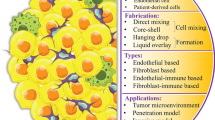
Abstract
Background
Cancer nanomedicines (NMs) have emerged as potential anticancer therapeutics with advantages of tumor-targeting drug delivery for improved efficacy against human solid tumors. Despite promising data obtained in preclinical studies, few clinical trials have demonstrated successful results. The failure in the bench-to-bedside translation of NM efficacy may be related to the lack of clinical relevance of the tumor models used for preclinical screening and evaluation. Consideration of the pathophysiological factors that reduce drug distribution and activity in solid tumor tissues should be part of the selection of models used in preclinical evaluations of NMs.
Area covered
We briefly describe the fundamental concepts of NM targeting strategies and current issues related to their preclinical evaluation. We then provide an overview of the conventional and three-dimensional (3D) models utilized in preclinical evaluations of the target-site pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of anticancer NMs. We further describe factors of the tumor microenvironment (TME) in solid tumors that significantly hinder the tissue distribution and therapeutic efficacy of anticancer drugs. Moreover, we focus on tumor spheroid (TS)-based microtumor models in terms of how they recapitulate TME conditions to represent a promising in vitro 3D tumor model for preclinical evaluations of anticancer NMs. Current state-of-the-art TS and TS-based microtumor generation methods are also reviewed.
Expert opinion
TS-based microtumors are promising in vitro models for the preclinical evaluation of NMs. The use of microtumor models is strongly recommended as the method of choice for the screening and evaluation of NMs with promising clinical efficacy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Abd AM, Lee JH, Kim SY, Kun N, Kuh HJ (2008) Novel application of multicellular layers culture for in situ evaluation of cytotoxicity and penetration of paclitaxel. Cancer Sci 99:423–431
Alessandri K, Sarangi BR, Gurchenkov VV, Sinha B, Kiessling TR et al (2013) Cellular capsules as a tool for multicellular spheroid production and for investigating the mechanics of tumor progression in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:14843–14848
Aung A, Kumar V, Theprungsirikul J, Davey SK, Varghese S (2020) An engineered tumor-on-a-chip device with breast cancer-Immune cell interactions for assessing T-cell recruitment. Cancer Res 80:263–275
Bae YH, Park K (2011) Targeted drug delivery to tumors: myths, reality and possibility. J Control Release 153:198–205
Balkwill FR, Capasso M, Hagemann T (2012) The tumor microenvironment at a glance. J Cell Sci 125:5591–5596
Barenholz Y (2012) Doxil®–the first FDA-approved nano-drug: lessons learned. J Control Release 160:117–134
Battistini L, Burreddu P, Sartori A, Arosio D, Manzoni L et al (2014) Enhancement of the uptake and cytotoxic activity of doxorubicin in cancer cells by novel cRGD-semipeptide-anchoring liposomes. Mo Pharm 11:2280–2293
Brown JM (2007) Tumor hypoxia in cancer therapy. Methods Enzymol 435:297–321
Carlsson J, Acker H (1988) Relations between pH, oxygen partial pressure and growth in cultured cell spheroids. Int J Cancer 42:715–720
Chabner BA, Roberts TG (2005) Chemotherapy and the war on cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 5:65–72
Chauhan VP, Jain RK (2013) Strategies for advancing cancer nanomedicine. Nat Mater 12:958–962
Chauhan VP, Stylianopoulos T, Boucher Y, Jain RK (2011) Delivery of molecular and nanoscale medicine to tumors: transport barriers and strategies. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng 2:281–298
