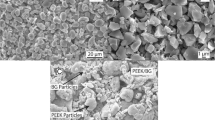
Abstract
There is increasing interest in the use of polyether ether ketone (PEEK) for orthopedic and dental implant applications due to its elastic modulus (close to that of bone), biocompatibility and radiolucent properties. However, PEEK is still categorized as bioinert owing to its low integration with surrounding tissues. Methods such as depositing hydroxyapatite (HA) onto the PEEK surface could increase its bioactivity. However, depositing HA without damaging the PEEK substrate is still required further investigation. Friction stir processing is a solid-state processing method that is widely used for composite substrate fabrication. In this study, a pinless tool was used to fabricate a HA/PEEK surface nanocomposite for orthopedic and dental applications. Microscopical images of the modified substrate confirmed homogenous distribution of the HA on the surface of the PEEK. The resultant HA/PEEK surface nanocomposites demonstrated improved surface hydrophilicity coupled with better apatite formation capacity (as shown in the simulated body fluid) in comparison to the pristine PEEK, making the newly developed material more suitable for biomedical application. This surface deposition method that is carried out at low temperature would not damage the PEEK substrate and thus could be a good alternative for existing commercial methods for PEEK surface modification.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed H, Van Tooren M, Justice J, Harik R, Kidane A, Reynolds AP (2018) Investigation and development of friction stir welding process for unreinforced polyphenylene sulfide and reinforced polyetheretherketone. J Thermoplast Compos Mater. https://doi.org/10.1177/0892705718785676
Alla RK, Ginjupalli K, Upadhya N, Shammas M, Ravi RK, Sekhar R (2011) Surface roughness of implants: a review. Trends Biomater Artif Organs 25:112–118
Almasi D, Iqbal N, Sadeghi M, Sudin I, Abdul Kadir MR, Kamarul T (2016) Preparation methods for improving PEEK’s bioactivity for orthopedic and dental application: a review. Int J Biomater 2016:12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8202653
Aravind K, Sangeetha D (2015) Characterization and in vitro studies of sulfonated polyether ether ketone/polyether sulfone/nano hydroxyapatite composite. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 64:220–227. https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2014.936594
Arima Y, Iwata H (2007) Effect of wettability and surface functional groups on protein adsorption and cell adhesion using well-defined mixed self-assembled monolayers. Biomaterials 28:3074–3082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.03.013
Bakar MA, Cheang P, Khor K (2003) Tensile properties and microstructural analysis of spheroidized hydroxyapatite–poly (etheretherketone) biocomposites. Mater Sci Eng A 345:55–63
Barletta M, Gisario A, Rubino G (2011) Scratch response of high-performance thermoset and thermoplastic powders deposited by the electrostatic spray and ‘hot dipping’fluidised bed coating methods: the role of the contact condition. Surf Coat Technol 205:5186–5198
Chou L, Marek B, Wagner WR (1999) Effects of hydroxylapatite coating crystallinity on biosolubility, cell attachment efficiency and proliferation in vitro. Biomaterials 20:977–985. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(98)00254-3
Costa MI, Verdera D, Vieira MT, Rodrigues DM (2014) Surface enhancement of cold work tool steels by friction stir processing with a pinless tool. Appl Surf Sci 296:214–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.01.094
Farnoush H, Abdi Bastami A, Sadeghi A, Aghazadeh Mohandesi J, Moztarzadeh F (2013a) Tribological and corrosion behavior of friction stir processed Ti-CaP nanocomposites in simulated body fluid solution. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 20:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2012.12.001
Farnoush H, Sadeghi A, Abdi Bastami A, Moztarzadeh F, Aghazadeh Mohandesi J (2013b) An innovative fabrication of nano-HA coatings on Ti-CaP nanocomposite layer using a combination of friction stir processing and electrophoretic deposition. Ceram Int 39:1477–1483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.07.092
Filiaggi MJ, Coombs NA, Pilliar RM (1991) Student research award in the undergraduate, Master candidate category, or health science degree candidate category, 17th annual meeting of the society for biomaterials, scottsdale, AZ may 1–5, 1991. Characterization of the interface in the plasma-sprayed HA coating/Ti-6Al-4V implant system. J Biomed Mater Res 25:1211–1229. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.820251004
Gan YX, Solomon D, Reinbolt M (2010) Friction stir processing of particle reinforced composite. Materials 3:329–350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3010329
Ha SW, Mayer J, Koch B, Wintermantel E (1994) Plasma-sprayed hydroxylapatite coating on carbon fibre reinforced thermoplastic composite materials. J Mater Sci Mater Med 5:481–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00058987
Ha SW, Gisep A, Mayer J, Wintermantel E, Gruner H, Wieland M (1997) Topographical characterization and microstructural interface analysis of vacuum-plasma-sprayed titanium and hydroxyapatite coatings on carbon fibre-reinforced poly(etheretherketone). J Mater Sci Mater Med 8:891–896
Hahn B-D et al (2013) Osteoconductive hydroxyapatite coated PEEK for spinal fusion surgery. Appl Surf Sci 283:6–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.05.073
Huang J, Best S, Bonfield W, Brooks R, Rushton N, Jayasinghe S, Edirisinghe M (2004) In vitro assessment of the biological response to nano-sized hydroxyapatite. J Mater Sci Mater Med 15:441–445
Kokubo T (1998) Apatite formation on surfaces of ceramics, metals and polymers in body environment. Acta Mater 46:2519–2527. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(98)80036-0
Kokubo T, Takadama H (2006) How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 27:2907–2915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.01.017
