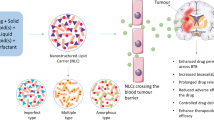
Abstract
The primary requirement for curing cancer is the delivery of essential drug load at the cancer microenvironment with therapeutic efficacy. Considering this, the present study aims to formulate “Rutin”-encapsulated solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) for effective brain delivery across the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Rutin-loaded SLNs were fabricated by oil-in-water microemulsion technique and were characterized for their physicochemical properties. The in vivo biodistribution study of rutin-loaded SLNs was studied using Rattus norvegicus rats. Subsequently, in silico molecular docking and dynamic calculations were performed to examine the binding affinity as well as stability of rutin at the active site of target protein “epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR).” Formulated rutin-loaded SLNs were predominantly spherical in shape with an average particle diameter of 100 nm. Additionally, the biocompatibility and stability have been proved in vitro. The presence and biodistribution of rutin in vivo after 54 h of injection were observed as 15.23 ± 0.32% in the brain, 8.68 ± 0.63% in the heart, 4.78 ± 0.28% in the kidney, 5.04 ± 0.37% in the liver, 0.92 ± 0.04% in the lung, and 11.52 ± 0.65% in the spleen, respectively. Molecular docking results revealed the higher binding energy of − 150.973 kJ/mol of rutin with EGFR. Molecular dynamic simulation studies demonstrated that rutin with EGFR receptor complex was highly stable at 30 ns. The observed results exemplified that the formulated rutin-loaded SLNs were stable in circulation for a period up to 5 days. Thus, rutin-encapsulated SLN formulations can be used as a promising vector to target tumors across BBB.

Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrahari V, Agrahari V, Mitra AK (2016) Nanocarrier fabrication and macromolecule drug delivery: challenges and opportunities. Ther Deliv 7(4):257–278
Asfour MH, Mohsen AM (2018) Formulation and evaluation of pH-sensitive rutin nanospheres against colon carcinoma using HCT-116 cell line. J Adv Res 9:17–26
Baskararaj S, Panneerselvam T, Govindaraj S, Arunachalam S, Parasuraman P, Pandian SRK, Sankaranarayanan M, Mohan UP, Palanisamy P, Ravishankar V (2020) Formulation and characterization of folate receptor-targeted PEGylated liposome encapsulating bioactive compounds from Kappaphycus alvarezii for cancer therapy. 3 Biotech 10(3):1–18
Bhatia S (2016) Nanoparticles types, classification, characterization, fabrication methods and drug delivery applications. In: Bhatia S (ed) Natural polymer drug delivery systems: nanoparticles, plants, and algae. Springer International Publishing, Cham, p 33–93
Cacabelos R, Cacabelos P, Torrellas C, Tellado I, Carril JC (2014) Pharmacogenomics of Alzheimer’s disease: novel therapeutic strategies for drug development. In Pharmacogenomics in drug discovery and development. Humana Press, New York, p 323–556
Chandramohan V, Kaphle A, Chekuri M, Gangarudraiah S, Bychapur Siddaiah G (2015) Evaluating andrographolide as a potent inhibitor of NS3-4A protease and its drug-resistant mutants using in silico approaches. Adv Virol 2015:1–9
Chen Z-L, Huang M, Wang X-R, Fu J, Han M, Shen Y-Q, Xia Z, Gao J-Q (2016) Transferrin-modified liposome promotes α-mangostin to penetrate the blood–brain barrier. Nanomedicine 12(2):421–430
Chua LS (2013) A review on plant-based rutin extraction methods and its pharmacological activities. J Ethnopharmacol 150(3):805–817
Dammalli M, Chandramohan V, Biradar MI, Nagaraju N, Gangadharappa BS (2014) In silico analysis and identification of novel inhibitor for new H1N1 swine influenza virus. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 4:S635–S640
Das S, Chaudhury A (2011) Recent advances in lipid nanoparticle formulations with solid matrix for oral drug delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 12(1):62–76
David AVA, Arulmoli R, Parasuraman S (2016) Overviews of biological importance of quercetin: a bioactive flavonoid. Pharmacogn Rev 10(20):84
