Abstract
Purpose of Review
The following describes the recent advancement in the diagnosis, imaging, and treatment of type B aortic dissections. We will review the recent updates of aortic dissection classifications, and potential impact on clinical management.
Recent Findings
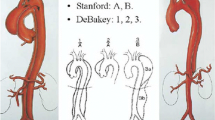
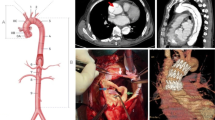
Type B aortic dissections can be classified anatomically and temporally using the recent Society for Vascular Surgery and Society of Thoracic Surgeons reporting standards. A number of high-risk features have been correlated with poor prognoses with medical management alone, leading to the expansion of indications for thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR). Emerging data suggest that timing of intervention may play a role in patient outcomes. Special attention to endovascular technique regarding landing zones and device selection can also significantly impact patient outcomes.
Summary
Anti-impulse therapy should promptly be initiated for all dissections. Type A dissections continue to depend largely on emergent open surgical intervention, whereas TEVAR remains first line for complicated type b aortic dissections. Uncomplicated type b aortic dissections are historically managed conservatively; however, data continue to emerge suggesting benefits of early endovascular intervention to prevent risk of late aortic degeneration or rupture. These approaches continue to be challenged as growing registry data and progressive endovascular technology develop. Regardless of initial management strategy, continued surveillance is crucial. Widespread utilization of standardized classification systems can aid in understanding the natural history and outcomes of aortic dissections.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Tsai TT, Trimarchi S, Nienaber CA. Acute aortic dissection: perspectives from the international registry of acute aortic dissection (IRAD). Eur J Asc Endovasc Surg. 2009;37(2):149–59.
Debakey ME, Henly WS, Cooley DA, Morris GC, Crawford ES, Beall AC. Surgical management of dissecting aneurysms of the aorta. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1965;49:130–49.
Daily PO, Trueblood HW, Stinson EB, Wuerflein RD, Shumway NE. Management of acute aortic dissections. Ann Thorac Surg. 1970;10(3):237–47.
Hagan PG, Nienaber CA, Isselbacher EM, Bruckman D, Karavite DJ, Russman PL, et al. The international registry of acute aortic dissection (IRAD): new insights into an old disease. JAMA. 2000;283(7):897–903.
•• Lombardi JV, Hughes GC, Appoo JJ, Bavaria JE, Beck AW, Cambria RP, et al. Society for vascular surgery (SVS) and society of thoracic surgeons (STS) reporting standards for type B aortic dissections. J Vasc Surg. 2020;71(3):723–47. Highlights most recent reporting standards and consensus international classifications.
Booher AM, Isselbacher EM, Nienaber CA, Trimarchi S, Evangelista A, Montgomery DG, et al. The IRAD classification system for characterizing survival after aortic dissection. Am J Med. 2013;126(8):730.e19-24.
Peterss S, Mansour AM, Ross JA, Vaitkeviciute I, Charilaou P, Dumfarth J, et al. Changing pathology of the thoracic aorta from acute to chronic dissection: literature review and insights. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68(10):1054–65.
Loewe C, Czerny M, Sodeck GH, Ta J, Schoder M, Funovics M, et al. A new mechanism by which an acute type B aortic dissection is primarily complicated, becomes complicated, or remains uncomplicated. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;93(4):1215–22.
Weiss G, Wolner I, Folkmann S, Sodeck G, Schmidli J, Grabenwöger M, et al. The location of the primary entry tear in acute type B aortic dissection affects early outcome. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012;42(3):571–6.
Evangelista A, Salas A, Ribera A, Ferreira-González I, Cuellar H, Pineda V, et al. Long-term outcome of aortic dissection with patent false lumen: predictive role of entry tear size and location. Circulation. 2012;125(25):3133–41.
Song JM, Kim SD, Kim JH, Kim MJ, Kang DH, Seo JB, et al. Long-term predictors of descending aorta aneurysmal change in patients with aortic dissection. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50(8):799–804.
Kodama K, Nishigami K, Sakamoto T, Sawamura T, Hirayama T, Misumi H, et al. Tight heart rate control reduces secondary adverse events in patients with type B acute aortic dissection. Circulation. 2008;118(14):S167–70.
Suzuki T, Isselbacher EM, Nienaber CA, Pyeritz RE, Eagle KA, Tsai TT, et al. Type-selective benefits of medications in treatment of acute aortic dissection (from the international registry of acute aortic dissection [IRAD]). Am J Cardiol. 2012;109(1):122–7.
Lombardi JV, Gleason TG, Panneton JM, Starnes BW, Dake MD, Haulon S, et al. STABLE II clinical trial on endovascular treatment of acute, complicated type B aortic dissection with a composite device design. J Vasc Surg. 2020;71(4):1077-87.e2.