Landi E, Tampieri A, Celotti G, Sprio S (2000) Densification behaviour and mechanisms of synthetic hydroxyapatites. J Eur Ceram Soc 20:2377–2387. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0955-2219(00)00154-0
Lee JH et al (2013) In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the bioactivity of hydroxyapatite-coated polyetheretherketone biocomposites created by cold spray technology. Acta Biomater 9:6177–6187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2012.11.030
Liu F et al (2009) Micro-scratch study of a magnetron-sputtered Zr-based metallic-glass film. Surf Coat Technol 203:3480–3484
Mendonça G, Mendonça DB, Aragao FJ, Cooper LF (2008) Advancing dental implant surface technology—from micron-to nanotopography. Biomaterials 29:3822–3835
Morishige T, Tsujikawa M, Hino M, Hirata T, Oki S, Higashi K (2008) Microstructural modification of cast Mg alloys by friction stir processing. Int J Cast Met Res 21:109–113. https://doi.org/10.1179/136404608X361774
Müller KH, Motskin M, Philpott AJ, Routh AF, Shanahan CM, Duer MJ, Skepper JN (2014) The effect of particle agglomeration on the formation of a surface-connected compartment induced by hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Biomaterials 35:1074–1088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.10.041
Pan YS, Wang J, Pan CL Research on biological properties of PEEK based composites. In: Applied mechanics and materials, 2013. Trans Tech Publ, pp 3–7
Paoletti A, Lambiase F, Di Ilio A (2016) Analysis of forces and temperatures in friction spot stir welding of thermoplastic polymers. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 83:1395–1407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7669-y
Prasad R, Raghava PM (2012) Fsw of polypropylene reinforced with Al2O3 nano composites, effect on mechanical and microstructural properties. Int J Eng Res Appl 2:288–296
Rabiei A, Sandukas S (2013) Processing and evaluation of bioactive coatings on polymeric implants. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 101A:2621–2629. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.34557
Radin SR, Ducheyne P (1992) Plasma spraying induced changes of calcium phosphate ceramic characteristics and the effect onin vitro stability. J Mater Sci Mater Med 3:33–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00702942
Ratna Sunil B, Sampath Kumar TS, Chakkingal U, Nandakumar V, Doble M (2014a) Friction stir processing of magnesium–nanohydroxyapatite composites with controlled in vitro degradation behavior. Mater Sci Eng C 39:315–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2014.03.004
Ratna Sunil B, Sampath Kumar TS, Chakkingal U, Nandakumar V, Doble M (2014b) Nano-hydroxyapatite reinforced AZ31 magnesium alloy by friction stir processing: a solid state processing for biodegradable metal matrix composites. J Mater Sci Mater Med 25:975–988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-013-5127-7
Roeder RK, Converse GL, Kane RJ, Yue W (2008) Hydroxyapatite-reinforced polymer biocomposites for synthetic bone substitutes. JOM 60:38–45
Shen X, Bo L, Zhao J, Wei-Zhong X, Sun W (2014) A review of hydroxyapatite microstructure regulation with hydrothermal method. J Funct Mater 45:03006–03010
Shi Z, Huang X, Cai Y, Tang R, Yang D (2009) Size effect of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on proliferation and apoptosis of osteoblast-like cells. Acta Biomater 5:338–345
Stanford C (2008) Surface modifications of dental implants. Austr Dental J 20:53
Strnad Z, Strnad J, Povysil C, Urban K (2000) Effect of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coating on the osteoconductivity of commercially pure titanium implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 15:483–490
Wang L, Weng L, Song S, Sun Q (2010) Mechanical properties and microstructure of polyetheretherketone–hydroxyapatite nanocomposite materials. Mater Lett 64:2201–2204
Wang L, Weng L, Song S, Zhang Z, Tian S, Ma R (2011) Characterization of polyetheretherketone–hydroxyapatite nanocomposite materials. Mater Sci Eng A 528:3689–3696
Wang L et al (2014) Polyetheretherketone/nano-fluorohydroxyapatite composite with antimicrobial activity and osseointegration properties. Biomaterials 35:6758–6775
Wu X, Liu X, Wei J, Ma J, Deng F, Wei S (2012) Nano-TiO2/PEEK bioactive composite as a bone substitute material: in vitro and in vivo studies. Int J Nanomed 7:1215
Xu S, Ma X, Wen H, Tang G, Li C (2014) Effect of annealing on the mechanical and scratch properties of BCN films obtained by magnetron sputtering deposition. Appl Surf Sci
Xue W, Tao S, Liu X, Zheng X, Ding C (2004) In vivo evaluation of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings having different crystallinity. Biomaterials 25:415–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(03)00545-3
Zhang G, Leparoux S, Liao H, Coddet C (2006) Microwave sintering of poly-ether-ether-ketone (PEEK) based coatings deposited on metallic substrate. Script Mater 55:621–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2006.06.010
Acknowledgements
This article was a result of a study conducted at Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences in Kermanshah, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Ethical statement
This research was evaluated in accordance with the ethical principles by Kermanshah University of Medical Science at 2018.07.31 and approved with the approval ID: IR.KUMS.RES.1397.285. The research was found to be in accordance with the ethical principles and the national norms and standards for conducting Medical Research in Iran. This research was not involving human participants and animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almasi, D., Lau, W.J., Rasaee, S. et al. Fabrication of a novel hydroxyapatite/polyether ether ketone surface nanocomposite via friction stir processing for orthopedic and dental applications. Prog Biomater 9, 35–44 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40204-020-00130-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40204-020-00130-7