Abstract
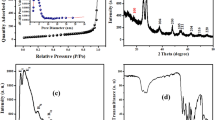
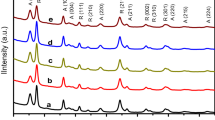
Adsorption technique has emerged as one of the promising protocols to mitigate the level of emerging contaminants from aqueous media owing to high viability, flexibility and productive recovery of adsorbent. The suitability of template induced mesoporous TiO2 nanoparticles having high surface area to expel out triclosan and chlorpyrifos from aqueous media was investigated in the present study. Biopolymer, xanthan gum templated synthesis of nanosized TiO2 was carried out imposing high frequency sound waves, and the as-synthesized sample was calcined at different temperatures (550–850 °C). The morphological features, crystal phase and size, pore size and surface area, and band gap of TiO2 nanoparticles were evaluated. XRD analysis divulged the 100% pure anatase phase of TiO2 even at 850 °C. Prior to adsorption studies, the persistence studies of triclosan and chlorpyrifos (day 1 to 75) have been carried out which showed the highly persistent nature of both the adsorbates. The nanosorbent anatase TiO2 having 87 m2g−1 surface area and 6.2 nm pore radius showed instant adsorption of triclosan (96%) and chlorpyrifos (89%) optimal conditions. Thermodynamic and adsorption isotherm studies were conducted at different temperatures (293–303 K) and initial concentrations (3–15 mg/L). The calculated thermodynamic parameters ΔG, ΔH and ΔS suggested that the adsorption is spontaneous and endothermic in nature. Further, the recyclability studies demonstrate that mesoporous TiO2 retains the adsorption efficiency for both the adsorbates even after 7 consecutive adsorption–desorption cycles. The findings of the present work have substantial implications for facile elimination of triclosan and chlorpyrifos from aqueous medium with mesoporous TiO2 nanostructures.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within this published article.
References
Abbas M (2020) Experimental investigation of titanium dioxide as an adsorbent for removal of Congo red (CR) from aqueous solution, equilibrium and kinetics modeling. J Water Reuse Desalin 10:251–266. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2020.038
Afruzi FH, Maleki A, Zare EN (2022) Efficient remediation of chlorpyrifos pesticide from contaminated water by superparamagnetic adsorbent based on Arabic gum-grafted-polyamidoxime. Int J Biol Macromol 203:445–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.157
Aisida SO, Madubuonu N, Alnasir MH, Ahmad I, Botha S, Maaza M, Ezema FI (2019) Biogenic synthesis of iron oxide nanorods using Moringa oleifera leaf extract for antibacterial applications. Appl Nanosci 10:305–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01099-x
Alias SS, Harun Z, Azhar FH, Ibrahim SA, Johar B (2019) Comparison between commercial and synthesised nano flower-like rutile TiO2 immobilised on green super adsorbent towards dye wastewater treatment. J Clean Prod 251:119448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119448
Alsawy T, Rashad E, El-Qelish M et al (2022) A comprehensive review on the chemical regeneration of biochar adsorbent for sustainable wastewater treatment. npj Clean Water 5:29. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-022-00172-3
Amiri H, Nabizadeh R, Silva Martinez S, Jamaleddin Shahtaheri S, Yaghmaeian K, Badiei A, Naddafi K (2018) Response surface methodology modeling to improve degradation of Chlorpyrifos in agriculture runoff using TiO2 solar photocatalytic in a raceway pond reactor. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:919–925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.09.062
Anwar S, Liaquat F, Khan QM, Khalid ZM, Iqbal S (2009) Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos and its hydrolysis product 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol by Bacillus pumilus strain C2A1. J Hazard Mater 168:400–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.059
Ba-Abbad MM, Kadhum AAH, Mohamad AB, Takrif MS, Sopian K (2012) Synthesis and catalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles for photochemical oxidation of concentrated chlorophenols under direct solar radiation. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:4871–4888
Bagheri S, Shameli K, Abd Hamid SB (2013) Synthesis and characterization of anatase titanium dioxide nanoparticles using egg white solution via sol–gel method. J Chem 2013:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/848205
Bariki R, Majhi D, Das K, Behera A, Mishra BG (2020) Facile synthesis and photocatalytic efficacy of UiO-66/CdIn2S4 nanocomposites with flowerlike 3D-microspheres towards aqueous phase decontamination of triclosan and H2 evolution. Appl Catal B 270:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118882
