Abstract
Only a small fraction of drugs widely used in neonatal intensive care units (NICU) are specifically authorized for this population. Even if unlicensed or off-label use is necessary, it is associated with increased adverse drug reactions, which must be carefully weighed against expected benefits. In particular, renal damage is frequent among preterm babies, and is considered a predisposing factor for the development of chronic kidney disease in adulthood. Apart from specific conditions affecting premature neonates (e.g. respiratory distress syndrome, perinatal asphyxia), drugs play an important role in impairing renal function because of well-known nephrotoxicity and/or interaction with renal developmental factors. From a review of the available studies on drug use in NICU patients, we identified and described the most commonly administered drugs that are correlated to renal damage. Early detection of kidney injury is becoming an essential aspects for clinicians because of the limited number of biomarkers applicable in the neonatal population. Postnatal changes of biochemical processes that influence pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic aspects need to be further investigated in order to better understand the mechanisms of drug toxicity in this population. The most promising strategies for dose adjustment and therapeutic schemes are discussed. The purpose of this review was to describe current knowledge on drug use among premature babies and their implication in kidney injury development, as well as to highlight available strategies for early detection of renal damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Drug-related injuries in preterm neonates involving, in particular, the kidney and acute renal damage often turn out to have long-term sequelae in adulthood (e.g. hypertension). |
Several molecules have been identified as potential biomarkers for the early detection of renal damage in neonates, however they still need to be validated. |
Regulatory agencies have identified the need for age-appropriate pharmaceutical research in pediatrics, indicating specific initiatives for the neonatal population. |
1 Introduction
Preterm neonates are defined as newborns less than 37 weeks of gestational age, including very low birth-weight infants (weight <1500 g) and extremely low birth-weight infants (weight <1000 g). The number of babies born preterm is rising every year [1] and, thanks to improved perinatal care, their survival rate has increased over time (almost 90 % of neonates born weighing 501–1500 g survived after discharge from the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) [2]), thus creating a novel population that have now reached early childhood. The percentage of unauthorized and off-label use of drugs in the NICU is very high (up to 90 %) [3] and clinicians often have to manage clinically needed treatments without clear evidence on their efficacy and/or safety, and only with a partial understanding of precise dose adjustment and pharmacokinetics. The long-term effects of these treatments are even more uncertain.
This situation reflects difficulties in performing research in term and preterm neonates; the feasibility of clinical trials is compromised by ethical (high vulnerability) and technical issues (multi-organ immaturity, lack of self-assessment, need for specific formulation, etc.), the number of neonates with a given disorder in each individual center is limited, and there is high variability in practices (drugs and duration of treatment, monitoring, medical care).
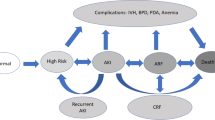
Due to its central role in drug excretion, the kidney is a major target for toxicity with a contribution from drugs, and also many typical conditions affecting premature babies (e.g. respiratory distress syndrome, perinatal asphyxia, severe infections, sepsis, hemodynamic instability) (Fig. 1) [4].
The aims of this review were (1) to describe current knowledge on drug use among NICUs; (2) the implication of the most commonly used therapeutic treatments in kidney injury development; and (3) to highlight available strategies to monitor renal safety profiles of pharmacological treatments among preterm neonates. To this end, we carried out a search in Pubmed/MEDLINE (time restrictions: 2006–October 2014) to select key publications in the English language, using a combination of the following keywords (free text search strategy): ‘preterms’, ‘preterm neonates’, ‘NICU’, ‘drug utilization’, ‘drug use’, ‘AKI’, ‘drug-induced kidney injury’, and ‘drug-induced renal damage biomarkers’. In order to identify possible additional references, the most authoritative publications were identified and a snowballing search was performed in some key reviews.
2 State of the Art on Drug Development and Use in Preterm Neonates
2.1 Regulatory Aspects
The general lack of appropriate pharmaceutical formulations for children promoted legal obligation to perform studies to support use in the pediatric population [5]. In particular, from 1997 the US FDA with the ‘Modernization Act’ and from 2002 the European Medicines Agency (EMA) with the consultation paper ‘Better Medicines for Children’ undertook actions to promote clinical trials in children for both authorized and investigational medicinal products [6, 7]. These documents were then implemented in the ‘Pediatric Research Equity Act’ (FDA, 2003) [8] and the ‘Regulation on Medicinal Products for Paediatric Use’ (EMA, 2006) [9].
The main objectives of the regulatory actions were to ensure high-quality research into the development of medicines for children, to make sure that the majority of them are specifically authorized for such use, and to ensure the availability of high-quality information [10]. To support companies in new development strategies, a recent FDA regulatory initiative (FDA Safety and Innovation Act [11]) included the neonatal population among its main topics; specific expertise in neonatology is requested within the Office of Pediatric Therapeutics and the Pediatric Review Committee. In Europe, the EU Regulation of 2006 established the Paediatric Committee (PDCO), within the EMA, which was responsible for the evaluation of Pediatric Investigation Plans (PIPs) presented by companies as mandatory programs for the pediatric indication [9]. Other health organizations have also faced the problem of appropriate drug use in the pediatric population; the World Health Organization (WHO) developed a program on medicines for children, resulting in the WHO Model Formulary on how to use essential medicines for children [12]. Several National Health Institutes published guidebooks on the use of widely administered drugs in children (e.g. Italian Institute of Health [13]).
Some results of the legislative actions undertaken so far have been provided by the approval of the 500th pediatric label change in 2013 by the FDA [14], the 221 changes regarding safety and efficacy, for submission of old or new studies, and 89 additions of dosing information for children in the EU [15]. Despite this, neonates (especially preterm newborns) are neglected in clinical trials and a worldwide gap of knowledge on the use of medicinal products in neonates still persists [16–27].
2.2 Unlicensed and Off-Label Drug Use Among Preterm Neonates
Definitions for ‘unauthorized’ (or ‘unlicensed’) and ‘off-label’ use of drugs may differ among authors but, in general, a medicinal product is considered unauthorized if it has no indication for the specific population, and is off-label when not included in the approved labeling; for example, a change in the formulation (i.e. to obtain a lower dose) or in the method of administration [16, 17, 23, 25, 26, 28].
Trials recruiting neonates have grown over time and have increased sixfold in the past decade, but registered trials targeting neonates still represent a minority. Analysing the ClinicalTrials.gov database, among all trials registered 22 % (30,912) involved the pediatric population and only 0.2 % (288) targeted neonates [24]. Among studies involving preterm neonates from the same international database (www.clinicaltrials.gov), 238 open studies emerged, mostly carried out in the US (89) and Europe (79) (Table 1). In Europe, France and the UK had the highest number of open studies in this population (26 and 12, respectively), followed by Germany (8), Italy (7), and Spain (7). Open studies represent 39.3 % of the total (606) worldwide studies in this population. Trials on preterm newborns involving medicinal products focused, in particular, on anti-infective agents (51), analgesics (24), pulmonary surfactants (9), and drugs for the management of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), i.e. indomethacin (6), acetaminophen (paracetamol; 6) and ibuprofen (3).
Recent studies investigated the off-label and unlicensed use of drugs in the European pediatric population (Table 2); however, these studies showed great heterogeneity in their methods (design, duration, definition of off-label use, etc).
Haslund-Krog et al. [25] took into account the 100 most used drugs in children from the national Danish database and found that 13 are used off-label (defined as one of the following: absence of pediatric information, lack of clinical data, contraindication for use in children, drug substances being an extemporaneous preparation or unlicensed). Twenty-one percent of drug substances reviewed had a PIP, and only six (28.6 %) of these included preterms and newborns in their PIPs. A study in Finland, carried out to verify the impact of the European Pediatric Regulation, actually found that off-label use in newborns was higher in 2011 than in 2001 (51 vs. 22 %), whereas prescriptions of unauthorized medicines decreased from 31 % in 2001 to 25 % in 2011 [26]. The prevalence of off-label use in NICUs was reported to be 46.5 % in Italy [16] and 39 % in Ireland [17].
In the US, less than 0.5 % of all drug exposures in neonates was approved by federal legislation. Revision of the FDA database for studies submitted between 1997 and 2010 involving the pediatric population, showed 406 pediatric labeling changes, of which only 6 % included new neonatal information [20].
