Abstract
Purpose
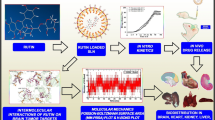
Systemic absorption is the process of drug movement from the site of drug administration to systemic circulation for therapeutic efficacy. Systemic absorption and distribution of therapeutics are affected by the route of administration and may further vary with different sites for the same route. Paclitaxel (PTX) remains one of the most powerful chemotherapeutic drugs to treat various tumors. Nevertheless, PTX has not been used to treat brain tumors because of its blood-brain barrier (BBB) impermeability and lack of drug accumulation in the brain. This study aimed to investigate systemic absorption and brain uptake of PTX following subcutaneous (SC) injection at different sites.
Methods
A hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) polymer was used to prepare the PTX-HPMC hydrogel. The PTX-HPMC hydrogel was characterized by sol-gel transition, drug release, and in situ hydrogel formation. Systemic absorption and distribution in the brain were investigated in mice after subcutaneous injection at three different sites (flank, head, and abdomen). The PTX concentrations in the plasma and brain homogenates were quantified using LC-MS/MS using the liquid-liquid extraction method.
Results
The PTX-HPMC hydrogel showed sol-gel transition at 37 ℃ and bi-phase release with burst and sustained release. Systemic absorption in the plasma at all SC injection sites showed no significant differences. However, the distribution to the brain after SC injection at the head was 2.5 times higher than at the flank, suggesting an injection site-dependent distribution of PTX.
Conclusion
Differences in blood and lymph flow among SC sites are expected to contribute to PTX distribution. SC injection into the head may be a promising route for drug delivery to brain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida N, Rakesh L, Zhao J (2014) Phase behavior of concentrated hydroxypropyl methylcellulose solution in the presence of mono and divalent salt. Carbohydr Polym 99:630–637
Anselmo AC, Gokarn Y, Mitragotri S (2019) Non-invasive delivery strategies for biologics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 18:19–40
Ardilouze JL, Karpe F, Currie JM, Frayn KN, Fielding BA (2004) Subcutaneous adipose tissue blood flow varies between superior and inferior levels of the anterior abdominal wall. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 28:228–233
Auda SH, El-Rasoul SA, Ahmed MM, Osman SK, El-Badry M (2015) In-vitro release and in-vivo performance of tolmetin from different topical gel formulations. J Pharm Investig 45:311–317
Bastiancich C, Danhier P, Préat V, Danhier F (2016) Anticancer drug-loaded hydrogels as drug delivery systems for the local treatment of glioblastoma. J Control Release 243:29–42
Ellis H, Mahadevan V (2014) The surgical anatomy of the scalp. Surg (Oxford) 32:e1–e5
Gao P, Rush BD, Pfund WP, Huang T, Bauer JM, Morozowich W, Kuo MS, Hageman MJ (2003) Development of a supersaturable SEDDS (S-SEDDS) formulation of paclitaxel with improved oral bioavailability. J Pharm Sci 92:2386–2398
Gong C, Qi T, Wei X, Qu Y, Wu Q, Luo F, Qian Z (2013) Thermosensitive polymeric hydrogels as drug delivery systems. Curr Med Chem 20:79–94
Gradel AKJ, Porsgaard T, Lykkesfeldt J, Brockhoff PB, Seested T, Refsgaard HHF (2020) Subcutaneous Administration of insulin is Associated with Regional differences in Injection Depot variability and kinetics in the rat. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 128:332–338
Guarve K, Kriplani P (2021) HPMC- A Marvel Polymer for Pharmaceutical Industry-Patent Review. Recent Adv Drug Deliv Formul 15:46–58
Habimana-Griffin L, Ye D, Carpenter J, Prior J, Sudlow G, Marsala L, Mixdorf M, Rubin J, Chen H, Achilefu S (2020) Intracranial glioma xenograft model rapidly reestablishes blood-brain barrier integrity for longitudinal imaging of tumor progression using fluorescence molecular tomography and contrast agents. J Biomed Opt 25:1–13
Hegde MM, Prabhu S, Mutalik S, Chatterjee A, Goda JS, Satish Rao B (2022) Multifunctional lipidic nanocarriers for effective therapy of glioblastoma: recent advances in stimuli-responsive, receptor and subcellular targeted approaches. J Pharm Investig :1–26
