Abstract
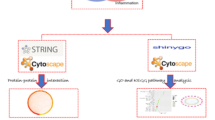
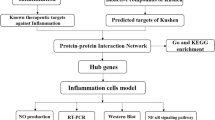
Squalene (SQ) has been documented in the past for its ability to reduce inflammation, but its mechanism needs more information. In this study, we investigated squalene as an anti-inflammatory drug candidate and the framework involved in treating inflammation (INF) using the network pharmacology concept. The molecular targets of SQ and INF that are available in databases and the overlaps between these targets were demonstrated using InteractiVenn. The protein-protein networks were generated that in turn revealed several key targets and were further processed with Cytoscape. The gene ontology enrichment and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway (KEGG) studies were performed. We also performed molecular docking tests that validated the binding affinity of molecular targets and drugs. A total of 100 SQ targets and 11,417 INF-related targets yielded 93 overlapping targets. Seven core targets, CRHR1, EGFR, ERBB2, HIF1A, SLC6A3, MAP2K1, and F2R were found to be relevant with respective to SQ’s anti-inflammatory activity. The underlying mechanism of SQ with regard to INF was interpreted by analyzing various enrichment analyses along with the KEGG pathway. In conclusion, SQ played a vital role in the management of INF by regulating CRHR1, EGFR, ERBB2, HIF1A, SLC6A3, MAP2K1, and F2R. The research outcomes are crucial as they offer significant insights into the use of SQ for combating inflammation.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Aisa Y, Yunusi K, Chen Q, Mi N (2020) Systematic understanding of the potential targets and pharmacological mechanisms of acteoside by network pharmacology approach. Med Chem Res 29(4):793–801. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00044-020-02524-5
Algül H, Wagner M, Lesina M, Schmid RM (2007) Overexpression of ErbB2 in the exocrine pancreas induces an inflammatory response but not increased proliferation. Int J Cancer 121(7):1410–1416. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.22843
Atkins JD, Boateng SY, Sorensen T, McGuffin LJ (2015) Disorder prediction methods, their applicability to different protein targets and their usefulness for guiding experimental studies. Int J Mol Sci 16(8):19040–19054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160819040
Avruch J (2007) MAP kinase pathways: the first twenty years. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - molecular Cell Research. 1773(8):1150–1160
Balkrishna A, Rohela A, Kumar A, Kumar A, Arya V, Thakur P et al (2021) Mechanistic insight into antimicrobial and antioxidant potential of Jasminum species: a Herbal Approach for Disease Management. Plants 10:1089
Brouwer E, Gouw ASH, Posthumus MD, Van Leeuwen MA, Boerboom AL, Bijzet J, Bos R, Limburg PC, Kallenberg CGM, Westra J (2009) Hypoxia inducible factor-1-alpha (HIF-1α) is related to both angiogenesis and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 27:945–951
Brown DN, Caffa I, Cirmena G, Piras D, Garuti A, Gallo M, Alberti S, Nencioni A, Ballestrero A, Zoppoli G (2016) Squalene epoxidase is a bona fide oncogene by amplification with clinical relevance in breast cancer. Sci Rep 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/SREP19435
Cárdeno A, Aparicio-Soto M, Montserrat-de la Paz S, Bermudez B, Muriana FJG, Alarcón-de-la-Lastra C (2015) Squalene targets pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators and pathways to modulate over-activation of neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages. J Funct Foods 14:779–790
Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V (2017) SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci Rep 7(1):1
Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V (2019) SwissTargetPrediction: updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res 47(W1):W357–W364
Das UN, Rao AA (2007) Gene expression profile in obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lipids Health Dis 6:35. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-511X-6-35
Desbien AL, Reed SJ, Bailor HR, Cauwelaert ND, Laurance JD, Orr MT et al (2015) Squalene emulsion potentiates the adjuvant activity of the TLR4 agonist, GLA, via inflammatory caspases, IL-18, and IFN-γ. Eur J Immunol 45:407–417
Dormont F, Brusini R, Cailleau C, Reynaud F, Reynaud F, Peramo A, Gendron A, Mougin J, Gaudin F, Gaudin F, Varna M, Couvreur P (2020) Squalene-based multidrug nanoparticles for improved mitigation of uncontrolled inflammation in rodents. Sci Adv 6:eaz5466
Emamian ES, Hall D, Birnbaum MJ, Karayiorgou M, Gogos JA (2004) Convergent evidence for impaired AKT1-GSK3beta signaling in schizophrenia. Nat Genet 36(2):131–137. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1296
Falcão HS, Lima IO, Santos VL, Dantas HF, Diniz MF, Barbosa-Filho JM, Batista LM (2005) Review of the plants with anti-inflammatory activity studied in Brazil. Rev Bras Farmacogn 15(4):381–391. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2005000400020
