Abstract
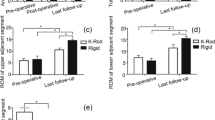
We wanted to know whether K-ROD (KD) internal fixation system could ameliorate lumbar adjacent segment degeneration (LASD) diseases. From May 2010 to May 2012, 66 patients with lumbar LASD were repaired via KD system. The outcome for LASD was analyzed using visual analogue scale (VAS), Oswestry disability index (ODI) and the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey. Meanwhile, range of motion (ROM) of total lumbar and dynamic fixation segments were also examined. Twelve patients inquired the removal of KD system because of fatigue during the first year after surgery. For remaining patients, the mean VAS score for back pain was 45.2±28.7 before operation, and decreased to 22.3±14.2 after two-year surgery (p<0.01); meanwhile, the mean ODI score was decreased from 76.5±11.2% to 21.1±5.4% (p<0.01). SF-36 parameters were significantly improved compared with those acquired the removal of KD system (p<0.01). Total 45 patients restored flexion-extension ROM after surgery (p<0.01). More than 80% disc generation was improved by KD system. KD system is an effective therapeutic way for treating LASD patients. The dynamic stabilization system preserves the motion of fixation segment and provides an alternative for therapy of lumbar LASD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battié MC, Ortega-Alonso A, Niemelainen R, Gill K, Levalahti E, Videman T, et al. Lumbar spinal stenosis is a highly genetic condition partly mediated by disc degeneration. Arthritis Rheumatol 2014;66:3505–3510.
Rushton A, Wright C, Heap A, White L, Eveleigh G, Heneghan N. Survey of current physiotherapy practice for patients undergoing lumbar spinal fusion in the United Kingdom. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2014;39:e1380–E1387.
Rothenfluh DA, Mueller DA, Rothenfluh E, Min K. Pelvic incidencelumbar lordosis mismatch predisposes to adjacent segment disease after lumbar spinal fusion. Eur Spine J 2014 Jul 14 [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00586-014-3454-0.
Ahn DK, Park HS, Choi DJ, Kim KS, Yang SJ. Survival and prognostic analysis of adjacent segments after spinal fusion. Clin Orthop Surg 2010;2: 140–147.
Kok D, Firkins PJ, Wapstra FH, Veldhuizen AG. A new lumbar posterior fixation system, the memory metal spinal system: an in-vitro mechanical evaluation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2013;14:269.
Tauchi R, Imagama S, Sakai Y, Ito Z, Ando K, Muramoto A, et al. The correlation between cervical range of motion and misplacement of cervical pedicle screws during cervical posterior spinal fixation surgery using a CT-based navigation system. Eur Spine J 2013;22:1504–1508.
Khan KM, Bhatti A, Khan MA. Posterior spinal fixation with pedicle screws and rods system in thoracolumbar spinal fractures. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2012;22:778–782.
Nachanakian A, El Helou A, Alaywan M. The interspinous spacer: a new posterior dynamic stabilization concept for prevention of adjacent segment disease. Adv Orthop 2013;2013:637362.
Zhou ZJ, Xia P, Zhao X, Fang XQ, Zhao FD, Fan SW. Can posterior dynamic stabilization reduce the risk of adjacent segment deterioration? Turk Neurosurg 2013;23:579–589.
Di N, Wang HM, Li HQ, Shi RM, Dai F, He QY, et al. A clinical report of K-Rod dynamic stabilization for 39 lumbar disc protrusion cases. Chin J Bone Jt 2013;2:322–327.
World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. J Postgrad Med 2002;48:206–208.
Zigler JE, Delamarter RB. Oswestry disability index. J Neurosurg Spine 2014;20:241–242.
Zanoli G, Jönsson B, Strömqvist B. SF-36 scores in degenerative lumbar spine disorders: analysis of prospective data from 451 patients. Acta Orthop 2006;77:298–306.
Griffith JF, Wang YX, Antonio GE, Choi KC, Yu A, Ahuja AT, et al. Modified Pfirrmann grading system for lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32:e708–E712.
Lumbar spine: agreement in the interpretation of 1.5-T MR images by using the Nordic Modic Consensus Group classification form. Radiology 2010;254:809–817.
