Abstract
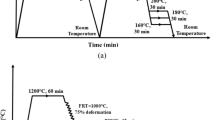
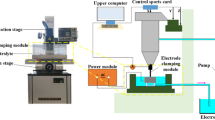
Intergranular penetration (IGP) of liquid filler metal (FM) into oxygen-free copper (OFC) occurred when OFC and Ni-plated materials were brazed with AgCu28 filler. In order to analyze the mechanism of IGP, nine different joints were brazed, and the diffusion behavior of Ni and Ag and the concentration distribution of Ni in liquid were studied. Results show that IGP occurs only when Ni element exists in the joints. In the brazing process, Ni element tends to diffuse from the liquid region with low Cu content to the liquid region with high Cu content, and then to solid. Therefore, the concentration distribution of Ni in liquid is uneven. Ni is enriched at the solid–liquid interface. After adding Ni in the joints, a saturated Cu solid solution layer is easy to form on the surface of base metal (BM), which hinders the interdiffusion between solid and liquid. But, a large number of Ni atoms in liquid are unstable due to the high chemical potential, and Ag concentration in liquid is still higher than the equilibrium concentration. Grain boundaries (GBs) become the channel for rapid diffusion of Ni and Ag atoms in liquid into BM. In addition, the saturated solubility of Ag in Cu solid solution decreases after adding Ni in the joints, making GBs easier to be liquefied. IGP further increases the area of solid–liquid interface.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar L, Limaye K (2003) Review of progress in indigenous design, development & production of microwave vacuum-electronic devices. IETE Tech Rev 20:75–93
Gamzina D, Kozina M, Mehta A, Nanni EA, Tantawi S, Welander PB, Horn T, Ledford C (2019) Copper reconsidered: material innovations to transform vacuum electronics. International Vacuum Electronics Conference (IVEC);
Wu M, He XB, Rafi UD, Ren SB, Qin ML, Qu XH (2009) Effect of various Ni plating layers and aging on microstructure and shear strength of Sn-2.5Ag-2.0Ni solder joint. Surf Coating Technol 203:3011–3018
Lu JB, Mu YC, Luo XW, Niu JT (2012) A new method for soldering particle-reinforced aluminum metal matrix composites. Mater Sci Eng B 177:1759–1763
Clarke DR, Gee ML (1992) Wetting of surfaces and grain boundaries. Materials interfaces (UK). ed. D. Wolf and S. Yip. Chapman & Hall, London 255–272.
Rappaz M, Jacot A, Boettinger WJ (2003) Last-stage solidification of alloys: theoretical model of dendrite-arm and grain coalescence. Metall Mater Trans A 34:467–479
Takashima M, Wynblatt P, Adams BL (2000) Correlation of grain boundary character with wetting behavior. Interface Sci 8:351–361
Favez D, Deillon L, Wagniere J-D, Rappaz M (2011) Intergranular penetration of liquid gold into stainless steel. Acta Mater 59:6530–6537
Asl KM, Luo J (2012) Impurity effects on the intergranular liquid bismuth penetration in polycrystalline nickel. Acta Mater 60:149–165
Fernandes PJL, Jones DRH (1997) Mechanisms of liquid metal induced embrittlement. Int Mater Rev 42:251–261
Joseph B, Picat M, Barbier F (1999) Liquid metal embrittlement: a state-of-the-art appraisal. EPJ Appl Phys 5:19–31
Pereiro-Lopez E, Ludwig W, Bellet D (2004) Discontinuous penetration of liquid Ga into grain boundaries of Al polycrystals. Acta Mater 52:321–332
Wolski K, Laporte V, Marie N (2001) About the importance of nanometer-thick intergranular penetration in the analysis of liquid metal embrittlement. Interf Sci 9:183–189
Fradkov VE (1994) Rapid liquid-metal corrosion along grain-boundaries. Scr Mater 30:1599–1603
Desre PJ (1997) A mechanism for the stress independent grain boundary penetration of a metal by a liquid metal. Application to the metallic couple Al-Ga. Scr Mater 37:875–881
Glickman EE (2003) Grain boundary grooving accelerated by local plasticity as a possible mechanism of liquid metal embrittlement. Interf Sci 11:451–459
Vilenkin A (2003) Grain boundary segregation and grain boundary wetting, diffusion, segregation and stresses in materials. Defect and Diffusion Forum 216:189–195
Mullins WW (1957) Theory of thermal grooving. J Appl Phys 28:333–339
Mullins WW (1960) Grain boundary grooving by volume. Trans Metal Soc AIMS 218:354–361
Klinger L, Rabkin E (2010) Strains and stresses caused by penetrative wetting of grain boundaries by the liquid phase. Script Mater 62:918–923
Klinger L, Rabkin E (2011) Theory of the Kirkendall effect during grain boundary interdiffusion. Acta Mater 59:1389–1399
Joseph B, Barbier F, Aucouturier M (2000) Mechanism of liquid Bi penetration along Cu grain boundaries. Scripta mater 42:1151–1158
Apykhtina I, Bokstein B, Gulevskii S, Kozlova O, Peteline A, Rakov S, Rodine A (2005) Model for grain boundary diffusion controlled growth of deep liquid channels. Defect Diff Forum 237:677–682
Wolski K, Laporte V (2008) Grain boundary diffusion and wetting in the analysis of intergranular penetration. Mater Sci Eng A 495:138–146
Joseph B, Barbier F, Aucouturier M (1999) Engraving and penetration of copper grain boundaries using liquid bismuth. J Phys IV 9:235–240
Joseph B, Barbier F, Aucouturier M (1999) Embrittlement of copper by liquid bismuth. Scripta Mater 40:893–897
Joseph B, Barbier F, Aucouturier M (1999) Grain boundary penetration of liquid Bi in Cu polycrystals. Intergranular and interphase boundaries in materials, IIB98 294:735–738.
