Abstract
Purpose
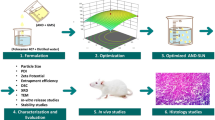
Recently, therapeutic effects of 6-methoxyflavone (6MF) have been reported. However, the use of 6MF is limited due to its poor water solubility. The low aqueous solubility of 6MF results in its low plasma level after oral administration, which limits its clinical application. Lymphatic uptake is a promising way to enhance oral bioavailability. Thus, the purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) on the lymphatic uptake of 6MF.
Methods
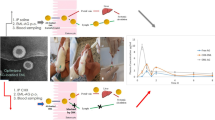
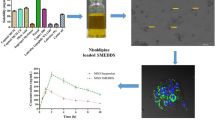
6MF-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle (6MF-SLN) and 6MF-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier (6MF-NLC) were fabricated with a hot homogenization and sonication technique. These 6MF-SLN and 6MF-NLC were characterized for their particle sizes, zeta potentials, in vitro release, cytotoxicity, and cellular uptake. They were also subjected to in vivo lymphatic uptake studies.
Results
In this study, 6MF-SLNs and 6MF-NLC were fabricated to achieve improved oral bioavailability and sustained therapeutic effect of 6MF. The composition of lipid matrix affected physicochemical properties and release profiles of 6MF. Encapsulation of 6MF in lipid nanoparticles resulted in an enhanced cellular uptake in Caco-2 cells. In vivo lymphatic uptake study in rats revealed that SLN and NLC significantly improved lymphatic uptake of 6MF than the control without SLN or NLC (6MF alone).
Conclusion
SLN and NLC could be promising oral delivery platforms for 6MF.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awaad A, Nakamura M, Ishimura K (2012) Imaging of size-dependent uptake and identification of novel pathways in mouse peyer’s patches using fluorescent organosilica particles. Nanomedicine: NBM 8(5):627–236
Baek JS, Cho CW (2017a) Surface modification of solid lipid nanoparticles for oral delivery of curcumin: improvement of bioavailability through enhanced cellular uptake, and lymphatic uptake. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 117:132–140
Baek JS, Cho CW (2017b) A multifunctional lipid nanoparticle for co-delivery of paclitaxel and curcumin for targeted delivery and enhanced cytotoxicity in multidrug resistant breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 8(18):30369–30382
Baek JS, Hwang CJ, Jung HW, Park YK, Kim YH et al (2013) Comparative pharmacokinetics of a marker compound, baicalin in KOB extract after oral administration to normal and allergic-induced rats. Drug Deliv 21(6):453–458
Baek JS, Choo CC, Qian C, Tan NS, Shen Z et al (2016) Multi-drug-loaded microcapsules with controlled release for management of Parkinson’s disease. Small 12(27):3712–3722
Baek JS, Yeo EW, Lee YH, Tan NS, Loo SCJ (2017) Controlled-release nanoencapsulating microcapsules to combat inflammatory diseases. Drug Des Dev Ther 11:1707–1717
Baek JS, Tan CH, Ng NKJ, Yeo YP, Rice SA et al (2018) A programmable lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticle system for localized, sustained antibiotic delivery to Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial biofilms. Nanoscale Horiz 3(3):305–311
Battaglia L, Ugazio E (2019) Lipid nano- and microparticles: an overview of patent-related research. J Nanomater 2019:1–22
Bhalekar MR, Upadhaya PG, Madgulkar AR, Kshirsagar SJ, Dube A et al (2015) In-vivo bioavailability and lymphatic uptake evaluation of lipid nanoparticulates of darunavir. Drug Deliv 23(7):2581–2586
Bhaskar K, Anbu J, Ravichandiran V, Venkateswarlu V, Rao YM (2009) Lipid nanoparticles for transdermal delivery of flurbiprofen: formulation in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo studies. Lipids Health Dis 8(1):6–20
Caliph SM, Charman WN, Porter CJ (2000) Effect of short-, medium-, and long-chain fatty acid-based vehicles on the absolute oral bioavailability and intestinal lymphatic transport of halofantrine and assessment of mass balance in lymph-cannulated and non-cannulated rats. J Pharm Sci 89(8):1073–1084
