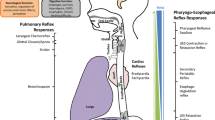
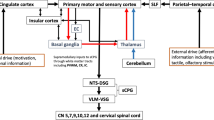
Abstract
Purpose of Review
This review article analyzes current evidence on the neurophysiology of swallowing during development and offers expert opinion on clinical implications and future research directions.
Recent Findings
In the past 5 years, basic and clinical research has offered advances in our understanding of pediatric swallowing neurophysiology. Animal models have elucidated the role of brainstem circuits and the peripheral and central nervous systems in neonatal swallowing. Recent human studies have further showcased that fetal and infant swallowing require cerebral inputs in order to develop functionally. Finally, neurophysiological and neuroimaging studies are starting to better define these cerebral inputs, as well as neuroplastic adaptations that may be needed for optimal feeding development.
Summary
The neural development of swallowing is a complex and dynamic process. Continued research is needed to better understand influences on swallowing neural development, which can be essential for improving prevention, diagnosis, and interventions for pediatric dysphagia.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Amri M, Car A, Jean A. Medullary control of the pontine swallowing neurones in sheep. Exp Brain Res. 1984;55(1):105–10.
Car A, Roman C. Deglutitions and oesophageal reflex contractions induced by electrical stimulation of the medulla oblongata. Exp Brain Res. 1969;11(1):75–92.
Doty RW. Influence of stimulus pattern on reflex deglutition. Am J Physiol. 1951;166(1):142–58.
Jean A, Car A, Roman C. Comparison of activity in pontine versus medullary neurones during swallowing. Exp Brain Res. 1975;22(2):211–20.
Martin RE, Kemppainen P, Masuda Y, Yao D, Murray GM, Sessle BJ. Features of cortically evoked swallowing in the awake primate (Macaca fascicularis). J Neurophysiol. 1999;82(3):1529–41.
Sumi T. Reticular ascending activation of frontal cortical neurons in rabbits, with special reference to the regulation of deglutition. Brain Res. 1972;13(46):43–54.
Daniels SK, Foundas AL. Lesion localization in acute stroke patients with risk of aspiration. J Neuroimaging. 1999;9(2):91–8.
Daniels SK, Pathak S, Mukhi SV, Stach CB, Morgan RO, Anderson JA. The relationship between lesion localization and dysphagia in acute stroke. Dysphagia. 2017;32(6):777–84.
Gordon C, Hewer RL, Wade DT. Dysphagia in acute stroke. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1987;295(6595):411–4.
Martin RE, Sessle BJ. The role of the cerebral cortex in swallowing. Dysphagia. 1993;8(3):195–202.
Meadows JC. Dysphagia in unilateral cerebral lesions. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973;36(5):853–60.
Robbins J, Levine RL, Maser A, Rosenbek JC, Kempster GB. Swallowing after unilateral stroke of the cerebral cortex. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1993;74(12):1295–300.
Hamdy S, Rothwell JC, Brooks DJ, Bailey D, Aziz Q, Thompson DG. Identification of the cerebral loci processing human swallowing with H2 15O PET activation. J Neurophysiol. 1999;81(4):1917–26.
Malandraki GA, Sutton BP, Perlman AL, Karampinos DC, Conway C. Neural activation of swallowing and swallowing-related tasks in healthy young adults: an attempt to separate the components of deglutition. Hum Brain Mapp. 2009;30(10):3209–26.
Malandraki GA, Johnson S, Robbins J. Functional MRI of swallowing: from neurophysiology to neuroplasticity. Head Neck. 2011;33(S1):S14-20.
Martin RE, Goodyear BG, Gati JS, Menon RS. Cerebral cortical representation of automatic and volitional swallowing in humans. J Neurophysiol. 2001;85(2):938–50.
Martin RE, MacIntosh BJ, Smith RC, Barr AM, Stevens TK, Gati JS, et al. Cerebral areas processing swallowing and tongue movement are overlapping but distinct: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Neurophysiol. 2004;92(4):2428–43.
Suzuki M, Asada Y, Ito J, Hayashi K, Inoue H, Kitano H. Activation of cerebellum and basal ganglia on volitional swallowing detected by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Dysphagia. 2003;18(2):71–7.
Toogood JA, Barr AM, Stevens TK, Gati JS, Menon RS, Martin RE. Discrete functional contributions of cerebral cortical foci in voluntary swallowing: a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) “Go, No-Go” study. Exp Brain Res. 2005;161(1):81–90.