Chen Y, Song Y, Du W, Gong L, Chang H et al (2019) Tumor-associated macrophages: an accomplice in solid tumor progression. J Biomed Sci 26:78
Cho C-Y, Chiang T-H, Hsieh L-H, Yang W-Y, Hsu H-H et al (2020) Development of a novel hanging drop platform for engineering controllable 3D microenvironments. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:327
Choi YH, Han HK (2018) Nanomedicines: current status and future perspectives in aspect of drug delivery and pharmacokinetics. J Pharm Investig 48:43–60
Choi SY, Lee DW, Song B, Kim SY, Kim HJ et al (2020) A rapid quantification of invasive phenotype in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a novel 3D pillar array system. Oral Oncol 108:104807
Costa EC, de Melo-Diogo D, Moreira AF, Carvalho MP, Correia IJ (2018) Spheroids formation on non-adhesive surfaces by liquid overlay technique: considerations and practical approaches. Biotechnol J 13:1700417
Cui X, Hartanto Y, Zhang H (2017) Advances in multicellular spheroids formation. J R Soc Interface 14:20160877
Dewhirst MW, Secomb TW (2017) Transport of drugs from blood vessels to tumour tissue. Nat Rev Cancer 17:738–750
Driehuis E, Kretzschmar K, Clevers H (2020) Establishment of patient-derived cancer organoids for drug-screening applications. Nat Protoc 15:3380–3409
Endo H, Inoue M (2019) Dormancy in cancer. Cancer Sci 110:474–480
Estrada MF, Rebelo SP, Davies EJ, Pinto MT, Pereira H et al (2016) Modelling the tumour microenvironment in long-term microencapsulated 3D co-cultures recapitulates phenotypic features of disease progression. Biomaterials 78:50–61
Fell HB, Robison R (1929) The growth, development and phosphatase activity of embryonic avian femora and limb-buds cultivated in vitro. Biochem J 23(767–784):5
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285:1182–1186
Foty R (2011) A simple hanging drop cell culture protocol for generation of 3D spheroids. J vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/2720
Frantz C, Stewart KM, Weaver VM (2010) The extracellular matrix at a glance. J Cell Sci 123:4195–4200
Gencoglu MF, Barney LE, Hall CL, Brooks EA, Schwartz AD et al (2018) Comparative study of multicellular tumor spheroid formation methods and implications for drug screening. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 4:410–420
Gould SE, Junttila MR, de Sauvage FJ (2015) Translational value of mouse models in oncology drug development. Nat Med 21:431–439
Guyton AC, Prather J, Scheel K, McGehee J (1966) Interstitial fluid pressure. IV. Its effect on fluid movement through the capillary wall. Circ Res 19:1022–1030
Hagendoorn J, Tong R, Fukumura D, Lin Q, Lobo J et al (2006) Onset of abnormal blood and lymphatic vessel function and interstitial hypertension in early stages of carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 66:3360–3364
He H, Liu L, Morin EE, Liu M, Schwendeman A (2019) Survey of clinical translation of cancer nanomedicines—lessons learned from successes and failures. Acc Chem Res 52:2445–2461
Henke E, Nandigama R, Ergün S (2020) Extracellular matrix in the tumor microenvironment and its Impact on cancer therapy. Front Mol Biosci 6:160–160
Herrmann D, Conway JRW, Vennin C, Magenau A, Hughes WE et al (2014) Three-dimensional cancer models mimic cell–matrix interactions in the tumour microenvironment. Carcinogenesis 35:1671–1679
Holle AW, Young JL, Spatz JP (2016) In vitro cancer cell–ECM interactions inform in vivo cancer treatment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 97:270–279
Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB, Johnston PG (2013) Cancer drug resistance: an evolving paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer 13:714–726
Hou S, Jin W, Xiao W, Deng B, Wu D et al (2019) Integrin alpha5 promotes migration and cisplatin resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Am J Cancer Res 9:2774–2788