Daha A, Horrman A (2006) Use of a dynamic in vitro lipolysis model to rationalize oral formulation development for poor water soluble drugs: correlation with in vivo data and the relationship to intra-enterocyte processes in rats. Pharm Res 23(9):2165–2174
Doktorovova S, Souto EB, Silva AM (2014) Nanotoxicology applied to solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers—a systematic review of in vitro data. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 87(1):1–18
Druker DJ (2020) Advances in oral peptide therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 19(4):277–289
Duan Y, Dhar A, Patel C, Khimani M, Neogi S et al (2020) A brief review on solid lipid nanoparticles: part and parcel of contemporary drug delivery systems. RSC Adv 10(45):26777–26791
Freitas C, Müller RH (1998) Effect of light and temperature on zeta potential and physical stability in solid lipid nanoparticle (SLN™) dispersions. Int J Pharm 168(2):221–229
Gan L, Zhang C, Wu FJ, Li H, Zhang WP et al (2018) Microencapsulated nanostructured lipid carriers as delivery system for rutin. Mater Technol 32(2):357–363
Haider M, Abdin SM, Kamal L, Orive G (2020) Nanostructured lipid carriers for delivery of chemotherapeutics: a review. Pharmaceutics 12(3):288
Hajialyani M, Tewari D, Sorbarzo-sanchez E, Nabavi SM, Farzaei MH et al (2018) Natural product-based nanomedicines for wound healing purpose: therapeutic targets and drug delivery systems. Int J Nanomed 13:5023–5043
Hall BJ, Karim N, Chebib M, Johnston GAR, Hanrahan JR (2014) Modulation of ionotropic GABA receptors by 6-methoxyflavanone and 6-methoxyflavone. Neurochem Res 39(6):1068–1078
Huh HW, Na YG, Bang KH, Kim SJ, Kim M et al (2020) Extended intake of mulberry leaf extract delayed metformin elimination via inhibiting the organic cation transporter 2. Pharmaceutics 12(1):49
Idrees H, Zaidi SZJ, Sabir A, Khan RU, Zhang X et al (2020) A review of biodegradable natural polymer-based nanoparticles for drug delivery applications. Nanomaterials 10(10):1970
Jain P, Rahi P, Pandey V, Asati S, Soni V (2017) Nanostructure lipid carriers: a modish contrivance to overcome the ultraviolet effects. Egypt J Basic Appl Sci 4(2):89–100
Jia L (2015) Nanoparticle formulation increases oral bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs: approaches experimental evidences and theory. Curr Nanosci 1(3):237–243
Khan S, Baboota S, Ali J, Khan S, Narang RS et al (2015) Nanostructured lipid carriers: an emerging platform for improving oral bioavailability of liphophilic drugs. Int J Pharm Investig 5(4):182–191
Khosa A, Reddi S, Saha RN (2018) Nanostructured lipid carriers for site-specific drug delivery. Biomed Pharmacother 103:598–613
Kim JH, Baek JS, Park JK, Lee BJ, Kim MS et al (2017) Development of Houttuynia cordata extract-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for oral delivery: high drug loading efficiency and controlled release. Molecules 22(12):2215
Lakshmi P, Kumar GA (2010) Nanosuspension technology: a review. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 2(4):35–40
Makwana V, Jain R, Patel K, Nivsarkar M, Joshi A (2015) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) of Efavirenz as lymph targeting drug delivery system: elucidation of mechanism of uptake using chylomicron flow blocking approach. Int J Pharm 495(1):439–446
Markovic M, Ben-Shabat S, Keinan S, Aponick A, Zimmermann EM et al (2018) Lipidic prodrug approach for improved oral drug delivery and therapy. Med Res Rev 39(2):579–607
Mishra V, Bansal KK, Verma A, Yadav N, Thakur S et al (2018) Solid lipid nanoparticles: emerging colloidal nano drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutics 10(4):191
Montoto SS, Muraca G, Ruiz ME (2020) Solid lipid nanoparticles for drug delivery: pharmacological and biopharmaceutical aspects. Font Mol Biosci 7:587997
