Abstract
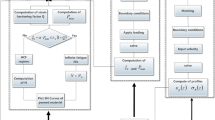
We describe a computationally efficient approach for predicting residual stresses induced by the shot peening process on welded specimens with simple geometry. Using this approach, we are able to simulate impact between tens of thousands of rigid shots and a deformable workpiece, which to the best of our knowledge goes significantly beyond the work reported so far in previous simulation efforts by others. Simulations of Almen strip peening show very good correlation with prior experimental and analytical works, validating the soundness of our numerical approach. Furthermore, we show that using this approach, it is relatively straightforward to incorporate pre-existing residual stresses from welding, and using a numerical approach rooted in fracture mechanics, we make the ultimate connection between residual stresses and the growth life of fatigue cracks in these specimens. We conclude our paper by contrasting model predictions with experimentally observed fatigue data.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almen JO (1943) Peened surfaces improve endurance of machine parts. Metal Prog 43(2):209–315
Brust FW, Dong P, and Zhang J (1997) A constitutive model for weld process modeling using finite element methods. Advances in Computational Science and Engineering, Eds. SN Atluri and G Yagawa, pp. 51–56
Deslaef D, Rouhaud E, Rasouli-Yazdi S (2000) 3D Finite element models of shot peening processes. Mat Sci Forum 347:241–246
Goldak J, Chakravarti A, Bibby M (1984) A new finite element model for welding heat sources. Metall Trans B 15(2):299–305
Guagliano M (2001) Relating Almen intensity to residual stresses induced by shot peening: a numerical approach. J Mat Process Tech 110:277–286
Kirk D (2006) Saturation curve analysis and quality control. The Shot Peener 20(3):24–30
Levers A, Prior A (1998) Finite element simulation of shot peening. J Mater Process Tech 80–81:304–308
Marsh KJ (ed) (1993) Shot peening: techniques and applications. Engineering Materials Advisory Services Ltd., London
Meguid SA, Shagal G, Stranart JC, Daly J (1999) Three-dimensional dynamic finite element analysis of shot-peening induced residual stresses. Finite Elem Anal Des 31:179–191
Meo M, Vignjevic R (2003) Finite element analysis of residual stress induced by shot peening process. Adv Engg Software 34(9):569–575
Miao HY, Larose S, Perron C, Levesque M (2009) On the potential applications of a 3D random finite element model for the simulation of shot peening. Adv Engg Software 40:1023–1028
Wohlfahrt W (1982) Residual stress and stress relaxation. Sagamore Army Mat Res Conf 28:71–92, Editor: Kula E, Weiss V, Plenum Press
Zimmerli FP (1940) How shot blasting increases fatigue life. Machine Design 12:62
Zinn W, Schulz J, Kopp R and Scholtes B (2002) The influence of the velocity of peening medium on the Almen intensities and residual stress states of shot peened specimens. Proc 8th Int Conf. on Shot Peening (ICSP8)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Doc. IIW-2383, recommended for publication by Commission XIII “Fatigue of Welded Components and Structures.”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Athreya, B.P., Singh, N.P., Pan, L. et al. A computational approach for fatigue life prediction in shot peened welded specimens. Weld World 57, 675–684 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-013-0065-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-013-0065-z