Abstract
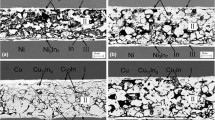
Cu/In-48Sn-xCuZnAl/Cu (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 wt.%) solder joints were prepared by transient liquid phase (TLP) bonding. The microstructure and shear property of the Cu/In-48Sn-xCuZnAl/Cu composite solder joints were investigated. The results show that there were γ-InSn4 phase and β-In3Sn phase in the composite solder joints, and Cu2(In,Sn) phase was obtained in the Cu/In-48Sn-0.6CuZnAl/Cu composite solder joint. CuZnAl particles can refine the microstructure of solder joints, and the average size of the γ-InSn4 phase decreased from 18.3 µm in the Cu/In-48Sn/Cu solder joint to 10.5 µm in the Cu/In-48Sn-0.2CuZnAl/Cu composite solder joint. The thickness of the interfacial intermetallic compound (IMC) layer was decreased with increasing content of CuZnAl particles, and the minimum thickness of the interfacial IMC layer of about 8.1 µm was obtained by the Cu/In-48Sn-0.6CuZnAl/Cu composite solder joint. The shear strength of the Cu/In-48Sn/Cu solder joint is approximately 8.6 MPa, and the maximum shear strength of 16.8 MPa was obtained by adding 0.2 wt.% CuZnAl particle. The fracture of the Cu/In-48Sn-xCuZnAl/Cu solder joints is located in the in situ reaction zone. The failure mode of the Cu/In-48Sn/Cu solder joints is ductile-brittle mixed fracture, and the failure mode of composite solder joints changes to ductile fracture after adding CuZnAl particles.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Kotadia HR, Howes PD, Mannan SH (2014) A review: on the development of low melting temperature Pb-free solders. Microelectron Reliab 54(6–7):1253–1273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2014.02.025
Son M-J, Kim H, Maeng S, Lee T-M, Lee H-J, Kim I (2021) Improvement of electrical and mechanical properties of In-48Sn solder bumps for flexible LED signage using Cu-Ag nanoparticles. Flex Print Electron 6(3):034006. https://doi.org/10.1088/2058-8585/ac264f
Chang F-L, Lin Y-H, Hung H-T, Kao C-W, Kao CR (2023) Artifact-free microstructures in the interfacial reaction between eutectic In-48Sn and Cu using ion milling. Materials (Basel) 16(9):3290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16093290
Choi J-H, Lee K-Y, Jun S-W, Kim Y-H, Oh T-S (2005) Contact resistance of the chip-on-glass bonded 48Sn–52In solder joint. Mater Trans 46:1042–1046. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.46.1042
Liu X, Davis RW, Hughes LC, Rasmussen MH, Bhat R, Zah C-E, Stradling J (2006) A study on the reliability of indium solder die bonding of high power semiconductor lasers. J Appl Phys 100(1):13104. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2209194
Kim D-G, Jung S-B (2005) Interfacial reactions and growth kinetics for intermetallic compound layer between In–48Sn solder and bare Cu substrate. J Alloys Compd 386(1–2):151–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2004.05.055
Mang S-R, Choi H, Lee H-J (2023) Investigation of Sn–Bi–In ternary solders with compositions varying from In–Sn eutectic to 59 °C ternary eutectic point. J Korean Phys Soc 82(11):1105–1113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-023-00788-9
Tsai C-H, Hung H-T, Chang F-L, Bickel S, Müller M, Panchenko I, Bock K, Kao CR (2022) Low-temperature transient liquid phase bonding via electroplated Sn/In–Sn metallization. J Mater Res Technol-JMRT 19:2510–2515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.06.030
Han DL, Shen Y-A, Jin S, Hiroshi N (2020) Microstructure and mechanical properties of the In–48Sn–xAg low-temperature alloy. J Mater Sci 55(24):10824–10832. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04691-7
Han DL, Shen Y-A, He S, Nishikawa H (2021) Effect of Cu addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of In–Sn-based low-temperature alloy. Mater Sci Eng A-Struct 804:140785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.140785
Liu K, Li J, Zhang J, Xiao Y (2022) Effect of Ni foam addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of In–48Sn eutectic alloy. J Mater Sci-Mater El 33(16):12594–12603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08209-6
Sun L, Chen M-h, Zhang L, Xie L-s (2020) Effect of addition of CuZnAl particle on the properties of Sn solder joint. J Mater Process Technol 278:116507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.116507
Xiong M, Zhang L, Sun L, He P, Long W (2019) Effect of CuZnAl particles addition on microstructure of Cu/Sn58Bi/Cu TLP bonding solder joints. Vacuum 167:301–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2019.06.024
Zhang L, Liu Z-q (2020) Inhibition of intermetallic compounds growth at Sn–58Bi/Cu interface bearing CuZnAl memory particles (2–6 μm). J Mater Sci-Mater El 31(3):2466–2480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02784-x
Yang F, Zhang L, Liu ZQ, Zhong SJ, Ma J, Bao L (2017) Effects of CuZnAl particles on properties and microstructure of Sn-58Bi solder. Materials (Basel) 10(5):558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10050558
