Abstract
Introduction
The globus pallidus internus (GPi) region has evolved as a potential target for deep brain stimulation (DBS) in Parkinson’s disease (PD). DBS of the GPi (GPi DBS) is an established, safe and effective method for addressing many of the motor symptoms associated with advanced PD. It is important that clinicians fully understand this target when considering GPi DBS for individual patients.
Methods
The literature on GPi DBS in PD has been comprehensively reviewed, including the anatomy, physiology and potential pitfalls that may be encountered during surgical targeting and post-operative management. Here, we review and address the implications of lead location on GPi DBS outcomes. Additionally, we provide a summary of randomized controlled clinical trials conducted on DBS in PD, together with expert commentary on potential applications of the GPi as target. Finally, we highlight future technologies that will likely impact GPi DBS, including closed-loop adaptive approaches (e.g. sensing-stimulating capabilities), advanced methods for image-based targeting and advances in DBS programming, including directional leads and pulse shaping.
Results
There are important disease characteristics and factors to consider prior to selecting the GPi as the DBS target of PD surgery. Prior to and during implantation of the leads it is critical to consider the neuroanatomy, which can be defined through the combination of image-based targeting and intraoperative microelectrode recording strategies. There is an increasing body of literature on GPi DBS in patients with PD suggesting both short- and long-term benefits. Understanding the GPi target can be useful in choosing between the subthalamic (STN), GPi and ventralis intermedius nucleus as lead locations to address the motor symptoms and complications of PD.
Conclusion
GPi DBS can be effectively used in select cases of PD. As the ongoing DBS target debate continues (GPi vs. STN as DBS target), clinicians should keep in mind that GPi DBS has been shown to be an effective treatment strategy for a variety of symptoms, including bradykinesia, rigidity and tremor control. GPi DBS also has an important, direct anti-dyskinetic effect. GPi DBS is easier to program in the outpatient setting and will allow for more flexibility in medication adjustments (e.g. levodopa). Emerging technologies, including GPi closed-loop systems, advanced tractography-based targeting and enhanced programming strategies, will likely be future areas of GPi DBS expansion. We conclude that although the GPi as DBS target may not be appropriate for all PD patients, it has specific clinical advantages.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
We review the history of the globus pallidus internus (GPi) as target for deep brain stimulation (DBS), which is now an established, safe and effective method of treating the motor complications of advanced Parkinson’s disease (PD). |
We comprehensively review the literature on GPi DBS for PD, including anatomy, physiology, somatotopy, surgical targeting and management, potential pitfalls and optimal location for lead placement. |
We outline the evidence underlying the effectiveness of GPi DBS in PD for managing PD symptoms. |
We present common patient programming strategies in GPi DBS and strategies to avoid adverse effects |
We discuss new emerging technologies that will modify application of GPi DBS in PD in the future. |
Digital Features
This article is published with digital features, including a summary slide, to facilitate understanding of the article. To view digital features for this article go to https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.13061327.
Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder resulting from progressive loss of nigrostriatal neurons and also from widespread degeneration and deposition of alpha synuclein across multiple basal ganglia networks [1]. Patients may manifest various combinations of the typical motor symptoms, such as tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, postural instability and gait and balance difficulties, and also non-motor symptoms, such as mood and cognitive difficulties, autonomic dysfunction, speech and swallowing difficulties and sexual dysfunction [1]. Although levodopa remains the gold standard pharmacological treatment for PD, long-term use coupled with disease progression often lead to complications, including dyskinesias and motor fluctuations in approximately 50% of patients at 5 years [2, 3]. These complications significantly impair quality of life and can transform into one of the major sources of disability in PD patients [4]. Invasive approaches, such as ablative procedures [5, 6], carbidopa/levodopa intestinal gel [7], subcutaneous apomorphine infusions and deep brain stimulation (DBS) [8], have been utilized over the past 3 decades to address these PD-related symptoms. Evolving from lesional therapies, DBS is a modality that can be applied to various brain regions, with the globus pallidus interna (GPi) and subthalamic nucleus (STN) being the most common targets of DBS for the management of PD. Occasionally, the ventralis intermedius nucleus (VIM) is used as the target, mainly in tremor-predominant cases where tremor is the sole disability.
The focus of this comprehensive review and expert commentary is on multiple aspects of pallidal stimulation for PD, including the history, anatomical and physiological characteristics of DBS of the GPi (GPi DBS), target selection, surgical planning and patient programming strategies. We also present the evidence on clinical effectiveness and on the potential for next-generation neuromodulatory approaches which may possibly utilize GPi DBS.
This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
GPi in the History of Deep Brain Stimulation
The first evidence of surgical interventions using the basal ganglia as a potential treatment modality to mitigate symptoms of PD dates back to 1939 with Meyers resecting the anterior two-thirds of the caudate nucleus. The procedure led to improvement of postencephalitic parkinsonian tremor [9, 10]. The subsequent advent of a functional neurosurgery apparatus in 1947 by Spiegel and Wycis (e.g. the head frame) opened the door to the era of stereotactic ablative therapies [11, 12]. Surgeons began to explore lesions of the pallidum and its connections (pallidoanostomies) for various disorders, including PD [11]. Subsequently, additional targets for surgical treatment of PD were also explored, including ligation of the anterior choroidal artery by Cooper [13], chemopallidotomy by Narabayashi and Okuma [14] and pallidotomy via electrical coagulation by Guiot and Brion [15]. These studies were all reported in the early 1950s. Also in the 1950s, Leksell and colleagues began performing stereotactic thermocoagulation-induced pallidotomies, shifting from the initial anterodorsal pallidum approach to posteroventral interventions. These surgeons felt that this shift yielded improved antiparkinsonian benefits [16]. In the same decade, Hassler and Riechert explored the thalamus as an additional surgical target for PD, ultimately resulting in 1954 with successful ablations of the VIM nucleus of the thalamus that improved parkinsonian tremor [17].
Lesional therapies thus became an important treatment for advanced PD and were considered the best treatment until the introduction of levodopa in 1968 [18]. With the initiation of a safe and effective medication therapy for PD, enthusiasm for surgical interventions dwindled. It was only with the emergence of complications resulting from prolonged dopaminergic therapy combined with disease progression (disabling peak-dose levodopa-induced dyskinesias, motor fluctuations including severe off-freezing) that led to the revisiting of lesion therapies. Posteroventral pallidotomy would reemerge as an ablative brain surgery for PD in the late 1980s [19].
In 1987, Benabid, Pollack and colleagues observed, while using intraoperative electrophysiological recordings to ensure accuracy of the target (prior to ablation), that high-frequency electrical stimulation (≥ 100 Hz) could reversibly suppress both parkinsonian rest tremor and postural tremor [20]. The notion of combining electrical stimulation (utilized for brain mapping prior to permanent lesioning therapy) with the existing implantable pulse generator technology (adapted from cardiac pacemakers) birthed a new chronic neuromodulatory approach [11]. This approach would largely replace bilateral thalamotomy as the treatment for PD tremor. In the early 1990s, additional targets for DBS emerged, including the STN [21] and the GPi [22], which have since been carefully evaluated in multiple clinical trials [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. The historical aspects of surgical therapies which later contributed to the rise of DBS as a means to address the motor symptoms and complications in PD are summarized in Fig. 1.