Bhatkhande DS, Pangarkar VG, Beenackers AA (2001) Photocatalytic degradation for environmental applications–a review. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 77:102–116. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.532
Castro SM, Araújo AB, Nogueira RFP, Guerini S (2017) Adsorption of triclosan on single wall carbon nanotubes: a first principle approach. Appl Surf Sci 403:519–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.01.215
Chang C, Yang H, Kan L, Mu W, Wang Q, Lu SY, Deng B (2021) Mechanism and impacts of inorganic ion addition on photocatalytic degradation of triclosan catalyzed by heterostructured Bi7O9I3/Bi. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 125:176–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2021.06.014
Chen J, Shu C, Wang N, Feng J, Ma H, Yan W (2017) Adsorbent synthesis of polypyrrole/TiO2 for effective fluoride removal from aqueous solution for drinking water purification: adsorbent characterization and adsorption mechanism. J Colloid Interface Sci 495:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.01.084
Chen M, Shen Y, Xu L, Xiang G, Ni Z (2021) Highly efficient and rapid adsorption of methylene blue dye onto vinyl hybrid silica nano-cross-linked nanocomposite hydrogel. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng 613:126050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.126050
Chen X, Ma X, Pan Y, Ji R, Gu X, Luo S, Gu X (2020) Dissipation, transformation and accumulation of triclosan in soil-earthworm system and effects of biosolids application. Sci Total Environ 712:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136563
Chu KH (2021) Revisiting the Temkin Isotherm: dimensional inconsistency and approximate forms. Ind Eng Chem Res 60:13140–13147. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.1c01788
Cusioli LF, Quesada HB, Barbosa de Andrade M, Gomes RG, Bergamasco R (2021) Application of a novel low-cost adsorbent functioned with iron oxide nanoparticles for the removal of triclosan present in contaminated water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 325:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111328
Das TK, Ilaiyaraja P, Sudakar C (2018) Template assisted nanoporous TiO2 nanoparticles: the effect of oxygen vacancy defects on photovoltaic performance of DSSC and QDSSC. Sol Energy 159:920–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.11.061
Deng M, Wu X, Zhu A, Zhang Q, Liu Q (2019) Well-dispersed TiO2 nanoparticles anchored on Fe3O4 magnetic nanosheets for efficient arsenic removal. J Environ Manag 237:63–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.02.037
Fernández García M, Rodriguez JA (2011) Metal oxide nanoparticles. Encycl Inorg Bioinorg Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119951438.eibc0331
Foucaud Y, Canevesi RLS, Celzard A, Fierro V, Badawi M (2021) Hydration mechanisms of scheelite from adsorption isotherms and ab initio molecular dynamics simulations. Appl Surf Sci 562:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150137
Gad YH, Nasef SM (2021) Radiation synthesis of graphene oxide/composite hydrogels and their ability for potential dye adsorption from wastewater. J Appl Polym Sci 138:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.51220
García-Espinoza D, Robles I, Gil V, Becerril-Bravo E, Barrios JA, Godínez LA (2019) Electrochemical degradation of triclosan in aqueous solution. A study of the performance of an electro-fenton reactor. J Environ Chem Eng 7:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103228
Gemici BT, Ozel HU, Ozel HB (2021) Removal of methylene blue onto forest wastes: adsorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic analysis. Environ Technol Innov 22:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101501
Ghelichpour M, Taheri Mirghaed A, Mirzargar SS, Joshaghani H, Ebrahimzadeh Mousavi H (2017) Plasma proteins hepatic enzymes thyroid hormones and liver histopathology of Cyprinus carpio (Linnaeus, 1758) exposed to an oxadiazin pesticide indoxacarb. Aquac Res 48:5666–5676. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13390
Gong B, Peng Q, Jur JS, Devine CK, Lee K, Parsons GN (2011) Sequential vapor infiltration of metal oxides into sacrificial polyester fibers: shape replication and controlled porosity of microporous/mesoporous oxide monoliths. Chem Mater 23(15):3476–3485
Hamadeen HM, Elkhatib EA, Badawy MEI, Abdelgaleil SAM (2021) Novel low cost nanoparticles for enhanced removal of chlorpyrifos from wastewater: sorption kinetics, and mechanistic studies. Arab J Chem 14:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.102981
Hamadeen HM, Elkhatib EA (2022) Nanostructured modified biochar for effective elimination of chlorpyrifos from wastewater: enhancement, mechanisms and performance. J Water Process Eng 47:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102703
