Abstract
Introduction
To establish the preclinical safety and equivalency of ophthalmic viscosurgical devices (OVDs) comprised of bacterially sourced sodium hyaluronate (HA) to animal sourced HA using pyrogenicity and aqueous exchange models in rabbits and a novel mini-pig model to evaluate corneal endothelial cell protection in vivo.
Methods
HEALON OVD and HEALON5 OVD containing animal-derived HA and HEALON PRO OVD and HEALON5 PRO OVD containing bacterial-derived HA were used. Two rabbit aqueous exchange studies were conducted where aqueous humor was exchanged with OVDs in six animals each to observe potential ocular inflammation, intraocular pressure (IOP) response, corneal health and pachymetry until 7 days post procedure, as well as overall assessment of the OVDs. Endothelial cell protection was evaluated in a Yucatan mini-pig cataract surgery model where HEALON PRO and HEALON5 PRO OVDs were compared to HEALON and HEALON5 OVDs, respectively. Following cataract surgery with use of OVDs in six animals per study, animals were evaluated for ocular and general health, IOP, corneal thickness, ocular inflammation, and endothelial cell protection on days 1, 3, 7 and 14 post-surgery.
Results
All rabbit studies demonstrated equivalence between bacterial-derived and animal-derived OVDs. Mild, post-surgical irritation, IOP increase, and corneal thickness measurements were not significantly different in HEALON PRO OVD and HEALON5 PRO OVD compared to HEALON and HEALON5 OVDs, respectively. The mini-pig model developed to investigate endothelial cell protection was successful in demonstrating equivalence between the OVDs studied. Changes in IOP mirrored actual surgical procedures, while corneal pachymetry and endothelial cell density remained constant for all OVDs used. Slit lamp observations showed expected inflammation following surgical procedures, likely due to challenges encountered during surgical procedures.
Conclusion
Rabbit pyrogenicity and aqueous exchanged paired with a novel simulated cataract surgery mini-pig model demonstrate equivalence of OVDs regardless of HA source. Albeit with challenges, the mini-pig model was shown to be a promising tool for endothelial cell evaluation during the development of new OVDs for ophthalmic use.
Funding
Johnson & Johnson Surgical Vision, Inc.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Since the invention of ophthalmic viscosurgical devices (OVDs) and the introduction of HEALON OVD (sodium hyaluronate 1%), the safety and clinical outcome of cataract surgery, the most frequently performed surgical procedure, has vastly improved [1, 2]. Decades ago, cataract surgery was performed with the aid of an air bubble or balanced salt solution injected into the anterior chamber, however these materials provided poor tissue protection and did little to create adequate space maintenance during intraocular lens (IOL) implantation [3, 4]. In addition to maintenance of anterior chamber space during IOL implantation, another critically important function of an OVD is the protection of the corneal endothelium [4, 5]. The corneal endothelium protects the inner layers of the cornea maintaining its hydration and transparency [6]. During cataract surgery, damage from surgical instruments, turbulence from irrigation fluids, or oxidative tissue damage from phacoemulsification can contribute to corneal endothelial cell loss [7, 8]. In humans, the corneal endothelium does not have a significant capacity for regeneration, thus when injury occurs, corneal endothelium cell function may be affected leading to corneal opacity and loss of vision [6]. OVDs also protect the endothelium by providing anti-free radical effects and reducing the temperature rise during phacoemulsification and aspiration stages of cataract surgery [9, 10]. Overall, OVDs have significantly increased the safety of cataract surgery, thus allowing tremendous improvements in surgical technique with less complications [5].
A key ingredient in OVDs is a viscoelastic material. Several viscoelastic materials are commercially available, including sodium hyaluronate (HA), chondroitin sulfate, and hydroxypropyolmethylcellulose (HPMC) [11]. HA, the most widely used viscoelastic material, is a naturally-occurring molecule identified in several human tissues including the vitreous and aqueous humor of the eye [7]. Historically, OVDs were developed with HA derived from rooster-combs [1]. Several currently available OVDs, including HEALON and HEALON5 OVDs, contain HA sourced from rooster combs. However, increasing concerns of environmental impact, animal welfare, and cost of production has led to increased popularity of OVDs and other consumer and medical devices comprised of HA derived from microbial sources [1, 12].
