factors such as the need for fasting and potential for adverse gastrointestinal effects influencing their decisions [89]. However, it should be noted that patients may evaluate drugs differently during actual treatment, and the impact of these various factors in practice may be less than patients anticipate. Indeed, it is interesting to note that, despite the dosing conditions and potential for gastrointestinal effects with oral semaglutide, satisfaction and convenience of treatment was reported to be comparable with sitagliptin [52]. This may suggest that the dosing conditions of oral semaglutide are manageable by most patients.
In recent years, the management of T2D has been evolving, with a more patient-centric and individualized approach being recommended by organizations [1, 58]. Shared decision-making to address the needs and preferences of each patient, and the individual characteristics that influence the risks and benefits of therapy for each patient are an important consideration [58]. Patient preferences for oral versus injectable GLP-1RAs need to be further explored in this context. In a recent online survey, N = 600 patients with T2D were asked to provide their treatment preferences regarding a once-daily oral GLP-1RA compared with a once-weekly injectable GLP-1RA. Initially, the majority of patients favored the use of a once-daily oral versus a once-weekly injectable GLP-1RA (76.5% vs. 23.5%). However, when patients were then presented with a video detailing the dosing conditions required with oral semaglutide and those with once-weekly injectable dulaglutide, 52.5% indicated a preference for oral semaglutide [90]. This study assessed patient preferences based only on the dosing conditions, but a wide range of treatment-related factors may be considered when selecting a GLP-1RA, including the expected efficacy and safety. A subsequent Japanese survey (N = 500) also assessed the willingness of patients with T2D to initiate different GLP-1RA therapies based on unbranded therapy profiles. These outlined the mode and frequency of administration, as well as the changes in HbA1c, body weight, and risk of nausea, expected with oral semaglutide 7 and 14 mg, liraglutide 0.9 mg, and dulaglutide 0.75 mg, based on the results from the PIONEER 9 and 10 trials. Of note, the doses of liraglutide and dulaglutide used in these trials are the highest doses approved in Japan. Overall, 88–91% of patients preferred the profile of oral semaglutide versus dulaglutide [91]. Cost-effectiveness must also be taken into account in addition to these clinical attributes. Studies have demonstrated oral semaglutide to be cost-effective versus both injectable GLP-1RAs and some oral agents; however, this varies by setting and healthcare system [74,75,76]. To date, there are no real-world studies assessing adherence rates with oral semaglutide and the injectable GLP-1RAs, or the impact that nonadherence has on outcomes; this is another important area for future research.
With both oral and subcutaneous formulations of semaglutide being available, physicians may be faced with a decision over which treatment to prescribe. As mentioned, a shared decision-making approach may help physicians understand which treatment would best fit a patient’s preferences and lifestyle. If it is clear that there is a fear of needles, or if good injection technique may be an issue (e.g., due to limitations with manual dexterity or lack of injection training opportunities), then oral semaglutide would seem a reasonable approach. Alternatively, if the dosing conditions of oral semaglutide are not suitable, whether it be due to a patient preference to avoid the fasting period or patients receiving other medications with potentially conflicting dosing conditions, then the once-weekly s.c. formulation of semaglutide may be the preferred option. Finally, if patients have no clear preference regarding injectable therapy and a little more efficacy is desirable, then once-weekly s.c. semaglutide should be considered.
In conclusion, GLP-1RAs provide effective glycemic control and body weight reductions with a low risk of hypoglycemia. However, until very recently, these agents were only available as s.c injections, which may not be the most desirable mode of delivery for some patients [90]. Oral semaglutide is the first GLP-1RA available in a tablet form, and therefore could be important in facilitating treatment intensification with GLP-1RAs and providing an alternative option for patients with a preference for oral glucose-lowering therapy to achieve better glycemic control.
Change history
14 May 2021
Incorrect xml tagging
References
Davies MJ, D’Alessio DA, Fradkin J. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2018;41(12):2669–701.
Garber AJ, Handelsman Y, Grunberger G, Einhorn D, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, et al. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm—2020 executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2020;26(1):107–39.