Huang YL, Ma Y, Wu C, Shiau C, Segall JE et al (2020) Tumor spheroids under perfusion within a 3D microfluidic platform reveal critical roles of cell-cell adhesion in tumor invasion. Sci Rep 10:9648
Hulikova A, Vaughan-Jones RD, Swietach P (2011) Dual role of CO2/HCO3(-) buffer in the regulation of intracellular pH of three-dimensional tumor growths. J Biol Chem 286:13815–13826
Hwang HJ, Oh MS, Lee DW, Kuh HJ (2019) Multiplex quantitative analysis of stroma-mediated cancer cell invasion, matrix remodeling, and drug response in a 3D co-culture model of pancreatic tumor spheroids and stellate cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:258
Ioannidis JPA, Kim BYS, Trounson A (2018) How to design preclinical studies in nanomedicine and cell therapy to maximize the prospects of clinical translation. Nat Biomed Eng 2:797–809
Jaganathan H, Gage J, Leonard F, Srinivasan S, Souza GR et al (2014) Three-dimensional in vitro co-culture model of breast tumor using magnetic levitation. Sci Rep 4:6468
Jain RK (2013) Normalizing tumor microenvironment to treat cancer: bench to bedside to biomarkers. J Clin Oncol 31:2205–2218
Jeong SY, Lee JH, Shin Y, Chung S, Kuh HJ (2016) Co-culture of tumor spheroids and fibroblasts in a collagen matrix-incorporated microfluidic chip mimics reciprocal activation in solid tumor microenvironment. PLoS ONE 11:e0159013
Jing X, Yang F, Shao C, Wei K, Xie M et al (2019) Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer 18:157
Joyce MH, Lu C, James ER, Hegab R, Allen SC et al (2018) Phenotypic basis for matrix stiffness-dependent chemoresistance of breast cancer cells to doxorubicin. Front Oncol 8:337
Kang A, Park J, Ju J, Jeong GS, Lee SH (2014) Cell encapsulation via microtechnologies. Biomaterials 35:2651–2663
Kang J, Lee DW, Hwang HJ, Yeon SE, Lee MY et al (2016) Mini-pillar array for hydrogel-supported 3D culture and high-content histologic analysis of human tumor spheroids. Lab Chip 16:2265–2276
Kapalczynska M, Kolenda T, Przybyla W, Zajaczkowska M, Teresiak A et al (2018) 2D and 3D cell cultures - a comparison of different types of cancer cell cultures. Arch Med Sci 14:910–919
Khawar IA, Kim JH, Kuh HJ (2015) Improving drug delivery to solid tumors: priming the tumor microenvironment. J Control Release 201:78–89
Khawar IA, Park JK, Jung ES, Lee MA, Chang S et al (2018) Three dimensional mixed-cell spheroids mimic stroma-mediated chemoresistance and invasive migration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Neoplasia 20:800–812
Kim SK, Jang SD, Kim H, Chung S, Park JK et al (2020) Phenotypic heterogeneity and plasticity of cancer cell migration in a pancreatic tumor three-dimensional culture model. Cancers (basel) 12:1305
Kimlin LC, Casagrande G, Virador VM (2013) In vitro three-dimensional (3D) models in cancer research: an update. Mol Carcinog 52:167–182
Ko J, Ahn J, Kim S, Lee Y, Lee J et al (2019) Tumor spheroid-on-a-chip: a standardized microfluidic culture platform for investigating tumor angiogenesis. Lab Chip 19:2822–2833
Lee KH, da No Y, Kim SH, Ryoo JH, Wong SF et al (2011) Diffusion-mediated in situ alginate encapsulation of cell spheroids using microscale concave well and nanoporous membrane. Lab Chip 11:1168–1173
Lee DW, Choi YS, Seo YJ, Lee MY, Jeon SY et al (2014) High-throughput screening (HTS) of anticancer drug efficacy on a micropillar/microwell chip platform. Anal Chem 86:535–542
Lee DW, Lee MY, Ku B, Nam DH (2015) Automatic 3D cell analysis in high-throughput microarray using micropillar and microwell chips. J Biomol Screen 20:1178–1184
Lee DW, Kang J, Hwang HJ, Oh M-S, Shin BC et al (2018a) Pitch-tunable pillar arrays for high-throughput culture and immunohistological analysis of tumor spheroids. RSC Adv 8:4494–4502