Johnson & Johnson Surgical Vision, Inc. has recently added two new formulations containing bacterial-sourced HA, HEALON PRO OVD and HEALON5 PRO OVD to its OVD portfolio. Prior to clinical testing, new OVD formulations undergo thorough preclinical evaluation of biocompatibility that allow scientists to observe OVD performance during surgery as well as identify possible immunogenic or inflammatory responses [3]. Although the derivation for the HA raw material for HEALON PRO OVD and HEALON5 PRO OVD was changed to a bacterial source, the final viscosity ranges of the two new OVD formulations closely overlapped those of the original formulations, HEALON OVD and HEALON5 OVD. The rheologic properties of the original and new formulations are so similar that during wet lab evaluations, surgeons could not distinguish a performance difference when comparing the original and new HEALON PRO OVD products [13].
Preclinical ocular biocompatibility testing has traditionally been performed in the rabbit model given the similarity of ocular anatomy to humans, ease of handling and maintenance, and the wealth of experimental data that exists on several rabbit species [14]. Additionally, rabbits have been widely used in corneal endothelium studies as the rabbit and human share similar corneal endothelium characteristics such as diameter, repair mechanisms, thickness, and composition [6]. In development of an OVD, a key endpoint to consider is the protection of endothelial cell layer integrity. Given the ability of rabbits to regenerate the endothelium, evaluation of cell loss at the point of injury and over time would be limited [6, 15]. Thus, this paper summarizes the preclinical evaluation of these two new OVD formulations in the traditional rabbit aqueous exchange model and in a novel Yucatan minipig model. Minipigs are increasingly being used in ocular toxicology studies due to their anatomical similarities with human eyes and as a substitute for nonhuman primates [16]. Minipigs, like humans, do not have the ability to regenerate the corneal endothelium post injury [17]. Due to this physiological similarity, the minipig was chosen as an additional model specifically to evaluate the corneal endothelium.
Methods
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed. These studies were carried out in strict accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the Public Health Service and Johnson & Johnson Corporate Human Animal Care and Use Policy. The intraocular implantation studies in rabbits, and the endothelial protection studies in mini-pigs were performed at Absorption Systems, Inc. (San Diego, CA). The rabbit pyrogenicity test was performed at Toxikon Corporation (Bedford, MA). Both laboratories are AAALAC accredited contract research organizations (CRO). During the studies, the care and use of animals was conducted in accordance with regulations of the USDA Animal Welfare Act. All study protocols were reviewed and approved by the CRO’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) prior to the initiation of study procedures. All studies were conducted in accordance with US FDA 21 CFR Part 58, Good Laboratory Practice for Nonclinical Laboratory Studies. Data analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism software with unpaired t-tests. The discovery was determined using the Original FDR method of Benjamini and Hochberg. Each time point was analyzed individually, without assuming a consistent standard deviation.
Rabbit Pyrogen Test
Four New Zealand White (NZW) rabbits at least 10 weeks old and weighing between 2.7 and 3.2 kg were used per study. A total of three studies were conducted to test three different lots of the investigational OVD. Rabbits were restrained for the course of the study with no food or water during the 3-h test period. Rectal temperature measuring probes were inserted throughout the testing period and the rabbits were placed in light-fitting stocks that allowed a natural resting position. Rabbits were weighed prior to the test to determine dose volume. The OVD was diluted 1:50 with 0.9% Sodium Chloride for Injection, which also served as the negative control. Diluted OVD (three rabbits) and control articles (one rabbit) were warmed to a temperature of 37 ± 2 °C and injected into the marginal ear vein at a volume of 10 mL/kg. Baseline temperatures were taken within 30 min prior to injection of the test article, then at 30-minute intervals between 1 and 3 h following the injection. Prior to actual pyrogen testing, a sham test was conducted within 7 days prior to pyrogen testing which included all steps except for injection of test or control articles.
Aqueous Exchange
Surgical Procedure
Six male naïve NZW rabbits approximately 11–13 weeks of age and weighing 2.7–3.0 kg at study initiation were used for each study. Surgical procedures were performed by a board-certified ophthalmologist. Rabbits were anesthetized with an intramuscular injection of ketamine hydrochloride (30 mg/kg) and xylazine (5 mg/kg). Both eyes were topically dosed with one drop of proparacaine hydrochloride (0.5%) and then cleaned with betadine and rinsed with balanced salt solution. A wire lid speculum was inserted to retract the lids. A 30G needle attached to a 1 mL syringe was inserted into the anterior chamber of each eye, and withdrawal of approximately 100 µL of aqueous humor was attempted. The amounts of aqueous humor withdrawn were recorded by weight, averaging 0.06 g, with a standard deviation of 0.015. Based on withdrawal amount, 0.04–0.1 mL of OVD was then injected into the anterior chamber to replace the aqueous humor that was withdrawn. The bacterially-derived OVD was injected into the right eye (OD) and the control, animal-derived OVD was injected into the left eye (OS). Three lots of bacterially-derived OVD were tested (two animals per lot), and one lot of animal-derived OVD was used as the control article. No incisions were required. The OVD remained in the eye for the duration of the study.