Several reasons explain why only few clinical trials are performed in neonates, i.e. ethics problems, parent distrust, low economic interest by drug companies, and low funds for specific age-related studies [29]. Moreover, feasibility problems occur in studying drugs in newborns according to good clinical practice, i.e. the amount of blood required for measuring safety laboratory values when added to the volume required for pharmacokinetic measurements quickly exceeds safe limits; additionally, organ function is difficult to measure, and even harder is the evaluation of efficacy without gold standards [18]. Other strong obstacles to research are the limited number of neonates with a given disease in each individual center, highly variable practices (drugs and duration of treatment, prophylaxis vs. treatment, monitoring, medical care, including type of ventilation) and lack of support for networks.
Although off-label or unlicensed use of medicines does not necessarily imply inappropriate use (i.e. benefits outweigh potential risks) and is often necessary, it has been associated with increased adverse drug reactions (ADRs) in children [30] and neonates [19]. Risks factors in newborns are the immaturity of most organ functions and the developmental changes occurring in the postnatal period, which could significantly influence plasma concentration of medicines, their safety, and their efficacy [31]. Since neonates frequently suffer from multiple concomitant conditions, a combination of medicinal products may result in a higher risk of interactions [19].
3 Kidney Development Steps and Pharmacological Implications
Term neonates (i.e. between 37 and 41 weeks of gestation) possess a full set of nephrons, whereas growth retardation, prematurity, or nephrotoxic drugs administered to the mother negatively affect the total number of nephrons in the neonate [32]. Among drugs shown to limit the formation of nephrons, high steroid level exposure of pregnant women (i.e. dexamethasone administration to advance maturation of the fetal lung in premature delivery) seems to impair fetal nephrogenesis and lead to reduced nephron number in the newborn [33]. Since the renin-angiotensin system is essential for tubular development during fetal life, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor antagonists during pregnancy may reduce nephron formation [34] and cause renal tubular dysgenesis [35]. Additionally, maternal use of NSAIDs as tocolytic agents affects renal development, leading to tubular alterations and low nephron numbers [36, 37].
Although evidence of ongoing nephrogenesis has been recorded up to 40 days after birth in neonates less than 30 weeks of gestational age [38, 39], those born at 23 or 24 weeks do not continue nephrogenesis until 36 weeks, as in normal gestations. Furthermore the ex utero environment makes kidney maturation particularly vulnerable (e.g. acute kidney injury (AKI) in early neonatal life, perinatal growth restriction, nephrotoxic drugs) [40]. The kidneys of premature babies show a higher number of histologically abnormal glomeruli and an increased glomerular volume compared with term neonates [39].
After birth, a sudden change in environmental conditions triggers the start of renal function and clearance, with marked difference in postnatal development between very low birth-weight (VLBW), premature, and term neonates, mainly because of immaturity and prolonged adaptation of extrauterine life. Normal glomerular filtration rate (GFR) maturational changes after birth are driven by the rise in renal blood flow (RBF), and alterations in intrarenal blood perfusion patterns. Growth and maturation of renal tubules and tubular processes will result in a more sophisticated regulation of acid base and electrolyte balance. RBF in premature babies is reported to be less than half the RBF value in term neonates, and although it progressively increases over time, it takes longer for preterms to reach the adult rate compared with term neonates [41]. Both glomerular and tubular renal functions are affected by gestational age at birth as well as postnatal age. Recent data suggest that, compared with maturational patterns in term neonates, the maturational creatinine clearance in preterm neonates matures slower, while there is already a higher capacity for postnatal tubular maturation in preterm neonates and at the age of 1 month [42]. Maturation of these renal tubular processes will also affect the capacity to dispose excess sodium or water via the kidney soon after birth. This reflects the need to redistribute body fluids and the ability to maintain a negative water and sodium balance. Since high sodium excretion is inversely proportional to maturity, this process results in greater and more prolonged losses in premature newborns, requiring sodium administration for the first several weeks of life [43]. Immaturity of renal functions also leads to the imbalance of other electrolytes, such as potassium, calcium, and phosphorus, resulting in hyperkalemia and hypocalcemia, and this last condition correlates with a high risk of tetany or decreased cardiac contractility [44]. The kidney plays an important role in the maintenance of the acid-base balance, in cooperation with the respiratory system; since preterm babies possess an immature regulatory mechanism, they tend to display intracellular acidosis due to imbalanced acid-base homeostasis [45]. Moreover, the lower response of the adrenal gland to aldosterone, which is involved in fluid and electrolyte balance regulation through the improvement of renal sodium absorption, may also contribute to the negative sodium and water balance seen in premature newborns [44].
4 Role of Drugs in Renal Damage
4.1 Drug-Induced Kidney Injury
Since the kidney is the main organ for excretion of a drug and its metabolites, preterm neonates are at higher risk of overdosing due to immature renal function [32]. The renal contribution to excretion occurs at several levels, i.e. glomerular filtration, tubular secretion and reabsorption, or intracellular enzymatic processing, mainly in proximal tubular cells [46, 47]. Preterm babies show specific glomerotubular imbalance because GFR sharply increases after birth while tubular secretion matures slower, but more steadily, to result in a proportional higher capacity for postnatal maturation of renal tubular function [42]. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters differ not only between preterm and term neonates but also among preterms. As a matter of fact, the cut-off for achieving nephrogenesis, and thus the capacity of drug renal elimination, is assumed at the 33rd week of gestational age [32].
4.1.1 Acute Kidney Injury
AKI classification has recently been reviewed by the international workgroup on kidney diseases (Kidney Diseases: Improving Global Outcomes; KDIGO), retaining the Acute Kidney Injury Network (AKIN) and Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss and End-stage kidney disease (RIFLE) staging criteria. The KDIGO criteria defined the abrupt decrease in kidney function according to changes in serum creatinine and urine output, whereas for children younger than 18 years of age, the evaluation of GFR is additionally required (stage 3 criteria included an acute decrease in estimated GFR to less than 35 mL/min/1.73 m2) [48].
AKI is common in the NICUs; the incidence is 15 % in near-term/term newborns admitted to the NICU [49], 19 % in premature neonates, and 18 % in very low birth neonates [50]. Askenazi et al. [49] found that low birth weight, lower gestational age, male sex, and lower 5-min Apgar score in near-term/term neonates were associated with AKI. Moreover, AKI correlates with higher mortality rates in both term and preterm babies, and in VLBW neonates it is considered an independent predictor of mortality [50]. Many of the specific conditions affecting preterm neonates could reduce GFR, or even cause AKI; for instance, respiratory distress syndrome is associated with a significant AKI frequency [51], as well as perinatal asphyxia [52]. Furthermore, severe infections and sepsis are considered risk factors of AKI [53, 54]. In addition, many of the widely used therapies and combinations in NICU hospitalized patients could cause kidney injury, either because of their well-known nephrotoxicity (i.e. aminoglycosides) or their impact on immature renal functions.
4.1.2 Chronic Damage
Immature kidneys of preterm neonates after early exposure to pharmacological treatments may undergo further impairment. Soon after birth, glomerular volume is abnormally increased in premature newborns, and a greater percentage of their glomeruli are histologically anomalous, with dilatation of the Bowman’s space [39]. Many nephrologists proposed that individual nephron enlargement (i.e. an increased total surface area available for renal work, potentially reflecting glomerular hyperfiltration) was a compensatory mechanism to maintain normal GFR [55]. However, this adaptive response leads to sodium retention and systemic hypertension, while glomerular hyperfiltration disrupts renal autoregulatory mechanisms, generating intraglomerular hypertension and proteinuria [56–59]. As a consequence, nephron number can further decrease [56, 60]. Since nephrons cannot be regenerated [61], renal injury can turn into chronic damage. As proof of this, renal diseases can worsen in the long-term, especially in immature babies [62]; low birth weight was strictly correlated with increased long-term risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in adolescence [63] and adulthood [64]. The same was noticed in neonates with kidney injury in the postnatal period who rarely experienced complete renal regeneration and damage due to AKI turning out to be irreversible [40]. A recent study among pediatric patients with a diagnosis of AKI found that 10.3 % developed CKD within 1–3 years after diagnosis, and nearly 50 % of the cohort was affected by hypertension, reduced GFR, or hyperfiltration [65], which are correlated with a risk of CKD. Similarly, other trials showed that children with AKI with different etiology all have an increased risk of developing CKD in the pediatric years [66, 67].