GPi: PD Pathophysiology, Anatomy and Somatotopy
The basal ganglia rate model, which postulated that an abnormal increase in GPi activity would result in thalamic inhibition and decreased prokinetic cortical activity, was one of the initial pathophysiological hypotheses potentially explaining PD symptoms [32, 33]. However, this model failed to elucidate the subsequent observations of GPi lesions not resulting in akinesia nor did it explain tremor control, dyskinesia reduction or the therapeutic benefit of dystonic symptoms. Much work has since been done, ultimately demonstrating that an aberrant network oscillatory activity is related to the pathophysiology of PD [34]. Exaggerated pallidal oscillations in the beta range (12–30 Hz) have been associated with bradykinesia severity and have been observed to attenuate with levodopa administration and with therapeutic DBS [35,36,37,38,39]. Beta power in the GPi in PD has also been shown to decrease with increased volitional movement, a phenomenon not exclusive to PD patients [38,39,40,41,42,43]. The results of subsequent DBS studies have suggested that neuromodulation may affect the oscillatory activity at a network circuitry level rather than by simply increasing or decreasing the firing rate of a single basal ganglia structure [34]. These findings have provided an opportunity for the further understanding of the network oscillations and physiology inclusive of multiple PD brain regions, including the GPi. Such information could facilitate the development of more targeted therapies using next-generation neuromodulatory devices.
Understanding the anatomy of the pallidum and its neighboring structures is of crucial importance to improve clinical DBS outcomes. The globus pallidus consists of internal (GPi) and external (GPe) segments. Along with the substantia nigra pars reticulata, the GPi relays information from the striatum, GPe and STN to the thalamus, although there are many other connections [44]. Post-mortem evaluations have reported GPi volumes ranging from 263.5 to 494.0 mm3; however, the mean volume values usually range between 400 and 500 mm3 [45]. A recent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) evaluation of ten healthy, right-handed controls reported a mean GPi volume of 541.4 ± 81.9 mm3 [46], revealing that the GPi has roughly threefold the volume of the STN [45], which typically ranges in size from 150 to 300 mm3. Important to understanding the volume of targets is the continuous atrophy which occurs faster in PD than in control subjects and that this atrophy could affect DBS outcomes [47].
A dissected view of the GPi and its surrounding structures is shown in Fig. 2. Within the GPi, there are three distinct functional regions: the postero-ventro-lateral sensorimotor territory [48], the anterior associative territory, and the anteroventral limbic territory [49]. Alternative atlases using multimodal MRI, histology and structural connectivity have defined primary motor, sensorimotor and sensory regions of the GPi [50]. These distinct functional regions, along with a potentially optimal DBS lead placement for the symptomatic control of PD patients, are illustrated in Fig. 3. The sensorimotor region of the GPi is usually the DBS target for both for PD and dystonia [51, 52]. In this region, upper extremity somatotopy is usually located ventral and lateral to the area representing the lower limb, and orofacial movement is located even further ventral to that of the upper extremities (Fig. 4) [53]. Although many of these representations have been shown mainly in primate models of PD and in dystonia [54], they have been replicated by imaging studies and human intraoperative studies [49, 55].
Dissection of white matter of the internal globus pallidus (GPi). a Lateral to medial dissections, b anterior to posterior dissections, c medial to lateral dissections, d inferior to superior dissections showing relationship of GPi to the optic tract, e inferior to superior dissections showing relationship of GPi to external globus pallidus (GPe), putamen and internal capsule (Int. Caps.), f deep brain stimulation of the GPi lead trajectory dissections until the GPi is reached. Accumb Accumbens, Ant. anterior, Comm. commissure, Caud. caudate, CN III third cranial nerve, Cor. Rad. corona radiata, Gl. gland, Innom. innominata, Nucl. nucleus, Olf. olfactory, Post. posterior, Subst. substantia, Tr. tract
Targeting and Intraoperative Physiology of the GPi: Pearls and Pitfalls
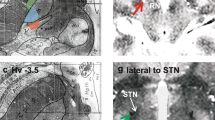
The GPi region includes the GPe dorsally and laterally, the optic tract ventrally and the internal capsule medially and posteriorly (Fig. 5). As previously mentioned, proper identification of these neighboring landmarks is important during intraoperative mapping and for selecting the final DBS lead position. Differences in targeting protocols, quality of imaging and utilization of microelectrode recordings together with macrostimulation may contribute significantly to the determination of final DBS lead localization. Many of these techniques have evolved over many years.
In the early years of DBS surgery, indirect stereotactic targeting methods were used, as first described by Laitinen and colleagues, [19, 56]. However, the substantial variability in GPi size, shape and position relative to the midcommissural point among patients [57], along with some variability in the technique used by neurosurgeons for identifying the midcommissural point [58], has rendered such indirect GPi targeting methods unreliable. As a result, indirect targeting has been largely abandoned as a stand-alone technique and is currently used primarily as a starting point for direct anatomical approaches using high-quality imaging [59].
Improvements in imaging technology have lead to the utilization of direct targeting methods, which better account for patient-specific anatomical variation and can be used to improve the accuracy of the final GPi DBS lead position [57]. The fast gray matter acquisition T1 inverse recovery (FGATIR) 3T MRI sequence has been used by many groups to achieve direct visualization and a sharper delineation of the boundaries of subcortical structures, such as the STN, GPe, GPi, and the internal capsule, thereby improving GPi DBS targeting [60]. The use of this sequence has resulted in up to a threefold improvement in contrast-to-noise ratio when compared to T1 and T2/fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) MRI sequences [60]. Hybrid quantitative susceptibility mapping has also been used as a method to visualize the GPi and, similar to FGATIR MRI, it has shown reproducibility across centers [61]. When utilizing imaging for direct targeting, attention should be directed not only to a target point, but also to the position of the DBS electrode array relative to the optimal target volume. For example, in a situation where the entry angle is adjusted to a more lateral position to avoid a cortical vein, the target point should be revised medially to accommodate the adjustment and to avoid a lateral placement of the DBS lead contacts in relation to the target. Subsequently, entry angles may significantly impact GPi outcomes. A GPi DBS lead with a more vertical trajectory produces a more favorable configuration, with more contacts positioned within an optimal target volume as compared to a GPi lead with an entry point that is excessively anterior or lateral.
In addition to the advances in imaging modalities and software that have facilitated direct targeting, neurophysiological data from microelectrode recording (MER) and macrostimulation via the implanted DBS lead can also be used to further refine the final DBS lead placement. A typical GPi DBS entry angle trajectory (60–70° sagittal angle relative to the intercommissural plane, 5–15° coronal angle relative to the median plane) will traverse the striatum, corona radiata, GPe, GPi and the optic tract. MER typically shows characteristic cell firing frequencies and patterns for each of these structures, and these data can aid in the localization of the anatomical position of the individual MER tracts. Striatal cells tend to fire irregularly, at very low frequency (4–6 Hz), and are commonly activated by mechanical or electrical stimulation. Neuronal activity in the GPe is characterized by a low firing frequency (19–34 Hz) with occasional bursting cells. GPi cells in PD typically exhibit high tonic frequency, often with bursts (24–82 Hz). In both GPe and GPi, both short and long pauses can occur during MER recordings, with fewer pauses occurring in the GPi which possesses a more tonic pattern. The GPe can also manifest intermittent and characteristic “bursting” cells. Border cells are commonly encountered between the GPe and GPi, inside of the GPi (lamina), or on the posterior or ventral border of the GPi. The position of the optic tract can also provide useful information to optimize the ventral GPi DBS lead position. During MER, visual evoked potentials can be elicited by shining a flashlight into the eye. In the majority of cases, a soft audible evoked potential can be elicited through the audio speakers. An evoked potential that is “loud or prominent” may suggest a medial position of the DBS lead, but it should be noted that the trajectory can impact this finding.
When optimally exploited, MER “mapping” can be used to more precisely localize the target in anatomical space. Increasing the number of microelectrode passes can improve localization of the target, but it can also increase the risk of the procedure (and the intraoperative time) [62]. The sophistication of MER data interpretation has improved, and in most centers the number of MER passes per case has decreased. For GPi DBS procedures performed in the future, it is conceivable that less MER exploiting macrostimulation will be required through the use of the MER guidetube sheath, which may generate sufficient information to inform optimal lead positioning. More data will be required to refine such an approach. These techniques, however, should each be adapted and be based on user experience and degree of comfort.