Hamadeen HM, Elkhatib EA, Badawy MEI, Abdelgaleil SAM (2021b) Green low cost nanomaterial produced from Moringa oleifera seed waste for enhanced removal of chlorpyrifos from wastewater: mechanism and sorption studies. J Environ Chem Eng 9:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105376
Hena S, Gutierrez L, Croué JP (2020) Removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) from wastewater using microalgae: a review. J Hazard Mater 403:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124041
Hussain M, Ceccarelli R, Marchisio DL, Fino D, Russo N, Geobaldo F (2010) Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic application of novel TiO2 nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 157:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.10.043
Jaramillo-Fierro X, González S, Montesdeoca-Mendoza F, Medina F (2021) Structuring of ZnTiO3/TiO2 adsorbents for the removal of methylene blue, using zeolite precursor clays as natural additives. Nanomaterials 11:1–25. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040898
Jiang N, Shang R, Heijman SGJ, Rietveld LC (2019) Adsorption of triclosan trichlorophenol and phenol by high-silica zeolites: adsorption efficiencies and mechanisms. Sep Purif Technol 235:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116152
Kamble RJ, Gaikwad PV, Garadkar KM, Sabale SR, Puri VR, Mahajan SS (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of malachite green using hydrothermally synthesized cobalt-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J Iran Chem Soc 19:303–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-021-02303-y
Kanna M, Wongnawa S, Sherdshoopongse P, Boonsin P (2005) Adsorption behavior of some metal ions on hydrated amorphous titanium dioxide surface. J Sci Technol 27:1017–1026
Kaur A, Singh D, Sud D (2020) A review on grafted, crosslinked and composites of biopolymer Xanthan gum for phasing out synthetic dyes and toxic metal ions from aqueous solutions. J Polym Res 27:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02271-6
Kaur P, Bansal P, Sud D (2013) Heterostructured nanophotocatalysts for degradation of organophosphate pesticides from aqueous streams. J Korean Chem Soc 57:382–388. https://doi.org/10.5012/jkcs.2013.57.3.382
Khalily MA, Eren H, Akbayrak S, Susapto HH, Biyikli N, Özkar S, Guler MO (2016) Facile synthesis of three-dimensional Pt-TiO2 nano-networks: a highly active catalyst for the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia–borane. Angew Chem Int Ed 128:12445–12449. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201605577
Kim KH, Kabir E, Jahan SA (2017) Exposure to pesticides and the associated human health effects. Sci Total Environ 575:525–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.009
Lee Y, Gerrity D, Lee M, Gamage S, Pisarenko A, Trenholm RA, Canonica S, Snyder SA, von Gunten U (2016) Organic contaminant abatement in reclaimed water by UV/H2O2 and a combined process consisting of O3/H2O2 Followed by UV/H2O2: prediction of abatement efficiency, energy consumption, and byproduct formation. Environ Sci Technol 50:3809–3819. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b04904
Lescano MR, Lopez AO, Romero RL, Zalazar CS (2020) Degradation of chlorpyrifos formulation in water by the UV/H2O2 process: lumped kinetic modelling of total organic carbon removal. J Photochem Photobio 404:112924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.112924
Li K, Yan J, Zhou Y, Li B, Li X (2021) β-cyclodextrin and magnetic graphene oxide modified porous composite hydrogel as a superabsorbent for adsorption cationic dyes: adsorption performance, adsorption mechanism and hydrogel column process investigates. J Mol Liq 335:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116291
Li M, Xu G, Guan Z, Wang Y, Yu H, Yu Y (2019b) Synthesis of Ag/BiVO4/rGO composite with enhanced photocatalytic degradation of triclosan. Sci Total Environ 664:230–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.027
Li Y, Liu S, Wang C, Ying Z, Huo M, Yang W (2019a) Effective column adsorption of triclosan from pure water and wastewater treatment plant effluent by using magnetic porous reduced graphene oxide. J Hazard Mater 386:121942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121942
Li Y, Wang S, Dong Y, Mu P, Yang Y, Liu X, Lin C, Huang Q (2020) Effect of size and crystalline phase of TiO2 nanotubes on cell behaviors: a high throughput study using gradient TiO2 nanotubes. Bioact Mater 5:1062–1070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.07.005
Li Z, Deng S, Zhang X, Zhou W, Huang J, Yu G (2010) Removal of fluoride from water using titanium-based adsorbents. Front Environ Sci En 4:414–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-010-0241-y
Liao J, Zhang Y, He X, Zhang L, He Z (2021) The synthesis of a novel titanium oxide aerogel with highly enhanced removal of uranium and evaluation of the adsorption mechanism. Dalton Trans 50:3616–3628. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0dt04320f