Observations/Measurements
General health assessment and gross ocular observations consisted of body weight measurements and a visual appraisal of the eye for swelling, discharge, and/or irritation. Prior to study placement and during the in-life phase, rabbits underwent an ophthalmic examination by a board-certified veterinary ophthalmologist using a slit-lamp biomicroscope (Haag-Streit BP 900) and an indirect ophthalmoscope (Keeler Vantage Plus). Ocular findings were scored following a modified McDonald–Shadduck scoring system. Rabbits were acclimated to intraocular pressure (IOP) measurement procedures once per day for two days prior to study initiation to determine baseline IOP levels. Prior to taking all IOP measurements, a 0.5% proparacaine solution was applied as a topical anesthetic and IOP measurements were performed using a Reichert Model 30 Classic pneumatonometer. Corneal pachymetry measurements were taken pre-treatment with a Sonogage Corneo-Gage Plus 4S pachymeter to determine baseline corneal thickness.
Endothelial Cell Protection Test
Surgical Procedure
Surgical procedures were performed by a board-certified ophthalmologist. Six male naïve Yucatan mini-pigs 17–18 weeks of age and weighing 19–23 kg at study initiation were used for each study. Animals were fasted (food only) approximately 12 h prior to the use of anesthesia. Animals were anesthetized using a combination of ketamine (10 mg/kg), xylazine (1 mg/kg), and atropine (0.04 mg/kg) via an intramuscular injection. Upon loss of responsiveness and spontaneous movement, animals were intubated and maintained on isoflurane (1–4%) in oxygen (1–3 L/min) as necessary. A single drop of topical proparacaine hydrochloride anesthetic (0.5%) was placed on each eye prior to the procedure. Following anesthesia, the eyes were cleaned with betadine and then rinsed with balanced salt solution (BSS). A wire lid speculum was inserted to retract the lids. A corneal incision of 2–3 mm was made approximately at the 12 o’clock position with a keratome. The bacterially-derived OVD was injected into the right eye (OD) and the control, animal-derived OVD was injected into the left eye (OS). The OVD was injected into the eye to maintain anterior chamber depth and a 5–6 mm continuous curvilinear capsulorrhexis was performed. Hydrodissection was executed to separate the capsule bag from the lens cortex. A 19 or 20-gage phacoemulsification tip was inserted through the corneal wound and an endocapsular lens extraction was performed utilizing phacoemulsification and irrigation/aspiration procedures with BSS, 5% heparin, and 1:1,000,000 epinephrine. Low-vacuum suction of both the anterior and posterior capsule was performed and viscoelastic was injected to deepen the anterior chamber and separate the anterior and posterior surfaces of the capsular bag. TECNIS intraocular lenses (IOLs) (Johnson & Johnson Surgical Vision, Inc., Santa Ana, CA) were implanted in all eyes and the viscoelastic was removed from the capsule bag. At the completion of the implantation procedure, the corneal incision was closed via sutures, and the procedure was repeated on the contralateral eye. Following surgery, 20 mg/0.25 mL of gentamicin and 2 mg/0.1 mL of dexamethasone was injected subconjunctivally and triple antibiotic ophthalmic solution was placed in both eyes. Prednisolone Acetate (1%) ophthalmic suspension was topically administered in both eyes of each animal up to 4 times a day for 13 days post-implantation.
Observations/Measurements
General health assessment and gross ocular observations consisted of body weight measurements and a visual appraisal for swelling, discharge, and/or irritation of the eye. Ophthalmic examinations by slit-lamp biomicroscopy (Haag-Streit BP 900) were performed by a board-certified veterinary ophthalmologist following the McDonald–Shadduck scoring system. IOP measurements were performed using a pneumatonometer (Reichert Model 30 Classic) on unanesthetized animals placed in slings at approximately the same time of day for each reading. Prior to all IOP measurements, a 0.5% proparacaine solution was applied as a topical anesthetic. Endothelial cell counts (3–5 scans per eye at different locations) and pachymetry measurements for corneal thickness were taken in parallel on anesthetized animals using a Konan Specular Microscope Model 7700. Prior to these measurements, 1–2 drops of 0.5% proparacaine topical anesthetic solution was applied to the eye.