DeLano WL (2002) Pymol: an open-source molecular graphics tool. CCP4 Newsl Protein Crystallogr 40(1):82–92
Dixit S (2014) Anticancer effect of rutin isolated from the methanolic extract of Triticum aestivum straw in mice. Med Sci 2(4):153–160
Dolatabadi JEN, Omidi Y (2016) Solid lipid-based nanocarriers as efficient targeted drug and gene delivery systems. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 77:100–108
Escuder-Gilabert L, Molero-Monfort M, Villanueva-Camanas R, Sagrado S, Medina-Hernandez M (2004) Potential of biopartitioning micellar chromatography as an in vitro technique for predicting drug penetration across the blood–brain barrier. J Chromatogr B 807(2):193–201
Gangadharappa BS, Sharath R, Revanasiddappa PD, Chandramohan V, Balasubramaniam M, Vardhineni TP (2020) Structural insights of metallo-betalactamase revealed an effective way of inhibition of enzyme by natural inhibitors. J Biomol Struct Dyn 38(13):1–15
Ganta S, Devalapally H, Shahiwala A, Amiji M (2008) A review of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug and gene delivery. J Control Release 126(3):187–204
Garcia-Garcia E, Andrieux K, Gil S, Couvreur P (2005) Colloidal carriers and blood–brain barrier (BBB) translocation: a way to deliver drugs to the brain? Int J Pharm 298(2):274–292
Gastaldi L, Battaglia L, Peira E, Chirio D, Muntoni E, Solazzi I, Gallarate M, Dosio F (2014) Solid lipid nanoparticles as vehicles of drugs to the brain: current state of the art. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 87(3):433–444
Graefe EU, Wittig J, Mueller S, Riethling AK, Uehleke B, Drewelow B, Pforte H, Jacobasch G, Derendorf H, Veit M (2001) Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of quercetin glycosides in humans. J Clin Pharmacol 41(5):492–499
Ishak RA, Mostafa NM, Kamel AO (2017) Stealth lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles loaded with rutin for effective brain delivery–comparative study with the gold standard (tween 80): optimization, characterization and biodistribution. Drug Deliv 24(1):1874–1890
Kreuter J, Alyautdin RN, Kharkevich DA, Ivanov AA (1995) Passage of peptides through the blood-brain barrier with colloidal polymer particles (nanoparticles). Brain Res 674(1):171–174
Kumari R, Kumar R (2014) C. open source drug discovery and A. Lynn. J Chem Inf Model 54:1951–1962
Kunjiappan S, Panneerselvam T, Somasundaram B, Arunachalam S, Sankaranarayanan M, Parasuraman P (2018a) Preparation of liposomes encapsulated Epirubicin-gold nanoparticles for tumor specific delivery and release. Biomed Phys Eng Express 4(4):045027
Kunjiappan S, Panneerselvam T, Somasundaram B, Sankaranarayanan M, Chowdhury R, Chowdhury A, Bhattacharjee C (2018b) Design, in silico modeling, biodistribution study of rutin and quercetin loaded stable human hair keratin nanoparticles intended for anticancer drug delivery. Biomed Phys Eng Express 4(2):025019
Kunjiappan S, Theivendran P, Baskararaj S, Sankaranarayanan B, Palanisamy P, Saravanan G, Arunachalam S, Sankaranarayanan M, Natarajan J, Somasundaram B (2019) Modeling a pH-sensitive Zein-co-acrylic acid hybrid hydrogels loaded 5-fluorouracil and rutin for enhanced anticancer efficacy by oral delivery. 3 Biotech 9(5):185
Kunjiappan S, Govindaraj S, Parasuraman P, Sankaranarayanan M, Arunachalam S, Palanisamy P, Mohan UP, Babkiewicz E, Maszczyk P, Vellaisamy S (2020a) Design, in silico modelling and functionality theory of folate-receptor-targeted myricetin-loaded bovine serum albumin nanoparticle formulation for cancer treatment. Nanotechnology 31(15):155102
Kunjiappan S, Theivendren P, Pavadai P, Govindaraj S, Sankaranarayanan M, Somasundaram B, Arunachalam S, Ram Kumar Pandian S, Ammunje DN (2020b) Design and in silico modeling of Indoloquinoxaline incorporated keratin nanoparticles for modulation of glucose metabolism in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biotechnol Prog 36(1):e2904
Liu Y, Guan S, Luo Z, Han F, Han W, Wang S, Zhang H (2020) How different substitution positions of F, Cl atoms in benzene ring of 5-methylpyrimidine pyridine derivatives affect the inhibition ability of EGFRL858R/T790M/C797S inhibitors: a molecular dynamics simulation study. Molecules 25(4):895
