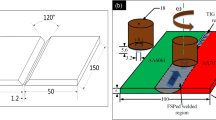
Abstract
In this paper, the effects of the deposition speed and thermal cycles in gas-metal arc-welding (GMAW) additive manufacturing on the quality of as-built 308L stainless steel thin walls were investigated. The results exhibit that the deposition speed and thermal cycles play a crucial role in the quality of produced parts. An increase in deposition speed results in an improvement in the surface waviness. The surface waviness (Sa) decreases from 286 to 138 µm as the deposition speed increases from 0.2 to 0.4 m/min. On the other hand, the growth of microstructures in the walls fabricated with different deposition speeds shows a similar trend. The microstructure of as-built 308L-stainless-steel walls consists of dominant columnar/equiaxed dendrites of austenite and small amount of ferrite remaining in grain boundaries. The deposition speed mainly influences the grain size in microstructures. In the middle part of the walls, an augmentation in the deposition speed leads to a decrease in the secondary dendrite arm spacing, which results in an enhancement in mechanical properties of the walls. The microhardness and ultimate tensile strength increase from 153 ± 7.16 to 164 ± 8.96 HV0.1 and from 483 ± 4.24 to 518 ± 2.83 MPa, respectively, when the deposition speed increases from 0.2 to 0.4 m/min.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Ashima R, Haleem A, Bahl S, Javaid M, Kumar Mahla S, Singh S (2021) Automation and manufacturing of smart materials in additive manufacturing technologies using Internet of Things towards the adoption of industry 4.0. Mater Today Proc 45:5081–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.01.583
Oliveira JP, LaLonde AD, Ma J (2020) Processing parameters in laser powder bed fusion metal additive manufacturing. Mater Des 193:108762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108762
Huang R, Riddle M, Graziano D, Warren J, Das S, Nimbalkar S et al (2016) Energy and emissions saving potential of additive manufacturing: the case of lightweight aircraft components. J Clean Prod 135:1559–1570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.04.109
Huang S, Liu P, Mokasdar A, Hou L (2013) Additive manufacturing and its societal impact: a literature review. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 67:1191–1203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4558-5
Herzog D, Seyda V, Wycisk E, Emmelmann C (2016) Additive manufacturing of metals. Acta Mater 117:371–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.07.019
Wippermann A, Gutowski TG, Denkena B, Dittrich M-A, Wessarges Y (2020) Electrical energy and material efficiency analysis of machining, additive and hybrid manufacturing. J Clean Prod 251:119731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119731
Lopes JG, Machado CM, Duarte VR, Rodrigues TA, Santos TG, Oliveira JP (2020) Effect of milling parameters on HSLA steel parts produced by wire and arc additive manufacturing (WAAM). J Manuf Process 59:739–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.10.007
Rodrigues TA, Bairrão N, Farias FWC, Shamsolhodaei A, Shen J, Zhou N et al (2022) Steel-copper functionally graded material produced by twin-wire and arc additive manufacturing (T-WAAM). Mater Des 213:110270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.110270
Queguineur A, Rückert G, Cortial F, Hascoët JY (2018) Evaluation of wire arc additive manufacturing for large-sized components in naval applications. Weld World 62:259–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-017-0536-8
Jafari D, Vaneker THJ, Gibson I (2021) Wire and arc additive manufacturing: opportunities and challenges to control the quality and accuracy of manufactured parts. Mater Des 202:109471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.109471
Liu J, Xu Y, Ge Y, Hou Z, Chen S (2020) Wire and arc additive manufacturing of metal components: a review of recent research developments. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 111:149–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05966-8
Ramalho A, Santos TG, Bevans B, Smoqi Z, Rao P, Oliveira JP (2022) Effect of contaminations on the acoustic emissions during wire and arc additive manufacturing of 316L stainless steel. Addit Manuf 51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2021.102585
Rodrigues TA, Escobar JD, Shen J, Duarte VR, Ribamar GG, Avila JA et al (2021) Effect of heat treatments on 316 stainless steel parts fabricated by wire and arc additive manufacturing: microstructure and synchrotron X-ray diffraction analysis. Addit Manuf 48:102428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2021.102428
Dinovitzer M, Chen X, Laliberte J, Huang X, Frei H (2019) Effect of wire and arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) process parameters on bead geometry and microstructure. Addit Manuf 26:138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.12.013
Xiong J, Li Y, Li R, Yin Z (2018) Influences of process parameters on surface roughness of multi-layer single-pass thin-walled parts in GMAW-based additive manufacturing. J Mater Process Technol 252:128–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.09.020
Rodrigues TA, Duarte V, Avila JA, Santos TG, Miranda RM, Oliveira JP (2019) Wire and arc additive manufacturing of HSLA steel: effect of thermal cycles on microstructure and mechanical properties. Addit Manuf 27:440–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.03.029