Results
Rabbit Pyrogenicity Assays Demonstrate HEALON5 PRO OVD is Non-pyrogenic
To rule out the presence of any chemical pyrogens in HEALON OVD products, a rabbit pyrogenicity study was conducted based on United States Pharmacopeia 38 <151> Pyrogen Test on HEALON5 PRO OVD. HEALON5 PRO OVD was selected for testing because it has a higher viscosity than HEALON PRO OVD and is considered a “worst case” product for this category of OVDs. Typically, this standard requires the injection of 10 mLs test article per 10 kg of rabbit body weight. However, the viscosity of HEALON/HEALON PRO OVDs, and especially HEALON5/HEALON5 PRO OVDs, precludes direct injection into the ear vein as the standard calls for. Instead, a sample comprised of HEALON5 PRO OVD diluted 1:50 in saline was injected based on rabbit body weight. Approximately 30 min prior to test article injection, baseline temperatures were determined for each rabbit. The baseline temperature served as a reference point for identifying temperature shifts following test article injection. After test article injection, temperature measurements were taken at 30-min intervals. Three identical studies were conducted on separate occasions, each with three rabbits injected with test article and one rabbit injected with saline control. Evaluation of results from all three studies shows that of the nine rabbits receiving test article, five experienced very minimal temperature changes between 0.1 and 0.3 °C (Fig. 1). If no rabbit shows an individual rise in temperature of 0.5 °C or more, then the test article meets the requirements of the pyrogenicity test. Thus, all nine rabbits tested in these studies clearly demonstrate that HEALON5 PRO OVD is non-pyrogenic.
Rabbit pyrogenicity study conducted on HEALON5 PRO OVD demonstrates HEALON OVD products are non-pyrogenic. Three separate studies were conducted on three different lots of HEALON5 PRO OVD. Each study was conducted with n = 4, one control “C” and three experimental animals (− 1, − 2, − 3). Temperatures were taken every 30 min for a total of 3 h. Bars from left to right in each grouping are baseline, 1 h, 1.5 h, 2 h, 2.5 h, and 3 h. Data from all three studies are graphed together
Aqueous Exchange in Rabbits Demonstrates Equivalence Between Bacterial-Derived HA and Animal-Derived HA
To conduct a head-to-head comparison between HEALON OVD comprised of bacterial-derived HA or animal-derived HA, aqueous exchange studies were conducted in New Zealand White rabbits. In this in vivo test, the safety of the OVD is evaluated by assessing ocular biocompatibility indicators including anterior and posterior segment inflammation, intraocular pressure changes and corneal pathology and pachymetry. One study compared HEALON OVD to HEALON PRO OVD, while a second compared HEALON5 OVD to HEALON5 PRO OVD. In both studies, approximately 25% of aqueous humor was removed and replaced with 0.04–0.1 mL OVD in the anterior chamber. Bacterial-derived OVD (HEALON PRO, HEALON5 PRO) was injected into the OD eye of each animal, while animal-derived OVD (HEALON, HEALON5) were injected into the OS eye.
Over the course of each study, routine health observations, gross ocular observations, and body weight measurements were taken daily. No adverse changes in weight occurred during the duration of either study. Mild, procedure-related ocular discharge and irritation were observed, as expected, on day 0 for all animals. Most animals still demonstrated procedure-related irritation in one or both eyes on days 1–3, but it was largely resolved in the following days. Incidental observations included one animal with irritation in a HEALON OVD treated eye on day 2, as well as diarrhea on day 3. Further, corneal haze was noted in one HEALON PRO OVD treated eye on day 2. These observations were considered routine and unremarkable.
Ophthalmic examinations by slit lamp were performed and scored by the McDonald-Shadduck scoring system at baseline as well as post-surgically at 6 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, and 7 days. Overall, all observations noted during the course of the study were typical for the aqueous exchange rabbit model and were expected following an ocular surgical procedure. At 6 h post procedure (Tables 1, 2), most animal eyes showed iritis, and conjunctival congestion and swelling. HEALON5 OVD and HEALON5 PRO OVD injected eyes also displayed mild conjunctival discharge, as well as aqueous cells in two HEALON5 OVD and two HEALON5 PRO OVD injected eyes. Over the course of the study, the observed tissue swelling and inflammation resolved, until Day 7 when the scores had largely returned to 0. Two observations of note were a hemorrhage in the anterior chamber in the HEALON PRO OVD injected eye of one animal, and a fibrin streak present on the corneal endothelium in the HEALON PRO OVD injected eye of a different animal. Both adverse findings were determined to be due to the injection procedure and unrelated to the HEALON OVD that was used.