Iwami K, Momota H, Natsume A, Kinjo S, Nagatani T, Wakabayashi T (2012) A novel method of intracranial injection via the postglenoid foramen for brain tumor mouse models. J Neurosurg 116:630–635
Kang JH, Ko YT (2022) Intraosseous administration into the skull: potential blood–brain barrier bypassing route for brain drug delivery. Bioeng Transl Med :e10424
Kim Y-C, Min KA, Jang D-J, Ahn TY, Min JH, Yu BE, Cho KH (2020) Practical approaches on the long-acting injections. J Pharm Investig 50:147–157
Klemp P, Peters K, Hansted B (1989) Subcutaneous blood flow in early male pattern baldness. J Invest Dermatol 92:725–726
Konno T, Watanabe J, Ishihara K (2003) Enhanced solubility of paclitaxel using water-soluble and biocompatible 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine polymers. J Biomed Mater Res A 65:209–214
Korea Central Cancer Registry NCC (2021) Annual report of cancer statistics in Korea in 2019. Ministry of Health and Welfare
Larsen OA, Lassen NA, Quaade F (1966) Blood flow through human adipose tissue determined with radioactive xenon. Acta Physiol Scand 66:337–345
Liu S, Joshi SC, Lam Y (2008) Effects of salts in the Hofmeister series and solvent isotopes on the gelation mechanisms for hydroxypropylmethylcellulose hydrogels. J Appl Polym Sci 109:363–372
Mathew EN, Berry BC, Yang HW, Carroll RS, Johnson MD (2022) Delivering therapeutics to glioblastoma: overcoming biological constraints. Int J Mol Sci 23:1711
Mcfaline-Figueroa JR, Lee EQ (2018) Brain Tumors Am J Med 131:874–882
Pardridge WM (2005) The blood-brain barrier: bottleneck in brain drug development. NeuroRx 2:3–14
Patel MM, Goyal BR, Bhadada SV, Bhatt JS, Amin AF (2009) Getting into the brain. CNS Drugs 23:35–58
Sarkar N (1979) Thermal gelation properties of methyl and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose. J Appl Polym 24:1073–1087
Shimizu S (2004) Routes of administration. The laboratory mouse, 1. 527–547
Taylor NA, Tipton MJ, Kenny GP (2014) Considerations for the measurement of core, skin and mean body temperatures. J Therm Biol 46:72–101
Turner PV, Brabb T, Pekow C, Vasbinder MA (2011) Administration of substances to laboratory animals: routes of administration and factors to consider. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 50:600–613
Wang Y, Li X, Wang L, Xu Y, Cheng X, Wei P (2011) Formulation and pharmacokinetic evaluation of a paclitaxel nanosuspension for intravenous delivery. Int J Nanomedicine 6:1497–1507
Wang Z, Peet NP, Zhang P, Jiang Y, Rong L (2021) Current development of Glioblastoma Therapeutic Agents. Mol Cancer Ther 20:1521–1532
Xu Y, Shen M, Li Y, Sun Y, Teng Y, Wang Y, Duan Y (2016) The synergic antitumor effects of paclitaxel and temozolomide co-loaded in mPEG-PLGA nanoparticles on glioblastoma cells. Oncotarget 7:20890–20901
Zhang K, Zhou L, Chen F, Chen Y, Luo X (2019) Injectable gel self-assembled by paclitaxel itself for in situ inhibition of tumor growth. J Control Release 315:197–205
Zhao M, Bozzato E, Joudiou N, Ghiassinejad S, Danhier F, Gallez B, Preat V (2019) Codelivery of paclitaxel and temozolomide through a photopolymerizable hydrogel prevents glioblastoma recurrence after surgical resection. J Control Release 309:72–81
Zou P, Wang F, Wang J, Lu Y, Tran D, Seo SK (2021) Impact of injection sites on clinical pharmacokinetics of subcutaneously administered peptides and proteins. J Control Release 336:310–321
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF- 2020R1A2B5B01001719), Korea; National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (Ministry of Education) (NRF- 2021R1I1A1A01042149); and a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (BK 21 four).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors (O.H. Lee, J.H. Kang, and Y.T. Ko) declare that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that may have influenced the work reported in this study.
Human and animal rights
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Gachon University (No. LCDI-2020-0062) and followed standard protocols for animal handling and care.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, O.H., Kang, J.H. & Ko, Y.T. Subcutaneous injection sites impact brain uptake of blood-brain barrier impermeable paclitaxel. J. Pharm. Investig. 53, 845–855 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-023-00634-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-023-00634-x