Lyseng-Williamson KA. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in type-2 diabetes: their uses and differential features. Clin Drug Invest. 2019;39(8):805–19.
Ahrén B. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for type 2 diabetes: a rational drug development. J Diabetes Investig. 2019;10(2):196–201.
Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz FG, Jódar E, Leiter LA, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(19):1834–44.
Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JFE, Nauck MA, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(4):311–22.
Gerstein HC, Colhoun HM, Dagenais GR, Diaz R, Lakshmanan M, Pais P, et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): a double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2019;394(10193):121–30.
Hernandez AF, Green JB, Janmohamed S, D’Agostino RB Sr, Granger CB, Jones NP, et al. Albiglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (Harmony Outcomes): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;392(10157):1519–29.
American Diabetes Association. 9 Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(suppl 1):S90-102.
Buse JB, Wexler DJ, Tsapas A, Rossing P, Mingrone G, Mathieu C, et al. 2019 update to: management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia. 2020;63(2):221–8.
Gilstrap LG, Blair RA, Huskamp HA, Zelevinsky K, Normand S. Assessment of second-generation diabetes medication initiation among medicare enrollees from 2007 to 2015. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(5):e205411.
Boye KS, Stein D, Matza LS, Jordan J, Yu R, Norrbacka K, et al. Timing of GLP-1 receptor agonist initiation for treatment of type 2 diabetes in the UK. Drugs R D. 2019;19(2):213–25.
Byetta. Summary of product characteristics. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/byetta-epar-product-information_en.pdf. Accessed 17 Aug 2020.
Lyxumia. Summary of product characteristics. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/lyxumia-epar-product-information_en.pdf. Accessed 17 Aug 2020.
Victoza. Summary of product characteristics. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/victoza-epar-product-information_en.pdf. Accessed 17 Aug 2020.
Ozempic. Summary of product characteristics. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/ozempic-epar-product-information_en.pdf. Accessed 17 Aug 2020.
Trulicity. Summary of product characteristics. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/trulicity-epar-product-information_en.pdf. Accessed 17 Aug 2020.
Bydureon. Summary of product characteristics. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/bydureon-epar-product-information_en.pdf. Accessed 17 Aug 2020.
Stewart KD, Johnston JA, Matza LS, Curtis SE, Havel HA, Sweetana SA, et al. Preference for pharmaceutical formulation and treatment process attributes. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2016;10:1385–99.
Bruno BJ, Miller GD, Lim CS. Basics and recent advances in peptide and protein drug delivery. Ther Deliv. 2013;4(11):1443–67.
Lau J, Bloch P, Schäffer L, Pettersson I, Spetzler J, Kofoed J, et al. Discovery of the once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue semaglutide. J Med Chem. 2015;58(18):7370–80.
Knudsen LB, Lau J. The discovery and development of liraglutide and semaglutide. Front Endocrinol. 2019;10:155.
Kaptiza C, Nosek L, Jensen L, Hartvig H, Jensen CB, Flint A. Semaglutide, a once-weekly human GLP-1 analog, does not reduce the bioavailability of the combined oral contraceptive, ethinylestradiol/levonorgestrel. J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;55(5):497–504.
Jensen L, Helleberg H, Roffel A, van Lier JJ, Bjørnsdottir I, Pedersen PJ, et al. Absorption, metabolism and excretion of the GLP-1 analogue semaglutide in humans and nonclinical species. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017;108:101–10.
Buckley ST, Bækdal TA, Vegge A, Maarbjerg SJ, Pyke C, Ahnfelt-Rønne J, et al. Transcellular stomach absorption of a derivatized glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(467):eaar7047.
Granhall C, Donsmark M, Blicher TM, Golor G, Søndergaard FL, Thomsen M, et al. Safety and pharmacokinetics of single and multiple ascending doses of the novel oral human GLP-1 analogue, oral semaglutide in healthy subjects and subjects with type 2 diabetes. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019;58(6):781–91.
Buckley ST, Schéele SG, Kirk RK, Knudsen LB. Mechanism of absorption mediated by SNAC in an oral formulation of semaglutide. Diabetes. 2017;66(Suppl 1):A322.