Lukowski G, Kasbohm J, Pflegel P, Illing A, Wulff H (2000) Crystallographic investigation of cetyl palmitate solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 196(2):201–205
Markoutsa E, Papadia K, Giannou A, Spella M, Cagnotto A, Salmona M, Stathopoulos G, Antimisiaris S (2014) Mono and dually decorated nanoliposomes for brain targeting, in vitro and in vivo studies. Pharm Res 31(5):1275–1289
Martins SM, Sarmento B, Nunes C, Lúcio M, Reis S, Ferreira DC (2013) Brain targeting effect of camptothecin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles in rat after intravenous administration. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 85(3):488–502
Mauludin R, Müller RH, Keck CM (2009) Kinetic solubility and dissolution velocity of rutin nanocrystals. Eur J Pharm Sci 36(4–5):502–510
Moghbelinejad S, Nassiri-Asl M, Farivar TN, Abbasi E, Sheikhi M, Taghiloo M, Farsad F, Samimi A, Hajiali F (2014) Rutin activates the MAPK pathway and BDNF gene expression on beta-amyloid induced neurotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Lett 224(1):108–113
Mohan UP, Sriram B, Panneerselvam T, Devaraj S, MubarakAli D, Parasuraman P, Palanisamy P, Premanand A, Arunachalam S, Kunjiappan S (2020) Utilization of plant-derived Myricetin molecule coupled with ultrasound for the synthesis of gold nanoparticles against breast cancer. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 393:1963–1976
Mukherjee S, Ray S, Thakur R (2009) Solid lipid nanoparticles: a modern formulation approach in drug delivery system. Indian J Pharm Sci 71(4):349–358
Nacht M, Qiao L, Sheets MP, St. Martin T, Labenski M, Mazdiyasni H, Karp R, Zhu Z, Chaturvedi P, Bhavsar D (2013) Discovery of a potent and isoform-selective targeted covalent inhibitor of the lipid kinase PI3Kα. J Med Chem 56(3):712–721
Naksuriya O, Okonogi S, Schiffelers RM, Hennink WE (2014) Curcumin nanoformulations: a review of pharmaceutical properties and preclinical studies and clinical data related to cancer treatment. Biomaterials 35(10):3365–3383
Nandeesh R, Vijayakumar S, Munnolli A, Alreddy A, Veerapur VP, Chandramohan V, Manjunatha E (2018) Bioactive phenolic fraction of Citrus maxima abate lipopolysaccharide-induced sickness behaviour and anorexia in mice: in silico molecular docking and dynamic studies of biomarkers against NF-κB. Biomed Pharmacother 108:1535–1545
Nichols JW, Bae YH (2012) Odyssey of a cancer nanoparticle: from injection site to site of action. Nano Today 7(6):606–618
Omwoyo WN, Ogutu B, Oloo F, Swai H, Kalombo L, Melariri P, Mahanga GM, Gathirwa JW (2014) Preparation, characterization, and optimization of primaquine-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine 9:3865
Pauptit RA, Dennis CA, Derbyshire DJ, Breeze AL, Weston SA, Rowsell S, Murshudov GN (2001) NMR trial models: experiences with the colicin immunity protein Im7 and the p85α C-terminal SH2–peptide complex. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 57(10):1397–1404
Roney C, Kulkarni P, Arora V, Antich P, Bonte F, Wu A, Mallikarjuana N, Manohar S, Liang H-F, Kulkarni AR (2005) Targeted nanoparticles for drug delivery through the blood–brain barrier for Alzheimer’s disease. J Control Release 108(2–3):193–214
Santos BLd (2011) Avaliação do potencial antitumoral de flavonóides polihidroxilados sobre células de glioblastoma humano
Selvaraj K, Chowdhury R, Bhattacharjee C (2013) Isolation and structural elucidation of flavonoids from aquatic fern Azolla microphylla and evaluation of free radical scavenging activity. Int J Pharm Sci 5(3):743–749
Shah KA, Joshi MD, Patravale VB (2009) Biocompatible microemulsions for fabrication of glyceryl monostearate solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) of tretinoin. J Biomed Nanotechnol 5(4):396–400
Sharma S, Sahni JK, Ali J, Baboota S (2015) Effect of high-pressure homogenization on formulation of TPGS loaded nanoemulsion of rutin–pharmacodynamic and antioxidant studies. Drug Deliv 22(4):541–551