Once MER mapping has been performed and a potential tract for the final DBS lead has been selected, macrostimulation via the implanted DBS lead can serve as a final test to confirm appropriate positioning. Macrostimulation is often performed at a pulse width of 60–90 μs with a frequency of 130–180 Hz (parameters commonly used in DBS in chronic PD). The amplitude (voltage) is gradually increased at each contact to determine thresholds for stimulation-induced optic, sensory and motor side effects. During macrostimulation, the distance of the most ventral DBS contact from the optic tract can be estimated. This is usually accomplished by the clinician darkening the operating suite, asking the patient to close her/his eyes and then determining the threshold voltage for perceptible light response in the contralateral visual field (e.g. phosphenes). Combined with capsular thresholds, optic tract information can be used to confirm or to adjust the lead position. If the optic tract threshold cannot be elicited by this technique and capsular thresholds are appropriate (2–4 V), then it is possible the lead is located in too shallow of a position. If the optic tract threshold is absent and capsular thresholds are high (4–6 V), the lead may be lateral or anterior. If the optic tract threshold is low and capsular thresholds are also low (< 2 V), the lead may possibly be medial. While intraoperative side effect thresholds do not always predict postoperative effects, excessively low side effect thresholds should prompt strong consideration of DBS lead repositioning.
While the DBS lead position can be estimated based on high-quality imaging, it is the physiological effect, and not radiographic imaging, that will ultimately determine the success or failure of the DBS surgery. A well-positioned DBS lead produces appropriately wide therapeutic windows for stimulation and facilitates easy DBS programming at the bedside. While directional stimulation and/or complex programming strategies can sometimes salvage a reasonable DBS outcome in a suboptimally placed lead, it is important to try to avoid the need for salvage. Optimizing the intraoperative testing protocol can ensure a DBS lead is well placed before exiting the operating room. Table 1 shows the typical lead location based on MER and macrostimulation effects. Though many experienced centers have abandoned intraoperative physiology in favor of asleep, image-guided DBS implantation, there are advantages to an awake approach. Interacting with an awake patient during DBS can help to determine the precise thresholds for adverse effects during macrostimulation; this approach may not be feasible with an asleep patient.
Our DBS team has implanted over 850 GPi DBS leads over the past 18 years, and many of the previously mentioned aspects of this section of the commentary pertain to observations and insights based on our cumulative experience [59, 61, 63]. Within the sensorimotor territory, positioning the DBS electrode 3 mm lateral to the medial internal capsule–GPi border, and 3–5 mm anterior to the posterior internal capsule–GPi border seems to be, in our experience, the optimal site for chronic therapeutic stimulation when using omnidirectional ring electrodes. The deepest contact is ideally situated immediately superior to the lateral aspect of the ipsilateral optic tract. With this lead position, there is a greater likelihood of maximum efficacious stimulation to the sensorimotor region of GPi without intolerable stimulation-induced side effects that may inadvertently occur from the spread of current into the internal capsule.
It is our group’s opinion that postoperative imaging should be obtained to carefully assess the position of every implanted DBS lead and that this information be used to facilitate programming. Appropriate DBS quality control should include neurosurgeons receiving feedback from the clinicians programming the implanted devices. Holanda et al. [63] performed a GPi DBS observational series of 299 patients over a 15-year period. These authors demonstrated a gradual shift over time toward a more lateral and ventral placement of the GPi DBS leads and hypothesized that the move was primarily driven by clinician feedback and based largely on device programmability within the clinic setting [63]. Following this overall strategy of utilizing imaging and direct targeting, intraoperative techniques with MER mapping and macrostimulation and with the implementation of postoperative imaging to provide feedback and adjustments a DBS team can usually increase the likelihood of achieving a successful outcome [64].
GPi DBS Versus STN DBS in PD: Effectiveness, Side Effect Profile and Long-Term Outcomes
Effectiveness and Side Effect Profile
The “best target for DBS in PD, whether STN versus GPi” has been the subject of a large body of recent literature [65, 66]. However, even though experts agree that targets should be chosen based on a patient’s unique characteristics [65, 66], worldwide STN remains the preferred target for DBS in patients with advanced PD. This was pointed out by the DBS for PD Study Group (2001), commenting on the bias towards STN DBS (n = 96) over GPi DBS (n = 38) [24, 67]. As a consequence of this bias, a greater amount of data on STN outcomes has been generated over the subsequent years when compared to data on GPi DBS outcomes. However, since the initial experience of GPi DBS in PD shared by Siegfried and Lippitz [22], several other case studies have replicated the positive GPi DBS results [68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84] and, more importantly, the efficacy of GPi as a target for PD has been confirmed in many randomized clinical trials.
The NIH COMPARE trial [29] and the VA study by Weaver et al. [85] both addressed the role of GPi in managing the motor symptoms of PD. Several more recent randomized, double-blind clinical trials have demonstrated that GPi and STN are both viable targets for the motor symptoms and complications of PD [23, 25, 29]. There was however one study (NSTAPS) where the secondary outcome of reducing akinesia favored STN [30]. Collectively, however, the current literature has revealed that stimulation of either STN or GPi can improve the motor features of parkinsonism and positively impact the quality of life.
While STN DBS has been the preferred target for medically refractory tremor in PD, a recent meta-analysis has shown that GPi DBS is effective for tremor control [86]. None of the randomized GPi versus STN DBS comparison trials have revealed an advantage of one target over the other in terms of addressing tremor. They have, however, collectively utilized the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) motor subscores to assess tremor outcomes, which was limited to single items without the ability to assess constancy, duration or associated disability related to the actual tremor.
Data from randomized clinical trials have shown that GPi DBS improves baseline UPDRS motor off-medication scores by 27–54% [68, 70,71,72], which is similar to the improvement in UPDRS motor off-medication scores of 30–67% obtained with STN DBS [28, 30, 68]. The activities of daily living scores have been found to improve on average by 30–39% in GPi DBS and by 6–56% in STN DBS [24, 70,71,72, 87]. The main findings reported for GPi DBS in randomized clinical trials are summarized in Table 2 (case reports in Electronic Supplementary Material Table 1) [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31, 87,88,89,90,91,92,93]. Overall, these results reveal sustained benefits for up to 3 years on motor function, motor fluctuations, dyskinesia and quality of life in both the STN DBS and GPi DBS [28, 94, 95].
In the domain of postoperative medication reduction, data support that STN DBS has a greater impact on reducing the total daily doses of dopaminergic drugs [92] as compared to GPi DBS [93]. However, GPi DBS has shown a powerful direct, anti-dyskinetic effect, with rates of improvement in levodopa-induced dyskinesia ranging from 47 to 88%, in comparison to STN DBS with rates of 20–83% [96]. GPi DBS has also been shown to have a greater anti-dyskinetic effect than STN DBS, a phenomenon that may be largely driven by the need for medication reduction in the STN (e.g. medication reduction required to avoid dyskinesia) [97, 98]. However, there is a subset of patients with STN DBS that have been shown to achieve a 12–16% reduction in dyskinesias, suggesting some possible direct anti-dyskinetic effects in some STN DBS patients [84, 89].