Joseph B, Barbier F, Dagoury G, Aucouturier M (1998) Rapid penetration of liquid Bi along Cu grain boundaries. Scripta Mater 39:775–781
Murugan SP, Jeon JB, Ji C, Park Y-D (2020) Liquid zinc penetration induced intergranular brittle cracking in resistance spot welding of galvannealed advanced high strength steel. Weld World 64:1957–1969
Wintjes E, DiGiovanni C, He L, Biro E, Zhou NY (2019) Quantifying the link between crack distribution and resistance spot weld strength reduction in liquid metal embrittlement susceptible steels. Weld World 63:807–814
Murugan SP, Mahmud K, Ji C, Jo I, Park YD (2019) Critical design parameters of the electrode for liquid metal embrittlement cracking in resistance spot welding. Weld World 63:1613–1632
Savage WF, Nippes EP, Mushala MC (1978) Copper contamination cracking in the weld heat-affected zone. Weld J 57:145s–152s
Asnis EA, Prokhorenko VM (1965) Mechanism of cracking during the welding or depositing of copper onto steel. Svar Proizvod 11:8–9
Savage WF, Nippes EF, Stanton RP (1978) Intergranular attack of steel by molten copper. Weld. J 9s-16s.
Bozhko AM (1968) Mechanism by which molten copper penetrates into steel. Art Svaka 6:23–25
Wang G, Sheng G, Yu Q, Sun J, Li R, Yuan X, Zhang Y (2021) Investigation on regulating inter-granular penetration in CoCrMnFeNi high-entropy alloy and 304 stainless steel dissimilar joints. Mater Sci Eng A 800:140291
Wang G, Sheng G, Yu Q, Yuan X, Sun J, Jiao Y, Zhang Y (2020) Investigation of intergranular penetration behavior in CrMnFeCoNi HEA/304 SS dissimilar brazing joints. Intermetallics 126:106940
Wang G, Sheng G, Sun J, Wei Y, Gao X, Yu Z, Yuan X (2020) Mechanical properties and microstructure evolution of CrMnFeCoNi HEA/304 SS dissimilar joints. J. Alloy. Comp 829:154520
Tomlinson WJ, Matthews SJ (1988) Intergranular corrosion of welds in type 405 stainless steel. J Mater Sci 23:2064–2068
Ludwig W, Pereiro-Lopez E, Bellet D (2005) In situ investigation of liquid Ga penetration in Al bicrystal grain boundaries: grain boundary wetting or liquid metal embrittlement? Acta Mater 53:151–162
Straumal BB, Kogtenkova O, Zieba P (2008) Wetting transition of grain-boundary triple junctions. Acta Mater 56:925–933
Rabkin E (1998) Coherency strain energy as a driving force for liquid grooving at grain boundaries. Script Mater 39:685–690
Glickman EE, Nathan M (1999) On the kinetic mechanism of grain boundary wetting in metals. J Appl Phys 85:3185–3191
Bokstein BS, Klinger LM, Apikhtina IV (1995) Liquid grooving at grain boundaries. Mater Sci Eng A 203:373–376
Redlich O, Kister A (1948) Algebraic representation of thermodynamic properties and the classification of solutions. Ind Eng Chem 40:349–354
Liu XJ, Gao F, Wang CP, Ishida K (2008) Thermodynamic assessments of the Ag-Ni binary and Ag-Cu-Ni ternary systems. J Electr Mater 37:210–217
Chen SW (1993) Interfacial reactions in the liquid (Ag, Cu)/Ni diffusion couples. Mater Chem Phys 33:271–276
Luo HT, Chen SW (1996) Phase equilibria of the ternary Ag-Cu-Ni system and the interfacial reactions in the Ag-Cu/Ni couples. J Mater Sci 31:5059–5067
Chatain D, Rabkin E, Derenne J, Bernardini J (2001) Role of the solid/liquid interface faceting in rapid penetration of a liquid phase along grain boundaries. Acta Mater 49:1123–1128
Acknowledgements
The authors of this paper sincerely thank the teachers of the testing center of the School of Materials Science and Engineering in Beihang University for their help.
Funding
This work was supported by key special projects of the national key R&D program (Grant No. 2017YFB0305700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, G., Zhang, Y., Qu, W. et al. Mechanism of intergranular penetration of liquid filler metal into oxygen-free copper. Weld World 66, 1447–1460 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-022-01278-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-022-01278-5