4.1.3 Classification of Drug-Induced Kidney Injury
The clinical classification of renal damage is challenging because symptoms are non-specific and simply consist of urine flow interruption. The pathophysiological classification of kidney injuries is based on the mechanism of renal dysfunction: (a) hemodynamically mediated, (b) glomerulonephritis, (c) acute tubular necrosis, (d) interstitial nephritis, (e) papillary necrosis, and (f) obstructive nephropathy (Fig. 2).
-
(a)
Hemodynamically-mediated renal failure arises when mechanisms of maintenance of intra-glomerular pressure are impaired, e.g. decrease in blood flow to the kidney, vasoconstriction of glomerular afferent arteriolar, or vasodilatation of glomerular efferent arterioles. The autoregulation of intraglomerular pressure is essential to maintain GFR and urine output, and the main influencing factors are circulating prostaglandins (vasodilatation of afferent arterioles) and circulating angiotensin II (vasoconstriction of efferent arteriole). Thus, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), angiotensin II-converting enzymes (ACEIs), angiotensin II-receptor blockers (ARBs), and calcineurin inhibitors are among the drugs inducing this type of injury [68].
-
(b)
Renal damage in glomerulonephritis syndrome is due to inflammation reactions, protein infiltration, and cell-mediated immunity processes. Decreased serum albumin levels induce over-production of proteins by the liver, which contributes to the development of nephrotic syndrome, i.e. proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia, and edema. Treatment with NSAIDs, ampicillin, rifampin, foscarnet, and lithium causes renal failure through this mechanism [68, 69].
-
(c)
Acute tubular necrosis is characterized by tubular cell death as a result of ischemic effects of toxic exposure to agents such as aminoglycosides and amphotericin B. Tubular cells have the highest exposure to circulating toxins because they concentrate and reabsorb the glomerular filtrate; tubular damage is mediated by the alteration of mitochondrial function, interfering with tubular transport, increasing oxidative stress, or forming free radicals [70, 71].
-
(d)
Administration of β-lactam antibiotics, vancomycin, NSAIDs, and calcineurin inhibitors correlates with acute allergic interstitial nephritis, which is mediated by inflammatory reactions in the renal tubules and interstitium [68, 70]. Most of those cases occur as a hypersensitivity reaction to a substance, thus heterogeneous classes of drugs may be the cause of this type of renal injury.
-
(e)
Papillary necrosis is associated with the use of analgesic agents, such as acetaminophen and NSAIDs, but also kidney infections are reported to cause this damage [72, 73].
-
(f)
Another type of injury is the mechanical obstruction of renal function; some drugs (acyclovir, ciprofloxacin, sulfonamides, methotrexate) or metabolites could precipitate, after glomerular filtration, into tubules and act as mechanical obstruction of urine flow, leading to renal insufficiency [70, 74].
4.2 Treatment-Related Renal Damage by Drug Class
Few and heterogeneous data are available on drug use in NICUs. In most cases, only unauthorized and off-label drug use was investigated, in order to understand the impact of the European Pediatric Regulation [16, 17, 22, 25–27], whereas Neubert et al. [28] and Clark et al. [75] reported overall medication use in German and US NICUs, respectively (Table 2). In these national reports, antimicrobial and cardiovascular agents, analgesics and respiratory drugs are the most commonly used in preterm neonates [16, 17, 25, 26, 28, 75]; antibiotics have the highest exposure rates and also the highest differences between nations in terms of drug substances. In the US, ampicillin and gentamicin have been reported as the most frequently used antibiotics, followed by cefotaxime and vancomycin [75]; the most used are piperacillin and vancomycin in Germany [28], cefotaxime in Finland [26], ampicillin and amikacin in Italy [16], and gentamicin in Ireland [17]. This heterogeneity in the choice of antibiotics is related to the lack of guidelines and comparative clinical studies, as documented by a Cochrane review comparing different antibiotic regimens for suspected late-onset sepsis in newborns [76].
Aminoglycosides, such as amikacin and gentamicin, are widely prescribed in NICUs for the prevention and treatment of infections. Aminoglycosides have well-known nephrotoxic effects; they are partially reabsorbed into proximal tubular cells and their cationic charge facilitates their binding to membrane phospholipids of tubular epithelial cells. This leads to the activation of intracellular transport into lysosomes, where they bind to phospholipids and inhibit phospholipase activity. This process precipitates in acute tubular necrosis development, as the result of accumulation of phospholipids, interruption of cellular functions, and cell death [77]. Aminoglycoside-induced AKI is characterized by elevation of serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, and reduction of urine output, but is reversible with drug discontinuation. Age, coadministration of other nephrotoxic drugs, and duration of therapy are among the factors increasing the risk of aminoglycoside-induced nephrotoxicity [68]. It has also been investigated whether different regimens of aminoglycoside treatment (gentamicin ‘once a day’ vs. ‘multiple doses a day’) may reduce nephrotoxicity, but no changes were found [78]. Recent studies on aminoglycoside use in preterm neonates evidenced that GFR levels were, surprisingly, almost unchanged, at least after short-term administration in the early postnatal period at therapeutic dosages [79].
Another class of antibacterial agents used for both the prevention and treatment of recurring infections in the NICU are β-lactam antibiotics, particularly ampicillin, piperacillin, and cefotaxime. The administration of these molecules has been correlated with nephrotoxicity, particularly with acute interstitial nephritis, affecting the renal tubules and interstitium with consequent acute renal failure. β-Lactam-induced nephrotoxicity is mediated by hypersensitivity reactions, believed to be cell mediated as T cells are the main pathological interstitial finding; it is also possible to find lymphocytes, monocytes, and eosinophils in the interstitial infiltrate. Renal effects come along with typical systemic manifestations, such as fever, eosinophilia, and skin rash, which are not commonly seen in acute interstitial nephritis caused by other drug classes. Kidney injury is reversible after discontinuation of the drug, and it may take weeks to months to be complete. In this case, glucocorticoid therapy may improve recovery [70, 80]. Acute interstitial nephritis can also result from vancomycin treatment, as a consequence of antigen precipitation into the interstitium, which triggers an immune reaction [70, 81].
Amphotericin B is the most nephrotoxic antimicrobial drug and remains the drug of choice to treat severe systemic fungal infections (also in neonatal wards). Tubular cell toxicity due to amphotericin B depends on its binding to sterols of cell membranes and consequent alteration of membrane permeability to sodium; the increase of intracellular sodium concentration and the activation of vasoconstrictor prostaglandins lead to vasoconstriction of renal vessels. As a consequence, RBF and GFR decrease and ischemic injury occurs [82]. Amphotericin B-induced distal tubulopathy is evidenced by increased serum urea and creatinine concentrations, as a result of decreased GFR, and hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis, hypomagnesemia, and loss of urine concentration ability [83]. Risk factors for amphotericin B nephrotoxicity include renal insufficiency, volume depletion, large individual and cumulative doses, and coadministration of other nephrotoxic drugs [84, 85]. Because of the clinical usefulness of amphotericin B, strategies were sought to decrease its adverse effects, e.g. its lipid-associated formulation, which showed similar efficacy but lower nephrotoxicity. However, the cost of these new formulations limited their use to patients at highest risk of renal failure [86]. To prevent amphotericin B nephrotoxicity in children, Goldman and Koren [83] suggested introducing, as standard care, sodium supplementation pre- and post-infusion to reduce vasoconstriction, as well as close monitoring of renal function over a lipid-associated formulation, unless significant nephrotoxicity develops [86].
Among diuretics, furosemide is the preferred drug in the NICUs [16, 28, 75] and, along with the other ‘loop’ diuretics, it increases the rate of urine flow and sodium excretion by affecting the delivery of solutes out of the loop of Henle. Furosemide intake is associated with water and electrolyte imbalances, particularly hyponatremia, hypokalemia, and hypochloremic alkalosis. Moreover, hypercalciuria occurs with long-term furosemide therapy, and the risk of developing nephrocalcinosis is higher in low birth-weight neonates (underdevelopment of renal functions, such as decreased GRF, low citrate excretion and alkaline urine). It is also reported that, in most cases, the discontinuation of treatment is associated with resolution of the renal calcification. The use of furosemide in neonates may also cause ototoxicity, and strategies have been studied in order to avoid hearing loss, including slow continuous infusion and short-term administration, and it is strongly recommended to avoid the association of furosemide with aminoglycosides. Additionally, furosemide enhances prostaglandin E2 synthesis, which acts as a potent dilator of the PDA, thus inhibiting the effect of drugs used to close it. Careful monitoring is needed in babies with respiratory distress syndrome treated with furosemide because they are at higher risk of precipitation of a symptomatic PDA [87].