Lee JH, Kim SK, Khawar IA, Jeong SY, Chung S et al (2018b) Microfluidic co-culture of pancreatic tumor spheroids with stellate cells as a novel 3D model for investigation of stroma-mediated cell motility and drug resistance. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37:4
Lee JM, Park DY, Yang L, Kim E-J, Ahrberg CD et al (2018c) Generation of uniform-sized multicellular tumor spheroids using hydrogel microwells for advanced drug screening. Sci Rep 8:17145
Lee SY, Doh I, Lee DW (2019) A high throughput apoptosis assay using 3D cultured cells. Molecules 24:3362
Levinger I, Ventura Y, Vago R (2014) Chapter Nine - Life is three dimensional—as in vitro cancer cultures should be. In: Tew KD, Fisher PB (eds) Advances in cancer research, vol 121. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 383–414
Lin RZ, Chang HY (2008) Recent advances in three-dimensional multicellular spheroid culture for biomedical research. Biotechnol J 3:1172–1184
Longati P, Jia X, Eimer J, Wagman A, Witt MR et al (2013) 3D pancreatic carcinoma spheroids induce a matrix-rich, chemoresistant phenotype offering a better model for drug testing. BMC Cancer 13:95
Ma X-L, Sun Y-F, Wang B-L, Shen M-N, Zhou Y et al (2019) Sphere-forming culture enriches liver cancer stem cells and reveals stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 as a potential therapeutic target. BMC Cancer 19:760
Maeda H, Wu J, Sawa T, Matsumura Y, Hori K (2000) Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: a review. J Control Release 65:271–284
Mak IW, Evaniew N, Ghert M (2014) Lost in translation: animal models and clinical trials in cancer treatment. Am J Transl Res 6:114–118
Markman JL, Rekechenetskiy A, Holler E, Ljubimova JY (2013) Nanomedicine therapeutic approaches to overcome cancer drug resistance. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:1866–1879
Matsumura Y, Maeda H (1986) A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs. Cancer Res 46:6387–6392
Mehta G, Hsiao AY, Ingram M, Luker GD, Takayama S (2012) Opportunities and challenges for use of tumor spheroids as models to test drug delivery and efficacy. J Control Release 164:192–204
Mirbagheri M, Adibnia V, Hughes BR, Waldman SD, Banquy X et al (2019) Advanced cell culture platforms: a growing quest for emulating natural tissues. Mater Horiz 6:45–71
Mitchell MJ, Billingsley MM, Haley RM, Wechsler ME, Peppas NA et al (2021) Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 20:101–124
Mittler F, Obeïd P, Rulina AV, Haguet V, Gidrol X et al (2017) High-Content Monitoring of drug effects in a 3D spheroid model. Front Oncol 7:293
Mó I, Sabino IJ, Melo-Diogo D, Lima-Sousa R, Alves CG et al (2020) The importance of spheroids in analyzing nanomedicine efficacy. Nanomedicine (lond) 15:1513–1525
Nam S, Khawar IA, Park JK, Chang S, Kuh HJ (2019) Cellular context-dependent interaction between cancer and stellate cells in hetero-type multicellular spheroids of pancreatic tumor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 515:183–189
Nath S, Devi GR (2016) Three-dimensional culture systems in cancer research: focus on tumor spheroid model. Pharmacol Ther 163:94–108
Nichols JW, Sakurai Y, Harashima H, Bae YH (2017) Nano-sized drug carriers: extravasation, intratumoral distribution, and their modeling. J Control Release 267:31–46
Nishida-Aoki N, Gujral TS (2019) Emerging approaches to study cell-cell interactions in tumor microenvironment. Oncotarget 10:785–797
Nunes AS, Barros AS, Costa EC, Moreira AF, Correia IJ (2019) 3D tumor spheroids as in vitro models to mimic in vivo human solid tumors resistance to therapeutic drugs. Biotechnol Bioeng 116:206–226
Oh MS, Khawar IA, Lee DW, Park JK, Kuh HJ (2020) Three-dimensional imaging for multiplex phenotypic analysis of pancreatic microtumors grown on a minipillar array chip. Cancers (basel) 12:3662