Maarbjerg SJ, Borregaard J, Breitschaft A, Donsmark M, Søndergaard FL. Evaluation of the effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of oral semaglutide. Diabetes. 2017;66(Suppl 1):A321.
Rybelsus. Summary of product characteristics. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/rybelsus-epar-product-information_en.pdf. Accessed 17 Aug 2020.
Connor A, Donsmark M, Hartoft-Nielsen M-L, Søndergaard FL, Bækdal TA. A pharmacoscintigraphic study of the relationship between tablet erosion and pharmacokinetics of oral semaglutide. Diabetes. 2017;66(Suppl 1):S319.
Bækdal TA, Borregaard J, Donsmark M, Breitschaft A, Søndergaard FL. Evaluation of the effects of water volume with dosing and post-dose fasting period on pharmacokinetics of oral semaglutide. Diabetes. 2017;66(Suppl 1):A315.
Hauge C, Breitschaft A, Hartoft-Nielsen ML, Jensen S, Baekdal T. SAT-140: a drug–drug interaction trial of oral semaglutide with levothyroxine and multiple co-administered tablets. J Endocr Soc. 2019;3(Suppl 1):SAT-140.
Overgaard RV, Navarria A, Hertz CL, Ingwersen SH. Similar efficacy and gastrointestinal tolerability versus exposure for oral and subcutaneous semaglutide. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020;22(Suppl 1):A187–8.
Bækdal TA, Breitchaft A, Navarria A, Hansen CW. A randomized study investigating the effect of omeprazole on the pharmacokinetics of oral semaglutide. Exp Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2018;14(8):869–77.
Meier JJ, Granhall C, Hoevelmann U, Navarria A Sr, Plum-Moerschel L, Ramesh C, et al. Effect of upper gastrointestinal disease on the pharmacokinetics of oral semaglutide in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2019;68(Suppl 1):1013P.
Granhall C, Søndergaard FL, Thomsen M, Anderson TW. Pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of oral semaglutide in subjects with renal impairment. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018;57(12):1571–80.
Bækdal TA, Thomsen M, Kupčová V, Hansen CW, Anderson TW. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of oral semaglutide in subjects with hepatic impairment. J Clin Pharmacol. 2018;58(10):1314–23.
Dahl K, Blundell J, Gibbons C, Brooks A, Almazedi F, Hoff S, et al. Oral semaglutide improves postprandial glucose and lipid metabolism and delays first-hour gastric emptying in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2019;62(Suppl 1):S26 [Abstract 50].
Hjerpsted JB, Flint A, Brooks A, Axelsen MB, Kvist T, Blundell J. Semaglutide improves post-prandial glucose and lipid metabolism, and delays first-hour gastric emptying in subjects with obesity. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20:610–9.
Blundell J, Gibbons C, Hoff ST, Dahl K, Søndergaard FL, Bækdal TA. Oral semaglutide reduces appetite and energy intake and improves control of eating in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2019;62(Suppl 1):S363 [Abstract 753].
Blundell J, Finlayson G, Axelsen M, Flint A, Gibbons C, Kvist T, et al. Effects of once-weekly semaglutide on appetite, energy intake, control of eating, food preference and body weight in subjects with obesity. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19:1242–51.
Bækdal TA, Borregaard J, Hansen CW, Thomsen M, Anderson TW. Effect of oral semaglutide on the pharmacokinetics of lisinopril, warfarin, digoxin, and metformin in healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019;58(9):1193–203.
Bækdal TA, Albayaty M, Manigandan E, Anderson TW, Skibsted S. A trial to investigate the effect of oral semaglutide on the pharmacokinetics of furosemide and rosuvastatin in healthy subjects. Diabetologia. 2018;61(Suppl 1):S346–7.
Jordy AB, Breitschaft A, Christiansen E, Granhall C, Hansen CW, Houshmand-Øregaard A, et al. Oral semaglutide does not affect the bioavailability of the combined oral contraceptive, ethinylestradiol/levonorgestrel. Diabetologia. 2018;61(Suppl 1):S346.
