Abstract
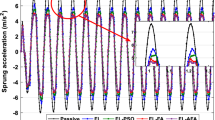
A vehicle suspension system is a crucial component of an automobile that ultimately determines the vehicle's road handling performance and comfortable ride quality. The passive suspension system cannot improve the two properties simultaneously due to their limited structure, leading to wheel bounce and roll cornering. Therefore, an active system has become the topic of research to overcome these limitations. In the present work, the modelling of passive and active suspension systems for a quarter-car model using MATLAB/Simulink has been done by importing the mathematical model of both systems in the mentioned software. A PID controller is used to explore the performance of the active suspension system in terms of body acceleration and settling time of vibration amplitudes. Comparative analysis is then fetched out for various combinations of suspension parameters like spring stiffness and damping coefficient. It was investigated that body acceleration decreased by 92.20% and settling time reduced by 30%, improving ride comfort and road handling in the active system. The objective to obtain zero peak overshoot and minimum settling time is achieved by applying the particle swarm optimization technique (PSO) to determine the optimized scaling factors. After simulation results, body acceleration decreases further by 94.15%, and settling time reduces further by 30%, which is attributed to a vehicle's smooth ride and stable road handling. The PID control and PSO algorithm combination are more effective as it has depicted the best stability and reliability. This latest type of swarm intelligent control method procured a new way of thinking about the automotive active suspension control theory.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Goodarzi, A. Khajepour, Vehicle suspension system technology and design, synthesis lectures on advances in automotive technology, Morgan & Claypool Publishers, 1(1), (2017)
M. Ravindran, S. Palanisamy, R.S. kumar, M. Soundarrajan, J. Prabakaran, Design & analysis of front suspension for light duty vehicle, IJSRD 6(09), 406–409 (2018)
A. Dubrovskiy, S. Aliukov, S. Dubrovskiy, A. Alyukov, Basic characteristics of adaptive suspensions of vehicles with new principle of operation. SAE Int. J. Commer. Veh. 10(1), 193–203 (2017)
M. Ghoniem, T. Awad, O. Mokhiamar, Control of a new low-cost semi-active vehicle suspension system using artificial neural networks. Alexandria Eng. J. 59(5), 4013–4025 (2020)
X. Shao, F. Naghdy, H. Du, Enhanced ride performance of electric vehicle suspension system based on genetic algorithm optimization. 20th Int Conf Electr Mach Syst ICEMS (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEMS.2017.8056265
A. Mehmood, A.A. Khan, A. Mehmood, Optimization of Suspension Damping Using Different Mathematical Car Models. Int. J. Mech. Eng. 3(10), 1–15 (2013)
K. Hassan, A.A. Dammed, Control and simulation of semi-active suspension system using PID controller for automobiles under LABVIEW simulink. Int. .J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 7(5), 1824–1830 (2017)
A. Aly, F. Salem, Vehicle suspension systems control: a review. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2(2), 46–54 (2013)
I. Martins, J. Esteves, F.P. da Silva, P. Verdelho, Electromagnetic hybrid active-passive vehicle suspension system. IEEE VTS 50th Veh Technol Conf VTC 1999-Fall 3, 2273–2277 (1999)
K.D. Rao, Modeling, simulation and control of semi active suspension system for automobiles under MATLAB simulink using PID controller. IFAC Proceedings Volumes 47(1), 827–831 (2014)
M. Issa, A. Samn, Passive vehicle suspension system optimization using Harris Hawk Optimization algorithm. Math. Comput. Simul 191, 328–345 (2022)
D. F. Sousa, S. M. Avila, Simulation of an active suspension using PID control. Proceedings of the PANACM, Argentina, (2015)
A. Anandan, A. Kandavel, A.S. Soosairaj, Comparison of quarter car suspension model using two different controllers. Innovative Design, Analysis and Development Practices in Aerospace and Automotive Engineering (I-DAD 2018). Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Singapore (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2697-4_22
Y. Chen, Skyhook surface sliding mode control on semi-active vehicle suspension system for ride comfort enhancement. Engineering 01(01), 23–32 (2009)
J.D.J. Lozoya, R.M. Morales, R.A. Ramirez, H. Ahuett, Efficient modeling of MR dampers. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 12(4), 550–556 (2014)
M.N. Khajavi, V. Abdollahi, Comparison between optimized passive vehicle suspension system and semi active fuzzy logic controlled suspension system regarding ride and handling. Int. J. Mech. Mechatronics Eng. 19(1), 57–61 (2007)
R.N. Yerrawar, R.R. Arakerimath, "Performance assessment and control policies for semiactive suspension using SIMSCAPE," International Conference on Automatic Control and Dynamic Optimization Techniques (ICACDOT), Pune, India, 1163–1168 (2016)