There may be DBS patients who are more susceptible to the occurrence of stimulation-induced dyskinesias (SID). Some authors have referred to this phenomenon as brittle dyskinesia [99, 100]. For example,, a patient who takes a low dose of levodopa (less than a tablet of carbidopa/levodopa 25/100 mg per dose) and experiences a brittle dyskinetic response may be more amenable to GPi DBS over STN DBS. However, these data are supported only by anecdotal experience and a few case reports. Direct comparative studies of this population have not been performed [100]. It is important to consider that following DBS surgery it may be necessary to escalate levodopa dosages to maintain symptom control resulting from disease progression, and GPi may be a more viable target in this scenario due mainly to its direct anti-dyskinetic effects [66]. GPi DBS may have an advantage in providing long-term flexibility for medication adjustments. Patients implanted in the STN have an increased likelihood of dyskinesia if they increase their doses of levodopa post-surgery, an effect that does not seem to occur in most patients implanted in the GPi [25, 28,29,30, 101]. Finally, SID are less commonly observed in GPi DBS when compared to STN DBS, but they can occur by stimulating the most dorsal DBS contact in the GPi/GPe border zone or in the GPe [102].
As neuropsychiatric comorbidities pose one of the main potential contraindications for DBS implantation in PD, postoperative complications and/or stimulation-induced limbic effects have been studied extensively. Mood and cognitive changes have been reported following both STN DBS and GPi DBS [25, 28, 29, 31]. In the 36-month outcome data drawn from the VA study, patients undergoing GPi DBS implantation experienced no change in the Mattis Dementia Rating Scale and Hopkins Verbal Learning Test. Patients in the STN arm of the study experienced worsening in these domains at 3 years postsurgery (p = 0.01) [28]. The COMPARE study did not reveal a difference between STN DBS or GPi DBS in its primary outcome of mood as measured by the eight subscales of the Visual Analogue Mood Scale; however, there were more cognitive adverse events reported in STN DBS [29].
Evaluation of the overall side effect profile has shown that the GPi is similar to the STN as DBS target. A few studies suggest that the more commonly encountered adverse effects on gait, speech and swallowing may possibly be less frequently encountered in GPi DBS [65]. A possible explanation is that the GPi size dimensions are larger and there is thus a more expansive sensorimotor territory when compared to the STN. This expanded territory may allow clinicians to deliver effective stimulation that is more contained within the region of interest, yielding wider therapeutic windows and theoretically fewer adverse effects.
Adverse effects in speech have been more commonly reported in STN DBS than in GPi DBS [103], with a greater proportion of irreversible speech side effects reported (STN: 16.7% irreversible and 5.1% reversible speech adverse effects; GPi: 22.2% reversible speech adverse effects) [104]. There is, however, a paucity of studies directly comparing swallowing function between the two targets [105]. In a retrospective study, Troche et al. demonstrated dysphagia, as measured by the penetration–aspiration scores, to be worse in unilateral STN DBS than in unilateral GPi DBS [106]. Gait disturbances are more commonly reported with STN DBS (16.7%) than with GPi DBS (5.6%); however, the distinct characteristics and elements of gait disturbance in the short and long term have yet to be evaluated [104].
Long-Term Benefit
Few studies have been able to document data for clinical efficacy in the long-term when comparing GPi and STN as targets for DBS. Three studies [92, 107, 108] have reported outcomes of GPi DBS for PD patients with a minimum of 5 years of follow-up. Moro et al. reported sustained improvement in tremor, rigidity and dyskinesia at 5–6 years after surgery in both STN DBS and GPi DBS for advanced PD [92]. Volkmann et al. reported continued improvement in rigidity and dyskinesia at 5 years following bilateral GPi DBS (n = 6) [107]. In two studies in STN DBS, UPDRS motor off-medication scores were reported to be maintained at 5 years, but deterioration at between 5 and 8 years was reported [109, 110], with cognitive dysfunction being present in 17.1 and 16.7% of cases at 5 and 8 years, respectively [109]. Another report on the comparison of GPi DBS and STN DBS showed a maintained benefit from bilateral STN DBS in tremor, bradykinesia and motor fluctuations (n = 18) at 10 years [111]. In a recent study on 16 patients who underwent either unilateral or bilateral GPi DBS with a mean follow-up period of 6 years, Lachenmayer et al. reported sustained improvement in tremor and dyskinesia for 5.5 years [108]. Similarly, in a recent systematic review, Limousin et al. [112] pooled the 5-year outcomes of STN DBS across 551 PD patients from 15 independent studies and demonstrated sustained improvements in tremor, rigidity and dyskinesia at 5 years, while benefits in bradykinesia and axial symptoms decreased between the 1- and 5-year assessments [112]. The evaluation of stimulation-induced dyskinesias has not been systematically reviewed in the long term when comparing GPi DBS and STN DBS for PD.
The overall long-term GPi DBS outcomes appear to be similar to those of STN DBS, including the waning therapeutic effect, specifically on axial symptoms [113]. However, there are considerable differences in clinical profiles and study designs, making a direct comparison difficult. Although randomized controlled trials of GPi DBS and STN DBS have revealed comparable benefits on motor symptoms, dyskinesia and quality of life for up to 3 years of follow-up [28, 94], longer follow-up studies are needed. The differences between GPi DBS and STN DBS use in PD are summarized in Table 3.
Several studies have focused on comparing the STN and GPi as the target of DBS, reporting that this exercise should be patient tailored, factoring in a variety of elements, such as the preoperative presence of dyskinesias, the need for medication reduction and the need for a pre-surgical risk assessment (co-morbid cognitive, psychiatric, balance, speech or swallow disorders). A full multidisciplinary screening is recommended for any patient seeking potential DBS therapy [66]. Many experts cite GPi as an easier target for long-term programming as compared to STN, especially in communities where expert clinicians are not available or are scarce; however, direct comparisons on ease of programming have not been performed. It is possible that GPi DBS gives more flexibility in the use of levodopa in the long term (e.g. less risk of dyskinesia as the need for more levodopa emerges), but again, there is lack of direct comparative data between STN and GPi [66].
Pearls in Programming GPi DBS for PD
Several algorithms have been developed to guide clinicians in GPi DBS programming for PD [8, 114,115,116]. Regarding initial programming, a monopolar review has classically been employed, with a careful assessment of the clinical benefit and therapeutic window for each individual DBS lead contact by using gradual increments in stimulation amplitude and by maintaining a constant pulse width and frequency of stimulation [114, 116]. Although there are slight differences in protocol across institutions, a monopolar survey is usually performed at pulse widths ranging between 60 and 120 μs and at frequencies of 130–185 Hz in the GPi target. These values reflect commonly used initial programming settings following DBS lead implantation [114, 116]. Corticospinal and corticobulbar side effects can be identified by examining for contralateral muscle contractions and dysarthria, respectively, when performing the monopolar review. For example, speech difficulties can be characterized by slurred, strained/strangled speech, imprecise voice quality with occasional bursts of loudness and unanticipated arrests. If the DBS lead is placed excessively medial within the GPi target, corticospinal or corticobulbar side effects can appear at low values of stimulation in all contacts (e.g. low voltage with a constant pulse width and frequency). If the lead is located too posteriorly in the GPi, speech difficulties or muscle contractions may occur with low voltages when activating the most posterior/ventral contacts. However, the threshold to induce side effects will increase (e.g. higher voltage) with more dorsally and anteriorly located contacts based largely on the chosen targeting approach/angle. If the DBS lead is placed excessively lateral, dorsal or anterior to the sensorimotor GPi, the threshold voltages for corticospinal side effects will be wider and, for example, no adverse effects may occur with the dorsal contacts. For leads placed ventrally, given the proximity to the optic tract, frequently there is appreciable visual phenomena (phosphenes), which can possibly be avoided by choosing the more dorsal DBS contacts on the lead. Programming considerations of the final GPi DBS settings should take into account the anatomy and the specific location of each DBS lead for contact.
Impact of GPi in Future Directions for DBS in PD
Is GPi a Viable Target for Closed-loop DBS Systems?