Liberini M, Astarita A, Campatelli G, Scippa A, Montevecchi F, Venturini G et al (2017) Selection of optimal process parameters for wire arc additive manufacturing. Procedia CIRP 62:470–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.06.124
Wen D, Long P, Li J, Huang L, Zheng Z (2020) Effects of linear heat input on microstructure and corrosion behavior of an austenitic stainless steel processed by wire arc additive manufacturing. Vacuum 173:109131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2019.109131
Su C, Chen X, Gao C, Wang Y (2019) Effect of heat input on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Mg alloys fabricated by WAAM. Appl Surf Sci 486:431–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.04.255
Zhou Y, Lin X, Kang N, Huang W, Wang J, Wang Z (2020) Influence of travel speed on microstructure and mechanical properties of wire + arc additively manufactured 2219 aluminum alloy. J Mater Sci Technol 37:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2019.06.016
Tawfik MM, Nemat-Alla MM, Dewidar MM (2021) Effect of travel speed on the properties of Al-Mg aluminum alloy fabricated by wire arc additive manufacturing. J Mater Eng Perform 30:7762–7769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05959-y
Le VT, Mai DS, Paris H (2021) Influences of the compressed dry air-based active cooling on external and internal qualities of wire-arc additive manufactured thin-walled SS308L components. J Manuf Process 62:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.11.046
Takagi H, Sasahara H, Abe T, Sannomiya H, Nishiyama S, Ohta S et al (2018) Material-property evaluation of magnesium alloys fabricated using wire-and-arc-based additive manufacturing. Addit Manuf 24:498–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.10.026
Haselhuhn AS, Buhr MW, Wijnen B, Sanders PG, Pearce JM (2016) Structure-property relationships of common aluminum weld alloys utilized as feedstock for GMAW-based 3-D metal printing. Mater Sci Eng A 673:511–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.07.099
Alali M, Todd I, Wynne BP (2017) Through-thickness microstructure and mechanical properties of electron beam welded 20 mm thick AISI 316L austenitic stainless steel. Mater Des 130:488–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.05.080
ASTM E8/E8M-13 (2013) Standard test methods for tension testing of metallic materials, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA . n.d. https://doi.org/10.1520/E0008_E0008M-13
Goldak J, Chakravarti A, Bibby M (1984) A new finite element model for welding heat sources. Metall Trans B 15:299–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02667333
Ke WC, Oliveira JP, Cong BQ, Ao SS, Qi ZW, Peng B et al (2022) Multi-layer deposition mechanism in ultra high-frequency pulsed wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) of NiTi shape memory alloys. Addit Manuf 50:102513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2021.102513
Huang J, Guan Z, Yu S, Yu X, Yuan W, Li N et al (2020) A 3D dynamic analysis of different depositing processes used in wire arc additive manufacturing. Mater Today Commun 24:101255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101255
Zhao H, Zhang G, Yin Z, Wu L (2011) A 3D dynamic analysis of thermal behavior during single-pass multi-layer weld-based rapid prototyping. J Mater Process Technol 211:488–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.11.002
Lee SH (2020) CMT-based wire arc additive manufacturing using 316L stainless steel: effect of heat accumulation on the multi-layer deposits. Metals (Basel) 10:278. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020278
Le VT, Mai DS, Hoang QH (2020) A study on wire and arc additive manufacturing of low-carbon steel components: process stability, microstructural and mechanical properties. J Brazilian Soc Mech Sci Eng 42:480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02567-0
Xiong J, Yin Z, Zhang W (2016) Forming appearance control of arc striking and extinguishing area in multi-layer single-pass GMAW-based additive manufacturing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87:579–586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8543-2
Yang D, He C, Zhang G (2016) Forming characteristics of thin-wall steel parts by double electrode GMAW based additive manufacturing. J Mater Process Technol 227:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.08.021
Xiong J, Zhang G (2014) Adaptive control of deposited height in GMAW-based layer additive manufacturing. J Mater Process Technol 214:962–968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2013.11.014
Zhang Z, Li Z, He Y, Song G, Liu L (2021) The effect of low-power laser on micro-forming of 316 stainless steel additive manufacturing part. J Manuf Process 68:583–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.05.060
Rodrigues TA, Duarte VR, Tomás D, Avila JA, Escobar JD, Rossinyol E et al (2020) In-situ strengthening of a high strength low alloy steel during wire and arc additive manufacturing (WAAM). Addit Manuf 34:101200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101200
Yang D, Wang G, Zhang G (2017) Thermal analysis for single-pass multi-layer GMAW based additive manufacturing using infrared thermography. J Mater Process Technol 244:215–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.01.024