Lombardi JV, Cambria RP, Nienaber CA, Chiesa R, Teebken O, Lee A, et al. Prospective multicenter clinical trial (STABLE) on the endovascular treatment of complicated type B aortic dissection using a composite device design. J Vasc Surg. 2012;55(3):629-40.e2.
Hanna JM, Andersen ND, Ganapathi AM, McCann RL, Hughes GC. Five-year results for endovascular repair of acute complicated type B aortic dissection. J Vasc Surg. 2014;59(1):96–106.
Fattori R, Montgomery D, Lovato L, Kische S, Di Eusanio M, Ince H, et al. Survival after endovascular therapy in patients with type B aortic dissection: a report from the international registry of acute aortic dissection (IRAD). JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;6(8):876–82.
Durham CA, Cambria RP, Wang LJ, Ergul EA, Aranson NJ, Patel VI, et al. The natural history of medically managed acute type B aortic dissection. J Vasc Surg. 2015;61(5):1192–8.
Nienaber CA, Kische S, Rousseau H, Eggebrecht H, Rehders TC, Kundt G, et al. Endovascular repair of type B aortic dissection: long-term results of the randomized investigation of stent grafts in aortic dissection trial. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;6(4):407–16.
Brunkwall J, Kasprzak P, Verhoeven E, Heijmen R, Taylor P, Alric P, et al. Endovascular repair of acute uncomplicated aortic type B dissection promotes aortic remodelling: 1 year results of the ADSORB trial. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2014;48(3):285–91.
Nienaber CA, Zannetti S, Barbieri B, Kische S, Schareck W, Rehders TC, et al. Investigation of STEnt grafts in patients with type B aortic dissection: design of the INSTEAD trial–a prospective, multicenter European randomized trial. Am Heart J. 2005;149(4):592–9.
Tsai TT, Evangelista A, Nienaber CA, Myrmel T, Meinhardt G, Cooper JV, et al. Partial thrombosis of the false lumen in patients with acute type B aortic dissection. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(4):349–59.
• Torrent DJ, McFarland GE, Wang G, Malas M, Pearce BJ, Aucoin V, et al. Timing of thoracic endovascular aortic repair for uncomplicated acute type B aortic dissection and the association with complications. J Vasc Surg. 2021;73(3):826–35. Evaluates an international vascular database to assess critical outcomes associated with aortic dissections.
Qato K, Conway A, Lu E, Tran NN, Giangola G, Carroccio A. Outcomes of thoracic endovascular aneurysm repair (TEVAR) in patients with connective tissue disorders. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2020;54(8):676–80.
• Kuo EC, Veranyan N, Johnson CE, Weaver FA, Ham SW, Rowe VL, et al. Impact of proximal seal zone length and intramural hematoma on clinical outcomes and aortic remodeling after thoracic endovascular aortic repair for aortic dissections. J Vasc Surg. 2019;69(4):987–95. Challenges important technical concepts for endovascular repair of aortic dissections.
Dong Z, Fu W, Wang Y, Wang C, Yan Z, Guo D, et al. Stent graft-induced new entry after endovascular repair for Stanford type B aortic dissection. J Vasc Surg. 2010;52(6):1450–7.
Berkarda Z, Kondov S, Kreibich M, Czerny M, Beyersdorf F, Rylski B. Landing zone remodelling after endovascular repair of dissected descending aorta. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2020;59(6):939–45.
• Piazza M, Squizzato F, Milan L, Miccoli T, Grego F, Antonello M, et al. Incidence and predictors of neurological complications following thoracic endovascular aneurysm repair in the global registry for endovascular aortic treatment. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;58(4):512–9. Highlights predictors for a critical outcome of endovascular repair of aortic dissections.
Xue Y, Ge Y, Ge X, Miao J, Fan W, Rong D, et al. Association between extent of stent-graft coverage and thoracic aortic remodeling after endovascular repair of type B aortic dissection. J Endovasc Ther. 2020;27(2):211–20.
Lou X, Duwayri YM, Jordan WD, Chen EP, Veeraswamy RK, Leshnower BG. The safety and efficacy of extended TEVAR in acute type B aortic dissection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2020;110(3):799–806.
Kische S, D’Ancona G, Ortak J, Bermaoui B, Stoeckicht Y, Ince H. Complicated type B aortic dissection should not be treated with uncovered stents: a lesson not yet learned. Ann Vasc Surg. 2015;29(4):841.e13-7.
Han SM, Patel K, Rowe VL, Perese S, Bond A, Weaver FA. Ultrasound-determined diameter measurements are more accurate than axial computed tomography after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2010;51(6):1381–7.