The expanding understanding of the physiology and network effects underpinning pallidal stimulation has led to a more comprehensive view of the pathophysiology underpinning human PD. Beta oscillations (12–30 Hz) have emerged as a potential marker for some PD-related symptoms, making them a potentially viable target for closed-loop neuromodulatory therapy. Commercially available DBS devices are becoming increasingly capable of measuring local field potentials. These devices thus have the potential for patient-tailored adaptive DBS paradigms designed to treat pathological oscillations in an on-demand, closed-loop manner. Sensing–stimulating technology offers the prospect for more efficient neuromodulatory therapy that can potentially prolong battery longevity, be more responsive to individual physiological demands and be associated with fewer side effects. In the first study of its kind in the GPi region, adaptive DBS was well-tolerated when applied to a single PD patient; however, long-term efficacy data was not assessed [37]. In a recent study, Eisinger et al. [34] demonstrated that a greater beta power was present in PD GPi as compared to PD STN, suggesting GPi to be a candidate for closed-loop DBS systems of the future [39]. Although preliminary work for the safety, feasibility and effectiveness of closed-loop systems in PD has been mostly restricted to targeting the STN [37, 117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124], more studies in the future will likely explore the GPi, especially given the robustness of the physiological signal [37].
Understanding Pallidal Sub-Regions and Their Role in Network Modeling
Going beyond a better understanding of the anatomy and physiology, it is likely that a comprehensive exploration of the relationship between the pallidum and other brain circuitries will be pursued. This information will shine a light on different diseases and techniques, such as MRI diffusion tractography. In 2018, Middlebrooks et al. [59] employed structural connectivity profiling techniques to parcellate the GPi based on axonal connectivity to other neural structures. This approach provided a method to visualize the GPi based on histology and on functional anatomy [59, 125, 126]. Eleven unilateral PD GPi DBS patients underwent modeling of the volume of tissue activation based on clinic programming parameters which were correlated with the connectivity-based segmentation. Across the ten pre-defined connectivity-based targets (caudate, GPe, primary motor cortex, pedunculopontine nucleus, prefrontal cortex, putamen, supplemental motor area, STN, substantia nigra and thalamus), the authors found greater improvement in the UPDRS part III (motor examination) with a greater activation of GPi regions. There was a strong connectivity to the primary motor cortex and supplemental motor area. This work is just one example of the importance of understanding GPi subregions and connectivity profiles as we develop new treatment approaches. As technology evolves, new methods and techniques will emerge and refine presurgical planning. This will hopefully improve the procedure, refine lead placement, expedite the DBS programming and ultimately lead to improved outcomes.
Conclusion
Surgery within the GPi region alleviates many of the symptoms of PD, and this approach has been refined from clinical experience using lesioning protocols. As the ongoing target debate continues (GPi vs. STN), clinicians should keep in mind that GPi DBS has been shown to be effective for a variety of symptoms, including bradykinesia, rigidity and tremor control. GPi DBS also has an important, direct anti-dyskinetic effect. Long-term outcomes of pallidal DBS appear to show sustained benefit for up to 6 years following surgery. The adverse effect profile of GPi DBS is similar to that of STN DBS, although it may be associated with less speech, swallow and gait difficulties. In addition to these potential advantages, GPi DBS might also be an easier target to program and allow more long-term flexibility for medication adjustments (e.g. levodopa) that are commonly required with PD progression. Emerging technologies, including GPi closed-loop systems, advanced tractography-based targeting and enhanced programming strategies, warrant further research. We conclude that although the GPi target may not be appropriate for all PD DBS patients, it has specific advantages.
References
Rizek P, Kumar N, Jog MS. An update on the diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease. Can Med Assoc J. 2016;188(16):1157–65. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.151179.
Pandey S, Srivanitchapoom P. Levodopa-induced dyskinesia: clinical features, pathophysiology, and medical management. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2017;20(3):190–8.
Ahlskog JE, Muenter MD. Frequency of levodopa-related dyskinesias and motor fluctuations as estimated from the cumulative literature. Mov Disord. 2001;16(3):448–58.
Maetzler W, Liepelt I, Berg D. Progression of Parkinson’s disease in the clinical phase: potential markers. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8(12):1158–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70291-1.
Moosa S, Martínez-Fernández R, Elias WJ, del Alamo M, Eisenberg HM, Fishman PS. The role of high-intensity focused ultrasound as a symptomatic treatment for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2019;34(9):1243–51.
Ohye C, Higuchi Y, Shibazaki T, et al. Gamma knife thalamotomy for Parkinson disease and essential tremor: a prospective multicenter study. Clin Neurosurg. 2012;70(3):526–35.
Wirdefeldt K, Odin P, Nyholm D. Levodopa-carbidopa intestinal gel in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review. CNS Drugs. 2016;30(5):381–404.
Hartmann CJ, Fliegen S, Groiss SJ, Wojtecki L, Schnitzler A. An update on best practice of deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2019;12(6):175628641983809. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756286419838096.
Abel TJ, Howard MA. Russell Meyers (1905–1999): pioneer of functional and ultrasonic neurosurgery. J Neurosurg. 2016;125(6):1589–95.
Meyers R. Surgical procedure for postencephalitic tremor with notes on the physiology of premotor fibers. Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1940;44:455–9.
Hariz MI, Blomstedt P, Zrinzo L. Deep brain stimulation between 1947 and 1987: the untold story. Neurosurg Focus. 2010;29(2):1–10.
Spiegel EA, Wycis HT, Marks M, Lee AJ. Stereotaxic apparatus for operations on the human brain. Science. 1947;106(2754):349–50. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.106.2754.349.
Cooper IS. Ligation of the anterior choroidal artery for involuntary movements—parkinsonism. Psychiatry Q. 1953;27(1–4):317–9.
Narabayashi H, Okuma T. Procaine-oil blocking of the globus pallidus for the treatment of rigidity and tremor of Parkinsonism (preliminary report). Proc Jpn Acad. 1953;29(3):134–7.
Guiot G, Brion S. Treatment of abnormal movement by pallidal coagulation. Rev Neurol (Paris). 1953;89(6):578–80.
Svennilson E, Torvik A, Lowe R, Leksell L. Treatment of parkinsonism by stereotatic thermolesions in the pallidal region. A clinical evaluation of 81 cases. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1960;35(3):358–77.
Hassler R, Riechert T. Indications and localization of stereotactic brain operations. Nervenarzt. 1954;25(11):441–7.
Cotzias GC. L-dopa for Parkinsonism. N Engl J Med. 1968;278(11):630. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM196803142781127.
Laitinen LV, Bergenheim AT, Hariz MI. Leksell’s posteroventral pallidotomy in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosurg. 1992;76(1):53–61. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1992.76.1.0053.
Benabid AL, Pollak P, Louveau A, Henry S, de Rougemont J. Combined (thalamotomy and stimulation) stereotactic surgery of the VIM thalamic nucleus for bilateral Parkinson disease. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1987;50(1–6):344–6.
Pollak P, Benabid AL, Gross C, et al. Effects of the stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson disease. Rev Neurol (Paris). 1993;149(3):175–6.
Siegfried J, Lippitz B. Bilateral chronic electrostimulation of ventroposterolateral pallidum. Neurosurgery. 1994;35(6):1126–30.
Anderson VC, Burchiel KJ, Hogarth P, Favre J, Hammerstad JP. Pallidal vs subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol. 2005;62(4):554–60.
Obeso JA, Olanow CW, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, et al. Deep-brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus or the pars interna of the globus pallidus in Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(13):956–63.
Follett KA, Weaver FM, Stern M, et al. Pallidal versus subthalamic deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(22):2077–91.
Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Obeso JA, Lang AE, et al. Bilateral deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: a multicentre study with 4 years follow-up. Brain. 2005;128(10):2240–9.
Weaver FM, Follett K, Stern M, et al. Bilateral deep brain stimulation vs best medical therapy for patients with advanced parkinson disease: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009;301(1):63. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2008.929.