Zhao M, Zhang L, Liu Z-q, Xiong M-y, Sun L, Jiang N, Xu K-k (2019) Microstructures and properties of SnAgCu lead-free solders bearing CuZnAl particles. J Mater Sci-Mater El 30(16):15054–15063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01878-w
Zhang L, Long W, Wang F (2020) Microstructures, interface reaction, and properties of Sn–Ag–Cu and Sn–Ag–Cu–0.5CuZnAl solders on Fe substrate. J Mater Sci-Mater El 31(9):6645–6653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03220-1
Fayegh A, Aghaie-Khafri M, Binesh B (2021) Interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties of transient liquid phase bonded IN718/Ti-6Al-4V joints. Weld World 65(10):1955–1968. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-021-01134-y
Sun L, Chen M-h, Zhang L (2019) Microstructure evolution and grain orientation of IMC in Cu-Sn TLP bonding solder joints. J Alloys Compd 786:677–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.384
Li JF, Agyakwa PA, Johnson CM (2010) Kinetics of Ag3Sn growth in Ag–Sn–Ag system during transient liquid phase soldering process. Acta Mater 58(9):3429–3443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2010.02.018
Bobzin K, Bagcivan N, Zhao L, Ferrara S, Perne J (2010) Development of new transient liquid phase system Au-Sn-Au for microsystem technology. Front Mech Eng China 5(4):370–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-010-0107-9
Feng H-L, Huang J-H, Yang J, Zhou S-K, Zhang R, Wang Y, Chen S-H (2017) Investigation of microstructural evolution and electrical properties for Ni-Sn transient liquid-phase sintering bonding. Electron Mater Lett. 13(6):489–496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-017-6317-0
Lee J-B, Hwang H-Y, Rhee M-W (2014) Reliability investigation of Cu/In TLP bonding. J Electron Mater 44(1):435–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-014-3373-1
Deng H, Wang K, Duan Y, Zhang W, Hu J (2022) Preparation of In/Sn nanoparticles (In3Sn and InSn4) by wet chemical one-step reduction and performance study. Coatings 12(4):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12040429
Chang MS, Salleh MAAM, Halin DSC, Ramli MII, Yasuda H, Nogita K (2022) The effect of Ni on the growth morphology of primary β-phase in an In-35 wt%Sn alloy. J Alloys Compd 897:163172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.163172
Rodrigues F, Watson J, Liu S, Madeni JC (2017) Study of intermetallic compounds (IMC) that form between indium-enriched SAC solder alloys and copper substrate. Weld World 61(3):603–611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-017-0445-x
Tian F, Li C-F, Zhou M, Liu Z-Q (2018) The interfacial reaction between In-48Sn solder and polycrystalline Cu substrate during solid state aging. J Alloys Compd 740:500–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.12.355
Tian F, Liu Z-Q, Shang P-J, Guo J (2014) Phase identification on the intermetallic compound formed between eutectic SnIn solder and single crystalline Cu substrate. J Alloys Compd 591:351–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.12.257
Tian F, Pang X, Xu B, Liu Z-Q (2020) Evolution and growth mechanism of Cu2 (In, Sn) formed between In-48Sn solder and polycrystalline Cu during long-time liquid-state aging. J Electron Mater 49(4):2651–2659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07909-w
Zhang L, Gao L-l (2015) Interfacial compounds growth of SnAgCu (nano La2O3)/Cu solder joints based on experiments and FEM. J Alloys Compd 635:55–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.02.110
Zhang Y, Liu Z, Yang L, Xiong Y (2022) Microstructure and shear property of Ni-coated carbon nanotubes reinforced InSn-50Ag composite solder joints prepared by transient liquid phase bonding. J Manuf Process 73:177–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.11.001
Zhang Y, Fan Z, Li Y, Zhong J, Pang S, Nagaumi H (2023) Intermediate temperature tensile behavior and processing map of a spray formed 7075 aluminum alloy. J Mater Res Technol-JMRT 26:4534–4550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.08.162
Liu X, Huang M, Wu CML, Wang L (2009) Effect of Y2O3 particles on microstructure formation and shear properties of Sn-58Bi solder. J Mater Sci-Mater El 21(10):1046–1054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-009-0025-y
Kim KS, Huh SH, Suganuma K (2003) Effects of intermetallic compounds on properties of Sn–Ag–Cu lead-free soldered joints. J Alloys Compd 352(1–2):226–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0925-8388(02)01166-0
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52165068) and the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation Project (2020GXNSFAA297004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Recommended for publication by Commission XVII - Brazing, Soldering and Diffusion Bonding
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Wu, H., Zhang, Y. et al. Effect of CuZnAl particle addition on the microstructure and shear property of Cu/In-48Sn/Cu solder joints by transient liquid phase bonding. Weld World 68, 61–69 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-023-01621-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-023-01621-4