Abstract
We numerically study the movement of two colliding fuzzy dark matter solitons without explicit self-interaction and find the effective cross section of dissipative change in velocity. The cross section turns out to be inversely proportional to the velocity cubed, and we present its analytic interpretation. Using the result we roughly estimate spatial offsets during head-on collisions of two fuzzy dark matter halos, which can be related to the spatial offsets between stars and dark matter in collisions of some galaxy clusters. We also show that the gravitational cooling plays an important role during the collisions.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Thus, \(\int d^3 \mathbf{{x}}\, |\psi |^2\) in the code space is no longer fixed to be unity in general.
Hence \(M_\mathrm{tot}=2M\) in our setup.
Labeling each soliton could be ambiguous since the collision is solely described by field profiles of our Schrödinger–Poisson system. However this ambiguity may be lifted by considering slightly different masses, e.g. \(M_L > M_R\), and tracking for instance the larger/smaller density peak as the soliton L/R.
We would like to thank the referee for clarification of the argument below.
The parameters A, B are related to \(\alpha ,\beta\) by \(A=f_0^3 \, \alpha\) and \(B=f_0^2\, \beta\).
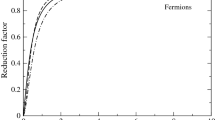
\(q_{\text {src}}\ll 1\) corresponds to the quantum regime in which \(q_{\text {src}}\) dependence in C can be ignored. See Figure 2 of Ref. [5] in this regard.
Interestingly, with \(G(q)=A q^3\), \(\sigma _\mathrm{eff}/M\) is independent of the soliton mass M.
The approximation here breaks down when \({|v-v_I|}/{v}\) becomes \(\mathcal{O}(1)\). In this regime, one has in general further enhancement of the offset ratio.
References
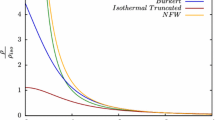
J.F. Navarro, C.S. Frenk, S.D.M. White, Astrophys. J. 462, 563–575 (1996)
W.J.G. de Blok, A. Bosma, S.S. McGaugh, astro-ph/0212102 (2002)
A. Tasitsiomi, Int. J. Mod. Phy. D 12, 1157 (2003)
W. Hu, R. Barkana, A. Gruzinov, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1158 (2000)
L. Hui, J.P. Ostriker, S. Tremaine, E. Witten, Phys. Rev. D 95(4), 043541 (2017)
J.W. Lee, EPJ Web Conf. 168, 06005 (2018). [arXiv:1704.05057]
D. Harvey, R. Massey, T. Kitching, A. Taylor, E. Tittley, Science 347, 1462–1465 (2015)
S. Tulin, H.B. Yu, Phys. Rept. 730, 1–57 (2018)
J. W. Lee, S. L., D. Choi, hep-ph:0805.3827 (2008)
A. Paredes, H. Michinel, Phys. Dark Univ. 12, 50–55 (2016)
F.S. Guzmán, J.A. González, J.P. Cruz-Pérez, Phys. Rev. D 93(10), 103535 (2016)
F.S. Guzman, L.A. Urena-Lopez, Astrophys. J. 645, 814 (2006)
D. Bak, S. Kim, H. Min, J.P. Song, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 74(8), 756 (2019)
N.A.Bahcall, [arXiv:astro-ph/9611148 [astro-ph]]
L. Diósi, Phys. Lett. A 105, 199 (1984)
I.M. Moroz, R. Penrose, P. Tod, Class. Quant. Grav. 15, 2733 (1998)
H.Y. Schive, T. Chiueh, T. Broadhurst, Nat. Phys. 10, 496 (2014)
F. Edwards, E. Kendall, S. Hotchkiss, R. Easther, JCAP 1810, 027 (2018)
P. Salzman: “Investigation of the Time Dependent Schrödinger- Newton Equation”, Ph.D. thesis, Univ. of California at Davis, 2005
L. Lancaster, C. Giovanetti, P. Mocz, Y. Kahn, M. Lisanti, D.N. Spergel, JCAP 01, 001 (2020)
F.S. Guzmán, A.A. Avilez, Phys. Rev. D 97(11), 116003 (2018)
F. S. Guzman, J. A. Gonzalez, I. Alvarez-Rios, [arXiv:1907.07990 [astro-ph.CO]]
S. Chandrasekhar, Astrophys. J. 97, 255 (1943)
D. Clowe et al., Astrophys. J. 648, L109 (2006)
A. Mahdavi et al., Astrophys. J. 668, 806 (2007)
B. Binggeli, A. Sandage, M. Tarenghi, Astron. J. 89, 64–82 (1984)
Acknowledgements
D Bak was supported in part by the 2021 Research Fund of the University of Seoul. J. W. Lee was supported in part by NRF-2020R1F1A1061160. S. Park was supported in part by NRF Grant 2020R1A2B5B01001473, by Basic Science Research Program through National Research Foundation funded by the Ministry of Education (2018R1A6A1A06024977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bak, D., Lee, JW. & Park, S. Effective cross section of fuzzy dark matter halos. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 79, 582–588 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-021-00263-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-021-00263-3