Abstract
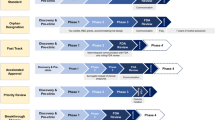
Voxelotor (Oxbryta™) is a haemoglobin S polymerization inhibitor that has been developed for the treatment of sickle cell disease. In November 2019, voxelotor received its first global approval in the USA for the treatment of sickle cell disease in adults and paediatric patients aged ≥ 12 years. The drug was granted accelerated approval based on the results of the phase III HOPE trial. Phase III clinical development of voxelotor for sickle cell disease is ongoing worldwide. Voxelotor also has Orphan Drug designation and Priority Medicine status in Europe for the treatment of sickle cell disease. This article summarizes the milestones in the development of voxelotor leading to this first approval as a disease-modifying agent for sickle cell disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gardner RV. Sickle cell disease: advances in treatment. Ochsner J. 2018;18(4):377–89.
Kato GJ, Piel FB, Reid CD, et al. Sickle cell disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2018.10.
Global Blood Therapeutics. Global Blood Therapeutics announces GBT440 receives FDA fast track designation for sickle cell disease [media release]. 12 Oct 2015. http://www.globalbloodtx.com.
Global Blood Therapeutics. Global Blood Therapeutics receives FDA orphan drug designation for GBT440 in sickle cell disease [media release]. 31 Dec 2015. http://www.globalbloodtx.com.
Global Blood Therapeutics. Global Blood Therapeutics receives rare pediatric disease designation from FDA for GBT440 for treatment of sickle cell disease (SCD) [media release]. 5 Sep 2017. http://www.globalbloodtx.com.
Global Blood Therapeutics. GBT receives FDA breakthrough therapy designation for voxelotor for treatment of sickle cell disease (SCD) [media release]. 9 Jan 2018. http://www.gbt.com.
Global Blood Therapeutics. GBT announces U.S. Food and Drug Administration acceptance of new drug application and priority review for voxelotor for the treatment of sickle cell disease [media release]. 5 Sep 2019. http://www.gbt.com.
Global Blood Therapeutics. Oxbryta™ (voxelotor) tablets, for oral use: US prescribing information. 2019. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov. Accessed 6 Jan 2020.
US Food & Drug Administration. FDA approves novel treatment to target abnormality in sickle cell disease [media release]. 25 Nov 2019. http://www.fda.gov.
Global Blood Therapeutics. FDA approves Oxbryta(TM) (voxelotor), the first medicine specifically targeting the root cause of sickle cell disease [media release]. 25 Nov 2019. http://www.gbt.com.
Global Blood Therapeutics. Global Blood Therapeutics announces GBT440 granted orphan drug designation in Europe for treatment of sickle cell disease [media release]. 30 Nov 2016. http://www.globalbloodtx.com.
Global Blood Therapeutics. Global Blood Therapeutics receives EMA PRIME designation for GBT440 for the treatment of sickle cell disease (SCD) [media release]. 28 Jun 2017. http://www.globalbloodtx.com.
Metcalf B, Chuang C, Dufu K, et al. Discovery of GBT440, an orally bioavailable R-state stabilizer of sickle cell hemoglobin. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2017;8(3):321–6.
Oksenberg D, Dufu K, Patel MP, et al. GBT440 increases haemoglobin oxygen affinity, reduces sickling and prolongs RBC half-life in a murine model of sickle cell disease. Br J Haematol. 2016;175(1):141–53.
Hutchaleelaha A, Patel M, Washington C, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of voxelotor (GBT440) in healthy adults and patients with sickle cell disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019;85(6):1290–302.
Dufu K, Oksenberg D. GBT440 reverses sickling of sickled red blood cells under hypoxic conditions in vitro. Hematol Rep. 2018;10(2):7419.
Dufu K, Patel M, Oksenberg D, et al. GBT440 improves red blood cell deformability and reduces viscosity of sickle cell blood under deoxygenated conditions. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2018;70(1):95–105.
Howard J, Hemmaway CJ, Telfer P, et al. A phase 1/2 ascending dose study and open-label extension study of voxelotor in patients with sickle cell disease. Blood. 2019;133(17):1865–75.
Chonat S, Fields E, Baratz H, et al. Improvement in red blood cell physiology in children with sickle cell anemia receiving voxelotor [abstract]. Blood. 2019;134(Suppl 1):2281.
Washington CB, Green M, Inati AC, et al. Pharmacokinetics (PK) of voxelotor (GBT440) using population pharmacokinetic (PPK) and physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling in pediatric subjects with sickle cell disease (SCD) [abstract no. PF713]. HemaSphere. 2018;2(Suppl 2):306.
Vichinsky E, Hoppe CC, Ataga KI, et al. A phase 3 randomized trial of voxelotor in sickle cell disease. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(6):509–19.
Howard J, vichinsky E, Knight-Madden J, et al. Correlation of voxelotor exposure with hemoglobin response and measures of hemolysis in patients from the HOPE study [abstract no. 712]. Blood. 2019;134(Suppl 1):1020.
Brown C, Hoppe C, Inati A, et al. Phase 2a study (GBT440-007) of voxelotor in adolescents with sickle cell disease [abstract no. 711]. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2019;66(Suppl 2):S241–S2.
Estepp JH, Wang W, Hwang S, et al. Cerebral blood flow in adolescents with sickle cell anemia receiving voxelotor [abstract no. PF740 plus poster]. HemaSphere. 2019;3(Suppl 1):324.
Blyden G, Bridges KR, Bronte L. Case series of patients with severe sickle cell disease treated with voxelotor (GBT440) by compassionate access. Am J Hematol. 2018;93(8):E188–90.
Washington CB, Goldstein B, Dixon S, et al. Voxelotor dose extrapolation in a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in pediatric patients with sickle cell disease (GBT440-032, HOPE KIDS 2) [abstract no. PS1453]. HemaSphere. 2018;2(Suppl 2):666.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Conflict of interest
During the peer review process the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on the article. Changes resulting from any comments received were made by the authors on the basis of scientific completeness and accuracy. Hannah A. Blair is a salaried employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature, is responsible for the article content and declares no relevant conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Enhanced material for this AdisInsight Report can be found at https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.11658999.
This profile has been extracted and modified from the AdisInsight database. AdisInsight tracks drug development worldwide through the entire development process, from discovery, through pre-clinical and clinical studies to market launch and beyond.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blair, H.A. Voxelotor: First Approval. Drugs 80, 209–215 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-020-01262-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-020-01262-7