IOP measurements were taken several times on the day of the procedure (baseline, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12 h), then at 24 h and 7 days (Fig. 2a, b). Anticipated increases in IOP levels were observed with all OVDs (HEALON, HEALON PRO, HEALON5, and HEALON5 PRO) at 4, 6, and 8 h following the aqueous exchange procedure before returning to baseline levels. There were no statistically significant differences in IOP between HEALON OVD and HEALON PRO OVD, with p values ranging from 0.07 (4 h) to 0.88 (7 days). Likewise, there were no statistically significant differences in IOP between HEALON5 OVD and HEALON5 PRO OVD, with p values ranging from 0.24 (4 h) to 0.90 (8 h). These IOP observations demonstrate that HEALON PRO OVD products made with bacterially-derived HA do not alter IOP in a manner different from HEALON OVD products made with animal-derived HA.
IOP measurements in aqueous exchange rabbit model demonstrate similarity between OVDs with bacterial derived versus animal derived HA. Average IOP measurement is graphed from n = 6, error bars are 1 standard deviation. No statistically significant differences were found between HEALON/HEALON5 OVD compared with HEALON PRO/HEALON5 PRO OVD. a OD eye injected with HEALON PRO OVD, OS eye injected with HEALON OVD. p values = 0.07–0.88, using unpaired t test; b OD eye injected with HEALON5 PRO OVD, OS eye injected with HEALON5 OVD. p values = 0.24–0.90, using unpaired t test
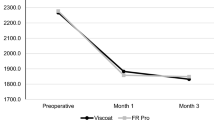
Pachymetry measurements were taken at baseline and after the procedure at 6 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, and 7 days (Fig. 3a, b). As expected, there was a very slight increase in corneal thickness 6 h post procedure that was observed with all four types of HEALON OVDs. There was no statistically significant difference between HEALON PRO OVD and HEALON5 PRO OVD compared to HEALON OVD and HEALON5 OVD, respectively, at any time point. Thus, pachymetry measurements demonstrate that there were no significant differences in corneal thickness between bacteria-derived and animal-derived HEALON OVD products.
Corneal thickness in aqueous exchange rabbit model is comparable between OVDs with bacterial-derived and animal-derived HA. Average pachymetry measurement is graphed from n = 6, error bars are 1 standard deviation. No statistically significant differences were found between HEALON/HEALON5 OVD compared with HEALON PRO/HEALON5 PRO OVD. a OD eye injected with HEALON PRO OVD, OS eye injected with HEALON OVD. p values = 0.250–1, using unpaired t test; b OD eye injected with HEALON5 PRO OVD, OS eye injected with HEALON5 OVD. p values = 0.527–0.911, using unpaired t test
A Novel Mini-Pig Model was Utilized for Preclinical Safety Evaluation of OVD Comprised of Bacterial or Animal Sourced HA
A novel model based on the Yucatan mini-pig was developed to evaluate the potential protective effects of OVDs on endothelial cells during cataract surgery. Pigs were chosen for this model based on the limited capacity, as that in humans, to regenerate the corneal endothelium post injury [17]. Two GLP studies were conducted in mini-pigs where the mini-pigs underwent intraocular lens implantation surgery in which the OS eye received HEALON or HEALON5 OVD and the OD eye received HEALON PRO or HEALON5 PRO OVD.
During the 14-day study period, routine health observations and gross ocular observations were taken daily. Mild ocular swelling, discharge and irritation related to the procedure were observed, as expected, on day 0 for all animals. In the study comparing HEALON OVD to HEALON PRO OVD, four of six animals continued to demonstrate intermittent swelling and irritation in one or both eyes throughout the duration of the study. In the study comparing HEALON5 OVD to HEALON5 PRO OVD, one of six animals had excessive discharge and swelling in the HEALON5 PRO OVD treated eye. Furthermore, fibrin was noted in the HEALON5 OVD eye of one animal, the HEALON5 PRO OVD eye of one animal, and both eyes in two animals. Several eyes, both HEALON5 OVD and HEALON5 PRO OVD treated, demonstrated corneal cloudiness (4/6 HEALON5 PRO OVD eyes), and haze (4/6 HEALON5 PRO OVD eyes; 4/6 HEALON5 OVD eyes). The body weight was measured at day 0 prior to surgery and after final examinations on day 14. No adverse changes in weight occurred during the duration of either study. Damage to the corneal endothelium during surgery, causing endothelial cell loss, may lead to an increased measurement of central corneal thickness, or pachymetry. Thus, pachymetry measurements indirectly informs on the health and integrity of the endothelial cell layer. In these studies, pachymetry measurements demonstrate no apparent changes over the course of the study for any OVD (Fig. 4a, b). All these observations were considered routine and unremarkable. This data suggests all four OVD products were able to protect the integrity of the endothelial cell layer.
