Abstract
Introduction
Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MP) strains in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients are thought to initiate the chronic infection stage of CF and are associated with pulmonary function decline.
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to assess the susceptibility of MP strains to ceftolozane/tazobactam and the efficacy of ceftolozane/tazobactam against MP strains compared with those for standard-of-care antipseudomonal antibiotics.
Methods
Ten clinical isolates of MP from CF patients were tested for susceptibility with Etest and time–kill analysis with ceftolozane/tazobactam compared with ceftazidime, cefepime, ciprofloxacin, meropenem, tobramycin, and polymyxin B. The physiologic free peak concentrations were used in the time–kill experiments.
Results
Ceftolozane/tazobactam minimum inhibitory concentrations ranged from 0.032 to 1.5 mg/L. In the time–kill analysis, the mean starting inoculum for the isolates was 6.29 ± 0.22 log10 colony forming units (CFU) per milliliter. On average, ceftolozane/tazobactam, cefepime, ciprofloxacin, meropenem, tobramycin, and polymyxin B all demonstrated bactericidal activity. With all isolates taken into account, polymyxin B, tobramycin, meropenem, and ceftolozane/tazobactam 3 g were the most potent, with reductions in inoculum of 5.07 ± 0.45, 4.58 ± 2.2, 4.76 ± 0.71, and 4.17 ± 0.94 log10 CFU/mL, respectively. Ceftolozane/tazobactam 1.5 g, cefepime, and ciprofloxacin reduced the starting inoculum by 3.74 ± 0.99, 3.42 ± 1.4, and 3.23 ± 2.0 log10 CFU/mL, respectively. Despite 90% susceptibility, ceftazidime was bactericidal against seven of ten strains, with an average reduction in starting inoculum of 2.91 ± 2.2 log10 CFU/mL.
Conclusion
Ceftolozane/tazobactam activity against MP strains derived from CF patients was comparable to that of standard-of-care agents at both the 1.5-g dose and the 3-g dose. Further in vitro modeling and clinical trials are warranted.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common cause of respiratory infections in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients [1]. P. aeruginosa strains in CF commonly become mucoid, an exopolysaccharide alginate overproducing phenotype that initiates the chronic infection stage of the disease and a decline in pulmonary function [2,3,4].
As CF patients age, mechanisms of resistance to P. aeruginosa accumulate [5]. As a result, newer antibiotics are needed. Ceftolozane/tazobactam is a novel cephalosporin/β-lactamase inhibitor that maintains activity against many multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa isolates. Resistance appears not to be driven by single-step mutations, which is promising for chronic respiratory infections in CF [6,7,8,9]. Although ceftolozane/tazobactam is not currently approved for treatment of pulmonary infections, it has been successfully used in acute pulmonary CF exacerbations [10, 11].
The purpose of this study was to compare the efficacy of ceftolozane/tazobactam against mucoid P. aeruginosa (MP) strains isolated from CF patients with that of standard-of-care (SOC) agents. This study also assessed resistance patterns of MP and specifically the ceftolozane/tazobactam minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs).
Methods
Bacterial Strains
Ten clinical MP isolates from CF patients at an academic medical center were tested for susceptibility, and time–kill analyses were performed with ceftolozane/tazobactam and the following SOC antimicrobials: ceftazidime, cefepime, meropenem, ciprofloxacin, tobramycin, and polymyxin B. This study was approved by the Institutional Biosafety Committee. This article does not contain any new studies with human or animals performed by any of the authors. This study does not meet the definition of a clinical trial, and so was not registered at ClinicalTrials.gov.
Antimicrobials
Ceftolozane powder was obtained from Merck (Kenilworth, NJ, USA). Tazobactam (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), ceftazidime (Sagent Pharmaceuticals, Schaumburg, IL, USA), cefepime and meropenem (Sandoz, Princeton, NY, USA), ciprofloxacin and tobramycin (Hospira, Lake Forest, IL, USA), and polymyxin B (XGen Pharmaceuticals, Big Flats, NY, USA) were obtained commercially.
Susceptibility Testing
MICs were determined with Etest according to standard procedures and read by two individuals. If there was a difference between the readings, a third individual analyzed the result. If there was a difference in MIC of more than a half dilution, the Etest was repeated.