Weaver FM, Follett KA, Stern M, et al. Randomized trial of deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease: thirty-six-month outcomes. Neurology. 2012;79(1):55–65.
Okun MS, Fernandez HH, Wu SS, et al. Cognition and mood in Parkinson’s disease in subthalamic nucleus versus globus pallidus interna deep brain stimulation: the COMPARE trial. Ann Neurol. 2009;65(5):586–95.
Odekerken VJJ, van Laar T, Staal MJ, et al. Subthalamic nucleus versus globus pallidus bilateral deep brain stimulation for advanced Parkinson’s disease (NSTAPS study): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12(1):37–44.
Rothlind JC, York MK, Carlson K, et al. Neuropsychological changes following deep brain stimulation surgery for Parkinson’s disease: comparisons of treatment at pallidal and subthalamic targets versus best medical therapy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015;86(6):622–9.
Albin RL, Young AB, Penney JB. The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders. Trends Neurosci. 1989;12(10):366–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-2236(89)90074-X.
DeLong MR. Primate models of movement disorders of basal ganglia origin. Trends Neurosci. 1990;13(7):281–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-2236(90)90110-V.
Eisinger RS, Cernera S, Gittis A, Gunduz A, Okun MS. A review of basal ganglia circuits and physiology: application to deep brain stimulation. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2019.01.009.
Weinberger M, Hutchison WD, Alavi M, et al. Oscillatory activity in the globus pallidus internus: comparison between Parkinson’s disease and dystonia. Clin Neurophysiol. 2012;123(2):358–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2011.07.029.
Jimenez-Shahed J, Telkes I, Viswanathan A, Ince NF. GPi oscillatory activity differentiates tics from the resting state, voluntary movements, and the unmedicated Parkinsonian state. Front Neurosci. 2016. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2016.00436.
Piña-Fuentes D, van Zijl JC, van Dijk JMC, et al. The characteristics of pallidal low-frequency and beta bursts could help implementing adaptive brain stimulation in the Parkinsonian and dystonic internal globus pallidus. Neurobiol Dis. 2019;121:47–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2018.09.014.
Wang DD, de Hemptinne C, Miocinovic S, et al. Pallidal Deep-brain stimulation disrupts pallidal beta oscillations and coherence with primary motor cortex in Parkinsons disease. J Neurosci. 2018;38(19):4556–68. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0431-18.2018.
Eisinger RS, Cagle J, Opri E, et al. Parkinsonian beta dynamics during rest and movement in the dorsal pallidum and subthalamic nucleus. J Neurosci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2113-19.2020.
Tsang EW, Hamani C, Moro E, et al. Movement related potentials and oscillatory activities in the human internal globus pallidus during voluntary movements. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2011;83(1):91–7. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2011.243857.
Tsiokos C, Malekmohammadi M, AuYong N, Pouratian N. Pallidal low β-low γ phase-amplitude coupling inversely correlates with Parkinson disease symptoms. Clin Neurophysiol. 2017;128(11):2165–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/2Fj.clinph.2017.08.001.
Liu X, Yianni J, Wang S, Bain PG, Stein JF, Aziz TZ. Different mechanisms may generate sustained hypertonic and rhythmic bursting muscle activity in idiopathic dystonia. Exp Neurol. 2006;198(1):204–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/2Fj.expneurol.2005.11.018.
Brücke C, Kempf F, Kupsch A, et al. Movement-related synchronization of gamma activity is lateralized in patients with dystonia. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27(9):2322–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/2Fj.1460-9568.2008.06203.x.
Nambu A. Globus pallidus internal segment. Prog Brain Res. 2007;160(06):135–50.
Mulder MJ, Keuken MC, Bazin P-L, Alkemade A, Forstmann BU. Size and shape matter: the impact of voxel geometry on the identification of small nuclei. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(4):e0215382.
Vasques X, Cif L, Hess O, Gavarini S, Mennessier G, Coubes P. Prognostic value of globus pallidus internus volume in primary dystonia treated by deep brain stimulation. J Neurosurg. 2009;110(2):220–8.
Martinez-Ramirez D, Morishita T, Zeilman PR, Peng-Chen Z, Foote KD, Okun MS. Atrophy and other potential factors affecting long term deep brain stimulation response: a case series. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:10.
Nambu A. Somatotopic organization of the primate basal ganglia. Front Neuroanat. 2011;5:1–9.
Cacciola A, Milardi D, Bertino S, et al. Structural connectivity-based topography of the human globus pallidus: Implications for therapeutic targeting in movement disorders. Mov Disord. 2019;34(7):987–96.
Ewert S, Plettig P, Li N, et al. Toward defining deep brain stimulation targets in MNI space: a subcortical atlas based on multimodal MRI, histology and structural connectivity. Neuroimage. 2018;170:271–82.
DeLong MR. Activity of pallidal neurons during movement. J Neurophysiol. 1971;34(3):414–27. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1971.34.3.414.
Heilbrun MP, Koehler S, McDonald P, Faour F. Optimal target localization for ventroposterolateral pallidotomy: the role of imaging, impedance measurement, macrostimulation and microelectrode recording. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1997;69(1–4):19–27.
DeLong MR, Crutcher MD, Georgopoulos AP. Primate globus pallidus and subthalamic nucleus: functional organization. J Neurophysiol. 1985;53(2):530–43. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1985.53.2.530.
Baker KB, Lee JYK, Mavinkurve G, et al. Somatotopic organization in the internal segment of the globus pallidus in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol. 2010;222(2):219–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.12.030.
da Silva NM, Ahmadi SA, Tafula SN, et al. A diffusion-based connectivity map of the GPi for optimised stereotactic targeting in DBS. Neuroimage. 2017;144:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.06.018.
Laitinen LV. Brain targets in surgery for Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosurg. 1985;62(3):349–51. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1985.62.3.0349.
Sharim J, Yazdi D, Baohan A, Behnke E, Pouratian N. Modeling laterality of the globus pallidus internus in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neuromodulation. 2017;20(3):238–42.
Pallavaram S, Yu H, Spooner J, et al. Intersurgeon variability in the selection of anterior and posterior commissures and its potential effects on target localization. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2008;86(2):113–9.
Middlebrooks EH, Tuna IS, Grewal SS, et al. Segmentation of the globus pallidus internus using probabilistic diffusion tractography for deep brain stimulation targeting in Parkinson disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018;39(6):1127–34.
Sudhyadhom A, Haq IU, Foote KD, Okun MS, Bova FJ. A high resolution and high contrast MRI for differentiation of subcortical structures for DBS targeting: the Fast Gray Matter Acquisition T1 Inversion Recovery (FGATIR). Neuroimage. 2009;47:44–52.
Wei H, Zhang C, Wang T, et al. Precise targeting of the globus pallidus internus with quantitative susceptibility mapping for deep brain stimulation surgery. J Neurosurg. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3171/2019.7.jns191254.
Mikos A, Pavon J, Bowers D, et al. Factors related to extended hospital stays following deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2010;16(5):324–8.
Holanda V, Almeida L, Okun M, et al. Evolution of globus pallidus internus (GPi) deep brain stimulation targeting over 15 years [abstract]. Mov Disord. 2017;15:148–60.
Ramirez-Zamora A, Almeida L, Okun MS. Microelectrode recordings in deep brain stimulation surgery for movement disorders, Chap 8. In: Brown JA, Pilitsis JG, Schulder M, editors. Functional Neurosurgery: The Essentials, 1st edn. Thieme Medical Publishers, Incorporated; 2019.
Williams NR, Foote KD, Okun MS. Subthalamic nucleus versus globus pallidus internus deep brain stimulation: translating the rematch into clinical practice. Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2014;1(1):24–35.