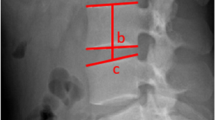
Loebl WY. Measurement of spinal posture and range of spinal movement. Ann Phys Med 1967;9:103–110.
Lu DC, Chou D. Flatback syndrome. Neurosurg Clin N Am 2007;18:289–294.
Liao YY, Lee TS, Lin YM. A Fisher exact test will be more proper. Radiology 2006;239:300–301; author reply 301.
Mineta K, Higashino K, Sakai T, Fukui Y, Sairyo K. Recurrence of type I Modic inflammatory changes in the lumbar spine: effectiveness of intradiscal therapy. Skeletal Radiol 2014;43:1645–1649.
Boyd BS, Villa PS. Normal inter-limb differences during the straight leg raise neurodynamic test: a cross sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2012;13:245.
Ren C, Song Y, Liu L, Xue Y. Adjacent segment degeneration and disease after lumbar fusion compared with motion-preserving procedures: a meta-analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 2014;24 Suppl 1:S245–S253.
Zencica P, Chaloupka R, Hladíková J, Krbec M. [Adjacent segment degeneration after lumbosacral fusion in spondylolisthesis: a retrospective radiological and clinical analysis]. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech 2010;77:124–130.
Xu JP, Yi HL, Li M, Shi ZC, Li JF, Zhao YC, et al. [Clinical application of Wallis interspinous dynamic stabilization in treating adjacent segment degeneration (ASD) after lumbar spinal fusion]. Zhongguo Gu Shang 2013;26:1005–1009.
Bordes-Monmeneu M, Bordes-Garcia V, Rodrigo-Baeza F, Saez D. [System of dynamic neutralization in the lumbar spine: experience on 94 cases]. Neurocirugia (Astur) 2005;16:499–506.
Schnake KJ, Schaeren S, Jeanneret B. Dynamic stabilization in addition to decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2006;31:442–449.
Welch WC, Cheng BC, Awad TE, Davis R, Maxwell JH, Delamarter R, et al. Clinical outcomes of the Dynesys dynamic neutralization system: 1-year preliminary results. Neurosurg Focus 2007;22:e8.
Grob D, Benini A, Junge A, Mannion AF. Clinical experience with the Dynesys semirigid fixation system for the lumbar spine: surgical and patient- oriented outcome in 50 cases after an average of 2 years. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005;30:324–331.
Gift AG. Visual analogue scales: measurement of subjective phenomena. Nurs Res 1989;38:286–288.
Sugiura S, Aoki Y, Toyooka T, Shiga T, Otsuki K, Aikawa E, et al. Characteristics of low back pain in adolescent patients with early-stage spondylolysis evaluated using a detailed visual analogue scale. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2015;40:e29–E34.
Aoki Y, Sugiura S, Nakagawa K, Nakajima A, Takahashi H, Ohtori S, et al. Evaluation of nonspecific low back pain using a new detailed visual analogue scale for patients in motion, standing, and sitting: characterizing nonspecific low back pain in elderly patients. Pain Res Treat 2012;2012: 680496.
Ruiz FK, Bohl DD, Webb ML, Russo GS, Grauer JN. Oswestry Disability Index is a better indicator of lumbar motion than the Visual Analogue Scale. Spine J 2014;14:1860–1865.
Hu J, Gruber KJ, Hsueh KH. Psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the SF-36 in older adults with diabetes in Beijing, China. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2010;88:273–281.
Hou Y, Yuan W. Influences of disc degeneration and bone mineral density on the structural properties of lumbar end plates. Spine J 2012;12:249–256.
Niu G, Yang J, Wang R, Dang S, Wu EX, Guo Y. MR imaging assessment of lumbar intervertebral disk degeneration and age-related changes: apparent diffusion coefficient versus T2 quantitation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2011;32:1617–1623.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Y., Dong, R., Kang, M. et al. K-ROD internal fixation system ameliorates lumbar adjacent segment degeneration: Two-year clinical outcomes of 66 patients. Tissue Eng Regen Med 12, 203–210 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-015-0089-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-015-0089-0