Abstract
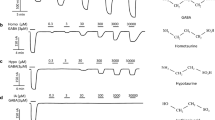
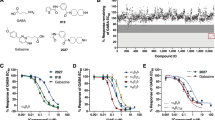
We evaluated the effects of 6-methoxyflavanone and 6-methoxyflavone on wild-type α1/α2β2γ2L GABAA and ρ1 GABAC receptors and on mutant ρ1I307S, ρ1W328 M, ρ1I307S/W328 M GABAC receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes using two-electrode voltage clamp and radioligand binding. 6-Methoxyflavanone and 6-methoxyflavone act as a flumazenil-insensitive positive allosteric modulator of GABA responses at human recombinant α1β2γ2L and α2β2γ2L GABAA receptors. However, unlike 6-methoxyflavone, 6-methoxyflavanone was relatively inactive at α1β2 GABAA receptors. 6-Methoxyflavanone inhibited [3H]-flunitrazepam binding to rat brain membranes. Both flavonoids were found to be inactive as modulators at ρ1, ρ1I307S and ρ1W328 M GABA receptors but acted as positive allosteric modulators of GABA at the benzodiazepine sensitive ρ1I307S/W328 M GABA receptors. This double mutant retains ρ1 properties of being insensitive to bicuculline and antagonised by TPMPA and THIP. Additionally, 6-methoxyflavanone was also a partial agonist at ρ1W328 M GABA receptors. The relative inactivity of 6-methoxyflavanone at α1β2 GABAA receptors and it’s partial agonist action at ρ1W328 M GABA receptors suggest that it exhibits a unique profile not matched by other flavonoids.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- GABA:
-
γ-Amino butyric acid
- GABAA :
-
γ-Amino butyric acid-A receptor
- THIP:
-
4,5,6,7-Tetrahydroisoxazolo[5,4-c]pyridin-3-ol
- TPMPA:
-
(1,2,5,6-Tetrahydropyridin-4-yl)methylphosphinic acid
References
Hanrahan JR, Chebib M, Johnston GAR (2011) Flavonoid modulation of GABAA receptors. Br J Pharmacol 163:234–245
Walters RJ, Hadley SH, Morris DW, Amin J (2000) Benzodiazepines act on GABAA receptors via two distinct and separable mechanisms. Nature Neurosci 3:1274–1281
Hui KM, Wang XH, Xue H (2000) Interaction of flavones from the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis with the benzodiazepine site. Planta Med 66:91–93
Marder M, Zinczuk J, Colombo MI, Wasowki C, Viola H, Wolfman C, Medina JH, Ruveda EA, Paladini A (1997) Synthesis of halogenated/nitrated flavone derivatives and evaluation of their affinity for the central benzodiazepine receptor. Bio Med Chem Lett 7:2003–2008
Medina JH, Viola H, Wolfman C, Marder M, Wasowski C, Calvo D, Paladini AC (1998) Neuroactive flavonoids: new ligands for the benzodiazepine receptors. Phytomedicine 5(2):235–243
Nielsen M, Frokjaer S, Braestrup C (1988) High affinity of the naturally-occurring biflavonoid, amentoflavone, to brain benzodiazepine receptors in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol 37:3285–3287
Griebel G, Perrault G, Tan S, Schoemaker H, Sanger DJ (1999) Pharmacological studies on synthetic flavonoids: comparison with diazepam. Neuropharmacol 38:965–977
Marder M, Viola H, Wasowski C, Wolfman C, Waterman PG, Medina JH, Paladini A (1995) 6,3′-Dinitroflavone, a novel high affinity ligand for the benzodiazepine receptor with potent anxiolytic properties. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 5:2717–2720
Salgueiro JB, Ardenghi P, Dias M, Ferreira MBC, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (1997) Anxiolytic and synthetic flavonoid ligands of the central benzodiazepine receptor have no effect on memory tasks in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 58:887–891
Viola H, Wasowki C, Levi de Stein M, Wolfman C, Silveira R, Dajas F, Medina JH, Paladini A (1995) Apigenin, a component of Matricaria recutita flowers, is a central benzodiazepine receptors-ligand with anxiolytic effects. Planta Med 61:213–216
Wolfman C, Viola H, Marder M, Ardenghi P, Wasowki C, Schroder N, Izquierdo I, Ruveda E, Paladini A, Medina JH (1998) Pharmacological characterisation of 6-bromo-3′-nitroflavone, a synthetic flavonoid with high affinity for the benzodiazepine receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 61:239–246
Hall BJ, Chebib M, Hanrahan JR, Johnston GAR (2004) Flumazenil-independent positive modulation of γ-aminobutyric acid action by 6-methylflavone at human recombinant α1β2γ2L and α1β2 GABAA receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 491:1–8
Hall BJ, Chebib M, Hanrahan JR, Johnston GAR (2005) 6-Methylflavanone, a more efficacious positive allosteric modulator of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) action at human recombinant α2β2γ2L than at α1β2γ2L and α1β2 GABAA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 512:97–104
Huen MSY, Hui K, Leung JWC, Sigel E, Baur R, Wong T, Xue H (2003) Naturally occurring 2′-hydroxyl-substituted flavonoids as high-affinity benzodiazepine site ligands. Biochem Pharmacol 66:2397–2407
Karim N, Curmi J, Gavande N, Johnston GAR, Hanrahan JR, Tierney ML, Chebib M (2012) 2′-Methoxy-6-methylflavone: a novel anxiolytic and sedative with subtype selective activating and modulating actions at GABAA receptors. Br J Pharmacol 165:880–896