Fang Z, Luo Z, Ji Y, Yang R, Gao J, Zhang N (2022) A network pharmacology technique used to investigate the potential mechanism of Ligustilide’s effect on atherosclerosis. J Food Biochem [Internet] 46(7):e14146. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.14146
Fernando IPS, Sanjeewa KKA, Samarakoon KW, Lee WW, Kim HS, Jeon YJ (2018) Squalene isolated from marine macroalgae Caulerpa racemosa and its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. J Food Biochem 42:e12628
Hari N, Nair VP (2018) FTIR spectroscopic analysis of leaf extract in hexane in Jasminum azoricum L. Int J Sci Res Technol 4:170–172
Heberle H, Meirelles VG, da Silva FR, Telles GP, Minghim R (2015) InteractiVenn: a web-based tool for the analysis of sets through Venn diagrams. BMC Bioinformatics 16(1):1–7
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4(1):44–57
Huang Y, Jin X, Liu J, Wu W, Wang H (2022) Systems pharmacology approach to investigate the mechanism of Artemisia argyi in treating rheumatic diseases. Sci Rep 12(1):1–9. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-23635-6
Ibrahim NI, Mohamed IN (2021) Interdependence of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of Squalene-Implication for Cardiovascular Health. Life 11(2):1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/LIFE11020103
Khan IA, Hussain M, Munawar SH, Iqbal MO, Arshad S, Manzoor A et al (2021) Jasminum sambac: a potential candidate for Drug Development to Cure Cardiovascular ailments. Molecules 26(18):5664. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185664
Kim S-K, Karadeniz F (2012) Marine medicinal foods - implications and applications - animals and microbes. In: Biological importance and applications of squalene and squalane. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 223–233
Kim EH, Woodruff MC, Grigoryan L, Maier B, Lee SH, Mandal P, Cortese M, Natrajan MS, Ravindran R, Ma H, Merad M, Gitlin AD, Mocarski ES, Jacob J, Pulendran B (2020) Squalene emulsion-based vaccine adjuvants stimulate CD8 T cell, but not antibody responses, through a RIPK3-dependent pathway. ELife 9:1–27. https://doi.org/10.7554/ELIFE.52687
Latief M, Muhaimin M, Amanda H, Prahandika G, Lasmana Tarigan I, Kimia J (2020) Anti-inflammatory activities of squalene compound of methanol extract of Abroma Augusta L. Jurnal Teknologi Laboratorium 9(2):176–185. https://doi.org/10.29238/TEKNOLABJOURNAL.V9I2.228
Liang JW, Wang MY, Olounfeh KM, Zhao N, Wang S, Meng FH (2019) Network pharmacology-based identification of potential targets of the flower of Trollius Chinensis Bunge acting on anti-inflammatory effects. Sci Rep 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52717-7
Lin HH, Zhang LLE, Yan R, Lu JJ, Hu Y (2017) Network analysis of drug-target interactions: a study on FDA-approved new molecular entities between 2000 to 2015. Sci Rep 7(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03022-3
Lipinski CA (2004) Lead- and drug-like compounds: the rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discov Today Technol 1(4):337–341
Liu Y, Yang X, Gan J, Chen S, Xiao ZX, Cao Y (2022) CB-Dock2: improved protein–ligand blind docking by integrating cavity detection, docking and homologous template fitting. Nucleic Acids Res 50(W1):W159–W164
Lou-Bonafonte JM, Martínez-Beamonte R, Sanclemente T, Surra JC, Herrera-Marcos LV, Sanchez-Marco J et al (2018) Current insights into the Biological Action of Squalene. Mol Nutr Food Res 62:1800136
Madson JG, Lynch DT, Tinkum KL, Putta SK, Hansen LA (2006) Erbb2 regulates inflammation and proliferation in the skin after Ultraviolet Irradiation. Am J Pathol 169(4):1402–1414. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2006.060332
Martín MC, Oliver J, Luis Mendoza J, Fernández-Arquero M, Martín J, Urcelay E (2008) Influence of mutations of proteinase activated receptors F2R/PAR1 and F2RL1/PAR2 on inflammatory bowel disease. Med Clin (Barc) 131(16):609–611
Martirosyan D, Ashoori MR, Serani A, Zhang K, Mirmiranpour H (2022) Assessment of squalene effect on antioxidant enzymes and free radicals in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Bioact Compd Heal Dis 5:236–250. https://doi.org/10.31989/BCHD.V5I11.1005
Oh KK, Adnan M, Cho DH (2021) Network pharmacology approach to decipher signaling pathways associated with target proteins of NSAIDs against COVID-19. Sci Rep 11(1)
Oh KK, Adnan M, Cho DH (2021a) A network pharmacology analysis on drug-like compounds from Ganoderma lucidum for alleviation of atherosclerosis. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-236410/v1
Pal J, Patil V, Kumar A, Kaur K, Sarkar C, Somasundaram K (2017) Genetic landscape of glioma reveals defective neuroactive ligand receptor interaction pathway as a poor prognosticator in glioblastoma patients. Cancer Res 77(13 Suppl):2454–2454. https://doi.org/10.1158/1538-7445.AM2017-2454