Davies M, Pieber TR, Hartoft-Nielsen ML, Hansen OKH, Jabbour S, Rosenstock J. Effect of oral semaglutide compared with placebo and subcutaneous semaglutide on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318(15):1460–70.
Aroda VR, Rosenstock J, Terauchi Y, Altuntas Y, Lalic NM, Morales Villegas EC, et al. PIONEER 1: randomized clinical trial of the efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide monotherapy in comparison with placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(9):1724–32.
Rodbard HW, Rosenstock J, Canani LH, Deerochanawong C, Gumprecht J, Lindberg SØ, et al. Oral semaglutide versus empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled on metformin: the PIONEER 2 trial. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(12):2272–81.
Rosenstock J, Allison D, Birkenfeld AL, Blicher TM, Deenadayalan S, Jacobsen JB, et al. Effect of additional oral semaglutide vs sitagliptin on glycated hemoglobin in adults with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled with metformin alone or with sulfonylurea: the PIONEER 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2019;321(15):1466–80.
Pratley RE, Amod A, Tetens Hoff S, Kadowaki T, Lingvay I, Nauck M, et al. Oral semaglutide versus subcutaneous liraglutide and placebo in type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 4): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3a trial. Lancet. 2019;394(10192):39–50.
Mosenzon O, Blicher TM, Rosenlund S, Eriksson JW, Heller S, Hels OH, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment (PIONEER 5): a placebo-controlled, randomised, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(7):515–27.
Husain M, Birkenfeld AL, Donsmark M, Dungan K, Eliaschewitz FG, Franco DR, et al. Oral semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(9):841–51.
Pieber TR, Bode B, Mertens A, Cho YM, Christiansen E, Hertz CL, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide with flexible dose adjustment versus sitagliptin in type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 7): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(7):528–39.
Zinman B, Aroda VR, Buse JB, Cariou B, Harris SB, Tetens Hoff S, et al. Efficacy, safety and tolerability of oral semaglutide versus placebo added to insulin ± metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: the PIONEER 8 trial. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(12):2262–71.
Yamada Y, Katagiri H, Hamamoto Y, Deenadayalan S, Navarria A, Nishijima K, et al. Dose-response, efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide monotherapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 9): a 52-week, phase 2/3a, randomised, multicentre trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020;8(5):377–91.
Yabe D, Nakamura J, Kaneto H, Deenadayalan S, Navarria A, Gislum M, et al. Safety and efficacy of oral semaglutide versus dulaglutide in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 10): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020;8(5):392–406.
American Diabetes Association. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(Suppl 1):S111–34.
American Diabetes Association. 11. Microvascular complications and foot care: standards of medical care in diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(Suppl 1):S135–51.
American Diabetes Association. 6. Glycemic targets: standards of medical care in diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(Suppl 1):S66-76.
Dungan KM, Hertz CL, Mellbin L, Abildlund Nielsen M, Sørrig R, Woo VC, et al. 964-P: glycemic and body weight responses to oral semaglutide in the PIONEER trial program. Diabetes. 2020;69(Suppl 1). https://doi.org/10.2337/db20-964-P.
Saisho Y. Use of Diabetes Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire in diabetes care: importance of patient-reported outcomes. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15(9):947.
Hansen BB, Hertz CL, Tarp-Johansen MJ. Patient treatment and study staff perceptions of oral semaglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Value Health. 2019;22(Suppl 3):S593–4.
Dalton M, Finlayson G, Hill A, Blundell J. Preliminary validation and principal components analysis of the control of eating questionnaire (CoEQ) for the experience of food craving. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2015;69(12):1313–7.
Aroda VR. A review of GLP-1 receptor agonists: evolution and advancement, through the lens of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20(Suppl 1):22–33.
Bain SC, Mosenzon O, Archavaleta R, Bogdański P, Comlekci A, Consoli A, et al. Cardiovascular safety of oral semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes: rationale, design and patient baseline characteristics for the PIONEER 6 trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21(3):499–508.