Han SM, Elsayed RS, Ham SW, Mahajan A, Fleischman F, Rowe VL, et al. Comparison of intravascular ultrasound- and centerline computed tomography-determined aortic diameters during thoracic endovascular aortic repair. J Vasc Surg. 2017;66(4):1184–91.
Bradshaw RJ, Ahanchi SS, Powell O, Larion S, Brandt C, Soult MC, et al. Left subclavian artery revascularization in zone 2 thoracic endovascular aortic repair is associated with lower stroke risk across all aortic diseases. J Vasc Surg. 2017;65(5):1270–9.
Chen X, Wang J, Premaratne S, Zhao J, Zhang WW. Meta-analysis of the outcomes of revascularization after intentional coverage of the left subclavian artery for thoracic endovascular aortic repair. J Vasc Surg. 2019;70(4):1330–40.
Conway AM, Qato K, Nguyen Tran N, Giangola G, Carroccio A. Management of the left subclavian artery in TEVAR for chronic type B aortic dissection. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2020;54(7):586–91.
Johnson CE, Zhang L, Magee GA, Ham SW, Ziegler KR, Weaver FA, et al. Periscope sandwich stenting as an alternative to open cervical revascularization of left subclavian artery during zone 2 thoracic endovascular aortic repair. J Vasc Surg. 2021;73(2):466-75
Magee GA, Veranyan N, Kuo EC, Ham SW, Ziegler KR, Weaver FA, et al. Anatomic suitability for off-the-shelf thoracic single side-branched endograft in patients with type B aortic dissection. J Vasc Surg. 2019;70(6):1776–81.
Wang ZG, Li C. Single-branch endograft for treating stanford type B aortic dissections with entry tears in proximity to the left subclavian artery. J Endovasc Ther. 2005;12(5):588–93.
Mougin J, Sobocinski J, Kratzberg J, Fabre D, Haulon S. Applicability of a standardized thoracic endograft with a single branch for the left subclavian artery to treat aortic disease involving the distal arch. J Vasc Surg. 2020;72(5):1516–23.
Tsilimparis N, Law Y, Rohlffs F, Spanos K, Debus ES, Kölbel T. Fenestrated endovascular repair for diseases involving the aortic arch. J Vasc Surg. 2020;71(5):1464–71.
Tsilimparis N, Detter C, Law Y, Rohlffs F, Heidemann F, Brickwedel J, et al. Single-center experience with an inner branched arch endograft. J Vasc Surg. 2019;69(4):977-985
Tsilimparis N, Debus ES, von Kodolitsch Y, Wipper S, Rohlffs F, Detter C, et al. Branched versus fenestrated endografts for endovascular repair of aortic arch lesions. J Vasc Surg. 2016;64(3):592–9.
Spear R, Clough RE, Fabre D, Roeder B, Hertault A, Martin Gonzalez T, et al. Total endovascular treatment of aortic arch disease using an arch endograft With 3 inner branches. J Endovasc Ther. 2017;24(4):534–8.
Spear R, Hertault A, Van Calster K, Settembre N, Delloye M, Azzaoui R, et al. Complex endovascular repair of postdissection arch and thoracoabdominal aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2018;67(3):685–93.
Gehringhoff B, Torsello G, Pitoulias GA, Austermann M, Donas KP. Use of chimney grafts in aortic arch pathologies involving the supra-aortic branches. J Endovasc Ther. 2011;18(5):650–5.
Huang C, Tang H, Qiao T, Liu C, Zhou M. Early results of chimney technique for type B aortic dissections extending to the aortic arch. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2016;39(1):28–35.
Ahanchi SS, Almaroof B, Stout CL, Panneton JM. In situ laser fenestration for revascularization of the left subclavian artery during emergent thoracic endovascular aortic repair. J Endovasc Ther. 2012;19(2):226–30.
Redlinger RE, Ahanchi SS, Panneton JM. In situ laser fenestration during emergent thoracic endovascular aortic repair is an effective method for left subclavian artery revascularization. J Vasc Surg. 2013;58(5):1171–7.
Li C, Xu P, Hua Z, Jiao Z, Cao H, Liu S, et al. Early and midterm outcomes of in situ laser fenestration during thoracic endovascular aortic repair for acute and subacute aortic arch diseases and analysis of its complications. J Vasc Surg. 2020;72(5):1524–33.
Zhao Z, Qin J, Yin M, Liu G, Liu X, Ye K, et al. In Situ Laser Stent Graft fenestration of the left subclavian artery during thoracic endovascular repair of type B aortic dissection with limited proximal landing zones: 5-year outcomes. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2020;31(8):1321–7.