Peng G, Liu Y (2015) Hypoxia-inducible factors in cancer stem cells and inflammation. Trends Pharmacol Sci 36(6):374–383
Peng W, Shen H, Lin B, Han P, Li C, Zhang Q, Ye B, Rahman K, Xin H, Qin L, Han T (2018) Docking study and antiosteoporosis effects of a dibenzylbutane lignan isolated from Litsea cubeba targeting Cathepsin. Med Chem Res K and MEK1(9):2062–2070. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00044-018-2215-8
Piñero J, Bravo Á, Queralt-Rosinach N, Gutiérrez-Sacristán A, Deu-Pons J, Centeno E et al (2017) DisGeNET: a comprehensive platform integrating information on human disease-associated genes and variants. Nucleic Acids Res 45(D1):D833–D839
Piñero J, Saüch J, Sanz F, Furlong LI (2021) The DisGeNET cytoscape app: exploring and visualizing disease genomics data. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 19:2960–2967
Qi Y, Zang R, Lu H, Wang Z, Ma Z (2020) Network pharmacology and bioinformatics approach reveals the hypolipidemic mechanism of Dan Tian Jiang Zhi pill. Med Chem Res 29(2):243–254
Rayego-Mateos S, Rodrigues-Diez R, Morgado-Pascual JL, Valentijn F, Valdivielso JM, Goldschmeding R et al (2018) Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and its ligands in kidney inflammation and damage. Mediators Inflamm 2018:8739473. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8739473
Recio CM, Andujar I, Rios JL (2012) Anti-inflammatory agents from plants: Progress and potential. Curr Med Chem 19(14):2088–2103. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986712800229069
Rehan M, Shafiullah, Mir SA (2020) Structural diversity, natural sources, and pharmacological potential of plant-based saponins with special focus on anticancer activity: a review. Med Chem Res 29:1707–1722
Shaito A, Thuan DTB, Phu HT, Nguyen THD, Hasan H, Halabi S, Abdelhady S, Nasrallah GK, Eid AH, Pintus G (2020) Herbal Medicine for Cardiovascular diseases: Efficacy, mechanisms, and Safety. Front Pharmacol 11:1. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPHAR.2020.00422
Shang Y, Gao L, Zou Q, Yu L (2021) Prediction of drug-target interactions based on multi-layer network representation learning. Neurocomputing 434:80–89
Sherman BT, Hao M, Qiu J, Jiao X, Baseler MW, Lane HC et al (2022) DAVID: a web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021). Nucleic Acids Res 50(W1):W216–W221
Srivastava M, Maurya P, Jyotshna, Shanker K (2021) Clerodendrum Viscosum: a critical review on phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality assurance, and safety data. Med Chem Res 30:2145–2167
Stelzer G, Rosen N, Plaschkes I, Zimmerman S, Twik M, Fishilevich S et al (2016) The GeneCards suite: from Gene Data Mining to Disease Genome sequence analyses. Curr Protoc Bioinf 54(1):1301–13033
Talhouk RS, Karam C, Fostok S, El-Jouni W, Barbour EK (2007) Anti-inflammatory bioactivities in plant extracts. J Med Food 10(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2005.055
Tian S, Wang J, Li Y, Li D, Xu L, Hou T (2015) The application of in silico drug-likeness predictions in pharmaceutical research. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 86:2–10
Tsatsanis C, Androulidaki A, Dermitzaki E, Gravanis A, Margioris AN (2007) Corticotropin releasing factor receptor 1 (CRF1) and CRF2 agonists exert an anti-inflammatory effect during the early phase of inflammation suppressing LPS-induced TNF-α release from macrophages via induction of COX-2 and PGE2. J Cell Physiol 210(3):774–783. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.20915
Von Herrmann KM, Anderson FL, Martinez EM, Young AL, Havrda MC (2020) Slc6a3-dependent expression of a CAPS-associated Nlrp3 allele results in progressive behavioural abnormalities and neuroinflammation in aging mice. J Neuroinflammation 17(1):1–15
Wang J, Li D, Ju W et al (2022a) A Network Pharmacology to explore the potential targets of Canagliflozin and Dapagliflozin in treating atherosclerosis. J Vasc Dis 1(1):53–70. https://www.mdpi.com/2813-2475/1/1/7/htm
Wang J, Li D, Ju W, Wang J, Li D, Ju W, Wang H (2022b) A Network Pharmacology to explore the potential targets of Canagliflozin and Dapagliflozin in treating atherosclerosis. J Vascular Dis 2022 1(1):53–70. https://doi.org/10.3390/JVD1010007
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M, Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O et al (2019) Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat Commun 10(1)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.L. prepared the main manuscript and performed the experiments. N.M. curated the results S.R. Prepared the figures for the manuscript. P.B. wrote and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Luke, S.S., Raj, M., Ramesh, S. et al. Network pharmacology prediction and molecular docking-based strategy to explore the potential mechanism of squalene against inflammation. In Silico Pharmacol. 12, 44 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-024-00217-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-024-00217-0