Abstract
Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of ramie leaf ethanol extract (RLE) on C75BL/KsJ-db/db mice were determined. The db/db mice were divided into diabetic control group (C), two experimental groups orally treated with low dose (200 mg/k, RLEL) and high dose (400 mg/kg, RLEH) of RLE. After 6 weeks, fasting blood glucose, serum insulin, and glycosylated hemoglobin levels decreased in RLE groups compared to those in the control group. The glucose levels in the oral glucose tolerance test and area under the curve for glucose in the RLE groups were also significantly lower than those in the control group (p <0.05). The serum total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels were significantly decreased in the RLEH group, whereas the serum HDL-cholesterol level was significantly increased in the RLEH group (p <0.05). These data suggest that RLE may improve blood glucose and lipid metabolism in mice with type 2 diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrink MJ, Newman T, and Davidson PC. (1979) Effect of high and low fiber diets on plasma lipids and insulin. Am J Clin Nutr 32, 1486–91.
Bailey CJ. (1999) Insulin resistance and antidiabetic drugs. Biochem Pharmacol 58, 1511–20.
Betteridge J. (2001) Dyslipidaemia and diabetes. Prac Diabetes Intern 18, 201–7.
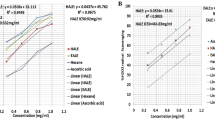
Chae SK, Kang GS, Ma SJ, Bang KW, Oh MW, and Oh SH. (2002) In Standard food analysis, Jigu-moonwha Sa, Korea.
Chang MW and Jhonson MA. (1980) Effect of garlic on carbohydrate metabolism and lipid synthesis in rats. J Nutr 110, 931–6.
Choi JM and Koo SJ. (2000) Effects of β-glucan from Agaricus blazei Murill on blood glucose and lipid composition in db/db mice. Korean J Food Sci Technol 32, 1418–25.
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stepens TW, Nyce MR, Ohannesian JP, Marco CC, McKee LJ, and Bauer TL. (1996) Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med 334, 292–5.
Coseteng MY and Lee CY. (1987) Changes in apple polyphenoloxidase and polyphenol concentrations in relation to degree of browning. J Food Sci 52, 985–9.
Folin O and Denis W. (1912) On phosphotungastic phosphomolybdic compounds as color regents. J Biol Chem 12, 239–49.
Friedwald W, Levy R, and Fredrickson D. (1972) Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 18, 499–502.
Institute of Drug and Plant. (1998) In Details of drug and plant (Revised version). Jimmeong Publish, Korea.
International Diabetes Federation. (2012) In IDF Diabetes Atlas, (5th ed.), International Diabetes Federation, Belgium.
Jenkins DJA, Gassull MA, Cocher B, and Alberti KG. (1977) Decrease in postprandial insulin and glucose concentration by guar and pectin. Ann Intern Med 86, 20–3.
Jeon SM and Choi MS. (2010) Comparison of the effects of cyclodextrinnaringin inclusion complex with naringin on lipid metabolism in mice fed a high-fat diet. J East Asian Soc Dietary Life 20, 20–9.
Jung UJ, Lee MK, Park YB, Jeon SM, and Choi MS. (2006) Antihyperglycemic and antioxidant properties of caffeic acid in db/db mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 318, 476–83.
Kim AJ, Yoo HS, and Kang SJ. (2012) Ameliorative effect of black ginseng on diabetic complications in C57BLKS/J-db/db mice. Korean J Food & Nutr 25, 99–104.
Kim E, Kim MS, Rhyu DY, Min OJ, Back HY, Kim YJ, and Kim HA (2009a) Hypoglycemic effect of Eriobotrya japonica (E. japonica) in db/ db mice. Korean J Food & Nutr 22, 159–65.
Kim HJ, Choi JH, Kim HD, and Park CC. (1994) A study on the improvement of antimicrobial activity and increase resistance of Korean traditional Hansan ramie fabrics. J Kor Soc Dyers and Finishers 6, 285–92.
Kim IS, Park KS, Yu HH, and Shin MK (2009b) Antioxidant activities and cell viability against cancer cells of Adenophora remotiflora leaves. J East Asian Soc Dietary Life 19, 384–94.
Kim MJ, Ahn JH, Choi KH, Lee YH, Woo GJ, Hong EK, and Chung YS. (2006) Effects of pine needle extract oil on blood glucose and serum insulin levels in db/db mice. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 35, 321–7.