In neonates, short-term treatment with NSAIDs (especially ibuprofen and indomethacin) is mostly for the management of PDA. Although the overall risk-benefit profile of this drug class is positive, NSAIDs are implicated in AKI development in patients with pre-existing renal diseases, poor RBF, or when other nephrotoxic agents are coadministered (i.e. aminoglycosides, diuretics). In these cases, activation of the renin-angiotensin system and the rise of circulating catecholamines stimulate renal prostaglandin production, which protects renal perfusion and glomerular filtration. The inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis by NSAIDs may lead to a rapid decline of renal function after only a few doses. In addition, NSAIDs are also responsible for acute interstitial nephritis and glomerulonephritis [77]. Renal failure is reversible after discontinuation.
A new therapeutic approach to close PDA in preterm neonates consists of the use of acetaminophen instead of classic NSAID treatment. Acetaminophen is widely prescribed among neonates to treat moderate pain or fever, and it seems to have a better safety profile than ibuprofen and indomethacin; however, the different therapeutic scheme used for the management of PDA has not been investigated in terms of respiratory and renal long-term outcomes [88].
When a drug with nephrotoxic potential is administered, drug-induced renal damage is reported to be reversible after prompt discontinuation of the offending agent, but it is also reported that coadministration of other nephrotoxic medications are always to be avoided (Table 3). However, preterm babies are characterized by ongoing nephrogenesis in the first postnatal period, which could be irreversibly impaired by drug exposure, and cellular injury to glomeruli or tubules may impair long-term renal functional capacity and increase susceptibility to renal disease later in life [40]. Moreover, the management of NICU patients entails the treatment of several concomitant diseases (such as respiratory distress syndrome, PDA, and infections), thus requiring the administration of a combination of potentially nephrotoxic medicinal products. There are well-known complications as a result of the association of two or more of the widely used drugs in NICUs. Attention should be paid to the concomitant use of furosemide and indomethacin or ibuprofen because of the increased risk of symptomatic PDA in neonates with respiratory distress syndrome; when used in combination with aminoglycosides, furosemide may also compromise hearing functions. It has been reported that NSAID treatment alters the renal clearance of other drugs; amikacin clearance is reduced by 21 % and vancomycin clearance by 18 % when concomitant ibuprofen is administered, and a higher decrease in vancomycin clearance is observed during indomethacin treatment [89].
In this scenario, we mention the use of caffeine citrate (caffeine), largely prescribed as a first-line drug for the treatment or prevention of apnea in preterm neonates [90]. It has been hypothesized that the hemodynamic effects of caffeine might have long-term consequences on the health status of previously exposed children. However, recent studies show that even if caffeine administration in NICU patients has short-term adverse effects, such as increased heart rate, jitteriness, irritability, seizures [91], and delayed weight gain [92], the survival rate of children up to 5 years of age is improved for caffeine treatment compared with placebo, without neurodevelopmental impairment [93].
Specific features of the neonatal kidney, which complicate renal drug handling, may influence drug-induced toxicity. Neonates seem to be more sensitive to vasoactive aspects (e.g. ibuprofen-induced reduction in GFR), and the immaturity of allergic reaction capacity may facilitate the onset of interstitial nephritis. The elimination of many drugs is mediated by tubular kidney transporters, which have lower activity in neonates [94]. This may cause intracellular accumulation of active substances; however, the implication of these factors on drug elimination and the development of nephrotoxicity in early infancy is a matter of investigation.
5 Strategies to Prevent Onset of Renal Damage in the Neonatal Population
5.1 Biomarkers to Monitor Renal Safety of Drugs
Serum creatinine levels (sCr) are widely used in the diagnosis of AKI, but sCr-based definitions are not highly predictive because (1) sCr measures function, not injury; (2) sCr may not change until 25–50 % of kidney function is compromised; (3) sCr overestimates renal function due to tubular secretion of creatinine at lower GFRs; (4) sCr varies by muscle mass, hydration status, sex, and age, and its measurement can be affected by endogenous substances; (5) sCr is not specific to different types of AKI; (6) in some conditions, such as pre-renal azotemia, sCr might be non-specific for AKI; and (7) sCr cannot be applied in the early postnatal period because serum Cr reflects maternal kidney function. In addition, sCr levels show significant variation, depending also on the degree of prematurity [95, 96].
The identification of novel biomarkers will allow early detection of AKI and could improve patient outcomes [51]. Figure 3 provides a general overview on promising biomarkers for renal damage in the entire population (especially in adults). In the neonatal population, the only biomarkers under investigation are serum and urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), urinary interleukin (IL-18), osteopontin (OPN), kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), β-trace protein (BTP), and serum cystatin C (CysC).
Promising biomarkers for early detection of renal damage [98, 102, 105, 108, 116]. MIF macrophage migration inhibitor factor, NGAL neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, KIM-1 kidney injury molecule-1, GST-α α-glutathione S-transferase, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor, Timp-1 tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1, NHE-3 sodium/hydrogen exchanger-3, L-FABP L-type fatty acid-binding protein, HGF hepatocyte growth factor, NAG N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase, RBP retinol binding protein, TFF-3 trefoil factor 3, Cyr61 cysteine-rich protein-61, H-FABP H-type fatty acid-binding protein, IL interleukin. Asterisk Biomarkers under investigation in the neonatal population
Studies on AKI biomarkers in neonates have been mainly performed in specific populations at risk, such as VLBW, asphyxiated newborns, and children undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB). Although several new candidate biomarkers have been studied, some turned out to depend on both gestational age and birth weight. Moreover, the results of these studies are often difficult to evaluate because sCr has been inappropriately used as the gold standard marker for AKI [97].
5.1.1 Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL)
This protein belongs to the family of lipocalin (NGAL) and has been proposed as an early biomarker of AKI and CKD. In these conditions, NGAL levels, which depend on distal tubule production, are high in both blood and urine. Serum and urinary levels are elevated in humans with AKI, including neonates undergoing CPB surgery [98, 99] and other critically ill pediatric populations [52, 100–102]. NGAL may also function as an iron-binding transporter modulating essential life processes. In addition, NGAL may play a role in cellular defense against toxic stimuli on kidney and other epithelia, and in nephrogenesis, as a mesenchymal differentiating factor produced by the ureteric bud [103].
However, at the moment, inflammatory status and prematurity limits the specificity of total NGAL measurement as a marker of AKI [104].
5.1.2 Interleukin-18
IL-18 is one of the most studied biomarkers of AKI, and a member of the IL-1 family of cytokines, synthesized as an inactive 23 kDa precursor in several cells, including monocytes, macrophages, and proximal tubular epithelial cells. It is processed into an active 18.3 kDa cytokine by caspase-1, and has been demonstrated in some animal studies as a mediator of renal ischemia–reperfusion injury, inducing acute tubular necrosis, and neutrophil and monocyte infiltration of the renal parenchyma. Urinary IL-18 may have an important role in non-septic, critically ill neonates as a non-invasive biomarker to independently predict AKI development during early life after birth [105].
Urinary IL-18 seems to be independent from renal maturity, whereas it can be influenced by sepsis, thus reducing its ability to detect AKI [97].
5.1.3 Cystatin C
CysC, a cysteine protease inhibitor, is predominantly localized in the proximal tubule of the cortex. In addition, it was observed in the lumen of the renal tubule in the cortex, corticomedullary junction, and medulla during the progression of renal damage, although its immune-reactive area ratio was very low. Apparently, CysC does not cross the placenta [105] and thus reflects the renal function of neonates in early postnatal life regardless of body composition and size [106]. Serum CysC was identified as an earlier marker of AKI in preterm neonates with respiratory distress syndrome [51] and was also predictive of AKI in non-septic, critically ill newborns [107].
Although other studies have evaluated CysC in older children, it is difficult to extend their results to the neonatal population, considering that normal values of urinary CysC decrease with tubular maturation [97].
Urinary CysC, as an independent biomarker with greater accuracy than urinary IL-18, could predict the development of AKI in non-septic, critically ill neonates [107].