Corneal thickness in the pig model is comparable between OVDs with bacterial-derived and animal-derived HA. Average pachymetry measurement is graphed from n = 6, error bars are 1 standard deviation. No statistically significant differences were found between HEALON/HEALON5 OVD compared with HEALON PRO/HEALON5 PRO OVD. a OD eye injected with HEALON PRO OVD, OS eye injected with HEALON OVD. Pachymetry measurements were not taken on day 1 post surgery. p values = 0.195–0.872, using unpaired t test; b OD eye injected with HEALON5 PRO OVD, OS eye injected with HEALON5 OVD. p values = 0.196–0.938, using unpaired t test
Ophthalmic examinations by slit lamp were performed and scored by the McDonald-Shadduck scoring system at baseline as well as after the procedure on days 1, 2, 3, 7, and 14. All baseline scores were reported as 0. Following the procedure, during day 1 of ophthalmic examinations by slit lamp, mild to severe conjunctival discharge, congestion, and swelling were observed in both eyes of all pigs (Tables 3, 4). Additional observations on Day 1 include mild to severe anterior chamber flare, fibrin, and inflammatory cells present in the anterior capsule in all eyes. Mild to severe aqueous flare was noted in both eyes of all but two animals (unable to observe posterior portion of the eye). Loss of corneal transparency was noted in the HEALON PRO OVD injected eye in three of six animals, HEALON5 PRO OVD in one of six animals, and in both eyes in one of six animals in the HEALON/HEALON PRO OVD study, and five of six animals in the HEALON5/HEALON5 PRO OVD study. In animals where HEALON5 OVD and HEALON5 PRO OVD were used, all animals also experienced mild conjunctival hyperemia. Stromal cloudiness was observed in two HEALON5 PRO OVD injected eyes and two HEALON5 OVD injected eyes. Over the course of the 14 days, the animal eyes continued to recover from procedural inflammation and irritation. On day 14, mild to moderate conjunctival congestion and swelling were still present in two of six HEALON PRO OVD injected eyes and one of six HEALON5 PRO OVD injected eyes. Loss of corneal transparency was present in two of six HEALON PRO OVD injected eyes, four of six HEALON5 PRO OVD injected eyes, and one of six HEALON5 OVD injected eyes. Anterior chamber flare was observed in one of six HEALON PRO OVD injected eyes and one of six HEALON5 PRO OVD injected eyes. Fibrin was present in the HEALON PRO OVD injected eye in five of six animals, in the HEALON OVD injected eye in three of six animals, in the HEALON5 PRO OVD injected eyes of two of six animals, and in the HEALON5 OVD injected eyes of one of six animals. Overall, ophthalmic observations noted were incidental, procedure related findings and not dependent on the type of viscoelastic device that was utilized.
IOP measurements were taken at baseline and on Days 1, 3, 7, and 14 (Fig. 5a, b). An initial variability in IOP at early time points, followed by a return to baseline levels at later time points was observed and is consistent with typical IOL surgical procedures. Figure 5a compares HEALON OVD with HEALON PRO OVD and HEALON5 OVD with HEALON5 PRO OVD, respectively. There were no statistically significant differences in IOP between HEALON OVD and HEALON PRO OVD, with p values ranging from 0.186 (Day 3) to 0.657 (Day 14). There were also no statistically significant differences in IOP between HEALON5 OVD and HEALON5 PRO OVD, with p values ranging from 0.476 (baseline) to 1 (Day 14) (Fig. 5b). These IOP observations demonstrate that OVD with bacterially-derived HA behave similar to OVD with animal-derived HA regarding IOP changes.
IOP measurements in the pig model demonstrate similarity between OVDs with bacterial derived versus animal derived HA. Average IOP measurement is graphed from n = 6, error bars are 1 standard deviation. No statistically significant differences were found between HEALON/HEALON5 OVD compared with HEALON PRO/HEALON5 PRO OVD. a OD eye injected with HEALON PRO OVD, OS eye injected with HEALON OVD. p values = 0.186–0.657, using unpaired t test; b OD eye injected with HEALON5 PRO OVD, OS eye injected with HEALON5 OVD. p values = 0.276–1, using unpaired t test
Corneal endothelial cell density was measured at baseline and on Days 3, 7, and 14 following the surgical procedure. To decrease postoperative damage and cell loss, OVDs are used to protect the integrity of the endothelial cell layer [18]. Corneal endothelial cell density measurements allow investigation of the effectiveness of this protective property of OVDs. In the studies evaluating HEALON OVD and HEALON PRO OVD or HEALON5 OVD and HEALON5 PRO OVD, all four OVD demonstrated corneal endothelial cell protection. There was not a statistically significant difference between HEALON OVD and HEALON PRO OVD at any time point, with p values of 0.705, 0.594, and 0.668 for baseline, day 3, and day 14 (p value of day 7 could not be calculated due to small n) (Fig. 6a). There was a slight reduction in endothelial cell density on day 7 in HEALON OVD injected eyes (p = 0.046) and on day 14 in HEALON PRO OVD injected eyes (p = 0.045). This very slight reduction did not appear to have a physiological impact and the cell numbers were not significantly different (data not shown). Likewise, there was not a statistically significant difference between HEALON5 OVD and HEALON5 PRO OVD at any time point, with p values of 0.287, 0.538, 0.745, and 0.828 for baseline, day 3, day 7 and day 14, respectively (Fig. 6b). Again, we observed a slight reduction in endothelial cell density at day 14 in HEALON5 PRO OVD eyes, and at days 3, 7, and 14 in HEALON5 OVD eyes, but without significant differences in cell numbers, except at day 3.