Park K (2013) Facing the truth about nanotechnology in drug delivery. ACS Nano 7:7442–7447
Pearce AK, O’Reilly RK (2019) Insights into active targeting of nanoparticles in drug delivery: advances in clinical studies and design considerations for cancer nanomedicine. Bioconjug Chem 30:2300–2311
Peng X, Gandhi V (2012) ROS-activated anticancer prodrugs: a new strategy for tumor-specific damage. Ther Deliv 3:823–833
Pinto B, Henriques AC, Silva PMA, Bousbaa H (2020) Three-dimensional spheroids as in vitro preclinical models for cancer research. Pharmaceutics 12:1186
Priwitaningrum DL, Blondé J-BG, Sridhar A, van Baarlen J, Hennink WE et al (2016) Tumor stroma-containing 3D spheroid arrays: A tool to study nanoparticle penetration. J Control Release 244:257–268
Raghunand N, Mahoney BP, Gillies RJ (2003) Tumor acidity, ion trapping and chemotherapeutics. II. pH-dependent partition coefficients predict importance of ion trapping on pharmacokinetics of weakly basic chemotherapeutic agents. Biochem Pharmacol 66:1219–1229
Ravizza R, Molteni R, Gariboldi MB, Marras E, Perletti G et al (2009) Effect of HIF-1 modulation on the response of two- and three-dimensional cultures of human colon cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil. Eur J Cancer 45:890–898
Rebelo SP, Pinto C, Martins TR, Harrer N, Estrada MF et al (2018) 3D-3-culture: a tool to unveil macrophage plasticity in the tumour microenvironment. Biomaterials 163:185–197
Rice AJ, Cortes E, Lachowski D, Cheung BCH, Karim SA et al (2017) Matrix stiffness induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogenesis 6:e352
Rodrigues J, Heinrich MA, Teixeira LM, Prakash J (2021) 3D In Vitro Model (R)evolution: Unveiling Tumor-Stroma Interactions. Trends Cancer 7:249–264
Rossi G, Manfrin A, Lutolf MP (2018) Progress and potential in organoid research. Nat Rev Genet 19:671–687
Safra T, Muggia F, Jeffers S, Tsao-Wei DD, Groshen S et al (2000) Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (doxil): reduced clinical cardiotoxicity in patients reaching or exceeding cumulative doses of 500 mg/m2. Ann Oncol 11:1029–1033
Sahai E, Astsaturov I, Cukierman E, DeNardo DG, Egeblad M et al (2020) A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Cancer 20:174–186
Sarisozen C, Abouzeid AH, Torchilin VP (2014) The effect of co-delivery of paclitaxel and curcumin by transferrin-targeted PEG-PE-based mixed micelles on resistant ovarian cancer in 3-D spheroids and in vivo tumors. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 88:539–550
Sharma P, Hu-Lieskovan S, Wargo JA, Ribas A (2017) Primary, adaptive, and acquired aesistance to cancer immunotherapy. Cell 168:707–723
Shin Y, Han S, Jeon JS, Yamamoto K, Zervantonakis IK et al (2012) Microfluidic assay for simultaneous culture of multiple cell types on surfaces or within hydrogels. Nat Protoc 7:1247–1259
Sontheimer-Phelps A, Hassell BA, Ingber DE (2019) Modelling cancer in microfluidic human organs-on-chips. Nat Rev Cancer 19:65–81
Su S, Kang M, P, (2020) Recent advances in nanocarrier-assisted therapeutics delivery systems. Pharmaceutics 12:837
Suggitt M, Bibby MC (2005) 50 years of preclinical anticancer drug screening: empirical to target-driven approaches. Clin Cancer Res 11:971–981
Swietach P, Hulikova A, Patiar S, Vaughan-Jones RD, Harris AL (2012) Importance of intracellular pH in determining the uptake and efficacy of the weakly basic chemotherapeutic drug, doxorubicin. PLoS ONE 7:e35949
Sykes EA, Dai Q, Sarsons CD, Chen J, Rocheleau JV et al (2016) Tailoring nanoparticle designs to target cancer based on tumor pathophysiology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:E1142-1151