Husain M, Bain SC, Jeppesen OK, Lingvay I, Sørrig R, Treppendahl MB, et al. Semaglutide (SUSTAIN and PIONEER) reduces cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes across varying cardiovascular risk. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020;22(3):442–51.
Haluzík M, Bauer R, Eriksson J, Hoff ST, Kallenbach K, Pratley RE, et al. Efficacy of oral semaglutide according to diabetes duration: an exploratory subgroup analysis of the PIONEER trial programme. Diab Technol Ther. 2020;22(Suppl 1):A-185.
Aroda VR, Bauer R, Hertz CL, Montanya E, Sørrig R, Warren ML, et al. 932-P: efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide by baseline age in the PIONEER clinical trial program. Diabetes. 2020;69(Suppl 1). https://doi.org/10.2337/db20-932-P.
Desouza C, Amod A, Kallenbach K, Lin PJ, Abildlund Nielsen M, Sørrig R, et al. 930-P: efficacy of oral semaglutide according to race: an exploratory sub-group analysis of the PIONEER trial program. Diabetes. 2020;69(Suppl 1). https://doi.org/10.2337/db20-930-P.
Meier J, Bauer R, Blicher TM. Efficacy of oral semaglutide according to baseline HbA1c: an exploratory sub-group analysis of the PIONEER trial programme. Diabetologia. 2019;62(Suppl 1):S27 [Abstract 51].
Rosenstock J, Allison DC, Birkenfeld AL, Blicher TM, Deenadayalan S, Kousholt A, et al. Oral semaglutide vs sitagliptin: efficacy by baseline HbA1c and background OAD in PIONEER 3. Diabetes. 2019;68(Suppl 1):111-LB.
Buse JB, Crowley M, Eriksson JW, Gislum M, Hertz CL, Kaiser M, et al. 957-P: efficacy of oral semaglutide according to background medication: an exploratory analysis of the PIONEER trial program. Diabetes. 2020;69(Suppl 1). https://doi.org/10.2337/db20-957-P.
Pratley RE, Bauer R, Inzucchi SE, Khunti K, Kreiner EB, Laursen PN, et al. 927P: effect of oral semaglutide with or without background SGLT2i in patients with T2D: subgroup analysis of PIONEER 4. Diabetes. 2020;69(Suppl 1). https://doi.org/10.2337/db20-927-P.
Mosenzon O, Aroda VR, Christiansen E, Harris SB, Boje Pedersen K, Tarp-Johansen MJ, et al. 956-p: efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide when added to basel, premix, or basel-bolus insulin. Diabetes. 2020;69(Suppl 1). https://doi.org/10.2337/db20-956-P.
Hansen BB, Nuhoho S, Ali SN, Dang-Tan T, Valentine WJ, Malkin SJP, et al. Oral semaglutide versus injectable glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonists: a cost of control analysis. J Med Econ. 2020;23(6):650–8.
Hunt B, Hansen BB, Ericsson Å, Kallenbach K, Ali SN, Dang-Tan T, et al. Evaluation of the cost per patient achieving treatment targets with oral semaglutide: a short-term cost-effectiveness analysis in the United States. Adv Ther. 2019;36(12):3483–93.
Bain SC, Hansen BB, Malkin SJP, Nuhoho S, Valentine WJ, Chubb B, et al. Oral semaglutide versus empagliflozin, sitagliptin and liraglutide in the UK: long-term cost-effectiveness analyses based on the PIONEER clinical trial programme. Diabetes Ther. 2020;11(1):259–77.
Liu AR, Bech PG, Fridhammer A, Nilsson A, Willis M, Nuhoho S. 1163P: cost-effectiveness of oral semalgutide 14 mg versus empagliflozin 25 mg. Diabetes. 2020;69(Suppl 1). https://doi.org/10.2337/db20-1163-P.
Alsumali A, Lautsch D, Kowal S, Li Q, Campbell C, Rajpathak S, et al. The budget impact of sitagliptin versus oral semaglutide from a US payer perspective. Value Health. 2020;23(Suppl 1):S116.