Endothelial cell density demonstrates equivalence in protective potential of OVDs with bacterial derived HA and animal derived HA. Average endothelial cell density measurement is graphed, error bars are one standard deviation. No statistically significant differences were found between HEALON/HEALON5 OVD compared with HEALON PRO/HEALON5 PRO OVD. a OD eye injected with HEALON PRO OVD, OS eye injected with HEALON OVD. Six animals were in the study, but endothelial cell density was not obtainable in every animal. For HEALON PRO OVD, n for baseline, day 3, day 7, day 14 are 6, 3, 1, 4, respectively. For HEALON OVD, n for baseline, day 3, day 7, day 14 are 6, 3, 4, 5, respectively. p values = 0.595–0.705, using unpaired t test; b OD eye injected with HEALON5 PRO OVD, OS eye injected with HEALON5 OVD. Six animals were in the study, but endothelial cell density was not obtainable in every animal. For HEALON5 PRO OVD, n for baseline, day 1, day 3, day 7, day 14 are 6, 4, 4, 4, 4, respectively. For HEALON5 OVD, n for baseline, day 1, day 3, day 7, day 14 are 6, 3, 6, 6, 6 respectively. p values = 0.286–0.951, using unpaired t test
Discussion
Advancements in cataract surgical techniques and OVD materials continuously create the need for more specialized OVD formulations with unique physio-chemical and rheologic features [1]. The International Standardization Organization (ISO), the US FDA, and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) all have implemented guidelines for preclinical testing [14] including ISO 15798: Ophthalmic Implants-Ophthalmic Viscosurgical Devices and ISO 10993: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices which apply to ophthalmic viscosurgical device development.
The studies reported here were designed to demonstrate the equivalence of animal-derived and bacterial-derived HA. Due to the inherent nature and purpose of this medical device, in addition to standard guidelines, the results reported here describe custom studies designed to address additional questions unique to OVDs. In our investigation, we first relied on rabbit models for pyrogenicity and aqueous exchange. The viscosity of HEALON OVD products precluded direct injection for pyrogenicity tests, thus studies were designed using diluted OVD. Prior to conducting this work, approval was needed from regulatory bodies recognizing the validity of the data. In our rabbit aqueous exchange model, the surgeon evaluated OVD performance parameters including ease of injection and removal, as well as anterior chamber space creation and maintenance. Post-surgery, ocular examinations and measurements for signs of ocular biocompatibility of the investigational OVD formulations (with bacterial-sourced HA) demonstrated equivalence to clinically approved OVDs (with animal-sourced HA).
One key attribute of OVD is the protection of corneal endothelial cells during cataract surgery. A useful animal model to investigate the protective properties of OVD has yet to be established. This study presents the use of a novel Yucatan mini-pig model for the first time, because like humans, mini-pigs have demonstrated a limited ability to proliferate and regenerate the corneal endothelium [6, 17]. In this model, we were able to perform a lens exchange to mimic cataract surgery while utilizing HEALON OVD products for protection of endothelial cells, among its other functions. The data gathered on general and ocular health, IOP, endothelial cell density, and corneal pachymetry were able to conclusively demonstrate equivalence of OVD comprised of animal-derived or bacterial-derived HA. However, use of the mini-pig model is not without its limitations and complications. Maintaining appropriate anesthesia throughout the procedure was a considerable challenge. When animals were deeply sedated, the eyes would roll out of position making it difficult for the surgeon to obtain an unimpaired view of the eye. If the sedation was lightened, animals were not completely physically restrained and may attempt to cough out the intubation tube. Both situations led to difficult surgeries and a higher level of post-operative inflammation than would normally occur.
Conclusions
Even considering the challenges that were encountered, through the use of both the rabbit pyrogenicity and aqueous exchange models and the mini-pig endothelial cell model, we establish the equivalence of HEALON OVDs regardless of their HA source.