Karim N, Gavande N, Wellendorph P, Johnston GAR, Hanrahan JR, Chebib M (2011) 3-Hydroxy-2′-methoxy-6-methylflavone: a potent anxiolytic with a unique selectivity profile at GABAA receptor subtypes. Biochem Pharmacol 82:1971–1983
Kavvadias D, Sand P, Youdim K, Qaiser M, Rice-Evans C, Baur R, Sigel E, Rausch W, Riederer P, Schreier P (2004) The flavone hispidulin, a benzodiazepine receptor ligand with positive allosteric properties, traverses the blood-brain barrier and exhibits anticonvulsive effects. Br J Pharmacol 142:811–820
Hanrahan JR, Chebib M, Davucheron NLM, Hall BJ, Johnston GAR (2003) Semisynthetic preparation of amentoflavone: a negative modulator at GABAA receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13(14):2281–2284
Wang F, Xu Z, Yuen CT, Chow CY, Lui YL, Tsang SY, Xue H (2007) 6,20-Dihydroxyflavone, a subtype-selective partial inverse agonist of GABAA receptor benzodiazepine site. Neuropharmacol 53:574–582
Huang XQ, Liu T, Gu JD, Luo XM, Ji RY, Cao Y, Xue H, Wong JTF, Wong BL, Pei G, Jiang HL, Chen KX (2001) 3D-QSAR model of flavonoids binding at benzodiazepine site in GABA(A) receptors. J Med Chem 44:1883–1891
Marder M, Estiu G, Blanch LB, Viola H, Wasowski C, Medina JH, Paladini AC (2001) Molecular modeling and QSAR analysis of the interaction of flavone derivatives with the benzodiazepine binding site of the GABAA receptor complex. Bioorg Med Chem 9:323–335
Hanrahan JR, Mewett KN, Chebib M, Burden PM, JGA R (2001) An improved, versatile synthesis of the GABAC antagonists (1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl)methylphosphinic acid (TPMPA) and (piperidin-4-yl)methylphosphinic acid (P4MPA). J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 1:2389–2392
Huang SH, Duke RK, Chebib M, Sasaki K, Wada K, Johnston GAR (2003) Bilobalide, a sesquiterpene trilactone from Gingko biloba, is an antagonist at recombinant α1β2γ2L GABAA receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 464:1–8
Hosie AM, Dunne EL, Harvey RJ, Smart TG (2003) Zinc-mediated inhibition of GABAA receptors: discrete binding sites underlie subtype specificity. Nature Neurosci 4:362–369
Wellendorph P, Høg S, Sabbatini P, Pedersen MH, Martiny L, Knudsen GM, Frølund B, Clausen RP, Bräuner-Osborne H (2010) Novel radioiodinated γ-hydroxybutyric acid analogues for radiolabeling and photo linking of high-affinity γ-hydroxybutyric acid binding sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 335:458–464
Ebert B, Wafford KA, Whiting PJ, Krogsgaard-Larsen P, Kemp JA (1994) Molecular pharmacology of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor agonists and partial agonists in oocytes Injected with different α, β, and γ -receptor subunit combinations. Mol Pharmacol 46:957–963
Kusama T, Spivak CE, Whiting P, Dawson VL, Scaeffer JC, Uhl GR (1993) Pharmacology of GABA ρ1 and GABA α/β receptors expressed in xenopus oocytes and COS cells. Br J Pharmacol 109:200–206
Hansen RS, Paulsen I, Davies M (2005) Determinants of amentoflavone interaction at the GABAA receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 519:199–207
Fernandez S, Mewett K, Hanrahan J, Chebib M, Johnston G (2008) Flavan-3-ol derivatives are positive modulators of GABAA receptors with higher efficacy for the alpha2 subtype and anxiolytic action in mice. Neuropharmacol 55:900–907
Alexander SPH, Mathie A, Peters JA (2009) Guide to receptors and channels (GRAC), 4th edition. Br J Pharmacol 158(Suppl. 1):S1–S254
Chebib M, Johnston GAR (2000) GABA-activated ligand gated ion channels: medicinal chemistry and molecular biology. J Med Chem 43:1–21
Amin J (1999) A single hydrophobic residue confers barbiturate sensitivity to γ-aminobutyric acid type C receptor. Mol Pharmacol 55:411–423
Belelli D, Pau D, Cabras G, Peters JA, Lambert JJ (1999) A single amino acid confers barbiturate sensitivity upon the GABA ρ1 receptor. Br J Pharmacol 127:601–604
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr Paul Whiting (Merck, Sharpe and Dohme Research Laboratories, Harlow, UK) for the gift of human α1, α2, β2 and γ2L DNA, Dr George Uhl (National Institute for Drug Abuse, Baltimore, MD, USA) for the gift of human ρ1 DNA, Professor Jeremy Lambert (University of Dundee, Dundee, UK) for the gift of human ρ1I307S, ρ1W328M and ρ1W328M/I307S DNA. THIP was a gift from Prof. Povl Krogsgaard-Larsen (Copenhagen). We are also grateful to all those who performed the surgery to provide the oocytes. This work was funded by a grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council (NH&MRC). BJH was supported by an Australian Postgraduate Award and the John Lamberton Scholarship. NK acknowledges funding from The University of Malakand, Pakistan (Faculty Development Programme Scholarship) and the John Lamberton Scholarship.
Conflict of interest
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue: In Honor of Richard Olsen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hall, B.J., Karim, N., Chebib, M. et al. Modulation of Ionotropic GABA Receptors by 6-Methoxyflavanone and 6-Methoxyflavone. Neurochem Res 39, 1068–1078 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1157-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1157-2