Abstract
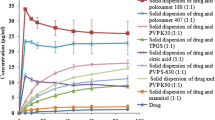
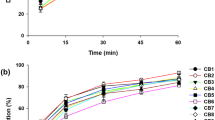
The main purpose of this investigation is increasing of the solubility and dissolution rate of Azithromycin by solid dispersion technique using Kolliphor P 237, Kolliphor P 338 and Kolliphor P 407. Kolliphor (P 237, P 338 and P 407) in various properties by weight {(1:0.5), (1:1), (1:1.5) and (1:2)}, utilizing solvent evaporation method. Dissolution studies carried out in phosphate buffer with pH 6.0 according to US pharmacopoeia method. The drug release profiles were studied, so we found that the dissolution rate of the drug (by calculating the dissolution parameters) was significantly increase compared to pure drug, also solubility of physical mixtures as well as solid dispersions increased compared to the intact drug. For example solubility of the drug increased from 85–753 μg mL−1 (for Kolliphor P 237; 8 times more). The best results were as follows: Kolliphor P 237 > Kolliphor P 338 > Kolliphor P 407. IR spectra revealed no chemical incompatibility between drug and polymer. Drug-polymer interactions were investigated using differential scanning calorimetry, powder X-ray diffraction and scanning election microscopy. The dissolution rate and solubility of Azithromycin solid dispersions was improved significantly using Kolliphor. In addition, the simplicity of this method is very effective and have been met the project objectives.















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Biopharmaceutics Classification System.
International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use.
References
Amidon GL, Lennernas H, Shah VP, Crison JR (1995) A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: the correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharm Res 12:413–420
Anderson NH, Bauer M, Boussac N, Khan-Malek R, Munden P, Sardaro M (1998) An evaluation of fit factors and dissolution efficiency for the comparison of in vitro dissolution profiles. J Pharm Biomed Anal 17(4–5):811–822
Babu GV, Kumar NR, Himasankar K, Seshasayana A, Murthy KV (2003) Nimesulide-modified gum karaya solid mixtures: preparation, characterization and formulation development. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 29:855–864
Bashiri-Shahroodi A, Nassab PR, Szabó-Révész P, Rajkó R (2008) Preparation of a solid dispersion by a dropping method to improve the rate of dissolution of Meloxicam. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 34:781–788
Bolourchian N, Mahboobian MM, Dadashzadeh S (2013) The effect of PEG molecular weights on dissolution behavior of Simvastatin in solid dispersions. Iran J Pharm Res 12(Supplement):11–20
Carson IW, Alexander JP, Hewitt JC, Dundee JW (1972) Clinical studies of induction agents XLI: venous sequelae following the use of the steroid anaesthetic agent, Althesin. Br J Anaesth 44:1311–1313
Carson IW, Clarke RSJ, Dundee JW (1973) Alterations in response to somatic pain associated with anaesthesia. Br J Pharmacol 47(679):590–592
Chiou WL, Riegelman S (1971) Pharmaceutical applications of solid dispersion systems. J Pharm Sci 60(9):1281–1302
Craig DQ (2002) The mechanisms of drug release from solid dispersions in water-soluble polymers. Int J Pharm 2:131–144
Deepti DH, Madan AK (2007) Solid dispersion adsorbents for enhancement of dissolution rates of drugs. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol 61(2):97–101
Ha JM, Kang SY, Park CW, Bin SA, Rhee YS, Seo JW, Kim SH, Chi SC, Park ES (2012) Effect of poloxamer on physicochemical properties of tacrolimus solid dispersion improving water solubility and dissolution rate. J Pharm Investig 42(4):171–176
Hinkelmann K, Kempthorne O (2008) Design and analysis of experiments I and II, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Irving R (1994) Physical basis for poloxamer interactions.Schmolka Company, Grosse Ile. Ann N Y Acad Sci 720:92–97
Khan KA (1975) The concept of dissolution efficiency. J Pharm Pharmacol 27:48–49
Leuner C, Dressman J (2000) Improving drug solubility for oral delivery using solid dispersions. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 50:47–60
Moffat AC, Osselton MD, Widdop B (2011) Clarke analysis of drug and poisons, 4th edn. Pharmaceutical Press, London, pp 1561–1562
Mura P, Moyano JR, Gonzalez-Rodrigue ML, Rabasco-Alvarez AM, Cirri M, Maestrelli F (2005) Characterization and dissolution properties of ketoprofeninbinary and ternary solid dispersions with polyethylene glycol and surfactants. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 31:425–434
Narasaiah L, Jimidi B, Goli V, Kanakam VB (2011) Enhancement of dissolution rate of atorvastatin calcium using solid dispersions by dropping method. Int J PharmTech Res 3(2):652–659
Okonogi S, Puttipipatkhachorn S (2006) Dissolution improvement of high drug loaded solid dispersion. AAPS PharmSci Tech 7:E148–E153
Okonogi S, Yonemochi E, Oguchi T, Puttipipatkhachorn S, Yamamoto K (1997) Enhanced dissolution of ursodeoxycholic acid from the solid dispersion. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 23:1115Y1121
Parmar KR, Shah SR, Sheth NR (2011) Preparation, characterization, and in vitro evaluation of ezetimibe binary solid dispersions with poloxamer 407 and PVP K30. J Pharm Innov 6(2):107–114
Patel PV, Panchal SS, Mehta TA (2013) Improvement of dissolution rate of tacrolimus by solid dispersion technique. J Pharm Investig 43(1):45–53
Shim JB, Kim MJ, Kim SJ, Kang SJ, Lee JH, Kim HS, Lee D, Khang G (2012) Dissolution properties of control released solid dispersion of carvedilol with HPMC and Eudragit RS. J Pharm Investig 42(5):285–291
Sweetman SC (2009) Martindale: the complete drug reference, 36th edn. Pharmaceutical Press, London, p 207
The Indian Pharmacopoeia, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (2007) Government of India, Azithromycin monograph
USP:United States Pharmacopeia and National Formulary USP 30-NF 25. (2007) The United States, Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Rockville, MD, pp 3179–3180
Valizadeh H, Nokhodchi A, Qarakhani N, Zakeri-Milani P, Azarmi S, Hassanzadeh D, Löbenberg R (2004) Physicochemical characterization of solid dispersions of indomethacin with PEG 6000, Myrj 52, lactose, sorbitol, dextrin, and Eudragit E100. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 30:303–317
van Belle G (2008) Statistical rules of thumb, vol 2. Wiley, Hoboken
Wipo, The World Intellectual Property Organization (2013) Azithromycin: A world best-selling antibiotic-Pliva. http://www.wipo.int/sme/en/case_studies/pliva.htm. Accessed June 2013
Acknowledgments
This article does not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any of the authors. All authors (E. Adeli. S. A. Mortazavi) declare that they have no conflict of interest. The paper is taken from a part of PharmD. Thesis of Ehsan Adeli, The International Branch, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adeli, E., Mortazavi, S.A. Design, formulation and evaluation of Azithromycin binary solid dispersions using Kolliphor series for the solubility and in vitro dissolution rate enhancement. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 44, 119–131 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-013-0108-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-013-0108-x