Abstract
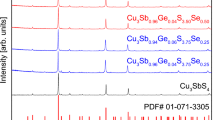
Cu3Sb1–y(Al/In)yS4 (0 ≤ y ≤ 0.08) famatinite compounds were synthesized, and phase analysis was conducted based on the Al or In doping level, followed by an examination of charge transport and thermoelectric properties. All specimens exhibited a tetragonal famatinite phase and demonstrated high-relative densities ranging from 97.2 to 99.5%. Al doping notably decreases the a-axis (0.5228–0.5231 nm) and marginally increases the c-axis (1.0764–1.0770 nm), whereas In doping marginally decreases the a-axis (0.5377–0.5380 nm) and significantly increases the c-axis (1.0781–1.0791 nm). The carrier concentration rose with increasing Al/In content, leading to an increase in electrical conductivity (σ), while the Seebeck coefficient (α) declined. The electrical conductivity increased to 450–1130 Sm−1 for Cu3Sb0.94Al0.06S4 and 250–1110 Sm−1 for Cu3Sb0.94In0.06S4 at 323–623 K. However, the Seebeck coefficient decreased to 105–243 μVK−1 for Cu3Sb0.94Al0.06S4 and 334–406 μVK−1 for Cu3Sb0.94In0.06S4 at 323–623 K. Consequently, the highest power factor of 0.18 mWm−1 K−2 was obtained at 623 K for Cu3Sb0.94In0.06S4. Cu3Sb0.96Al0.04S4 demonstrated the lowest thermal conductivity (κ), while Cu3Sb0.94In0.06S4 achieved the highest thermoelectric figure of merit (ZT = 0.16) at 623 K.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.M. Rowe, CRC Handbook of Thermoelectrics (CRC Press, 1995), pp.19–23
G.S. Nolas, J. Sharp, H.J. Goldsmid, Thermoelectrics (Springer, Berlin, 2001), pp.1–13
E.J. Skoug, J.D. Cain, D.T. Morelli, J. Electron. Mater. 41, 1232 (2012)
Z.H. Ge, L.D. Zhao, D. Wu, X. Liu, B.P. Zhang, J.F. Li, J. He, Mater. Today 19, 227 (2016)
K.I. Amirkhanov, G.G. Gadzhiev, Y.B. Magomedov, High Temp. 16, 1050 (1978)
K. Chen, Synthesis and Thermoelectric Properties of Cu-Sb-S Compounds, Ph.D. Thesis, UK: Queen Mary University of London (2016)
B. Xu, X. Zhang, Y. Sun, J. Zhang, Y. Wang, L. Yi, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 83, 094606 (2014)
D. Chen, Y. Zhao, Y. Chen, T. Lu, Y. Wang, J. Zhou, Z. Liang, Adv. Electron. Mater 2, 1500473 (2016)
U. Chalapathi, B. Poornaprakash, S.H. Park, Cer. Intl. 43, 5229 (2017)
K. Chen, B. Du, N. Bonini, C. Weber, H. Yan, M.J. Reece, J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 27135 (2016)
A. Suzumura, M. Watanabe, N. Nagasako, R. Asahi, J. Electron. Mater. 43, 2356 (2014)
Y. Goto, Y. Sakai, Y. Kamihara, M. Matoba, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 84, 044706 (2015)
K. Chen, C.D. Paola, B. Du, R. Zhang, S. Laricchia, N. Bonini, C. Weber, I. Abrahams, H. Yan, M. Reece, J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 8546 (2018)
M. Shen, S. Lu, Z. Zhang, H. Liu, W. Shen, C. Fang, Q. Wang, L. Chen, Y. Zhang, X. Jia, A.C.S. Appl, Mater. Interf. 12, 8271 (2020)
J.H. Pi, G.E. Lee, I.H. Kim, J. Electron. Mater. 49, 2755 (2020)
R.D. Shannon, Acta Crystallogr. A 32, 751 (1976)
A.L. Allred, J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 17, 215 (1961)
Y. Li, X. Qin, D. Li, X. Li, Y. Liu, J. Zhang, C. Son, H. Xin, RSC Adv. 5, 31399 (2015)
O. Madelung, Semiconductors: Data Handbook (Springer, Berlin, 2004), p.385
G.J. Snyder, E.S. Toberer, Nat. Mater. 7, 105 (2008)
B. Madaval, S.J. Hong, J. Electron. Mater. 45, 6059 (2016)
S.G. Kwak, J.H. Pi, G.E. Lee, I.H. Kim, Korean J. Met. Mater. 58, 272 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Capacity Enhancement Project (National Research Facilities and Equipment Center) through the Korea Basic Science Institute funded by the Ministry of Education (Grant No. 2019R1A6C1010047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yun, S., Kim, IH. Thermoelectric properties of mechanically alloyed Cu3Sb1–y(Al/In)yS4 famatinites. J. Korean Phys. Soc. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-024-01061-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-024-01061-3