Carnaby GD, LaGorio L, Silliman S, Crary M. Exercise-based swallowing intervention (McNeill Dysphagia Therapy) with adjunctive NMES to treat dysphagia post-stroke: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. J Oral Rehabil. 2020;47(4):501–10.
Huckabee M-L, Lamvik-Gozdzikowska K. Reconsidering rehabilitation for neurogenic dysphagia: strengthening skill in swallowing. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep. 2018;6(3):186–91.
Malandraki GA, Rajappa A, Kantarcigil C, Wagner E, Ivey C, Youse K. The intensive dysphagia rehabilitation approach applied to patients with neurogenic dysphagia: a case series design study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;97(4):567–74.
Zimmerman E, Carnaby G, Lazarus Cathy L, Malandraki Georgia A. Motor learning, neuroplasticity, and strength and skill training: moving Ffom compensation to retraining in behavioral management of dysphagia. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2020;29(2S):1065–77.
Bhattacharyya N. The prevalence of pediatric voice and swallowing problems in the United States. Laryngoscope. 2015;125(3):746–50.
Borowitz KC, Borowitz SM. Feeding problems in infants and children. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2018;65(1):59–72.
Kovacic K, Rein LE, Szabo A, Kommareddy S, Bhagavatula P, Goday PS. Pediatric feeding disorder: a nationwide prevalence study. J Pediatr. 2021;1(228):126-131.e3.
Linscheid TR. Behavioral treatments for pediatric feeding disorders. Behav Modif. 2006;30(1):6–23.
Lefton-Greif MA, Arvedson JC. Pediatric feeding and swallowing disorders: state of health, population trends, and application of the international classification of functioning, Disability, and Health. Semin Speech Lang. 2007;28(3):161–5.
Lefton-Greif MA, Arvedson JC. Pediatric feeding/swallowing: yesterday, today, and tomorrow. Semin Speech Lang. 2016;37(4):298–309.
Delaney AL, Arvedson JC. Development of swallowing and feeding: prenatal through first year of life. Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2008;14(2):105–17.
Miller JL, Sonies BC, Macedonia C. Emergence of oropharyngeal, laryngeal and swallowing activity in the developing fetal upper aerodigestive tract: an ultrasound evaluation. Early Human Dev. 2003;71(1):61–87.
•• Maynard TM, Zohn IE, Moody SA, LaMantia A-S. Suckling, feeding, and swallowing: behaviors, circuits, and targets for neurodevelopmental pathology. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2020 8;43(1):315–36. This clinical review paper laid out a developmental program of feeding development and described an animal model of developmental pediatric dysphagia.
Ross MG, Nijland MJM. Fetal swallowing: relation to amniotic fluid regulation. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1997;40(2):352–65.
de Vries JI, Visser GH, Prechtl HF. The emergence of fetal behaviour. II Quantitative aspects Early Hum Dev. 1985;12(2):99–120.
Carruth BR, Ziegler PJ, Gordon A, Hendricks K. Developmental milestones and self-feeding behaviors in infants and toddlers. J Am Diet Assoc. 2004;1(104):51–6.
Hennessey NW, Fisher G, Ciccone N. Developmental changes in pharyngeal swallowing acoustics: a comparison of adults and children. Logoped Phoniatr Vocol. 2018;43(2):63–72.
Hahn Arkenberg R, Mitchell S, Brown B, Goffman L, Malandraki GA. The neuromuscular development of swallowing continues into the school-age years: evidence from a preliminary cross-sectional study. Dysphagia Research Society Meeting. In Virtual; 2021.
Thelen E. Dynamic systems theory and the complexity of change. Psychoanalytic Dialogues. 2005;15(2):255–83.
Haddad JM, Claxton LJ, Keen R, Berthier NE, Riccio GE, Hamill J, et al. Development of the coordination between posture and manual control. J Exp Child Psychol. 2012;111(2):286–98.
Jean A. Brainstem organization of the swallowing network. BBE. 1984;25(2–3):109–16.
Jean A. Brain stem control of swallowing: neuronal network and cellular mechanisms. Physiol Rev. 2001;81(2):929–69.
Miller AJ. The search for the central swallowing pathway: the quest for clarity. Dysphagia. 1993;8(3):185–94.
Miller AJ. The neurobiology of swallowing and dysphagia. Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2008;14(2):77–86.
Pitts T, Huff A, Reed M, Iceman K, Mellen N. Evidence of intermediate reticular formation involvement in swallow pattern generation, recorded optically in the neonate rat sagittally sectioned hindbrain. J Neurophysiol. 2021;125(4):993–1005.