5.1.4 Kidney Injury Molecule-1
KIM-1, a transmembrane tubular protein with unknown function, is undetectable in normal kidneys but is markedly induced in experimental renal injury. The KIM-1 ectodomain is cleaved, detectable in urine, and reflects renal damage. Urinary KIM-1 levels are strongly related to tubular KIM-1 expression in experimental and human renal disease. Studies in humans also indicated that urinary KIM-1 was sensitive and a specific marker of injury as well as predictors of outcome [108]. Recently, two systematic reviews have reported that KIM-1 was an efficient novel urinary biomarker in the diagnosis of AKI within 24 h after kidney injury [108, 109], especially in the diagnosis of ischemic injury [110]. However, due to small population settings, heterogeneous patient type, few clinical trials, and heterogeneity in detection time, the application of KIM-1 in the early diagnosis of AKI still needs to be validated by larger studies. Moreover, age is still insufficiently evaluated as an influencing factor [111].
5.1.5 β-Trace Protein
BTP is a low-molecular-weight protein belonging to the lipocalin protein family. In adult patients, serum BTP is reported to inversely correlate with GFR, and increases with renal diseases [112]. In the neonatal population, BTP is shown to be independent from gestational age and muscle mass, and is a good predictor of GFR reduction [113, 114]. Ranges for serum BTP in term and preterm neonates have been provided and a steady decline of BTP values with increasing age was observed [115]. In the newborn population, threshold values for AKI identification have not yet been defined [114].
5.1.6 Osteopontin
The cytokine OPN is involved in the pathophysiology of experimental acute kidney injury and could be a specific biomarker of AKI in the case of loop of Henle damage.
In the neonatal population, a nested case-control study [102] in 30 patients (only nine with AKI) showed that AKI newborns had greater OPN values than controls. Prospective studies are needed to ascertain OPN value in predicting neonatal AKI.
5.1.7 β2-Microglobulin
Tubular proteinuria is traditionally referred to low-molecular-weight proteins that are normally produced in the body, freely filtered across the glomerulus, and normally reabsorbed in the proximal tubule but appear in the urine due to proximal tubular damage. Examples include α1-microglobulin, β2-microglobulin, and retinol-binding protein. β2-microglobulin is a 12-kD protein, is part of the class I major histocompatibility complex, and is presented at the membrane of nucleated cells. Urinary concentration may rise after toxins (radiocontrast) or cardiac surgery, or transplantation-induced renal injury, but may poorly predict the need for renal replacement therapy. Also, the concentration of β2-microglobulin increases with glomerular diseases, and an increase in β2-microglobulin may be predictive for a decrease in renal function. Therefore, β2-microglobulin may not be a specific marker of tubular injury [116].
Recently, more and more experts have suggested that a combination of multiple biomarkers to form a biomarkers panel was an optimal way to detect AKI more efficiently and accurately [107].
5.1.8 Metabolomics
Metabolomics represents an efficient way to contemporarily measure many biomarkers by analysing global sets of low-molecular-weight metabolites (including amino acids, organic acids, sugars, fatty acids, lipids, steroids, small peptides, vitamins, etc.), thus providing a ‘snapshot’ of the metabolic status of a cell, tissue, or organism in relation to genetic variations or external stimuli. The use of metabolomics appears to be a promising tool in neonatology. Urine is a biofluid particularly suitable for metabolomic analysis in neonatology because it may be collected by using simple, non-invasive techniques and may provide valuable diagnostic information [117].
The field of metabolomics uses analytical techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and mass spectrometry (MS) to identify and quantify a sample’s metabolite pool. Quantification of metabolites serves not only as a biomarker of certain cellular or tissue injuries but also to elucidate mechanisms of AKI.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic Aspects
The real impact of immaturity on drug disposition in this population has not been fully defined, especially because of the great heterogeneity in disease characteristics and comedications, in addition to age (postnatal, postmenstrual), and, moreover, because performing pharmacokinetic studies in the neonatal population remains challenging. A novel and promising approach to improve drug therapy and to facilitate studies in neonates and young infants is knowledge integration through pharmacokinetic modeling, which is either driven by mechanism-based pharmacokinetics or by physiology-based pharmacokinetics. Mechanism-based models use a ‘from compound to model’ approach; based on compound-specific observations, covariates are described, resulting in mechanism-based models that reflect a semiphysiological maturational function [118–120]. In contrast, physiology-based pharmacokinetics use a ‘from physiology to clinical observations’ approach; driven by characteristics of neonatal physiology (e.g. weight, cardiac output, renal function) and anatomy, as well as its age-related changes, a physiology-based pharmacokinetic model is developed [118–120]. Population pharmacokinetic approaches hereby provide a statistical tool to study and explore variability in pediatric drug responses among and within individuals representative of those in whom the drug will be used clinically [121–123]. Such models can drive study design and convert neonatal pharmacological studies from explorative to confirmatory [121–123]. Once a model is developed, validation is needed in a prospective trial. This methodology will improve dosing guidelines at the individual level [121–123].
The feasibility of these concepts for GFR-driven clearance in neonates has been described using a stepwise approach. In the first step, amikacin clearance was predicted by weight at birth (maturation until delivery), postnatal age (maturation since delivery), and disease characteristics (ibuprofen exposure, peripartum asphyxia) [124]. Since amikacin clearance reflects GFR ontogeny, it is reasonable to assume that the same pharmacokinetic model and its covariates will also accurately predict clearance maturation of other compounds that are cleared by the same route. Using datasets of netilmicin, vancomycin, tobramycin, and gentamicin in neonates, it was confirmed that the performance of the amikacin GFR model was similar to the independent, compound-specific models [125]. This provides evidence that the neonatal amikacin covariate model indeed contains physiological information since the information extracted from the first dataset on a given compound can be extrapolated to another compound that undergoes elimination by the same route as long as the clinical characteristics remain similar. Consequently, the same approach has been used to describe GFR maturation throughout life [125].
A very specific covariate that also needs further exploration in combination with all the aforementioned aspects on drug-related renal toxicity in preterm neonates is the relation between pharmacogenomics, drug disposition, and drug-induced renal damage. The preterm newborn is deficient in drug-handling capacity, including drug metabolizing enzymes (e.g. cytochromes P450), drug transporters (e.g. renal tubular organic anion transporters), or receptors (e.g. renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, dopamine) [4]. This immature drug-handling capacity may potentially be superimposed to genetic polymorphisms determining drug metabolism and transport, thereby further increasing the interpatient variability in drug dose, response, and renal side effects [126]. To illustrate the potential relevance of pharmacogenetic, polymorphism-driven renal drug toxicity, we refer to the work on ifosfamide in infants and toddlers [127].
6 Ongoing Research Initiatives and Consortia
The lack of clinical evidence supporting pharmacological treatments in newborns calls for investigations focused on this population. Table 4 reports some of these, aimed at validating dosage regimen and evaluating the short-term safety of single agents belonging to the anti-infective class.
Among recently launched funding programs of the European Commission, a call topic is specifically devoted to the improvement of healthcare interventions in the pediatric population, aimed at decreasing the risk of treatments and filling the gap of knowledge on healthcare interventions.
Research on preterm neonates may be very challenging because of well-known technical issues (multi-organ immaturity, prematurity, lack of self-assessment, need for specific formulations, etc.), the great heterogeneity in clinical practice, and the restricted number of neonates prematurely born with a given disease in each center. Thus, it is important to support and improve already existent networks in order to study the actual clinical practice among countries, and integrate the risk-benefit profiles of the currently used and new medicines among NICUs for the creation of international guidelines for the management of preterm babies.
7 Conclusions and Perspectives
The specific pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic aspects of neonates need to be further investigated in order to improve drug use. In this sense, the development of physiology-based pharmacokinetic models is a promising approach that could facilitate studies in neonates and improve drug therapy [121]. In addition to the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic peculiarities, the preterm population is characterized by organ immaturity and specific pathological conditions (e.g. respiratory distress syndrome, PDA) [3], improving risk of drug-related injuries. In particular, AKI is very common among NICUs [49] and correlates with higher mortality rates [50] and increased long-term risk of CKD [63–65].
Many of the widely used therapeutics in NICUs could impair renal function, either because of their well-known nephrotoxicity (i.e. aminoglycosides [77], β-lactam antibiotics [70], amphotericin B [83]) and their interaction with renal developmental factors (e.g. furosemide [87], NSAIDs [77]), but also because specific conditions affecting preterm neonates are correlated to AKI [51–54]. Difficulties still exist in discriminating the role of multiple factors (drugs, diet, age-related organ immaturity, diseases) in determining the onset of kidney damage. In this context, the validation of biomarkers for the early detection of renal injury could significantly improve clinical practice in this population.
