Abstract
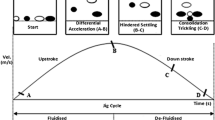
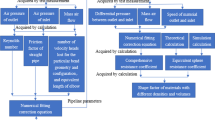
This study investigates the use of continuous pneumatic jigging as an efficient technique of solid waste separation, with a focus on the different materials of copper wire and rubber insulator. The research investigates the effect of several parameters on separation efficiency, such as air flow, pulse rate, vibrational force, and bed thickness. The 7-min experiment, which included the simultaneous use of jigging and vibration, gives light on the subtle relationships that govern particle movement. The results of the air flow and pulse rate investigation highlight the importance of concentration criteria and density discrepancies in obtaining appropriate separation. The usage of small particles refines the process for greater efficiency. A persuasive case is presented in the analysis of the vibrational impact for the efficacy of lower air flow rates coupled with higher vibrational force. This is consistent with the minimal fluidization velocity notion, emphasising the critical role of effective fluidization in particle separation performance. The analysis of bed thickness emphasises the significance of proportional modifications in air flow rate to maintain optimal separation efficiency. The research finishes with a synthesis of these findings, emphasising the attractive prospects of pneumatic jigging for solid waste separation, notably with copper wire and rubber insulator materials. The implications for waste processing scenarios, notably in the beneficiation or pre-treatment of waste electrical and electronic equipment prior to recycling, are discussed. This research lays a foundation for further exploration and application of pneumatic jigging in sustainable waste management practices.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd Aziz MAB (2014). Development of a continuous pneumatic jig for solid waste separation. University of Nottingham
Abd Aziz MA, Md Isa K, Rashid RA (2017) Pneumatic jigging: influence of operating parameters on separation efficiency of solid waste materials. Waste Manag Res 35(6):647–655. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X17697815
Abdu Rahman NW, Japar NSA, Aziz MAA, Razik AHA, Yunus MYM (2019) Sodium grease formulation from waste engine oil. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 257(1):012018. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/257/1/012018
Akiyama T, Aoki KM, Yamamoto K, Yoshikawa T (1998) Experimental study on vibration-induced convection and heaping in granular beds. Granul Matter 1(1):15–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00010905
Aziz MAA, Isa KM, Miles NJ, Rashid RA (2019) Pneumatic jig: effect of airflow, time and pulse rates on solid particle separation. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16(1):11–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1648-4
Chandraseagar S, Abdulrazik AH, Abdulrahman SN, Abdaziz MA (2019) Aspen Plus simulation and optimization of industrial spent caustic wastewater treatment by wet oxidation method. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 702(1):012011. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/702/1/012011
Chapman WR, Mott RA (1928) The cleaning of coal. Chapman & Hall. https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1130000794637671680
Collins JD (1995) Reclamation and groundwater restoration in the uranium milling industry: an assessment of UMTRCA, Title II. J Nat Resour & Environ Law 11(1):23
Dahawi YA, Abdulrazik A, Abu Seman MN, Abd Aziz MA, Mohd Yunus MY (2019) Aspen plus simulation of bio-char production from a biomass-based slow pyrolysis process. Key Eng Mater 797:336–341
Erdész, K., & Mujumdar, A. S. (1986). Hydrodynamic aspects of conventional and vibrofluidized beds —a comparative evaluation. Powder Technology, 46(2), 167–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/0032-5910(86)80023-7
Gupta S (2003) Construction and characterization of an attenuated feline immunodeficiency virus proviral DNA vaccine that co-expresses interferon gamma. University of California, Davis
Hairunnaja MA, Aziz MAA, Bashari NAF, Arifin MA, Nedumaran N, Isa KM, Ali UFM (2023a) The grease formulation using waste substances from palm oil refinery and other industrial wastes: a review. Pertanika J Sci Technol 31(5):2505–2529. https://doi.org/10.47836/pjst.31.5.25
Hairunnaja MA, Aziz MAA, Rahman NWA, Arifin MA, Isa KM, Ali UFM (2023b) Innovative formulation and characterisation of grease made from waste engine oil. Pertanika J Sci Technol 31(5):2375–2387. https://doi.org/10.47836/pjst.31.5.17
He X, Xu T, Xu X, Zeng Y, Xu J, Sun L, Wang C, Xing H, Wu B, Lu A, Liu D, Chen X, Chu J (2014) In situ atom scale visualization of domain wall dynamics in VO2 insulator-metal phase transition. Sci Rep 4(1):6544. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06544
Holdich RG (2002) Foundamentals of particle technology departmment of chemical engineernig. Loughborough University, Leicestershire, LE11 3TU, UK.