Gould FD, Lammers AR, Mayerl CJ, German RZ. Specific vagus nerve lesion have distinctive physiologic mechanisms of dysphagia. Front Neurol. 2019;10:1301.
Gould FDH, Lammers AR, Mayerl C, Ohlemacher J, German RZ. Muscle activity and kinematics show different responses to recurrent laryngeal nerve lesion in mammal swallowing. J Neurophysiol. 2020;124(6):1743–53.
Gould FDH, Yglesias B, Ohlemacher J, German RZ. Pre-pharyngeal swallow effects of recurrent laryngeal nerve lesion on bolus shape and airway protection in an infant pig Model. Dysphagia. 2017;32(3):362–73.
Ding P, Campbell-Malone R, Holman SD, Lukasik SL, Fukuhara T, Gierbolini-Norat EM, et al. Unilateral superior laryngeal nerve lesion in an animal model of dysphagia and its effect on sucking and swallowing. Dysphagia. 2013;28(3):404–12.
Stricklen BM, Bond LE, Gould FDH, German RZ, Mayerl CJ. Swallow safety in infant pigs with and without recurrent laryngeal nerve lesion. Dysphagia. 2020;35(6):978–84.
Mayerl CJ, Catchpole EA, Edmonds CE, Gould FDH, McGrattan KE, Bond LE, et al. The effect of preterm birth, recurrent laryngeal nerve lesion, and postnatal maturation on hyoid and thyroid movements, and their coordination in infant feeding. J Biomech. 2020;22(105):109786.
• Mayerl CJ, Myrla AM, Gould FDH, Bond LE, Stricklen BM, German RZ. Swallow safety is determined by bolus volume during infant feeding in an animal model. Dysphagia. 2021;36(1):120–9. A study of swallow safety in preterm and full-term infant pigs, with and without RLN lesions. They found that bolus size (swallowing larger boluses) was more predictive of swallow safety than either lesion status or preterm/term status.
Wong NS, Feng Z, Rappazzo C, Turk C, Randall C, Ongkasuwan J. Patterns of dysphagia and airway protection in infants with 22q11.2-Deletion syndrome. The Laryngoscope. 2020;130(11):2532–6.
LaMantia A-S, Moody SA, Maynard TM, Karpinski BA, Zohn IE, Mendelowitz D, et al. Hard to swallow: developmental biological insights into pediatric dysphagia. Dev Biol. 2016;409(2):329–42.
Welby L, Caudill H, Yitsege G, Hamad A, Bunyak F, Zohn IE, Maynard T, LaMantia AS, Mendelowitz D, Lever TE. Persistent feeding and swallowing deficits in a mouse model of 22q11. 2 deletion syndrome. Front Neurol. 2020;11:4.
Maynard TM, Horvath A, P Bernot J, Karpinski BA, Tavares ALP, Shah A, et al. Transcriptional dysregulation in developing trigeminal sensory neurons in the LgDel mouse model of DiGeorge 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2020;29(6):1002–17.
Vijayakumar K, Rockett J, Ryan M, Harris R, Pitt M, Devile C. Experience of using electromyography of the genioglossus in the investigation of paediatric dysphagia. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2012;54(12):1127–32.
Lefton-Greif MA, Carroll JL, Loughlin GM. Long-term follow-up of oropharyngeal dysphagia in children without apparent risk factors. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2006;41(11):1040–8.
Kooi-van Es M, Erasmus CE, de Swart BJM, Voet NBM, van der Wees PJ, de Groot IJM, et al. Dysphagia and dysarthria in children with neuromuscular diseases, a prevalence study. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2020;7(3):287–95.
Sherman V, Greco E, Moharir M, Beal D, Thorpe K, Martino R. Feeding and swallowing impairment in children with stroke and unilateral cerebral palsy: a systematic review. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2019;61(7):761–9.
Sherman V, Martino R, Bhathal I, DeVeber MG, Dlamini N, MacGregor D, et al. Swallowing, oral motor, motor speech, and language impairments following acute pediatric ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2021;52(4):1309–18.
Shewmon DA. Anencephaly: selected medical aspects. Hastings Cent Rep. 1988;18(5):11–9.
Peleg D, Goldman JA. Fetal deglutition: a study of the anencephalic fetus. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1978;8(3):133–6.