Müller RH, Mäder K, Gohla S (2000) Solid lipid nanoparticle (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—a review of the state of the art. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 50(1):161–177
Müller RH, Jacobs C, Kayser O (2001) Nanosuspensions as particulate drug formulations in therapy Rationale for development and what we can expect for the future. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 47(1):3–19
Mura P, Maestrelli F, D’Ambrosio M, Luceri C, Cirri M (2021) Evaluation and comparison of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) as vectors to develop hydrochlorothiazide effective and safe pediatric oral liquid formulation. Pharmaceutics 13(4):437
Murthy A, Ravi RR, Kathuria H, Malekar S (2020) Oral bioavailability enhancement of raloxifene with nanostructured lipid carriers. Nanomaterials 10(6):1085
Ota M, Hashimoto Y, Sato M, Sato Y, Smith RL Jr, Inomata H (2016) Solubility of flavone, 6-methoxyflavone and anthracene in supercritical CO2 with/without a co-solvent of ethanol correlated by using a newly proposed entropy-based solubility parameter. Fluid Phase Equilib 425:65–71
Santos CMM, Silva AMS (2020) The antioxidant activity of prenylflavonoids. Molecules 25(3):696–728
Shahid M, Subhan F, Ahmad N, Sewell RDE (2017) The flavonoid 6-methoxyflavone allays cisplatin-induced neuropathic allodynia and hypoalgesia. Biomed Pharmacother 95:1725–1733
So JS, Kim GC, Song M, Lee CG, Park E et al (2014) 6-Methoxyflavon inhibits NFAT translocation into the nucleus and suppresses T cell activation. J Immunol Res 193(6):2772–2783
Son GH, Na YG, Huh HW, Wang M, Kim MK et al (2019) Systemic design and evaluation of ticagrelor-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for enhancing bioavailability and antiplatelet activity. Pharmaceutics 11(5):222
Trevaskis NL, Kaminskas LM, Porter CJH (2015) From sewer to saviour - targeting the lymphatic system to promote drug exposure and activity. Nat Rev Drug Discov 14:781–803
Tungmunnithum D, Thongboonyou A, Philboonn A, Yangsabai A (2018) Flavonoids and other phenolic compounds from medicinal plants for pharmaceutical and medical aspects: an overview. Medicines 5(3):93–108
Vishwakarma N, Jain A, Sharma R, Mody N, Vyas S et al (2019) Lipid-based nanocarriers for lymphatic transportation. AAPS PharmSciTech 20(2):83
Wang T, Wang N, Zhang Y, Shen W, Gao X et al (2010) Solvent injection-lyophilization of tert-butyl alcohol/water cosolvent systems for the preparation of drug-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B 79(1):254–261
Wang T, Li Q, Bi K (2018) Bioactive flavonoid in medicinal plants: structure, activity and biological fate. Asian J Pharm Sci 13(1):12–23
Wright L, Barnes TJ, Prestidge CA (2020) Oral delivery of protein-based therapeutics: Gastroprotective strategies, physiological barriers and in vivo permeability prediction. Int J Pharm 585(2):119488
Zhang L, Alfano J, Race D, Davé RN (2018) Zero-order release of poorly water-soluble drug from polymeric films made via aqueous slurry casting. Eur J Pharm Sci 117:245–254
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (grant number 2020R1G1A101121112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors (S. Ryu, M. Jin, H.‑K. Lee, M.‑H. Wang, J.‑S. Baek, and C.‑W. Cho) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All experiments were conducted according to the guidelines of the Animal Care Commission of Kangwon National University. This study was approved by Kangwon National University Institutional Animal Care Committee (Protocol no. KW-201117-5).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryu, S., Jin, M., Lee, HK. et al. Effects of lipid nanoparticles on physicochemical properties, cellular uptake, and lymphatic uptake of 6-methoxflavone. J. Pharm. Investig. 52, 233–241 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-021-00557-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-021-00557-5