Abstract
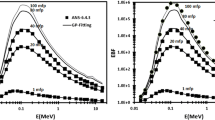
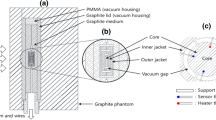
Although accurate X-ray dosimetry standards are crucial for certain medical and industrial applications, insufficient research attention has been given to the standards concerning the absorbed dose to water for kV X-rays. To determine the absorbed dose to water based on measurement standards for the air kerma, it is necessary to evaluate the dose conversion factor from the air kerma to the absorbed dose to water. This factor can be derived from the dose conversion parameter, obtained through theoretical calculations such as Monte Carlo (MC) simulations, and the response ratio of the ion chamber in water and air, obtained through measurements. In this study, the dose conversion parameters were preliminarily evaluated for kilovolt X-ray beams using MC simulations. The modeling of the X-ray tube at the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS) was optimized to reproduce the beam qualities of the reference kilovolt X-ray beams recommended by the Consultative Committee for Ionizing Radiation (CCRI) using the Electron Gamma Shower MC code from the National Research Council Canada. The spectral distributions of the reproduced X-ray beams were used to calculate the dose conversion parameters in MC simulations. To obtain the dose conversion parameter, the air kerma and absorbed dose to water at the reference positions were calculated, and responses of an ion chamber in the air and in a water phantom were calculated, as well. The evaluated dose conversion parameters were found to be in the range of 1.0355–1.0961 for the KRISS reference X-ray beams of 100–250 kV. These results were agreed within 1% of those of other research groups. To understand the sensitivity of the obtained conversion parameters, case studies were performed under different conditions, such as different X-ray beam qualities and geometric specifications of the ion chamber. A maximum difference of 0.56% was found in the case studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.T. Burns, C. Kessler, B. Rapp, Metrologia 57, 06008 (2020)
D.T. Burns et al., Metrologia 55, 06006 (2018)
IAEA, Absorbed Dose Determination in External Beam Radiotherapy: An International Code of Practice for Dosimetry Based on Standards of Absorbed Dose to water, Technical Report TRS-398 (IAEA, Vienna, 2000)
C.-M. Ma et. al., Med. Phys. 28(6), 868–893 (2001)
S.M. Seltzer et al., J. ICRU 14, 1–110 (2014)
I.J. Kim et al., Nucl. Eng. Technol. 49, 810–816 (2017)
KRISS, Development of measurement standards for ionizing radiation, report IR-2017-051 (KRISS, 2017)
S.R. Domen, J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 99, 121–141 (1994)
ARPANSA, The Australian primary standard for absorbed dose to water, Technical Report Series No. 166 (2016)
D.T. Burns et al., Metrologia 59, 06009 (2022)
D.T. Burns et al., Metrologia 59, 06011 (2022)
I. Kawrakow et. al., The EGSnrc Code System: Monte Carlo Simulation of Electron and Photon Transport, Technical Report PIRS-701, (2015)
M.J. Berger et al., J. ICRU 19, 2 (1984)
M.J. Berger et. al., XCOM: Photon Cross Sections Database, NBSIR87-3597 (1987, last update at Nov. 2010)
J.H. Hubbell, S.M. Seltzer, Table of X-ray mass attenuation coefficients and mass energy-absorption coefficients 1 keV to 20 MeV for elements Z = 1 to 92 and 48 additional substances of dosimetric interest, NISTIR 5632 (NIST, 1995)
M.J. Berger, ESTAR PSTAR ASTAR, Stopping Power and Range of electrons, Protons, Alpha (NEA, 1995)
G. Poludniowski, M. Evans, Med. Phys. 34(6), 2164–2174 (2007)
G. Poludniowski, Med. Phys. 34(6), 2175–2186 (2007)
G. Poludniowski et al., Phys. Med. Biol. 54(19), 433–438 (2009)
F. Salvat et al., PENELOPE-2008: A Code System for Monte Carlo Simulation of Electron and Photon Transport (Nuclear Energy Agency, 2009)
D.T. Burns, C. Kessler, P. Roger, New BIPM absorbed-dose standard for medium-energy x-rays, report for Consultative Committee for Ionizing Radiation CCRI(I)/17-06 Bureau International Poids et Mesures (BIPM, 2017)
L. Büermann et al., Metrologia 53, 06007 (2016)
P. Andreo, D.B. Burns, F. Salvat, Phys. Med. Biol. 57, 2117 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science, Rep. of Korea under the project “Development of measurement standards and techniques for medical ionizing radiation,” [23011069].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y., Yi, CY., Kim, I.J. et al. Preliminary study on dose conversion parameters for absorbed dose to water in kV X-ray beams. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 83, 226–232 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-023-00866-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-023-00866-y