Abstract
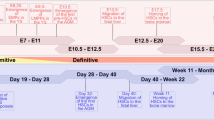
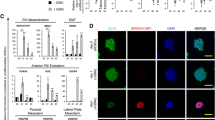
Hemangioblasts or blood islands only arise in early development thereby the sources to obtain these bi-potential cells are limited. While previous studies have isolated both lineages in vitro through the hemangioblast, derivation efficiency was rather low due to cellular damage attributed by enzyme usage and fluorescent activated cell sorting (FACS). This study focused on avoiding the use of damaging factors in the derivation of endothelial cells (ECs). Single cell H9-human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) were obtained by using a mild dissociation protocol then human embryoid body (hEB) formation was performed under hemangioblast differentiation conditions. The hEBs were subjected to a two-stage cytokine treatment procedure. Subsequent culture of the adhesive cells in day 4 hEBs gave arise to a seemingly pure population of ECs. The hESC-derived ECs were characterized by identifying signature endothelial gene and protein markers as well as testing for in vitro functionality. Furthermore, in vivo functionality was also confirmed by transplanting the cells in hindlimb ischemic murine models. We demonstrate that the genetic change required for EC derivation precedes blast colony formation. Furthermore, cell damage was prevented by abating enzyme usage and FACS, resulting in a high yield of ECs upon adhesion. Under this method, confluent cultures of ECs were obtainable 4 days after hEB formation which is significantly faster than previous protocols.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kennedy M, Firpo M, Choi K, Wall C, Robertson S, Kabrun N, et al. A common precursor for primitive erythropoiesis and definitive haematopoiesis. Nature 1997;386:488–493.
Robertson S, Kennedy M, Keller G. Hematopoietic commitment during embryogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1999;872:9–15. discussion 15-16.
Choi K. The hemangioblast: a common progenitor of hematopoietic and endothelial cells. J Hematother Stem Cell Res 2002;11:91–101.
Forrai A, Robb L. The hemangioblast—between blood and vessels. Cell Cycle 2003;2:86–90.
Bollerot K, Pouget C, Jaffredo T. The embryonic origins of hematopoietic stem cells: a tale of hemangioblast and hemogenic endothelium. APMIS 2005;113:790–803.
Jaffredo T, Bollerot K, Sugiyama D, Gautier R, Drevon C. Tracing the hemangioblast during embryogenesis: developmental relationships between endothelial and hematopoietic cells. Int J Dev Biol 2005;49:269–277.
Sumpio BE, Riley JT, Dardik A. Cells in focus: endothelial cell. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2002;34:1508–1512.
Yoder MC. A bipotent mesoderm subset identified via colony-forming assay. Cell Stem Cell 2010;7:643–644.
Cogle CR, Scott EW. The hemangioblast: cradle to clinic. Exp Hematol 2004;32:885–890.
Li Z, Han Z, Wu JC. Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial cells for vascular diseases. J Cell Biochem 2009;106:194–199.
Asahara T, Kawamoto A, Masuda H. Concise review: circulating endothelial progenitor cells for vascular medicine. Stem Cells 2011;29:1650–1655.
Lu SJ, Lee RJ, Napoli C, Oh S, Kimbrel EA, Feng Q. The promise and therapeutic potential of human ES and iPS cells. Stem Cells Int 2011; 2011:959275.
Choi K, Kennedy M, Kazarov A, Papadimitriou JC, Keller G. A common precursor for hematopoietic and endothelial cells. Development 1998;125:725–732.
Levenberg S, Golub JS, Amit M, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Langer R. Endothelial cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002;99:4391–4396.
Huang HL, Hsing HW, Lai TC, Chen YW, Lee TR, Chan HT, et al. Trypsin-induced proteome alteration during cell subculture in mammalian cells. J Biomed Sci 2010;17:36.
Gil CH, Lee JH, Seo J, Park SJ, Park Z, Kim J, et al. Well-defined differentiation of hESC-derived hemangioblasts by embryoid body formation without enzymatic treatment. Biotechnol Lett 2015;37:1315–1322.
Cho SW, Moon SH, Lee SH, Kang SW, Kim J, Lim JM, et al. Improvement of postnatal neovascularization by human embryonic stem cell derived endothelial-like cell transplantation in a mouse model of hindlimb ischemia. Circulation 2007;116:2409–2419.
Kocher AA, Schuster MD, Szabolcs MJ, Takuma S, Burkhoff D, Wang J, et al. Neovascularization of ischemic myocardium by human bone-marrow-derived angioblasts prevents cardiomyocyte apoptosis, reduces remodeling and improves cardiac function. Nat Med 2001;7:430–436.
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 1998;282:1145–1147.
Kim IG, Hwang MP, Du P, Ko J, Ha CW, Do SH, et al. Bioactive cell-derived matrices combined with polymer mesh scaffold for osteogenesis and bone healing. Biomaterials 2015;50:75–86.
Basak GW, Yasukawa S, Alfaro A, Halligan S, Srivastava AS, Min WP, et al. Human embryonic stem cells hemangioblast express HLA-antigens. J Transl Med 2009;7:27.
Park TS, Zimmerlin L, Zambidis ET. Efficient and simultaneous generation of hematopoietic and vascular progenitors from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Cytometry A 2013;83:114–126.
Islam MS, Ni Z, Kaufman DS. Use of human embryonic stem cells to understand hematopoiesis and hematopoietic stem cell niche. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 2010;5:245–250.
Bhatia M. Hematopoiesis from human embryonic stem cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2007;1106:219–222.
Wang L. Endothelial and hematopoietic cell fate of human embryonic stem cells. Trends Cardiovasc Med 2006;16:89–94.
Keller GM, Webb S, Kennedy M. Hematopoietic development of ES cells in culture. Methods Mol Med 2002;63:209–230.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gil, CH., Ki, BS., Seo, J. et al. Directing human embryonic stem cells towards functional endothelial cells easily and without purification. Tissue Eng Regen Med 13, 274–283 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-016-9076-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-016-9076-3