Abstract
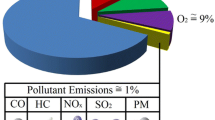
Due to the growing population and industrialization, the use of diesel is increasing day by day. Diesel engine emits exhaust emissions like NOx, SOx, CO, CO2 and particulate matter. To overcome this problem new development in diesel is emulsion fuel, which can decrease the exhaust emission. Emulsion fuel is made up of water in diesel emulsion stabilized by surfactants. A considerable part of emulsion fuel is diesel and has properties of diesel hence can be replaced in an existing diesel engine. Emulsion fuel was prepared three different instruments and at different HLB (Hydrophilic Lipophilic Balance) values. The emulsion prepared using HPH (High-pressure homogenizer) at 9 HLB had the most similar properties to pure diesel. Emulsion fuel was successful in decreasing the exhaust emission by 50–70%. Some part of diesel in emulsion fuel is replaced with water and surfactants, which does not contribute to energy, hence it lacks in performance test compared with same quantity of pure diesel. If we compare emulsion fuels, HPH based emulsion outperformed the sonication emulsion. Overall, emulsion fuel can be the better option with 60% of pollution reduction, whereas it does not help in enhancement of the engine performance.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourdrel, T., Bind, M.-A., Béjot, Y., Morel, O., Argacha, J.-F.: Cardiovascular effects of air pollution. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 110(11), 634–642 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acvd.2017.05.003
Hamra, G.B., Laden, F., Cohen, A.J., Raaschou-Nielsen, O., Brauer, M., Loomis, D.: Lung cancer and exposure to nitrogen dioxide and traffic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 123(11), 1107–1112 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1408882
Mazlan, N.A., et al.: Effects of different water percentages in non-surfactant emulsion fuel on performance and exhaust emissions of a light-duty truck. J. Clean. Prod. 179, 559–566 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.143
Reddy, S.R., Titu, D., Chadha, A.: Erratum: a novel method for monitoring the transesterification reaction of oil in biodiesel production by estimation of glycerol (JAOCS, Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-010-1549-2). JAOCS, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 87(7), 837, (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-010-1570-5
Debnath, B.K., Saha, U.K., Sahoo, N.: A comprehensive review on the application of emulsions as an alternative fuel for diesel engines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 42, 196–211 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.10.023
Kruczyński, P., Orliński, P., Kamela, W., Ślęzak, M.: Analysis of selected toxic components in the exhaust gases of a CI engine supplied with water-fuel emulsion. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 27(1), 129–136 (2018). https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/74689
Ithnin, A.M., Ahmad, M.A., Bakar, M.A.A., Rajoo, S., Yahya, W.J.: Combustion performance and emission analysis of diesel engine fuelled with water-in-diesel emulsion fuel made from low-grade diesel fuel. Energy Convers. Manag. 90, 375–382 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2014.11.025
Mishrif, M.R., Ragab, A.M.: Colloids and surfaces a: physicochemical and engineering aspects rheological behavior of water-in-diesel fuel nanoemulsions stabilized by mixed surfactants. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 436, 318–324 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.06.044
Perumal, V., Ilangkumaran, M.: Water emulsified hybrid pongamia biodiesel as a modified fuel for the experimental analysis of performance, combustion and emission characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine. Renew. Energy 121, 623–631 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.01.060
Ashok, M.P.: Effect of dimethyl ether in a selected ethanol/diesel emulsified fuel ratio and comparing the performance and emission of the same to diesel fuel. Energy Fuels 25(8), 3799–3805 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/ef2007547
Vellaiyan, S., Subbiah, A., Chockalingam, P.: Multi-response optimization to obtain better performance and emission level in a diesel engine fueled with water-biodiesel emulsion fuel and nanoadditive. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26(5), 4833–4841 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3979-6
Nemade, P.R., Ganjare, A.V., Ramesh, K., Rakte, D.M., Vaishnavi, P.S.V., Thapa, G.: Low fouling sulphonated carbon soot-polysulphone membranes for rapid dehydration of stabilized oil-water emulsions. J. Water Process Eng. 38, no. December 2017, p. 101590 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101590
Canselier, J.P., Delmas, H., Wilhelm, A.M., Abismaïl, B.: Ultrasound emulsification—an overview. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 23(1–3), 333–349 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1080/01932690208984209
Saeedi Dehaghani, A.H., Rahimi, R.: An experimental study of diesel fuel cloud and pour point reduction using different additives. Petroleum 5(4), 413–416 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petlm.2018.06.005
Luning Prak, D.J., Simms, G.R., Hamilton, M., Cowart, J.S.: Impact of low flash point compounds (hydrocarbons containing eight carbon atoms) on the flash point of jet fuel and n-dodecane. Fuel 286(P1), 119389 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119389
Keil, F.J.: Process intensification. Rev. Chem. Eng. 34(2), 135–200 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1515/revce-2017-0085
Method, C.C.R., Tensiometer, F.: Application report. Met. Finish. 101(10), 87 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0026-0576(03)90164-4
Danaei, M., et al.: Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Pharmaceutics 10(2), 1–17 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020057
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the Institute of Chemical Technology (ICT), Mumbai for providing the facilities and equipment for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attar, A., Waghmare, J. & Mane, S. Water in diesel emulsion fuel: production, properties, performance, and exhaust emission analysis. Int J Energy Environ Eng 13, 729–738 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-021-00459-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-021-00459-0