Peyrot M, Rubi RR, Kruger DF, Travis LB. Correlates of insulin injection omission. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(2):240–5.
Nguygen H, Dufour R, Caldwell-Tarr A. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) therapy adherence for patients with type 2 diabetes in a medicare population. Adv Ther. 2017;34(3):658–73.
Bain SC, Hansen BB, Hunt B, Chubb B, Valentine WL. Evaluating the burden of poor glycemic control associated with therapeutic inertia in patients with type 2 diabetes in the UK. J Med Econ. 2020;23(1):98–105.
Nuhoho S, Gupta J, Hansen BB, Fletcher-Louis M, Dang-Tan T, Paine A. Orally administered semaglutide versus GLP-1 RAs in patients with type 2 diabetes previously receiving 1–2 oral antidiabetics: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Ther. 2019;10(6):2183–99.
Madsbad S. Review of head-to-head comparisons of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016;18(4):317–32.
Miyagawa J, Odawara M, Takamura T, Iwamoto N, Takita Y, Imaoka T. Once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist dulaglutide is non-inferior to once-daily liraglutide and superior to placebo in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a 26-week randomized phase III study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17(10):974–83.
Odawara M, Miyagawa J, Iwamoto N, Takita Y, Imaoka T, Takamura T. Once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist dulaglutide significantly decreases glycated haemoglobin compared with once-daily liraglutide in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: 52 weeks of treatment in a randomized phase III study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016;18(3):249–57.
Seino Y, Terauchi Y, Osonoi T, Yabe D, Abe N, Nishida T, et al. Safety and efficacy of semaglutide once weekly vs sitagliptin once daily, both as monotherapy in Japanese people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20(2):378–88.
Alfayez O, Alkhezi O, Almutairi AR. 455-P: network meta-analysis of seven glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: a focus on cardiovascular outcomes trials data. Diabetes. 2020;69(Suppl 1). https://doi.org/10.2337/db20-445-P.
Clinicaltrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03914326. Accessed 2 Jun 2020.
Savarese G, Sharma A, Pang C, Wood R, George JT, Soleymanlou N. Patient preferences for newer oral therapies in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2020;69(Suppl 1). https://doi.org/10.2337/db20-2216-PUB.
Boye K, Ross M, Mody R, Konig M, Gelhorn H. Patients’ preferences for once-daily oral versus once-weekly injectable diabetes medications: the REVISE study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021;23(2):508–519.
Igarashi A, Hansen BB, Langer J, Tavella F, Collings H, Davies N, et al. Preference for oral and injectable GLP-1RA therapy profiles in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a discrete choice experiment. Adv Ther. 2021;38(1):721–738.
Seaquist ER, Anderson J, Childs B, Cryer P, Dagogo-Jack S, Fish L, et al. Hypoglycemia and diabetes: a report of a workgroup of the American Diabetes Association and the Endocrine Society. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(5):1384–95.
Acknowledgments
Under the direction of the authors, medical writing and editorial support, including the literature search, were provided by Graham Allcock of Axis, a division of Spirit Medical Communications Group Limited (funded by Novo Nordisk A/S).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This article was supported by Novo Nordisk; the company was provided with the opportunity to perform a medical accuracy review.
Conflicts of interest
Andreas Andersen declares no conflicts of interest. Filip Krag Knop has served on scientific advisory panels and/or been part of speakers’ bureaus for, served as a consultant to, and/or received research support from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Carmot Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, Gubra, MedImmune, MSD/Merck, Mundipharma, Norgine, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Zealand Pharma. Tina Vilsbøll has served on scientific advisory panels, been part of speakers’ bureaus for, served as a consultant to, and/or received research support from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Mundipharma, MSD/Merck, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Sun Pharmaceuticals.
Availability of Data and Material
Not applicable.
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author Contributions
The authors directed the content and reviewed and critically revised all drafts.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Andersen, A., Knop, F.K. & Vilsbøll, T. A Pharmacological and Clinical Overview of Oral Semaglutide for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Drugs 81, 1003–1030 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-021-01499-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-021-01499-w