Ramirez-Zamora A, Ostrem JL. Globus pallidus interna or subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease a review. JAMA Neurol. 2018;75(3):367–72.
Okun MS, Foote KD. Subthalamic nucleus vs globus pallidus interna deep brain stimulation, the rematch: Will pallidal deep brain stimulation make a triumphant return? Arch Neurol. 2005;62(4):533–6.
Volkmann J, Allert N, Voges J, Weiss PH, Freund HJ, Sturm V. Safety and efficacy of pallidal or subthalamic nucleus stimulation in advanced PD. Neurology. 2001;56(4):548–51.
Krack P, Pollak P, Limousin P, et al. Opposite motor effects of pallidal stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol. 1998;43(2):180–92.
Lyons KE, Wilkinson SB, Tröster AI, Pahwa R. Long-term efficacy of globus pallidus stimulation for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2002;79(3–4):214–20.
Kumar R, Lang AE, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, et al. Deep brain stimulation of the globus pallidus pars interna in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Neurology. 2000;55(12 Suppl 6):S34–9.
Kumar R, Lozano AM, Montgomery E, Lang AE. Pallidotomy and deep brain stimulation of the pallidum and subthalamic nucleus in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 1998;13(Suppl 1):73–82.
Gross C, Rougier A, Guehl D, Boraud T, Julien J, Bioulac B. High-frequency stimulation of the globus pallidus internalis in Parkinson’s disease: a study of seven cases. J Neurosurg. 1997;87(4):491–8.
Volkmann J, Sturm V, Weiss P, et al. Bilateral high-frequency stimulation of the internal globus pallidus in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol. 1998;44(6):953–61.
Krack P, Pollak P, Limousin P, et al. Subthalamic nucleus or internal pallidal stimulation in young onset Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 1998;121(3):451–7.
Pahwa R, Wilkinson S, Smith D, Lyons K, Miyawaki E, Koller WC. High-frequency stimulation of the globus pallidus for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Neurology. 1997;49(1):249–53.
Durif F, Lemaire JJ, Debilly B, Dordain G. Acute and chronic effects of anteromedial globus pallidus stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999;67(3):315–21.
Durif F, Lemaire JJ, Debilly B, Dordain G. Long-term follow-up of globus pallidus chronic stimulation in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2002;17(4):803–7.
Ghika J, Villemure JG, Fankhauser H, Favre J, Assal G, Ghika-Schmid F. Efficiency and safety of bilateral contemporaneous pallidal stimulation (deep brain stimulation) in levodopa-responsive patients with parkinson’s disease with severe motor fluctuations: a 2-year follow-up review. J Neurosurg. 1998;89(5):713–8.
Visser-Vandewalle V, Der Linden C, Van TY, Nieman F, Celik H, Beuls E. Long-term motor effect of unilateral pallidal stimulation in 26 patients with advanced Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg. 2003;99(4):701–7.
Loher TJ, Burgunder JM, Pohle T, Weber S, Sommerhalder R, Krauss JK. Long-term pallidal deep brain stimulation in patients with advanced Parkinson disease: 1-year follow-up study. J Neurosurg. 2002;96(5):844–53.
Krause M, Fogel W, Heck A, et al. Deep brain stimulation for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease: subthalamic nucleus versus globus pallidus internus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001;70(4):464–70.
Volkmann J, Albanese A, Kulisevsky J, et al. Long-term effects of pallidal or subthalamic deep brain stimulation on quality of life in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2009;24(8):1154–61.
Oyama G, Foote KD, Jacobson CE, et al. GPi and STN deep brain stimulation can suppress dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012;18(7):814–8.
Weaver F, Follett K, Hur K, Ippolito D, Stern M. Deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease: a metaanalysis of patient outcomes. J Neurosurg. 2005;103(6):956–67.
Wong JK, Cauraugh JH, Ho KWD, et al. STN vs GPi deep brain stimulation for tremor suppression in Parkinson disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Park Relat Disord. 2019;58:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.08.017.
Zahodne LB, Okun MS, Foote KD, et al. Greater improvement in quality of life following unilateral deep brain stimulation surgery in the globus pallidus as compared to the subthalamic nucleus. J Neurol. 2009;256(8):1321–9.
Burchiel KJ, Anderson VC, Favre J, Hammerstad JP. Comparison of pallidal and subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for advanced Parkinson’s disease: Results of a randomized, blinded pilot study. Neurosurgery. 1999;45(6):1375–84.
Katayama Y, Kasai M, Oshima H, Fukaya C, Yamamoto T, Mizutani T. Double blinded evaluation of the effects of pallidal and subthalamic nucleus stimulation on daytime activity in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Park Relat Disord. 2000;7(1):35–40.
Robertson LT, St George RJ, Carlson-Kuhta P, Hogarth P, Burchiel KJ, Horak FB. Site of deep brain stimulation and jaw velocity in Parkinson disease: clinical article. J Neurosurg. 2011;115(5):985–94.
Rocchi L, Carlson-Kuhta P, Chiari L, Burchiel KJ, Hogarth P, Horak FB. Effects of deep brain stimulation in the subthalamic nucleus or globus pallidus internus on step initiation in Parkinson disease: laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg. 2012;117(6):1141–9.
Moro E, Lozano AM, Pollak P, et al. Long-term results of a multicenter study on subthalamic and pallidal stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2010;25(5):578–86.
St George RJ, Carlson-Kuhta P, King LA, Burchie KJ, Horak FB. Compensatory stepping in parkinson’s disease is still a problem after deep brain stimulation randomized to STN or GPi. J Neurophysiol. 2015;114(3):1417–23.
Odekerken VJJ, Boel JA, Schmand BA, et al. GPi vs STN deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2016;86(8):755–61. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000002401.
Rughani A, Schwalb JM, Sidiropoulos C, et al. Congress of neurological surgeons systematic review and evidence-based guideline on subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus internus deep brain stimulation for the treatment of patients with Parkinson’s disease: executive summary. Neurosurgery. 2018;82(6):753–6.
Munhoz RP, Cerasa A, Okun MS. Surgical treatment of dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurol. 2014;5:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2014.00065/abstract.
Fan SY, Wang KL, Hu W, et al. Pallidal versus subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2020;7(1):59–68.
Liu Y, Li F, Luo H, et al. Improvement of deep brain stimulation in dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. Front Neurol. 2019;10:151. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00151/full.
Sriram A, Foote KD, Oyama G, Kwak J, Zeilman PR, Okun MS. Brittle dyskinesia following STN but not GPi deep brain stimulation. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y). 2014;4:242.
Martinez-Ramirez D, Giugni J, Vedam-Mai V, et al. The “Brittle Response” to Parkinson’s disease medications: characterization and response to deep brain stimulation. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(4):94856. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0094856.
Tagliati M. Turning tables: should GPi become the preferred DBS target for Parkinson disease? Neurology. 2012;79(1):19–20.
Elkouzi A, Tsuboi T, Burns MR, Eisinger RS, Patel A, Deeb W. Dorsal GPi/GPe stimulation induced dyskinesia in a patient with Parkinson’s disease. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov. 2019;9:1–5.
Skodda S. Effect of deep brain stimulation on speech performance in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2012; 22:850596, https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/850596.
Buhmann C, Huckhagel T, Engel K, et al. Adverse events in deep brain stimulation: a retrospective long-term analysis of neurological, psychiatric and other occurrences. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(7):1–21.
Troche MS, Brandimore AE, Foote KD, Okun MS. Swallowing and deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2013;19(9):783–8.
Troche MS, Brandimore AE, Foote KD, et al. Swallowing outcomes following unilateral STN vs GPi surgery: a retrospective analysis. Dysphagia. 2014;29(4):425–31.
