Abstract
Background
Specific (s)IgG antibodies against environmental and occupational antigens, especially from bacteria, moulds, yeasts, birds and chemicals play an important role for hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP). An increased serum level of sIgG is one criterion in the diagnostic procedure of HP and crucial for the detection of the triggering antigen for successful avoidance of further exposure. In contrast to specific IgE, sIgG concentrations in healthy individuals vary greatly depending on the antigen, which makes it difficult to differentiate from patients with HP. The aim of this study is to update or establish sIgG-reference values for important HP antigens in a healthy blood donor group.
Methods
Therefore a study including six clinical centres in Germany was conducted to collect sera from 121 subjects without any signs of HP and without obvious exposure to potential HP antigens. Specific IgG to 32 typical HP antigens were quantified by ImmunoCAP (ThermoFisher Scientific; Phadia, Uppsala, Sweden). For validation selected measurements were repeated, total IgG was determined, sera were tested for unspecific binding with the human serum albumin ImmunoCAP Ro401, and influence of potential confounders was analysed. Statistical distribution of the antigen-specific IgG values was evaluated and the nonparametric method of percentile calculation was applied.
Results
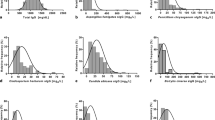
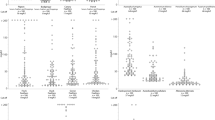
The levels of IgG antibodies to the different antigens varied considerably in the study group from < 0.02 to 726 mgA/L. Low sIgG levels were found against the chemicals and the highest levels to fungal antigens, especially to Aspergillus fumigatus and Botrytis cinerea. For three isocyanates, three acid anhydrides, Trichosporon pullulans and Acremonium kiliense reference values were proposed for the first time. For several avian antigens, moulds, and bacteria pre-existing reference values nearly could be confirmed without significant deviations, but already the 90 % quantile for sIgG against Penicillium chrysogenum, Aspergillus fumigatus and pigeon antigen (Ge91) clearly exceeded the pre-existing values. In contrast, the 97.5 % quantile value for Candida albicans was nearly half of the pre-existing cut-off value.
Discussion
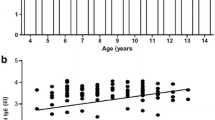
In most cases specific IgG values were not significantly influenced by smoking and gender and most of them were unaffected by age. For implementation of these sIgG reference values into the routine diagnosis of HP, we provide an online available calculator to rank measured sIgG concentrations to the 32 different ImmunoCAP antigens.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- EAA:
-
Extrinsic allergic alveolitis
- FEIA:
-
Fluorescent enzyme immunoassay
- HSA:
-
Human serum albumin
- HP:
-
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- MBP:
-
Maltose-binding protein
- mgA/L:
-
Milligrams of antigen-specific IgG per liter
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- (s)IgG:
-
Specific immunoglobulin G
References
Riario Sforza GG, Marinou A. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: a complex lung disease. Clin Mol Allergy. 2017;15:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12948-017-0062-7
Nogueira R,Melo N,Novais E, Bastos H,Martins N, Delgado L, et al. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: antigen diversity anddiseaseimplications. Pulmonol. 2018;https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2018.07.003
Cormier Y. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (extrinsic allergic alveolitis): a Canadian historical perspective. Can Respiratory J. 2014;21:277–8
Girard M, Cormier Y. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;10:99–103
Sennekamp J, Müller-Wening D, Amthor M, Baur X, Bergmann K-C, Costabel U, et al. Empfehlungen zur Diagnostik der exogen-allergischen Alveolitis. Arbeitgemeinschaft Exogen-Allergische Alveolitis der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Pneumologie und Beatmungsmedizin e. V. (DGP) und der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Allergologie und Klinische Immunologie (DGAKI). Pneumologie. 2007;61:52–6. Guidelines for diagnosing extrinsic allergic alveolitis (hypersensitivity pneumonitis) (German Extrinsic Allergic Alveolitis Study Group)
Quirce S, Vandenplas O, Campo P, Cruz MJ, deBlay F, Koschel D, et al. Occupational hypersensitivity pneumonitis. An EAACI positionpaper. Allergy 2016;71:765–79