A.J. Qazi, C.W. De Silva, A. Khan, M.T. Khan, Performance analysis of a semiactive suspension system with particle swarm optimization and fuzzy logic control. Sci. World J. 2014, 1–12 (2014)
M.H. Ab Talib et al., Vibration control of semi-active suspension system using PID controller with advanced firefly algorithm and particle swarm optimization. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 12(1), 1119–1137 (2021)
P. Choudhary, S. Sachar, T. Khurana, U. Jain, Y. Parvez, M. Soni, Energy analysis of a single cylinder 4-stroke diesel engine using diesel and diesel-biodiesel blends. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 13(12), 10779–10788 (2018)
Y.P. Urvashi Jain, T. Khurana, S. Sachar, P. Choudhary, Performance characteristics and energy analysis of a 4-stroke single cylinder diesel engine using diesel and diesel-kerosene blends. Int. J. Res. Anal. Rev. 5(3), 194–203 (2018)
Y.P. Shruti Srivastava, H. Chaubey, Performance evaluation of CI engine using diesel, diesel-biodiesel blends and diesel-kerosene blends through exergy analysis performance evaluation of CI engine using diesel, diesel- biodiesel blends and diesel-kerosene blends through exergy analysis. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 691(1), 012066 (2019)
S. Sachar, Y. Parvez, T. Khurana, H. Chaubey, Heat transfer enhancement of the air-cooled engine fins through geometrical and material analysis: a review. Mater. Today. Proc. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.03.447
A. Turnip, I.R. Setiawan, M.F. Amri, T.A. Tamba, Controller design for active suspension system based on skyhook reference model. Proc 2015 Int. Conf. Technol. Inform. Manag. Eng. Environ. TIME-E 2015 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIME-E.2015.7389764
A.S. Taksale, Modeling, analysis and control of passive and active suspension system for a quarter car. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 8(12), 1405–1414 (2013)
A. Goyal, A. Sharma, Advances in active suspension system, IJCRT, | International Conference Proceeding, 177–1881 (2017)
K. Hyniova, Energy control principles in an automotive active suspension system, Trans Motauto World 4 (3), 107–110 (2019)
S. Shastri, Y. Parvez, N.R. Chauhan, Wireless power transfer system for scorbot Er-4U robotic arm. Int. J. Power Energy Syst (2020). https://doi.org/10.2316/J.2020.203-0044
D.S. Yoon, G.W. Kim, S.B. Choi, Response time of magnetorheological dampers to current inputs in a semi-active suspension system: modeling, control and sensitivity analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 146, 106999 (2020)
E.A. Alandoli, M.Z.A. Rashid, M. Sulaiman, A comparison of PID and LQR controllers for position tracking and vibration suppression of flexible link manipulator. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 95(13), 2949–2955 (2017)
L. Geng, M. Cui, Z. Wu, Stochastic control of semi-active suspension system, Proc. 29th Chinese Control Decis. Conf. CCDC 2017, pp. 3791–3796, (2017)
D. Choi, Min-max control for vibration suppression of mobile manipulator with active suspension system. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 20(2), 618–626 (2022)
N.D. Pandey, D.P. Tiwari, Comparison between speed control DC motor using fuzzy PID and PSO-PID. Int. J. Inf. Res. Rev. 04(01), 3493–3496 (2017)
M.H. Mat, I.Z. Mat Darns, Self-tuning PID controller for active suspension system with hydraulic actuator. IEEE Symp. Comput. Inform. Isc. 2013(4), 86–91 (2013)
A.G. Neve, G.M. Kakandikar, O. Kulkarni, Application of grasshopper optimization algorithm for constrained and unconstrained test functions. Int. J. Swarm. Intell. Evol. Comput. (2017). https://doi.org/10.4172/2090-4908.1000165
Y. Shahid, M. Wei, Comparative analysis of different model-based controllers using active vehicle suspension system. Algorithms (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/a13010010
Y.Q. Han, W.J. He, N. Li, S.L. Zhu, Adaptive tracking control of a class of nonlinear systems with input delay and dynamic uncertainties using multi-dimensional taylor network. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 19(12), 4078–4089 (2021)
S. Dhawan, R. Sinha, S. Chaturvedi, Y. Parvez, A.U. Haq, Development and performance analysis of an automated solar-powered thermoelectric refrigeration system. Appl. Sol. Energy (English Transl Geliotekhnika) 59(3), 226–238 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0003701X22600874
H. Choudhary, V. Mandawaria, M. Sharma, A Comparative analysis of PID controller in closed loop system and open loop system. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Comput. 7(3), 6039–6041 (2017)
J. Chen, M.N. Omidvar, M. Azad, X. Yao, Knowledge-based particle swarm optimization for PID controller tuning. 2017 IEEE Congr. Evol. Comput. CEC 2017—Proc (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2017.7969522
R. Zou, V. Kalivarapu, E. Winer, J. Oliver, S. Bhattacharya, Particle swarm optimization-based source seeking. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 12(3), 865–875 (2015)
S.P. Tee, M.M. Ghazaly, A.C. Amran, I.W. Jamaludin, Experimental investigation of a passive quarter car suspension system. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 13(4), 1181–1187 (2018)