Tchoryk A, Taresco V, Argent RH, Ashford M, Gellert PR et al (2019) Penetration and uptake of nanoparticles in 3D tumor spheroids. Bioconjug Chem 30:1371–1384
Torras N, García-Díaz M, Fernández-Majada V, Martínez E (2018) Mimicking epithelial tissues in three-dimensional cell culture models. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 6:197
Tseng H, Gage JA, Raphael RM, Moore RH, Killian TC et al (2013) Assembly of a three-dimensional multitype bronchiole coculture model using magnetic levitation. Tissue Eng Part C Methods 19:665–675
Tseng H, Gage JA, Shen T, Haisler WL, Neeley SK et al (2015) A spheroid toxicity assay using magnetic 3D bioprinting and real-time mobile device-based imaging. Sci Rep 5:13987
Tung YC, Hsiao AY, Allen SG, Torisawa YS, Ho M et al (2011) High-throughput 3D spheroid culture and drug testing using a 384 hanging drop array. Analyst 136:473–478
van der Meel R, Sulheim E, Shi Y, Kiessling F, Mulder WJM et al (2019) Smart cancer nanomedicine. Nat Nanotechnol 14:1007–1017
Vinci M, Gowan S, Boxall F, Patterson L, Zimmermann M et al (2012) Advances in establishment and analysis of three-dimensional tumor spheroid-based functional assays for target validation and drug evaluation. BMC Biol 10:29
Warburg O (1956) On the origin of cancer cells. Science 123:309–314
Ware MJ, Keshishian V, Law JJ, Ho JC, Favela CA et al (2016) Generation of an in vitro 3D PDAC stroma rich spheroid model. Biomaterials 108:129–142
Weeks JC, Catalano PJ, Cronin A, Finkelman MD, Mack JW et al (2012) Patients’ expectations about effects of chemotherapy for advanced cancer. N Engl J Med 367:1616–1625
Wenzel C, Riefke B, Gründemann S, Krebs A, Christian S et al (2014) 3D high-content screening for the identification of compounds that target cells in dormant tumor spheroid regions. Exp Cell Res 323:131–143
Whatley BR, Li X, Zhang N, Wen X (2014) Magnetic-directed patterning of cell spheroids. J Biomed Mater Res A 102:1537–1547
Wu LY, Di Carlo D, Lee LP (2008) Microfluidic self-assembly of tumor spheroids for anticancer drug discovery. Biomed Microdevices 10:197–202
Wu PH, Opadele AE, Onodera Y, Nam JM (2019) Targeting integrins in cancer nanomedicine: applications in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Cancers (basel) 11:1783
Xin H, Sha X, Jiang X, Zhang W, Chen L et al (2012) Anti-glioblastoma efficacy and safety of paclitaxel-loading Angiopep-conjugated dual targeting PEG-PCL nanoparticles. Biomaterials 33:8167–8176
Youn YS, Bae YH (2018) Perspectives on the past, present, and future of cancer nanomedicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 130:3–11
Yuan J, Dong X, Yap J, Hu J (2020) The MAPK and AMPK signalings: interplay and implication in targeted cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol 13:113
Zanoni M, Piccinini F, Arienti C, Zamagni A, Santi S et al (2016) 3D tumor spheroid models for in vitro therapeutic screening: a systematic approach to enhance the biological relevance of data obtained. Sci Rep 6:19103
Ziolkowska K, Stelmachowska A, Kwapiszewski R, Chudy M, Dybko A et al (2013) Long-term three-dimensional cell culture and anticancer drug activity evaluation in a microfluidic chip. Biosens Bioelectron 40:68–74
Funding
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT (grant numbers 2019R1A5A2027588 and 2019R1A2B5B02070524).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors (I. A. Khawar, T. Gosh, J. K. Park and H. J. Kuh) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khawar, I.A., Ghosh, T., Park, J.K. et al. Tumor spheroid-based microtumor models for preclinical evaluation of anticancer nanomedicines. J. Pharm. Investig. 51, 541–553 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-021-00534-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-021-00534-y