Xiong J, Zhang G, Zhang W (2015) Forming appearance analysis in multi-layer single-pass GMAW-based additive manufacturing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 80:1767–1776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7112-4
Geng H, Li J, Xiong J, Lin X (2017) Optimisation of interpass temperature and heat input for wire and arc additive manufacturing 5A06 aluminium alloy. Sci Technol Weld Join 22:472–483. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2016.1259031
Lippold JC, Kotecki DJ (2005) Welding metallurgy and weldability of stainless steels. John Wiley and Sons Inc
Kou S (2003) Welding metallurgy. Second Edi. John Wiley & Sons Inc, Hoboken, New Jersey
Li K, Li D, Liu D, Pei G, Sun L (2015) Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of multiple-layer laser cladding coating of 308L stainless steel. Appl Surf Sci 340:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.02.171
Li W, Sugio K, Liu X, Yamamoto M, Guo Y, Zhu S et al (2021) Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of 308L stainless steel coatings fabricated by laser hot wire cladding. Mater Sci Eng A 824:141825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.141825
Wu W, Xue J, Zhang Z, Yao P (2019) Comparative study of 316L depositions by two welding current processes. Mater Manuf Process 34:1502–1508. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2019.1643473
Pramod R, Mohan Kumar S, Rajesh Kannan A, Siva Shanmugam N, Tangestani R (2021) Fabrication of gas metal arc welding based wire plus arc additive manufactured 347 stainless steel structure: behavioral analysis through experimentation and finite element method. Met Mater Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-021-01026-2
Yi HJ, Kim JW, Kim YL, Shin S (2020) Effects of cooling rate on the microstructure and tensile properties of wire-arc additive manufactured Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Met Mater Int 26:1235–1246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00563-1
Wang L, Xue J, Wang Q (2019) Correlation between arc mode, microstructure, and mechanical properties during wire arc additive manufacturing of 316L stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng A 751:183–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.02.078
Su C, Chen X, Konovalov S, Arvind Singh R, Jayalakshmi S, Huang L (2021) Effect of deposition strategies on the microstructure and tensile properties of wire arc additive manufactured Al-5Si alloys. J Mater Eng Perform. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05528-3
Zuback JS, DebRoy T (2018) The hardness of additively manufactured alloys. Materials (Basel) 11:2070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112070
Li SX, Cui GR (2007) Dependence of strength, elongation, and toughness on grain size in metallic structural materials. J Appl Phys 101:083525. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2720184
Naghizadeh M, Mirzadeh H (2019) Effects of grain size on mechanical properties and work-hardening behavior of AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel. Steel Res Int 90:1900153. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201900153
Singh KK, Sangal S, Murty GS (2002) Hall-Petch behaviour of 316L austenitic stainless steel at room temperature. Mater Sci Technol 18:165–172. https://doi.org/10.1179/026708301125000384
Li M, Lu T, Dai J, Jia X, Gu X, Dai T (2020) Microstructure and mechanical properties of 308L stainless steel fabricated by laminar plasma additive manufacturing. Mater Sci Eng A 770:138523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138523
Zhang K, Wang S, Liu W, Shang X (2014) Characterization of stainless steel parts by laser metal deposition shaping. Mater Des 55:104–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.09.006
Wu W, Xue J, Wang L, Zhang Z, Hu Y, Dong C (2019) Forming process, microstructure, and mechanical properties of thin-walled 316L stainless steel using speed-cold-welding additive manufacturing. Metals (Basel) 9:109. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9010109
Funding
This research is funded by the Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 107.99–2019.18.
The authors would like also to thank great support from Le Quy Don Technical University for our projects (grant number 107.99–2019.18 and 20.1.118).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Van Thao Le: conceptualization, methodology, data analysis, writing — original draft preparation, reviewing and editing; Dinh Si Mai, Duc Manh Dinh, Van Anh Nguyen: validation, investigation; Manh Cuong Bui, Duc Manh Dinh, Van Canh Nguyen: formal analysis, software, data curation; Kilian Wasmer, Van Anh Nguyen, Duong Vu: reviewing, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Recommended for publication by Commission I—Additive Manufacturing, Surfacing, and Thermal Cutting.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le, V.T., Mai, D.S., Bui, M.C. et al. Influences of the process parameter and thermal cycles on the quality of 308L stainless steel walls produced by additive manufacturing utilizing an arc welding source. Weld World 66, 1565–1580 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-022-01330-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-022-01330-4