Neonates, especially those born prematurely, can be considered an ‘orphan’ population with regard to specifically approved drugs [16–27]. Because of inherent difficulties in carrying out clinical trials in preterm infants, the collection of ‘real-world’ data is necessary to fully address clinical issues. The creation of multinational, multidisciplinary consortia is an approach with great potential to identify and compare real-world practice and relevant outcomes in NICUs. More specifically, the following areas need further investigation:
-
1.
The development of pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic models is a promising approach to address specific pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic aspects, and can improve drug therapy also through dose optimization [121].
-
2.
Since the preterm population is characterized by organ immaturity and specific disorders [3], reducing the risk of drug-related injuries must be addressed by active pharmacovigilance. Although some difficulties remain in discriminating the role of multiple factors in determining kidney damage (drugs, diet, age-related organ immaturity, diseases), some of these, such as drugs and diet, are certainly modifiable. The creation of networks for conducting postmarketing surveillance of emerging safety issues based on ‘real-world’ data in preterm neonates fits well with the new European pharmacovigilance legislation, which aims at strengthening the post-authorization monitoring of medicinal products and now includes adverse reactions observed with off-label use.
-
3.
Identification of drug- and patient-related characteristics associated with a higher risk of renal damage and related clinical sequelae will allow the development of risk scores and risk charts, which are actually missing in neonatology. The incorporation of validated renal function biomarkers into clinical practice will truly allow personalized medicine [128, 129].
The increased interest of regulatory agencies and funding programs in the neonatal population reflects the need for international guidelines for the management of newborns, and also calls for international consortia, which should plan observational studies to systematically access the current clinical practice in NICUs. After careful review of current real-world practices across countries, a more informed strategy will be achievable towards improvement of clinical recommendations and more informed regulatory decisions.
References
World Health Organization. Fact sheet on preterm birth. 2013. Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs363/en/. Accessed 15 Jan 2015.
Horbar JD, Carpenter JH, Badger GJ, Kenny MJ, Soll RF, Morrow KA, et al. Mortality and neonatal morbidity among infants 501 to 1500 grams from 2000 to 2009. Pediatrics. 2012;129:1019–26.
European Medicines Agency. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) and Paediatric Committee (PDCO). Guideline on the investigation of medicinal products in the term and preterm neonate. 2009. Available at: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guideline/2009/09/WC500003750.pdf. Accessed 15 Jan 2015.
Schreuder MF, Bueters RR, Allegaert K. The interplay between drugs and the kidney in premature neonates. Pediatr Nephrol. 2014;29:2083–91.
European Medicines Agency. The European paediatric initiative: history of the Paediatric Regulation. 2007. Available at: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Other/2009/09/WC500003693.pdf. Accessed 15 Jan 2015.
US FDA. Modernization Act of 1997. Available at: http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/PLAW-105publ115/pdf/PLAW-105publ115.pdf. Accessed 15 Jan 2015.
European Medicines Agency. Better medicines for children. 2002. Available at: http://ec.europa.eu/health/files/pharmacos/docs/doc2002/feb/cd_pediatrics_en.pdf. Accessed 15 Jan 2015.
US FDA. Pediatric Research Equity Act. 2003. Available at: http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/PLAW-108publ155/html/PLAW-108publ155.htm. Accessed 15 Jan 2015.
Regulation on medicinal products for paediatric use. European Parliament and of the Council. 2006. Available at: http://ec.europa.eu/health/files/eudralex/vol-1/reg_2006_1901/reg_2006_1901_en.pdf. Accessed 15 Jan 2015.
European Medicines Agency. Better medicines for children from concept to reality: progress report on the Paediatric Regulation (EC) N°1901/2006. 2013. Available at: http://ec.europa.eu/health/files/paediatrics/2013_com443/paediatric_report-com%282013%29443_en.pdf. Accessed 15 Jan 2015.
US FDA. Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act (FDASIA). 2012. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/RegulatoryInformation/Legislation/FederalFoodDrugandCosmeticActFDCAct/SignificantAmendmentstotheFDCAct/FDASIA/. Accessed 15 Jan 2015.
World Health Organization. WHO model formulary for children. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010. Available at: http://www.who.int/selection_medicines/list/WMFc_2010.pdf. Accessed 15 Jan 2015.
Ministero della salute. Direzione generale della valutazione dei medicinali e della farmacovigilanza. Guida all'uso dei farmaci per i bambini. Rome : Istituto poligrafico e Zecca dello Stato; 2003 [SBN Code: SNT0002326].
US FDA. New pediatric labeling information database. Available at: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/sda/sdNavigation.cfm?sd=labelingdatabase. Accessed 15 Jan 2015.
European Medicines Agency. Success of the Paediatric Regulation after 5 years. 2013. Available at: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Other/2013/06/WC500143984.pdf. Accessed 15 Jan 2015.
Laforgia N, Nuccio MM, Schettini F, Dell’aera M, Gasbarro AR, Dell’erba A, et al. Off-label and unlicensed drug use among neonatal intensive care units in Southern Italy. Pediatr Int. 2014;56:57–9.
Kieran EA, O’Callaghan N, O’Donnell CP. Unlicensed and off-label drug use in an Irish neonatal intensive care unit: a prospective cohort study. Acta Paediatr. 2014;103:e139–42.
Stiers JL, Ward RM. Newborns, one of the last therapeutic orphans to be adopted. JAMA Pediatr. 2014;168:106–8.
Conroy S, McIntyre J. The use of unlicensed and off-label medicines in the neonate. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2005;10:115–22.
Laughon MM, Avant D, Tripathi N, Hornik CP, Cohen-Wolkowiez M, Clark RH, et al. Drug labeling and exposure in neonates. JAMA Pediatr. 2014;168:130–6.
Kimland E, Nydert P, Odlind V, Bottiger Y, Lindemalm S. Paediatric drug use with focus on off-label prescriptions at Swedish hospitals: a nationwide study. Acta Paediatr. 2012;101:772–8.
Dell’Aera M, Gasbarro AR, Padovano M, Laforgia N, Capodiferro D, Solarino B, et al. Unlicensed and off-label use of medicines at a neonatology clinic in Italy. Pharm World Sci. 2007;29:361–7.
Frattarelli DA, Galinkin JL, Green TP, Johnson TD, Neville KA, Paul IM, et al. Off-label use of drugs in children. Pediatrics. 2014;133:563–7.
Pansieri C, Bonati M, Choonara I, Jacqz-Aigrain E. Neonatal drug trials: impact of EU and US paediatric regulations. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014;99(5):F438.
Haslund-Krog S, Mathiasen R, Christensen HR, Holst H. The impact of legislation on drug substances used off-label in paediatric wards: a nationwide study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;70:445–52.
Lindell-Osuagwu L, Hakkarainen M, Sepponen K, Vainio K, Naaranlahti T, Kokki H. Prescribing for off-label use and unauthorized medicines in three paediatric wards in Finland, the status before and after the European Union Paediatric Regulation. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2014;39:144–53.
Dessi A, Salemi C, Fanos V, Cuzzolin L. Drug treatments in a neonatal setting: focus on the off-label use in the first month of life. Pharm World Sci. 2010;32:120–4.
Neubert A, Lukas K, Leis T, Dormann H, Brune L, Rascher W. Drug utilisation on a preterm and neonatal intensive care unit in Germany: a prospective, cohort-based analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;66:87–95.
Pandolfini C, Bonati M. European paediatric research and children’s therapeutic needs. A trial review. Acta Paediatr. 2008;97:1232–7.
Bellis JR, Kirkham JJ, Nunn AJ, Pirmohamed M. Adverse drug reactions and off-label and unlicensed medicines in children: a prospective cohort study of unplanned admissions to a paediatric hospital. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;77:545–53.
Alcorn J, McNamara PJ. Pharmacokinetics in the newborn. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003;55:667–86.
European Medicines Agency. Discussion paper on the impact of renal immaturity when investigating medicinal products intended for paediatric use. European Medicines Agency (EMA). 2004. Available at: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guideline/2009/09/WC500003807.pdf. Accessed 15 Jan 2015.
Singh RR, Moritz KM, Bertram JF, Cullen-McEwen LA. Effects of dexamethasone exposure on rat metanephric development: in vitro and in vivo studies. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;293:F548–54.
Lasaitiene D, Chen Y, Guron G, Marcussen N, Tarkowski A, Telemo E, Friberg P. Perturbed medullary tubulogenesis in neonatal rat exposed to renin-angiotensin system inhibition. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003;18:2534–41.