Volkmann J, Allert N, Voges J, Sturm V, Schnitzler A, Freund HJ. Long-term results of bilateral pallidal stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol. 2004;55(6):871–5.
Lachenmayer ML, Bettschen C, Bernasconi C, et al. Stimulation of the globus pallidus internus in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease: Long-term results of a monocentric cohort. Park Relat Disord. 2019;64:118–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2019.03.009.
Aviles-Olmos I, Kefalopoulou Z, Tripoliti E, et al. Long-term outcome of subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease using an MRI-guided and MRI-verified approach. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2014;85(12):1419–25. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2013-306907.
Fasano A, Romito LM, Daniele A, et al. Motor and cognitive outcome in patients with Parkinson’s disease 8 years after subthalamic implants. Brain. 2010;133(9):2664–76. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq221.
Castrioto A. Ten-year outcome of subthalamic stimulation in parkinson disease. Arch Neurol. 2011;68(12):1550. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2011.182.
Limousin P, Foltynie T. Long-term outcomes of deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(4):234–42. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-019-0145-9.
Mei S, Eisinger RS, Hu W, et al. Three-Year Gait And Axial Outcomes Of Bilateral STN and GPi Parkinson’s disease deep brain stimulation. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020;14:1.
Volkmann J, Moro E, Pahwa R. Basic algorithms for the programming of deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2006;21(Suppl. 14):284–9.
Picillo M, Lozano AM, Kou N, Puppi Munhoz R, Fasano A. Programming deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: the Toronto Western Hospital algorithms. Brain Stimul. 2016;9(3):425–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2016.02.004.
Koeglsperger T, Palleis C, Hell F, Mehrkens JH, Bötzel K. Deep brain stimulation programming for movement disorders: current concepts and evidence-based strategies. Front Neurol. 2019;10:1–20.
Little S, Pogosyan A, Neal S, et al. Adaptive deep brain stimulation in advanced Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol. 2013;74(3):449–57. https://doi.org/10.1002/2Fana.23951.
Rosa M, Arlotti M, Ardolino G, et al. Adaptive deep brain stimulation in a freely moving parkinsonian patient. Mov Disord. 2015;30(7):1003–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/2Fmds.26241.
Little S, Beudel M, Zrinzo L, et al. Bilateral adaptive deep brain stimulation is effective in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015;87(7):717–21. https://doi.org/10.1136/2Fjnnp-2015-310972.
Little S, Tripoliti E, Beudel M, et al. Adaptive deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease demonstrates reduced speech side effects compared to conventional stimulation in the acute setting. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2016;87(12):1388–9. https://doi.org/10.1136/2Fjnnp-2016-313518.
Piña-Fuentes D, Little S, Oterdoom M, et al. Adaptive DBS in a Parkinson’s patient with chronically implanted DBS: a proof of principle. Mov Disord. 2017;32(8):1253–4. https://doi.org/10.1002/2Fmds.26959.
Tinkhauser G, Pogosyan A, Little S, et al. The modulatory effect of adaptive deep brain stimulation on beta bursts in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2017;140(4):1053–67. https://doi.org/10.1093/2Fbrain/2Fawx010.
Velisar A, Syrkin-Nikolau J, Blumenfeld Z, et al. Dual threshold neural closed loop deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease patients. Brain Stimul. 2019;12(4):868–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/2Fj.brs.2019.02.020.
Tinkhauser G, Pogosyan A, Tan H, Herz DM, Kühn AA, Brown P. Beta burst dynamics in Parkinson’s disease OFF and ON dopaminergic medication. Brain. 2017;140(11):2968–81. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awx252.
Schaltenbrand G, Wahren W. Atlas for stereotaxy of the human brain. Stuttgart: Thieme; 1977.
Yelnik J, Damier P, Bejjani BP, et al. Functional mapping of the human globus pallidus: contrasting effect of stimulation in the internal and external pallidum in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience. 2000;101(1):77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-4522(00)00364-x.
Acknowledgements
We thank all participants in the studies that we have reviewed in this article.
Funding
No funding or sponsorship was received for this study or publication of this article.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Authorship Contributions
Ka Loong Kelvin Au: manuscript draft, project organization. Joshua K Wong: data acquisition, manuscript revision. Takashi Tsuboi: data acquisition, manuscript revision. Robert S Eisinger: data acquisition, manuscript revision. Kathryn Moore: data acquisition, manuscript revision. Janine Lemos Melo Lobo Jofili Lopes: data acquisition, manuscript revision. Marshall Holland: data acquisition, manuscript revision. Vanessa M Holanda: data acquisition, manuscript revision. Zhongxing Peng-Chen: data acquisition, manuscript revision. Addie Patterson: manuscript revision. Kelly Foote: manuscript revision. Adolfo Ramirez-Zamora: manuscript revision. Michael S Okun: manuscript revision. Leonardo Almeida: study supervision, conception and design of study and manuscript revision.
Disclosures
Ka Loong Kelvin Au, Takashi Tsuboi, Robert S Eisinger, Kathryn Moore, Janine Lemos Melo Lobo Jofili Lopes, Marshall T Holland, Zhongxing Peng-Chen and Addie Patterson declare that they have no conflict of interest. Joshua K Wong’s research is supported by NIH grant 1R25NS108939. Vanessa M Holanda has served as consultant for Abbott, Boston Scientific, Gusmed (Epimed affiliated) and Medicicor (Medtronic affiliated). Kelly Foote has received occasional consulting fees from Medtronic and Boston Scientific. His research is primarily funded by NIH and multiple foundation sources. Implantable devices for Dr. Foote's DBS-related research have been provided by Medtronic and Neuropace. Dr. Foote has participated as a site-implanting surgeon in multicenter DBS-related research studies sponsored by Abbott/St. Jude, Boston Scientific, and Functional Neuromodulation. The University of Florida receives partial funding for Dr. Foote's functional neurosurgery fellowship from Medtronic. Adolfo Ramirez-Zamora has received support from the Parkinson's Foundation and consulting honoraria from Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Stealth, Rho, CNS Raters and Bracket INC in the past 24 months. Michael S Okun serves as a consultant for the Parkinson’s Foundation, and has received research grants from NIH, Parkinson’s Foundation, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, the Parkinson Alliance, Smallwood Foundation, the Bachmann-Strauss Foundation, the Tourette Syndrome Association, and the UF Foundation. Dr. Okun’s DBS research is supported by: NIH grants R01 NR014852 and R01NS096008. Dr. Okun is PI of the NIH R25NS108939 Training Grant. Dr. Okun has received royalties for publications with Demos, Manson, Amazon, Smashwords, Books4Patients, Perseus, Robert Rose, Oxford and Cambridge (movement disorders books). Dr. Okun is an associate editor for New England Journal of Medicine Journal Watch Neurology. Dr. Okun has participated in Continuing Medical Education and educational activities on movement disorders sponsored by the Academy for Healthcare Learning, PeerView, Prime, QuantiaMD, WebMD/Medscape, Medicus, MedNet, Einstein, MedNet, Henry Stewart, American Academy of Neurology, Movement Disorders Society and Vanderbilt University. The institution and not Dr. Okun receives grants from Medtronic, Abbvie, Boston Scientific, Abbott and Allergan and the PI has no financial interest in these grants. Dr. Okun has participated as a site PI and/or co-PI for several NIH-, foundation- and industry-sponsored trials over the years but has not received honoraria. Research projects at the University of Florida receive device and drug donations. Leonardo Almeida has served as an educational consultant and has participated in advisory boards for Medtronic and Boston Scientific, and has received honoraria for his services.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Au, K.L.K., Wong, J.K., Tsuboi, T. et al. Globus Pallidus Internus (GPi) Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease: Expert Review and Commentary. Neurol Ther 10, 7–30 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40120-020-00220-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40120-020-00220-5