Isa KM, Kasim FH, Saad SA, Rahim MAA, Aziz MAA, Ali UFM (2017) Influence of operating parameters on biomass conversion under sub-and supercritical water conditions. Chem Eng Technol 40(3):537–545. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.201600343
Ismail NA, Abd Aziz MA, Hisyam A, Abidin MA (2021) Separation of samarium from medium rare earth mixture using multi-stage counter-current extraction. Chem Eng Commun 208(5):764–774. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2020.1746654
Jain AK, Dubes RC, Chen CC (1987) Bootstrap techniques for error estimation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell PAMI 9(5):628–633. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.1987.4767957
Japar NSA, Aziz MAA, Razali MN (2019) Formulation of fumed silica grease from waste transformer oil as base oil. Egypt J Pet 28(1):91–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpe.2018.12.001
Japar NSA, Aziz MAA, Abdu Rahman NW (2020a) Conversion of Waste Transformer Oil into Grease. In: John N (ed) Advances in waste processing technology. Springer, Singapore, pp 23–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4821-5_2
Japar NSA, Aziz MAA, Hamid N (2020b) Synthesis and properties evaluation of sodium grease formulated from used transformer oil as base oil. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 863(1):012058. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/863/1/012058
Jones AG, Budz J, Mullin JW (1987) Batch crystallization and solid-liquid separation of potassium sulphate. Chem Eng Sci 42(4):619–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(87)80023-4
Jones MP (1987) Applied mineralogy: a quantitative approach. (No Title)
Jong T (1999) Density separation of non-ferous metals by means of jigging and fluidization. Doctor of Philosophy, Delft University of Technology
Mayer MG (1964) The shell model. Science 145(3636):999–1006. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.145.3636.999
Miles N, Shah C, Wotruba H, Weitkamper L, Fraunholcz N, Houwelingen J, Jong T (2003) An evaluation of the economics benefits of pneumatic dry cleaning process. University of Nottingham, Nottingham
Mishra BK, Mehrotra SP (1998) Modelling of particle stratification in jigs by the discrete element method. Miner Eng 11(6):511–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0892-6875(98)00033-8
Mohd Sofi SNA, Abd Aziz MA, Abdu Rahman NW, Anang Japar NS, Abdulhalim AR, Mohd Yunus MY (2019) Preparation and characterization of grease formulated from waste transformer oil. In: IOP conference series: materials science and engineering
Nam CH, Pfeffer R, Dave RN, Sundaresan S (2004) Aerated vibrofluidization of silica nanoparticles. AIChE J 50(8):1776–1785. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.10237
Noda K, Mawatari Y, Uchida S (1998) Flow patterns of fine particles in a vibrated fluidized bed under atmospheric or reduced pressure. Powder Technol 99(1):11–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-5910(98)00079-5
Nwafor F (2008) Pneumatic dry jigging: a new scheme for solid waste separation. Ph. D. in Chemical Engineering, University of Nottingham
Rahman NWBA, Aziz MABA (2022) The effects of additives on anti-wear properties of lubricating grease formulated from waste engine oil. Egypt J Pet 31(3):71–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpe.2022.07.002
Razali MN, Isa SNEM, Salehan NAM, Musa M, Abd Aziz MA, Nour AH, Yunus RM (2020) Formulation of emulsified modification bitumen from industrial wastes. Indones J Chem 20(1):96–104. https://doi.org/10.22146/ijc.40888
Richardson JF (2002) Coulson and Richardson’s chemical engineering
Rong RX, Lyman GJ (1992) The effect of jigging time and air cycle on bed stratification in a pilot scale Baum jig. Fuel 71(1):115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-2361(92)90201-X
Sadeghi M, Khoshtaghaza MH (2012) Vibration effect on particle bed aerodynamic behavior and thermal performance of black tea in fluidized bed dryers. J Agric Sci Technol 14(4):781–788
Shinde HV (2014) Investigation of air jigging and air classification to recover metallic particles from analytical samples. Michigan Technological University
Suhaila N, Japar A, Aizudin M, Aziz A, Razali MN (2018) Formulation of lubricating grease using Beeswax thickener. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 342(1):012007. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/342/1/012007
Tasirin SM, Anuar N (2001) Fluidization behavior of vibrated and aerated beds of starch powders. J Chem Eng Jpn 34(10):1251–1258. https://doi.org/10.1252/jcej.34.1251
Tsunekawa M, Naoi B, Ogawa S, Hori K, Hiroyoshi N, Ito M, Hirajima T (2005) Jig separation of plastics from scrapped copy machines. Int J Miner Process 76(1):67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2004.12.001
Tsunekawa Y, Britto JM, Takahashi M, Polleux F, Tan SS, Osumi N (2012) Cyclin D2 in the basal process of neural progenitors is linked to non-equivalent cell fates. EMBO J 31(8):1879–1892. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2012.43
Wang Z, Hall P, Miles NJ, Wu T, Lambert P, Gu F (2015) The application of pneumatic jigging in the recovery of metallic fraction from shredded printed wiring boards. Waste Manag Res 33(9):785–793. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242x15589782
Wills B, Napier-Munn T (1981) An introduction to the practical aspects of ore treatment and mineral recovery. Mineral processing Technology. In: Pergamon press
Acknowledgements
The authors wished to acknowledge the financial support from the Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia, for providing funding for this research under Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS/1/2021/TKO/UMP/02/76; RDU 210147) and University Malaysia Pahang research fund (RDU 190398 & PGRS 200356).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, analysis and interpretation of results and manuscript preparation were performed by Mohd. Aizudin Abd. Aziz1, Nur Amira Fatihah Bashari1, Muhammad Auni Hairunnaja1, Mohd Azmir Arifin1 and Khairuddin Md Isa2.The first draft of the manuscript was written by Mohd. Aizudin Abd. Aziz1 and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.”
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: S. Hussain.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abd Aziz, M.A., Bashari, N.A.F., Hairunnaja, M.A. et al. The application of continuous pneumatic jig for solid waste separation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05691-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05691-9