Gubler MC, Antignac C. Renin-angiotensin system in kidney development: renal tubular dysgenesis. Kidney Int. 2010;77:400–6.
Kent AL, Maxwell LE, Koina ME, Falk MC, Willenborg D, Dahlstrom JE. Renal glomeruli and tubular injury following indomethacin, ibuprofen, and gentamicin exposure in a neonatal rat model. Pediatr Res. 2007;62:307–12.
Sutherland MR, Yoder BA, McCurnin D, Seidner S, Gubhaju L, Clyman RI, et al. Effects of ibuprofen treatment on the developing preterm baboon kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012;302:F1286–92.
Rodriguez MM, Gomez AH, Abitbol CL, Chandar JJ, Duara S, Zilleruelo GE. Histomorphometric analysis of postnatal glomerulogenesis in extremely preterm infants. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2004;7:17–25.
Sutherland MR, Gubhaju L, Moore L, Kent AL, Dahlstrom JE, Horne RS, et al. Accelerated maturation and abnormal morphology in the preterm neonatal kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22:1365–74.
Carmody JB, Charlton JR. Short-term gestation, long-term risk: prematurity and chronic kidney disease. Pediatrics. 2013;131:1168–79.
Musso CG, Ghezzi L, Ferraris J. Renal physiology in newborns and old people: similar characteristics but different mechanisms. Int Urol Nephrol. 2004;36:273–6.
Gubhaju L, Sutherland MR, Horne RS, Medhurst A, Kent AL, Ramsden A, et al. Assessment of renal functional maturation and injury in preterm neonates during the first month of life. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014;307:F149–58.
Jose PA, Fildes RD, Gomez RA, Chevalier RL, Robillard JE. Neonatal renal function and physiology. Curr Opin Pediatr. 1994;6:172–7.
Sulemanji M, Vakili K. Neonatal renal physiology. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2013;22:195–8.
Berg CS, Barnette AR, Myers BJ, Shimony MK, Barton AW, Inder TE. Sodium bicarbonate administration and outcome in preterm infants. J Pediatr. 2010;157:684–7.
Alcorn J, McNamara PJ. Ontogeny of hepatic and renal systemic clearance pathways in infants: part I. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002;41:959–98.
van den Anker JN, Schwab M, Kearns GL. Developmental pharmacokinetics. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2011;205:51–75.
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;2:1–138.
Askenazi DJ, Koralkar R, Hundley HE, Montesanti A, Patil N, Ambalavanan N. Fluid overload and mortality are associated with acute kidney injury in sick near-term/term neonate. Pediatr Nephrol. 2013;28:661–6.
Koralkar R, Ambalavanan N, Levitan EB, McGwin G, Goldstein S, Askenazi D. Acute kidney injury reduces survival in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res. 2011;69:354–8.
Elmas AT, Tabel Y, Elmas ON. Serum cystatin C predicts acute kidney injury in preterm neonates with respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2013;28:477–84.
Sarafidis K, Tsepkentzi E, Agakidou E, Diamanti E, Taparkou A, Soubasi V, et al. Serum and urine acute kidney injury biomarkers in asphyxiated neonates. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012;27:1575–82.
Walker MW, Clark RH, Spitzer AR. Elevation in plasma creatinine and renal failure in premature neonates without major anomalies: terminology, occurrence and factors associated with increased risk. J Perinatol. 2011;31:199–205.
Kandasamy Y, Smith R, Wright IM. Measuring cystatin C to determine renal function in neonates. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2013;14:318–22.
Luyckx VA, Brenner BM. Low birth weight, nephron number, and kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2005;97:S68–77.
Brenner BM, Garcia DL, Anderson S. Glomeruli and blood pressure. Less of one, more the other? Am J Hypertens. 1988;1:335–47.
Brenner BM, Chertow GM. Congenital oligonephropathy and the etiology of adult hypertension and progressive renal injury. Am J Kidney Dis. 1994;23:171–5.
Bidani AK, Griffin KA. Pathophysiology of hypertensive renal damage: implications for therapy. Hypertension. 2004;44:595–601.
Helal I, Fick-Brosnahan GM, Reed-Gitomer B, Schrier RW. Glomerular hyperfiltration: definitions, mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012;8:293–300.
D’Amico G, Bazzi C. Pathophysiology of proteinuria. Kidney Int. 2003;63:809–25.
Hartman HA, Lai HL, Patterson LT. Cessation of renal morphogenesis in mice. Dev Biol. 2007;310:379–87.
Luyckx VA, Brenner BM. The clinical importance of nephron mass. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21:898–910.
Vikse BE, Irgens LM, Leivestad T, Hallan S, Iversen BM. Low birth weight increases risk for end-stage renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;19:151–7.
White SL, Perkovic V, Cass A, Chang CL, Poulter NR, Spector T, et al. Is low birth weight an antecedent of CKD in later life? A systematic review of observational studies. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;54:248–61.
Mammen C, Al AA, Skippen P, Nadel H, Levine D, Collet JP, et al. Long-term risk of CKD in children surviving episodes of acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit: a prospective cohort study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;59:523–30.
Garg AX, Suri RS, Barrowman N, Rehman F, Matsell D, Rosas-Arellano MP, et al. Long-term renal prognosis of diarrhea-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. JAMA. 2003;290:1360–70.
Slack R, Hawkins KC, Gilhooley L, Addison GM, Lewis MA, Webb NJ. Long-term outcome of meningococcal sepsis-associated acute renal failure. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2005;6:477–9.
Taber SS, Pasko DA. The epidemiology of drug-induced disorders: the kidney. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2008;7:679–90.
Naughton CA. Drug-induced nephrotoxicity. Am Fam Physician. 2008;78:743–50.
Markowitz GS, Perazella MA. Drug-induced renal failure: a focus on tubulointerstitial disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2005;351:31–47.
Zager RA. Pathogenetic mechanisms in nephrotoxic acute renal failure. Semin Nephrol. 1997;17:3–14.
Bennett WM, DeBroe ME. Analgesic nephropathy: a preventable renal disease. N Engl J Med. 1989;320:1269–71.
Griffin MD, Bergstralhn EJ, Larson TS. Renal papillary necrosis: a sixteen-year clinical experience. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1995;6:248–56.
Perazella MA. Drug-induced nephropathy: an update. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2005;4:689–706.
Clark RH, Bloom BT, Spitzer AR, Gerstmann DR. Reported medication use in the neonatal intensive care unit: data from a large national data set. Pediatrics. 2006;117:1979–87.
Gordon A, Jeffery HE. Antibiotic regimens for suspected late onset sepsis in newborn infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;3:CD004501.
Patzer L. Nephrotoxicity as a cause of acute kidney injury in children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2008;23:2159–73.
Rao SC, Srinivasjois R, Hagan R, Ahmed M. One dose per day compared to multiple doses per day of gentamicin for treatment of suspected or proven sepsis in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;11:CD005091.
Vieux R, Fresson J, Guillemin F, Hascoet JM. Perinatal drug exposure and renal function in very preterm infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2011;96:F290–5.
Michel DM, Kelly CJ. Acute interstitial nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9:506–15.
Wai AO, Lo AM, Abdo A, Marra F. Vancomycin-induced acute interstitial nephritis. Ann Pharmacother. 1998;32:1160–4.
Sawaya BP, Briggs JP, Schnermann J. Amphotericin B nephrotoxicity: the adverse consequences of altered membrane properties. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1995;6:154–64.
Goldman RD, Koren G. Amphotericin B nephrotoxicity in children. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2004;26:421–6.
Joannidis M. Drug-induced renal failure in the ICU. Int J Artif Organs. 2004;27:1034–42.
Deray G. Amphotericin B nephrotoxicity. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2002;49(Suppl 1):37–41.
Turkova A, Roilides E, Sharland M. Amphotericin B in neonates: deoxycholate or lipid formulation as first-line therapy: is there a ‘right’ choice? Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2011;24:163–71.
Pacifici GM. Clinical pharmacology of furosemide in neonates: a review. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2013;6:1094–129.
Allegaert K, Anderson B, Simons S, van Overmeire B. Paracetamol to induce ductus arteriosus closure: is it valid? Arch Dis Child. 2013;98:462–6.
Allegaert K. The impact of ibuprofen or indomethacin on renal drug clearance in neonates. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2009;22(Suppl 3):88–91.