Han SM, Kuo EC, Woo K, Elsayed R, Nguyen BS, Ham SW, et al. Remodeling of abdominal aortic branch perfusion after thoracic endovascular aortic repair for aortic dissections. J Vasc Surg. 2016;64(4):902–11.
Kölbel T, Carpenter SW, Lohrenz C, Tsilimparis N, Larena-Avellaneda A, Debus ES. Addressing persistent false lumen flow in chronic aortic dissection: the knickerbocker technique. J Endovasc Ther. 2014;21(1):117–22.
Kotani S, Inoue Y, Kasai M, Suzuki S, Hachiya T. Modified candy-plug technique for chronic type B aortic dissection with aneurysmal dilatation: a case report. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2017;12(1):77.
Kölbel T, Lohrenz C, Kieback A, Diener H, Debus ES, Larena-Avellaneda A. Distal false lumen occlusion in aortic dissection with a homemade extra-large vascular plug: the candy-plug technique. J Endovasc Ther. 2013;20(4):484–9.
Kazimierczak A, Rynio P, Jędrzejczak T, Mokrzycki K, Samad R, Brykczyński M, et al. Expanded petticoat technique to promote the reduction of contrasted false lumen volume in patients with chronic type B aortic dissection. J Vasc Surg. 2019;70(6):1782–91.
Kazimierczak A, Rynio P, Jędrzejczak T, Samad R, Rybicka A, Gutowski P. Aortic remodeling after extended PETTICOAT technique in acute aortic dissection type III B. Ann Vasc Surg. 2020;66:183–92.
Han SM, Tenorio ER, Mirza AK, Zhang L, Weiss S, Oderich GS. Low-profile zenith alphaTM thoracic stent graft modification using preloaded wires for urgent repair of thoracoabdominal and pararenal abdominal aortic aneurysms. Ann Vasc Surg. 2020;67:14–25.
Oderich GS, Ribeiro M, de Reis SL, Hofer J, Wigham J, Cha S. Endovascular repair of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms using fenestrated and branched endografts. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;153(2):S32–41.
Starnes BW, Tatum B. Early report from an investigator-initiate investigational device exemption clinical trial on physician-modified endovascular grafts. J Vasc Surg. 2013;58(2):311–7.
Sweet MP, Starnes BW, Tatum B. Endovascular treatment of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm using physician-modified endografts. J Vasc Surg. 2015;62(5):1160–7.
Hu Z, Li Y, Peng R, Liu J, Jia X, Liu X, et al. Multibranched stent-grafts for the treatment of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Endovasc Ther. 2016;23(4):626–33.
Oderich GS, Farber MA, Silveira PG, Tadros R, Marin M, Fillinger M, et al. Technical aspects and 30-day outcomes of the prospective early feasibility study of the GORE EXCLUDER thoracoabdominal branched endoprosthesis (TAMBE) to treat pararenal and extent IV thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2019;70(2):358-68.e6.
Coselli JS, Bozinovski J, LeMaire SA. Open surgical repair of 2286 thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;83(2):S862–4.
Coselli JS, LeMaire SA, Preventza O, de la Cruz KI, Cooley DA, Price MD, et al. Outcomes of 3309 thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repairs. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;151(5):1323–37.
Rigberg DA, McGory ML, Zingmond DS, Maggard MA, Agustin M, Lawrence PF, et al. Thirty-day mortality statistics underestimate the risk of repair of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms: a statewide experience. J Vasc Surg. 2006;43(2):217–22.
Ham SW, Chong T, Moos J, Rowe VL, Cohen RG, Cunningham MJ, et al. Arch and visceral/renal debranching combined with endovascular repair for thoracic and thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2011;54(1):30–40.
Fulton JJ, Farber MA, Marston WA, Mendes R, Mauro MA, Keagy BA. Endovascular stent-graft repair of pararenal and type IV thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms with adjunctive visceral reconstruction. J Vasc Surg. 2005;41(2):191–8.
Moulakakis KG, Mylonas SN, Antonopoulos CN, Liapis CD. Combined open and endovascular treatment of thoracoabdominal aortic pathologies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2012;1(3):267–76.
Famularo M, Meyermann K, Lombardi JV. Aneurysmal degeneration of type B aortic dissections after thoracic endovascular aortic repair: a systematic review. J Vasc Surg. 2017;66(3):924–30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Alyssa J Pyun, MD declares that she has no conflict of interest. Sukgu M Han, MD MS is a consultant for WL Gore and associates, Cook Medical, Terumo Aortic, Medtronic.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical collection on Vascular Surgery.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pyun, A.J., Han, S.M. Modern Management of Type B Aortic Dissections. Curr Surg Rep 9, 22 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40137-021-00299-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40137-021-00299-1