D. Wang, D. Zhao, M. Gong, B. Yang, Research on robust model predictive control for electro-hydraulic servo active suspension systems. IEEE Access 6, 3231–3240 (2017)
A. Ahmed, S.A. Ahmed, N.M. Ghazaly, G.T.A. El-Jaber, PID controller of active suspension system for a quarter car model. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 8(6), 899–909 (2015)
C. Kuber, Modelling simulation and control of an active suspension system. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. 5(11), 66–75 (2014)
T. Yuvapriya, P. Lakshmi, Numerical analysis and performance enhancement of active suspension system using bat optimization. Int. J. Dyn. Control 9(2), 590–601 (2021)
M. Ehtesham, M. Jamil, Control Techniques to Optimize PV System Performance for Smart Energy Applications, vol. 58. Springer Singapore, (2020)
M. Jamil, M. Ehtesham, P.V. Optimizing, system performance considering the impacts of non-uniform irradiance and partial shading. Int. Conf. Energy Econ. Environ.—1st IEEE Uttar Pradesh Sect. Conf. UPCON-ICEEE 2015 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/EnergyEconomics.2015.7235090
A.J. Qazi, U.A. Farooqui, A. Khan, M.T. Khan, F. Mazhar, A. Fiaz, Optimization of semi-active suspension system using particle swarm optimization algorithm. AASRI Procedia 4, 160–166 (2013)
M. Li, J. Li, G. Li, J. Xu, Analysis of active suspension control based on improved fuzzy neural network PID. World Electr Veh J (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj13120226
Y. Shiao, C. C. Lai, Q. A. Nguyen, The analysis of a semi-active suspension system, Proc. SICE Annu. Conf., pp. 2077–2082, (2010)
C.Y. Hsiao, Y.H. Wang, Evaluation of ride comfort for active suspension system based on self-tuning fuzzy sliding mode control. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 20(4), 1131–1141 (2022)
A.A. Ahmed, B. Özkan, Using of fuzzy pid controller to improve vehicle stability for planar model and full vehicle models. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 12(5), 671–680 (2017)
Y.J. Gong et al., Genetic learning particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 46(10), 2277–2290 (2016)
Q.B. Begume, M. Saad, S. Akhtar, A.K. Rathore, M. Reyaz-ur-Rahim, Control of semi-active suspension system using PID controller. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 404, 012039 (2018)
D. Peng, G. Tan, K. Fang, L. Chen, P.K. Agyeman, Y. Zhang, Multiobjective optimization of an off-road vehicle suspension parameter through a genetic algorithm based on the particle swarm optimization. Math. Probl. Eng. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9640928
C.C. Chen, Y.T. Chen, Global optimization control for nonlinear full-car active suspension system with multi-performances. IET Control Theory Appl. 15(14), 1882–1905 (2021)
H. Wu, L. Zheng, Y. Li, Coupling effects in hub motor and optimization for active suspension system to improve the vehicle and the motor performance. J. Sound Vib. 482, 115426 (2020)
S.R. Gampa et al., Pareto optimality based PID controller design for vehicle active suspension system using grasshopper optimization algorithm. J Electr Syst Inf Technol (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43067-022-00065-y
A. Tandel, A.R. Deshpande, S.P. Deshmukh, K.R. Jagtap, Modeling, analysis and PID controller implementation on double wishbone suspension using SimMechanics and Simulink. Procedia Eng. 97, 1274–1281 (2014)
U.C. Allard, G. Dube, R. Khoury, L. Lamontagne, B. Gosselin, F. Laviolette, Time adaptive dual particle swarm optimization. 2017 IEEE Congr. Evol. Comput. CEC 2017—Proc (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2017.7969613
S.U. Khan, S. Yang, L. Wang, L. Liu, A modified particle swarm optimization algorithm for global optimizations of inverse problems. IEEE Trans. Magn. 52(3), 1–4 (2016)
M.R. Bonyadi, Z. Michalewicz, Stability analysis of the particle swarm optimization without stagnation assumption. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 20(5), 814–819 (2016)
S. Shastri, Y. Parvez, R. Chauhan, Inverse kinematics for A 3-R robot using artificial neural network and modified particle swarm optimization. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. C (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40032-019-00539-5
J. Hurel, J. Amaya, J. Peralta, D. Alvarado, F. Flores, Particle Swarm Optimization applied on Fuzzy Control: Comparative analysis for an Quarter-car Active Suspension Model, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Ind. Technol., vol. 2022-Augus (2022)
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support was received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Parvez, Y., Chauhan, N.R. & Srivastava, M. Vibration Control and Comparative Analysis of Passive and Active Suspension Systems Using PID Controller with Particle Swarm Optimization. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. C (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40032-024-01038-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40032-024-01038-y