Henderson-Smart DJ, De Paoli AG. Methylxanthine treatment for apnoea in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;12:CD000140.
Spitzer AR. Evidence-based methylxanthine use in the NICU. Clin Perinatol. 2012;39:137–48.
Schmidt B, Roberts RS, Davis P, Doyle LW, Barrington KJ, Ohlsson A, et al. Caffeine therapy for apnea of prematurity. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2112–21.
Schmidt B, Anderson PJ, Doyle LW, Dewey D, Grunau RE, Asztalos EV, et al. Survival without disability to age 5 years after neonatal caffeine therapy for apnea of prematurity. JAMA. 2012;307:275–82.
Sekine T, Endou H. Children’s toxicology from bench to bed: Drug-induced renal injury (3). Drug transporters and toxic nephropathy in childhood. J Toxicol Sci. 2009;34 Suppl 2:SP259–65.
Gallini F, Maggio L, Romagnoli C, Marrocco G, Tortorolo G. Progression of renal function in preterm neonates with gestational age < or = 32 weeks. Pediatr Nephrol. 2000;15:119–24.
Brion LP, Fleischman AR, McCarton C, Schwartz GJ. A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in low birth weight infants during the first year of life: noninvasive assessment of body composition and growth. J Pediatr. 1986;109:698–707.
Liborio AB, Branco KM, Torres de Melo BC. Acute kidney injury in neonates: from urine output to new biomarkers. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:601568.
Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes MM, Ma Q, Kelly C, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet. 2005;365:1231–8.
Krawczeski CD, Woo JG, Wang Y, Bennett MR, Ma Q, Devarajan P. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin concentrations predict development of acute kidney injury in neonates and children after cardiopulmonary bypass. J Pediatr. 2011;158:1009–15.
Wheeler DS, Devarajan P, Ma Q, Harmon K, Monaco M, Cvijanovich N, et al. Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children with septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:1297–303.
Zappitelli M, Washburn KK, Arikan AA, Loftis L, Ma Q, Devarajan P, et al. Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is an early marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care. 2007;11:R84.
Askenazi DJ, Montesanti A, Hunley H, Koralkar R, Pawar P, Shuaib F, et al. Urine biomarkers predict acute kidney injury and mortality in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr. 2011;159:907–12.
La MG, Galletti S, Capelli I, Vandini S, Nisi K, Aquilano G, et al. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin at birth predicts early renal function in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res. 2011;70:379–83.
Askenazi DJ, Ambalavanan N, Goldstein SL. Acute kidney injury in critically ill newborns: what do we know? What do we need to learn? Pediatr Nephrol. 2009;24:265–74.
Cataldi L, Mussap M, Bertelli L, Ruzzante N, Fanos V, Plebani M. Cystatin C in healthy women at term pregnancy and in their infant newborns: relationship between maternal and neonatal serum levels and reference values. Am J Perinatol. 1999;16:287–95.
Sharma AP, Kathiravelu A, Nadarajah R, Yasin A, Filler G. Body mass does not have a clinically relevant effect on cystatin C eGFR in children. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:470–4.
Li Y, Fu C, Zhou X, Xiao Z, Zhu X, Jin M, et al. Urine interleukin-18 and cystatin-C as biomarkers of acute kidney injury in critically ill neonates. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012;27:851–60.
Huang Y, Don-Wauchope AC. The clinical utility of kidney injury molecule 1 in the prediction, diagnosis and prognosis of acute kidney injury: a systematic review. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2011;10:260–71.
Coca SG, Yalavarthy R, Concato J, Parikh CR. Biomarkers for the diagnosis and risk stratification of acute kidney injury: a systematic review. Kidney Int. 2008;73:1008–16.
Sprenkle P, Russo P. Molecular markers for ischemia, do we have something better then creatinine and glomerular filtration rate? Arch Esp Urol. 2013;66:99–114.
Parikh CR, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Garg AX, Kadiyala D, Shlipak MG, Koyner JL, et al. Performance of kidney injury molecule-1 and liver fatty acid-binding protein and combined biomarkers of AKI after cardiac surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;8:1079–88.
Hoffmann A, Nimtz M, Conradt HS. Molecular characterization of beta-trace protein in human serum and urine: a potential diagnostic marker for renal diseases. Glycobiology. 1997;7:499–506.
Filler G, Priem F, Lepage N, Sinha P, Vollmer I, Clark H, et al. Beta-trace protein, cystatin C, beta(2)-microglobulin, and creatinine compared for detecting impaired glomerular filtration rates in children. Clin Chem. 2002;48:729–36.
Bariciak E, Yasin A, Harrold J, Walker M, Lepage N, Filler G. Preliminary reference intervals for cystatin C and beta-trace protein in preterm and term neonates. Clin Biochem. 2011;44:1156–9.
Zwiers AJ, Cransberg K, de Rijke YB, Willemsen SP, de Mol AC, Tibboel D, et al. Reference ranges for serum beta-trace protein in neonates and children younger than 1 year of age. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2014;52:1815–21.
Trof RJ, Di MF, Leemreis J, Groeneveld AB. Biomarkers of acute renal injury and renal failure. Shock. 2006;26:245–53.
Fanos V, Antonucci R, Barberini L, Noto A, Atzori L. Clinical application of metabolomics in neonatology. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012;25(Suppl 1):104–9.
Krekels EH, Neely M, Panoilia E, Tibboel D, Capparelli E, Danhof M, et al. From pediatric covariate model to semiphysiological function for maturation: part I. Extrapolation of a covariate model from morphine to zidovudine. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2012;1:e9.
Krekels EH, Johnson TN, den Hoedt SM, Rostami-Hodjegan A, Danhof M, Tibboel D, et al. From pediatric covariate model to semiphysiological function for maturation: part II. Sensitivity to physiological and physicochemical properties. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2012;1:e10.
Allegaert K, Smits A, van den Anker JN. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling in pediatric drug development: a clinician’s request for a more integrated approach. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:103763.
De Cock RF, Piana C, Krekels EH, Danhof M, Allegaert K, Knibbe CA. The role of population PK-PD modelling in paediatric clinical research. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;67(Suppl 1):5–16.
Anderson BJ, Allegaert K, Holford NH. Population clinical pharmacology of children: general principles. Eur J Pediatr. 2006;165:741–6.
Anderson BJ, Allegaert K, Holford NH. Population clinical pharmacology of children: modelling covariate effects. Eur J Pediatr. 2006;165:819–29.
De Cock RF, Allegaert K, Schreuder MF, Sherwin CM, de Hoog M, van den Anker JN, et al. Maturation of the glomerular filtration rate in neonates, as reflected by amikacin clearance. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012;51:105–17.
De Cock RF, Allegaert K, Sherwin CM, Nielsen EI, de Hoog M, van den Anker JN, et al. A neonatal amikacin covariate model can be used to predict ontogeny of other drugs eliminated through glomerular filtration in neonates. Pharm Res. 2014;31:754–67.
Kapur G, Mattoo T, Aranda JV. Pharmacogenomics and renal drug disposition in the newborn. Semin Perinatol. 2004;28:132–40.
Aleksa K, Halachmi N, Ito S, Koren G. Renal ontogeny of ifosfamide nephrotoxicity. J Lab Clin Med. 2004;144:285–93.
Hanna MH, Brophy PD. Metabolomics in pediatric nephrology: emerging concepts. Pediatr Nephrol. 2014. doi:10.1007/s00467-014-2880-x.
Fanos V, Fanni C, Ottonello G, Noto A, Dessi A, Mussap M. Metabolomics in adult and pediatric nephrology. Molecules. 2013;18:4844–57.
Acknowledgments
Anna Girardi, Emanuel Raschi, Silvia Galletti, Elisabetta Poluzzi, Giacomo Faldella, Karel Allegaert, and Fabrizio De Ponti have no conflicts of interest to declare that are directly relevant to the content of this study.
Authors at the University of Bologna are supported by Institutional Research Funds (Ricerca Fondamentale Orientata). Karel Allegaert is supported by the Fund for Scientific Research, Flanders (Fundamental Clinical Investigatorship 1800214N) and by the Agency for Innovation by Science and Technology in Flanders (IWT) through the SAFEPEDRUG project (IWT/SBO 130033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Girardi, A., Raschi, E., Galletti, S. et al. Drug-Induced Renal Damage in Preterm Neonates: State of the Art and Methods for Early Detection. Drug Saf 38, 535–551 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40264-015-0288-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40264-015-0288-6