Su Z, Sun F, Shi Y, Jiang C, Meng Q, Teng L, Li Y (2009) Effects of formulation parameters on encapsulation efficiency and release behavior of risperidone poly (D, L-lactide-co-glycolide) microsphere. Chem Pharm Bull 57(11):1251–1256
Tapeinos C, Battaglini M, Ciofani G (2017) Advances in the design of solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers for targeting brain diseases. J Control Release 264:306–332
Trotta M, Debernardi F, Caputo O (2003) Preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles by a solvent emulsification–diffusion technique. Int J Pharm 257(1–2):153–160
Ud Din F, Aman W, Ullah I, Qureshi OS, Mustapha O, Shafique S, Zeb A (2017) Effective use of nanocarriers as drug delivery systems for the treatment of selected tumors. Int J Nanomedicine 12:7291–7309
Üner M, Yener G (2007) Importance of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) in various administration routes and future perspectives. Int J Nanomedicine 2(3):289–300
Venishetty VK, Chede R, Komuravelli R, Adepu L, Sistla R, Diwan PV (2012) Design and evaluation of polymer coated carvedilol loaded solid lipid nanoparticles to improve the oral bioavailability: a novel strategy to avoid intraduodenal administration. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 95:1–9
Wang SW, Monagle J, McNulty C, Putnam D, Chen H (2004) Determination of P-glycoprotein inhibition by excipients and their combinations using an integrated high-throughput process. J Pharm Sci 93(11):2755–2767
Welti S, Kühn S, d'Angelo I, Brügger B, Kaufmann D, Scheffzek K (2011) Structural and biochemical consequences of NF1 associated nontruncating mutations in the Sec14-PH module of neurofibromin. Hum Mutat 32(2):191–197
Wong HL, Bendayan R, Rauth AM, Li Y, Wu XY (2007) Chemotherapy with anticancer drugs encapsulated in solid lipid nanoparticles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59(6):491–504
Xiao G, Gan L-S (2013) Receptor-mediated endocytosis and brain delivery of therapeutic biologics. Int J Cell Biol 2013:1–14
Yan H, Wang J, Yi P, Lei H, Zhan C, Xie C, Feng L, Qian J, Zhu J, Lu W (2011) Imaging brain tumor by dendrimer-based optical/paramagnetic nanoprobe across the blood-brain barrier. Chem Commun 47(28):8130–8132
Yan S, Zhang L, Wang S, Wu T, Gong Z (2018) Inhibition of the Ras/Raf/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling pathway by compounds of natural origin for possible treatment of spinal cord injury: an in silico approach. Exp Ther Med 15(3):2860–2868
Yang S, Zhu J, Lu Y, Liang B, Yang C (1999a) Body distribution of camptothecin solid lipid nanoparticles after oral administration. Pharm Res 16(5):751–757
Yang SC, Lu LF, Cai Y, Zhu JB, Liang BW, Yang CZ (1999b) Body distribution in mice of intravenously injected camptothecin solid lipid nanoparticles and targeting effect on brain. J Control Release 59(3):299–307
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr. P. Kathirvel, Mr. V. Krishnaprabhu Technicians for FT-IR and XRD analysis, and Sir CV Raman, KS Krishnan International Research Center, Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education, Krishnankoil, Tamilnadu, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SRK, PP, SV, VR, PP, TP, MS, and SK conceived and designed the research. SRK, PP, SV, VR, PP, LMS, VC, TP, MS, and SK conducted the experiments. SRK, MS, TP, PP, and SK analyzed the data. KS, SRK, MS, and TP wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript. All data were generated in-house and no paper mill was used.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. Further, all experimental procedures were performed in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the local animal protection committee.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandian, S.R.K., Pavadai, P., Vellaisamy, S. et al. Formulation and evaluation of rutin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for the treatment of brain tumor. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 394, 735–749 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-02015-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-02015-9