Time–Kill Experiments
Time–kill experiments were performed in duplicate in Mueller–Hinton broth (BBL; Becton, Dickinson, Sparks, MD, USA) in 24-well macrowell plates as previously described [12]. The plate was filled with 100 µL of antibiotic stock solution, 200 µL of a 1:10 dilution of a 1.75 McFarland-standard organism suspension for a target bacterial inoculum of 106 colony-forming units (CFU) per milliliter, and sufficient volume of Mueller–Hinton broth for a total volume of 2 mL. Sample aliquots of 100 µL were obtained from each well at 0, 4, 8, and 24 h, and were serially diluted in cold 0.9% sodium chloride. Bacterial counts were determined with a Whitely automatic spiral plater (Don Whitely Scientific, Shipley, UK). The lower limit of detection for time–kill studies was 101 CFU/mL. Plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h, at which time colony counts were performed with a ProtoCOL colony counter (Synoptics, Frederick MD, USA). All strains were tested against ceftolozane/tazobactam (1.5 and 3 g), ceftazidime (2 g), cefepime (2 g), ciprofloxacin (400 mg), meropenem (1 g), tobramycin (25 mg/L), and polymyxin B (1.25 mg/kg) with use of free physiologic peak concentrations. The physiologic free peak concentrations were 60/12.6, 120/25.2, 151, 112, 3.2, 110, 25, and 2.1 mg/L, respectively [13,14,15,16,17,18]. Time–kill curves were generated by plotting mean colony counts (log10 CFU/mL) versus time to compare 24-h killing effects (Fig. 1). Bactericidal activity was defined as a 3 log10 CFU/mL reduction or greater from the baseline.
Statistical Analysis
Differences in log10 CFU per milliliter were analyzed by analysis of variance with Tukey’s post hoc test. P < 0.05 was considered significant. All statistical analyses were performed with IBM SPSS Statistics (version 24.0; IBM, Armonk, NY, USA).
Results
Susceptibility Testing
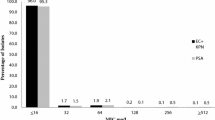
All strains were susceptible to ceftolozane/tazobactam with MICs that ranged from 0.032 to 1.5 mg/L (susceptible if MIC is 4/4 mg/L or less) (Table 1) [19]. Meropenem and polymyxin B resulted in 100% susceptibility. Although cefepime and ciprofloxacin were the least effective agents, both were active against eight of the ten strains.
,
Time–Kill Studies
The mean starting inoculum was 6.29 ± 0.22 log10 CFU/mL. The most potent activity was for polymyxin B, tobramycin, meropenem, and ceftolozane/tazobactam 3 g, demonstrated by reductions in starting inoculums of 5.07 ± 0.45, 4.58 ± 2.2, 4.76 ± 0.71, and 4.17 ± 0.94 log10 CFU/mL, respectively. Bactericidal activity was also observed with ceftolozane/tazobactam 1.5 g, cefepime, and ciprofloxacin, with average reductions of 3.74 ± 0.99, 3.42 ± 1.37, and 3.23 ± 1.98 log10 CFU/mL, respectively, from the starting inoculum.
Ceftolozane/tazobactam was bactericidal against 80% of evaluated strains. Despite lack of bactericidal activity against two strains, there were no differences between the inoculum reductions of ceftolozane/tazobactam and those of the other agents (P > 0.05), with the exception of tobramycin. No regrowth was noted at 24 h for any strain with either ceftolozane/tazobactam dose. Tobramycin displayed bactericidal activity rapidly (within 4 h) against seven of the ten strains and achieved killing to the limit of detection in nine strains by 24 h. However, strain HR21 displayed regrowth within 8 h after tobramycin exposure, although this could be explained by a tobramycin MIC greater than 1024 mg/L. When this tobramycin-resistant strain was excluded, tobramycin demonstrated the most potent killing effect, with an average reduction in starting inoculum of 5.26 ± 0.24 log10 CFU/mL.
The least active agents were ceftazidime and ciprofloxacin. Ceftazidime displayed bactericidal activity against only seven strains, with an average reduction in starting inoculum of 2.91 ± 2.22 log10 CFU/mL. Two of ten ceftazidime-treated strains displayed regrowth at 24 h. Additionally, five strains treated with ceftazidime displayed less potent reductions in starting inoculum than with the comparator agents (P < 0.05). Ciprofloxacin displayed bactericidal activity against six strains, with an average reduction in starting inoculum in these strains of 4.62 ± 0.36 log10 CFU/mL. Despite initial killing activity in all strains, 40% of ciprofloxacin-treated strains displayed regrowth at 24 h.
Discussion
Ceftolozane/tazobactam demonstrates bactericidal killing similar to that of SOC antimicrobials with regard to MP isolated from CF patients. The highest MIC with ceftolozane/tazobactam, 1.5 mg/L, corresponded to the strain that was resistant to the other cephalosporins tested. Ceftolozane/tazobactam MICs did not correlate with non-β-lactam MICs.