References
Arshinoff S. Ophthalmic viscosurgical devices. In: Kohnen T, Koch D, editors. Cataract and refractive surgery essentials in ophthalmology. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2005. p. 37–62.
Belda JI, Artola A, Garcia-Manzanares MD, et al. Hyaluronic acid combined with mannitol to improve protection against free-radical endothelial damage: experimental model. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31(6):1213–8.
Buratto L, Giardini P, Bellucci R. Viscoelastic materials, chapter 2. In: Drummon A, Plummer L, editors. Viscoelastics in ophthalmic surgery. USA: SLACK Inc; 2000. pp. 5–9.
Liesegang TJ. Viscoelastic substances in ophthalmology. Surv Ophthalmol. 1990;34(4):268–93.
Schulze SD, Bertelmann T, Manojlovic I, Bodanowitz S, Irle S, Sekundo W. Changes in corneal endothelium cell characteristics after cataract surgery with and without use of viscoelastic substances during intraocular lens implantation. Clin Ophthalmol. 2015;9:2073–80.
Valdez-Garcia JE, Lozano-Ramirez JF, Zavala J. Adult white New Zealand rabbit as suitable model for corneal endothelial engineering. BMC Res Notes. 2015;8:28.
Higashide T, Sugiyama K. Use of viscoelastic substance in ophthalmic surgery—focus on sodium hyaluronate. Clin Ophthalmol. 2008;2(1):21–30.
Shimmura S, Tsubota K, Oguchi Y, Fukumura D, Suematsu M, Tsuchiya M. Oxiradical-dependent photoemission induced by a phacoemulsification probe. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992;33(10):2904–7.
Suzuki H, Igarashi T, Shiwa T, Takahashi H. Efficacy of ophthalmic viscosurgical devices in preventing temperature rise at the corneal endothelium during phacoemulsification. Curr Eye Res. 2016;41(12):1548–52.
Takahashi H. Free radical development in phacoemulsification cataract surgery. J Nippon Med Sch. 2005;72(1):4–12.
Arshinoff S, Carbonneau M. Using OVDs for glaucoma surgery. J Emmetropia. 2013;4:161–9.
Liu L, Liu Y, Li J, Du G, Chen J. Microbial production of hyaluronic acid: current state, challenges, and perspectives. Microb Cell Fact. 2011;10:99.
Abbott Medical Optics. Data on file—Evaluation of the rhelogical properties of Healon PRO OVD and Healon5 PRO OVD. 2016.
Gwon A. The rabbit in cataract/IOL surgery. In: Tsonis P, editor. Animal models in eye research. Dayton, OH: Elsevier Ltd; 2008. p. 184–204.
Van Horn DL, Sendele DD, Seideman S, Buco PJ. Regenerative capacity of the corneal endothelium in rabbit and cat. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977;16(7):597–613.
Atzpodien EA, Jacobsen B, Funk J, et al. Advanced clinical imaging and tissue-based biomarkers of the eye for toxicology studies in Minipigs. Toxicol Pathol. 2016;44(3):398–413.
Nicholls SM, Mitchard LK, Laycock GM, et al. A model of corneal graft rejection in semi-inbred NIH miniature swine: significant T-cell infiltration of clinically accepted allografts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(6):3183–92.
Storr-Paulsen A, Norregaard JC, Farik G, Tarnhoj J. The influence of viscoelastic substances on the corneal endothelial cell population during cataract surgery: a prospective study of cohesive and dispersive viscoelastics. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2007;85(2):183–7.
Acknowledgements
Funding
These studies and article processing charges were funded by Johnson & Johnson Surgical Vision, Inc. All authors had access to all of the data in this study and take complete responsibility for the integrity of the data and accuracy of the data analysis.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Disclosures
Ronika S. Leang is an employee of Johnson & Johnson Surgical Vision, Inc. Lisa J. Kloft is an employee of Johnson & Johnson Surgical Vision, Inc. Brad Gray is an employee of Johnson & Johnson Surgical Vision, Inc. Arlene E. Gwon is a paid consultant of Johnson & Johnson Surgical Vision, Inc. Ling C. Huang is an employee of Johnson & Johnson Surgical Vision, Inc.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Enhanced Digital Features
To view enhanced digital features for this article go to https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.7637171.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Leang, R.S., Kloft, L.J., Gray, B. et al. Preclinical Safety Evaluation of Ophthalmic Viscosurgical Devices in Rabbits and a Novel Mini-Pig Model. Ophthalmol Ther 8, 101–114 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40123-019-0167-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40123-019-0167-9