Kränke B, Woltsche M, Woltsche-Kahr I, Aberer W. IgG-Antikörper gegen „EAA-spezifische Umweltantigene“ Die Problematik der Normalwertdefinition. Allergologie 2001;24:145–54
Koschel D, Lutzkendorf L, Wiedemann B, Hoffken G. Antigen-specific IgG antibodiesin feather duvet lung. Eur J Clin Invest 2010;40:797–802
Lopata AL, Schinkel M, Potter PC, Jeebhay MF, Hashemi C, Johansson SG, et al. Qualitative andquantitative evaluation of bird-specific IgG antibodies. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2004;134:173–8
van Hoeyveld E, Dupont L, Bossuyt X. Quantification of IgG antibodies to Aspergillus fumigatus andpigeon antigens by ImmunoCAP technology:analternative to theprecipitation technique? Clin Chem 2006;52:1785–93
Sennekamp J, Lehmann E, Joest M. Berufsbedingte exogen allergische Alveolitis. Arbeitsmed Sozialmed Umweltmed 2015;50:38–52
McSharry C, Dye GM, Ismail T, Anderson K, Spiers EM, Boyd G. Quantifying serum antibodyinbird fanciers’hypersensi tivitypneumonitis. BmcPulmMed 2006;6:16. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2466/6/16
Bañales JL, Vázquez L, Mendoza F, Baltazares M, Raymond Y, Nava A, et al. On the correct determination of reference values for serum antibodies against pigeon serum antigen using a group of healthy blood donors. Arch Med Res. 1997;28:289–91
Rodrigo MJ, Benavent MI, Cruz MJ, Rosell M,Murio C, Pascual C, Morell F. Detection of specific antibodies to pigeon serum and bloom antigens by enzyme linked immunosorbent assayinpigeonbreeder’sdisease. OccupEnvironMed. 2000;57:159–64
Sennekamp H-J. Extrinsic allergic alveolitis, Hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Munich, Orlando: Dustri-Verl. Feistle; 2004. ISBN 3-87185-309-7
Makkonen K, Viitala KI, Parkkila S, Niemelä O. Serum IgG and IgE antibodies against mold-derived antigens in patients with symptoms of hypersensitivity. Clin Chim Acta. 2001;305:89–98
Bernstein DI, Ott MG, Woolhiser M, Lummus Z, Graham C. Evaluation of antibody binding to diisocyanate protein conjugates in a general population. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006;97:357–64
Pronk A, Preller L, Raulf-Heimsoth M, Jonkers ICL, Lammers J-W, Wouters IM, et al. Respiratory symptoms, sensitization, and exposure response relationships in spray painters exposed to isocyanates. Am J RespirCritCareMed. 2007;176:1090–7
Hemmer W, Altmann F, Holzweber F, Gruber C, Wantke F, Wöhrl S. ImmunoCAP cellulose displays cross-reactive carbohydrate determinant (CCD) epitopes and can cause false-positive test results in patients with high anti-CCD IgE antibody levels. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141:372–81
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful for the support of ThermoFisher Scientific, who had provided ImmunoCAPs/reagents free of charge. Neither the design of the study nor the evaluation of the data were influenced by ThermoFisher Scientific. We thank C. Bittner, Hamburg, for help in collecting the samples, B. Kendzia, Bochum, for statistical support and U. Meurer, Bochum, for skilful technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study design and the protocol were reviewed and approved by the ethical committee of the Technische Universität Dresden (EK 195052014) in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and ethical approval was obtained from the local ethic committee of each centre.
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
M. Raulf received honorarium for lectures on scientific meetings from HAL Allergy, ThermoFisher Scientific and Astellas. D. Koschel received honorarium for lectures on scientific meetings from Boehringer Ingelheim and Roche. M. Joest received lecture fees for a webinar from ThermoFisher Scientific Phadia. I. Sander, F. Hoffmeyer, D. Nowak, U. Ochmann, A. Preisser, J. Schreiber and J. Sennekamp declare that they have no competing interests.
Cite this as Raulf M, Joest M, Sander I, Hoffmeyer F, Nowak D, Ochmann U, Preisser A, Schreiber J, Sennekamp J, Koschel D. Update of reference values for IgG antibodies against typical antigens of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Data of a German multicentre study. Allergo J Int 2019;28:192–203
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raulf, M., Joest, M., Sander, I. et al. Update of reference values for IgG antibodies against typical antigens of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Allergo J 28, 52–63 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s15007-019-1917-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s15007-019-1917-7