The MIC50/MIC90 of ceftolozane for P. aeruginosa isolates from adults was reported as 0.5/2 mg/L [9]. In that study, the ceftolozane MIC was 8 mg/L or less for 94% of MP isolates, with a mean MIC of 0.8 mg/L. Another study found that the ceftolozane MIC was greater than 8 mg/L for 36% of P. aeruginosa isolates from CF patients ; 57% were not susceptible to ceftazidime [8]. Another study evaluated ceftolozane/tazobactam against P. aeruginosa in CF: 48% of isolates were MP, and the MIC50/MIC90 was 2/8 mg/L, with 86% susceptibility [7]. However, there was a high frequency of multidrug-resistant isolates. In a trial evaluating the dynamics of resistance development using wild-type and mutator strains of P. aeruginosa, resistance development with ceftolozane/tazobactam was slower than with comparators, reaching eight times the MIC (basal MIC of 0.5 ug/mL) after 7 days of experiments (versus 64 times the MIC at 4 days with ceftazidime) in wild-type strains. In mutator strains, resistance development was much more rapid and significant with all compounds [20]. Our study, in comparison, showed MIC50/MIC90 of 0.25/0.5 mg/L, and all isolates were susceptible according to the breakpoint of 4/4 mg/L or less [19]. It is unlikely that our study included any mutator strains.
The activity of ceftolozane alone against P. aeruginosa isolates, including a wild-type reference, its alginate-hyperproducing mucoid mutant (mucA knockout), its mismatch-repair-deficient hypermutatable mutant (mutS knockout), and the double mucA–mucS mutant [6], has been studied. These phenotypes are fairly relevant in chronic conditions such as CF. Ceftolozane was found to have potent, concentration-independent biofilm bactericidal activity against both the mucoid strain and the hypermutatable strains. This study suggests that resistance to ceftolozane cannot be driven by single-step mutations in wild-type, mucoid, or hypermutatable strains, which is important in infections where P. aeruginosa eradication from the respiratory tract is not generally attainable after colonization has been established.
Although the only currently approved ceftolozane/tazobactam dosage is 1.5 g every 8 h, there is an ongoing clinical trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of ceftolozane/tazobactam at 3 g every 8 h for pneumonia [13, 21]. In addition, the 3-g dose has been used safely with success in patients with CF exacerbations [10, 11]. In one study, ceftolozane/tazobactam use resulted in a pharmacodynamic target attainment of more than 90% at MICs up to 8, 4, and 2 mg/L with 1.5 g every 8 h and 16, 8, and 4 mg/L with 3 g every 8 h with free time above the MIC target of 39%, 60%, and 100%, respectively [11]. There is no currently accepted free time above the MIC required for successfully treating acute CF exacerbations with ceftolozane/tazobactam. Until this is established, the authors of that study recommend the use of 3 g for CF patients with pulmonary exacerbations. Our study demonstrates that ceftolozane/tazobactam achieved bactericidal killing in MP strains from CF patients, but a more potent reduction of inoculum occurred with the 3-g dose as compared with the 1.5-g dose. Given our results, use of the higher-dose regimen seems appropriate for these patients.
There are some limitations to the study, as the data represent only in vitro efficacy. Only ten isolates were included in the study; therefore, we cannot extrapolate the conclusions of the time–kill analysis to other isolates, especially ones demonstrating higher ceftolozane/tazobactam MICs. In addition, although a deeper characterization of resistance mechanisms would have been interesting, we did not have the financial resources to determine β-lactam resistance mechanisms for ceftazidime and cefepime at this time.
Conclusion
As resistance in P. aeruginosa increases, newer antibiotics with expanded activity are needed. Ceftolozane/tazobactam (1.5 and 3 g) demonstrates activity against MP strains derived from CF patients comparable to that of SOC agents. However, further in vitro modeling and clinical trials are warranted.
References
Govan JR, Deretic V. Microbial pathogenesis in cystic fibrosis: mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia. Microbiol Rev. 1996;60(3):539–74.
Boucher JC, Yu H, Mudd MH, Deretic V. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: characterization of muc mutations in clinical isolates and analysis of clearance in a mouse model of respiratory infection. Infect Immun. 1997;65(9):3838–46.
Lyczak JB, Cannon CL, Pier GB. Lung infections associated with cystic fibrosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002;15(2):194–222.
Parad RB, Gerard CJ, Zurakowski D, Nichols DP, Pier GB. Pulmonary outcome in cystic fibrosis is influenced primarily by mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection and immune status and only modestly by genotype. Infect Immun. 1999;67(9):4744–50.