• Radford K, Taylor RC, Hall JG, Gick B. Aerodigestive and communicative behaviors in anencephalic and hydranencephalic infants. Birth Defects Res. 2019;111(2):41–52. Review of published data on aerodigestive and communicative behaviors of fetuses/infants with anencephaly or hydranencephaly included in older studies.
Sanchez K, Morgan AT, Slattery JM, Olsen JE, Lee KJ, Anderson PJ, et al. Neuropredictors of oromotor feeding impairment in 12month-old children. Early Human Dev. 2017;1(111):49–55.
Kashou NH, Dar IA, El-Mahdy MA, Pluto C, Smith M, Gulati IK, Lo W, Jadcherla SR. Brain lesions among orally fed and gastrostomy-fed dysphagic preterm infants: can routine qualitative or volumetric quantitative magnetic resonance imaging predict feeding outcomes? Front Pediatr. 2017;5:73.
•• Tamilia E, Parker MS, Rocchi M, Taffoni F, Hansen A, Grant PE, et al. Nutritive sucking abnormalities and brain microstructural abnormalities in infants with established brain injury: a pilot study. J Perinatol. 2019;39(11):1498–508. A pilot neuroimaging study of 10 infants with brain injury, which found a correlation between microstructural white matter damage and sucking deficits.
Mishra A, Sheppard JJ, Kantarcigil C, Gordon AM, Malandraki GA. Novel mealtime duration measures: reliability and preliminary associations with clinical feeding and swallowing performance in self-feeding children with cerebral palsy. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2018;27(1):99–107.
Mishra A, Malandraki GA, Sheppard JJ, Gordon AM, Levy ES, Troche MS. Voluntary cough and clinical swallow function in children with spastic cerebral palsy and healthy controls. Dysphagia. 2019;34(2):145–54.
Kantarcigil C, Sheppard JJ, Gordon AM, Friel KM, Malandraki GA. A telehealth approach to conducting clinical swallowing evaluations in children with cerebral palsy. Res Dev Disabil. 2016;1(55):207–17.
•• Mourão LF, Friel KM, Sheppard JJ, Kuo H-C, Luchesi KF, Gordon AM, et al. The role of the corpus callosum in pediatric dysphagia: preliminary findings from a diffusion tensor imaging study in children with unilateral spastic cerebral palsy. Dysphagia. 2017;32(5):703–13. A study examining the association between brain lesion characteristics and corpus callosum connectivity and clinical swallowing outcomes in 20 self-feeding children with UCP. Findings showed that type and/or side of lesion plays a role in severity of clinical dysphagia in UCP and that corpus callosum integrity correlates with feeding/swallowing performance when sensorimotor areas of the left hemisphere are affected.
Malandraki GA, Mourão LF, Lu K-H, Friel KM, Luchesi KF, Sheppard JJ, et al. Functional and structural connectivity in children with unilateral cerebral palsy and clinical dysphagia: a multimodal neuroimaging study. European Society of Swallowing Disorders Congress.In Barcelona, Spain; 2017.
Malandraki GA, Mitchell S, Brown B, Hahn Arkenberg R, Lundine J, Burdo-Hartman W, et al. Feeding skills and eating efficiency are reduced in self-feeding school-age children with unilateral CP: an unrecognized reality. Dysphagia Research Society Meeting. In 2021.
Malandraki GA, Mitchell S, Hahn Arkenberg R, Brown B, Lundine J, Burdo-Hartman W, et al. The neuromuscular control of swallowing and speech in unilateral CP: overactivation and lack of specificity are overlapping traits. Dysphagia Research Society Meeting. In Virtual; 2021.
Crary MA, Carnaby GD, LaGorio LA, Carvajal PJ. Functional and physiological outcomes from an exercise-based dysphagia therapy: a pilot investigation of the McNeill Dysphagia Therapy Program. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;93(7):1173–8.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders Early Investigator R21 Grant (Grant 1R21DC015867-01A1, PI: Malandraki) and by an American Academy of Cerebral Palsy and Developmental Medicine Pedal-with-Pete research grant (PI: Malandraki).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Human and Animal Rights
All reported studies/experiments with human or animal subjects performed by the authors have been previously published and complied with all applicable ethical standards (including the Helsinki declaration and its amendments, institutional/national research committee standards, and international/national/institutional guidelines).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Swallowing Disorders
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malandraki, G.A., Arkenberg, R.H. Advances in Swallowing Neurophysiology Across Pediatric Development: Current Evidence and Insights. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep 9, 267–276 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40141-021-00334-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40141-021-00334-3