Kim OS. (2010) Physiological and quality characteristics of bakery products added with mosi leaf powder. PhD Thesis, Sejong University, Korea.
KDA. (2012) Diabetes fact sheet in Korean 2012. Korean Diabetes Association, Korea.
Lawes CM, Parag V, Bennett DA, Suh I, Lam TH, and Whitlock G. (2004) Blood glucose and risk of cardiovascular disease in the Asia Pacific region. Diabetes Care 27, 2836–42.
Lee J, Seo KI, Kim MJ, Lee SJ, Park EM, and Lee MK. (2012) Chlorogenic acid enhances glucose metabolism and antioxidant system in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. J Korean Soc Food Sci ai]Nutr 41, 774–81.
Lee JJ, Park MR, Kim AR, and Lee MY. (2011) Effects of ramie leaves on improvement of lipid metabolism and antiobesity effect in rats fed a high fat/high cholesterol diet. Korea J Food Sci Technol 43, 83–90.
Lee SH, Lim SW, Lee YM, Hur JM, Lee HS, and Kim DK. (2010) Antidiabetic effects of Triticum aestivum L. water extracts in db/db mice as an animal model of diabetes mellitus type. Kor J Pharmacogn 41, 282–8.
Lee YL, Nho JH, Hwang IG, Kim WJ, Lee YJ, and Jeong HS. (2009) Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of ramie leaf (Boehmeria nivea L.). Food Sci Biotechnol 18, 1096–9.
Matsumoto N, Ishigaki F, Ishigaki A, Iwashima H, and Hara Y. (1992) Reduction of blood glucose levels by tea catechin. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 57, 525–7.
Mullarkey CJ, Edelstein D, and Brownlee M. (1990) Free radical generation by glycation products: a mechanism for accelerated atherogenesis in diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 173, 932–9.
NSOK. (2011) Annual report on the cause of death statistics. National Statistical Office of Korea, Korea.
Oh SH. (2012) Effects of ramie leaf on the loperamide-induced constipation in rats. MS Thesis, Chosun University, Korea.
Ong KW, Hus A, and Tan BKH. (2013) Anti-diabetic and anti-lipidemic effects of chlorogenic acid are mediated by ampk activation. Pharmacol 85, 1341–51.
Park KJ, Oh YJ, Lee SY, Kim HS, and Ha HC. (2007) Anti-diabetic effect of crude polysaccharides from Grifola frondosa in KK-Ay diabetic mouse and 3T3-L1 adipocyte. Korean J Food Sci Technol 39, 330–5.
Pruessner JC, Kirschbaum C, Meinlschmid G, and Hellharmmer DH. (2003) Two formulas for computation of the area under the curve represent measures of total hormone concentration versus time-dependent change. Psychoneuroendocrinology 28, 916–31.
Reeves PG, Nielson FH, and Fahey GC. (1993) AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American institute of nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nut 123, 1939–51.
Roberfroid M. (1993) Dietary fiber, inulin and oligofructose: A review comparing their physiological effects. Cri Rev Food Sci Nutr 33, 103–48.
Schneider SH, Kim HC, Khachadurian AK, and Ruderman NB. (1988) Impaired fibrinolytic response to exercise in type diabetes mellitus: Effect of exercise and physical training. Metabolism 37, 924–9.
Shanmugasundaram ER, Gopith KI, Radha SK, and Rajendran VM. (1990) Possible regeneration of the islets of langerhans in streptozotocindiabetic rats given Gymnema sylvestere leaf extract. J Ethnopharmacol 30, 265–9.
Son MH. (2007) The physicochemical properties and antimicrobial activity of Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaudich. MS Thesis, Sunchon National University, Korea.
Tan Z, Wang C, Yi Y, Wang H, Li M, Zhou W, Tan S, and Li F. (2014) Extraction and purification of chlorogenic acid from ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.) leaf using an ethanol/salt aqueous two-phase system. Sep Purif Technol 132, 396–400.
Yoon SJ and Jang MS. (2006) Characteristics of quality in Jeolpyun with different amounts of ramie. Korean J Food Cookery Sci 23, 636–41.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, HJ., Kim, AR. & Lee, JJ. Effects of ramie leaf extract on blood glucose and lipid metabolism in db/db mice. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 57, 639–645 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-014-4193-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-014-4193-y