Llanes C, Pourcel C, Richardot C, et al. Diversity of β-lactam resistance mechanisms in cystic fibrosis isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a French multicentre study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013;68(8):1763–71.
Riera E, Macia MD, Mena A, et al. Anti-biofilm and resistance suppression activities of CXA-101 against chronic respiratory infection phenotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO1. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010;65(7):1399–404.
Kuti JL, Pettit RS, Neu N, et al. Microbiological activity of ceftolozane/tazobactam, ceftazidime, meropenem, and piperacillin/tazobactam against Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from children with cystic fibrosis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015;83(1):53–5.
Livermore DM, Mushtaq S, Ge Y, Warner M. Activity of cephalosporin CXA-101 (FR264205) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia group strains and isolates. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009;34(5):402–6.
Zamorano L, Juan C, Fernandez-Olmos A, Ge Y, Canton R, Oliver A. Activity of the new cephalosporin CXA-101 (FR264205) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from chronically-infected cystic fibrosis patients. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010;16(9):1482–7.
Vickery SB, McClain D, Wargo KA. Successful use of ceftolozane-tazobactam to treat a pulmonary exacerbation of cystic fibrosis caused by multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pharmacotherapy. 2016;36(10):e154–9.
Monogue ML, Pettit RS, Muhlebach M, Cies JJ, Nicolau DP, Kuti JL. Population pharmacokinetics and safety of ceftolozane/tazobactam in adult cystic fibrosis patients admitted with acute pulmonary exacerbation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(11):6578–84.
Barber KE, Ireland CE, Bukavyn N, Rybak MJ. Observation of “seesaw effect” with vancomycin, teicoplanin, daptomycin and ceftaroline in 150 unique MRSA strains. Infect Dis Ther. 2014;3(1):35–43.
US National Library of Medicine. Dailymed. 2017. http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/index.Cfm. Accessed 15 Sep 2016.
Harding SM, Monro AJ, Thornton JE, Ayrton J, Hogg MI. The comparative pharmacokinetics of ceftazidime and cefotaxime in healthy volunteers. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981;8(Suppl B):263–72.
Barbhaiya RH, Forgue ST, Gleason CR, et al. Pharmacokinetics of cefepime after single and multiple intravenous administrations in healthy subjects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992;36(3):552–7.
Barbhaiya RH, Knupp CA, Forgue ST, Matzke GR, Guay DR, Pittman KA. Pharmacokinetics of cefepime in subjects with renal insufficiency. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1990;48(3):268–76.
Smyth A, Tan KH, Hyman-Taylor P, et al. Once versus three-times daily regimens of tobramycin treatment for pulmonary exacerbations of cystic fibrosis—the topic study: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;365(9459):573–8.
Zavascki AP, Goldani LZ, Cao G, et al. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous polymyxin B in critically ill patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47(10):1298–304.
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. M100. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. 27th ed. Wayne: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2017.
Cabot G, Bruchmann S, Mulet X, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa ceftolozane-tazobactam resistance development requires multiple mutations leading to overexpreession and structural modification of AmpC. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(6):3091–9.
ClinicalTrails.gov. Safety and efficacy of ceftolozane/tazobactam to treat ventilated nosocomial pneumonia (MK-7625A-008) (ASPECT-NP). 2017. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02070757. Accessed 15 Sept 2016.
Acknowledgements
We thank Merck for providing ceftolozane powder and ceftolozane/tazobactam Etests. No funding or sponsorship was received for this study or publication of this article. The article processing charges were funded by the authors. No professional medical writers were involved in the preparation of the manuscript, and no reimbursement was received for preparation of this article. All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors criteria for authorship of the manuscript, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given final approval for the version to be published.
Disclosures
Kayla R. Stover has received grant support from Astellas and MAD-ID. Jamie L. Wagner has received grant support through MAD-ID. Katie E. Barber has received grant support through Allergan and MAD-ID. Hana Rac, S. Travis King, and Henderson D. Warnock have nothing to declare. We do not own any stocks or shares relevant to this study. Hana Rac was a PGY2 Infectious Diseases Resident (University of Mississippi Medical Center) at the time of completion of this manuscript. Her current affiliation is University of South Carolina College of Pharmacy.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This study was approved by the Institutional Biosafety Committee. This article does not contain any new studies with humans or animals performed by any of the authors.
Data Availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Enhanced content
To view enhanced content for this article go to http://www.medengine.com/Redeem/27CCF060674E9060.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Rac, H., Stover, K.R., Wagner, J.L. et al. Time–Kill Analysis of Ceftolozane/Tazobactam Efficacy Against Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains from Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Infect Dis Ther 6, 507–513 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40121-017-0176-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40121-017-0176-8