Liu B, Du C, Chen JJ, Zhai JY, Wang Y, Li HL (2021) Preparation of well-developed mesoporous activated carbon fibers from plant pulp fibers and its adsorption of methylene blue from solution. Chem Phys Lett 771:138535
Liu H, Chen J, Wu N, Xu X, Qi Y, Jiang L, Wang X, Wang Z (2019) Oxidative degradation of chlorpyrifos using ferrate(VI): kinetics and reaction mechanism. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 170:259–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.11.132
Lu J, Guo Z, Wang S, Li M, Wang N, Zhou L, Wu H, Zhang J (2021) Remove of triclosan from aqueous solutions by nanoflower MnO2: Insight into the mechanism of oxidation and adsorption. Chem Eng J 426:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131319
Lu YC, Mao JH, Zhang W, Wang C, Cao M, Wang XD, Wang YK, Xiong XH (2019) A novel strategy for selective removal and rapid collection of triclosan from aquatic environment using magnetic molecularly imprinted nano−polymers. Chemosphere 238:124640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124640
Maryskova M, Rysova M, Novotny V, Sevcu A (2019) Polyamide-laccase nanofiber membrane for degradation of endocrine-disrupting bisphenol A, 17α-ethinylestradiol and triclosan. Polymers 11:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101560
Matolia J, Shukla SP, Kumar S, Kumar K, Singh AR (2019) Physical entrapment of chitosan in fixed-down-flow column bed enhances triclosan removal from water. Water Sci Technol 80:1374–1383. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2019.386
Mohamed MG, Atayde EC Jr, Matsagar BM, Na J, Yamauchi Y, Wu KCW, Kuo SW (2020) Construction hierarchically mesoporous/microporous materials based on block copolymer and covalent organic framework. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 112:180–192
Mojiri A, Zhou JL, Robinson B, Ohashi A, Ozaki N, Kindaichi T, Farraji H, Vakili M (2020) Pesticides in aquatic environments and their removal by adsorption methods. Chemosphere 253:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126646
Mutsak Ahmed R, Hasan I (2021) A review on properties and applications of TiO2 and associated nanocomposite materials. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.04.381
Nabi D, Aslam I, QAZI IA, (2009) Evaluation of the adsorption potential of titanium dioxide nanoparticles for arsenic removal. Res J Environ Sci 21:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(08)62283-4
Noguera-Oviedo K, Aga DS (2016) Lessons learned from more than two decades of research on emerging contaminants in the environment. J Hazard Mater 316:242–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.04.058
Oluwole AO, Omotola EO, Olatunji OS (2020) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in water and wastewater: a review of treatment processes and use of photocatalyst immobilized on functionalized carbon in AOP degradation. BMC Chem 14:1–29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-020-00714-1
Orhon KB, Orhon AK, Dilek FB, Yetis U (2017) Triclosan removal from surface water by ozonation–kinetics and by-products formation. J Environ Manag 204:327–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.09.025
Pathiratne A, Chandrasekera LWHU, De Seram PKC (2007) Effects of biological and technical factors on brain and muscle cholinesterases in Nile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus: implications for biomonitoring neurotoxic contaminations. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54:309–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-007-9025-1
Peng FJ, Ying GG, Pan CG, Selck H, Salvito D, Van den Brink PJ (2018) Bioaccumulation and biotransformation of triclosan and galaxolide in the freshwater Oligochaete Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri in a water/sediment microcosm. Environ Sci Technol 52:8390–8398. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b02637
Peng J, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Shao S, Wang P, Liu G, Dong H, Liu D, Shi J, Cao Z, Liu H, Gao S (2020) Efficient removal of triclosan via peroxymonosulfate activated by a ppb level dosage of Co(II) in water: reaction kinetics, mechanisms and detoxification. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 198:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110676
Phromma S, Wutikhun T, Kasamechonchung P, Eksangsri T, Sapcharoenkun C (2020) Effect of calcination temperature on photocatalytic activity of synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles via wet ball milling sol–gel method. Appl Sci 10:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030993
Poolakkandy RR, Menamparambath MM (2020) Soft-template-assisted synthesis: a promising approach for the fabrication of transition metal oxides. Nanoscale Adv 2:5015–5045. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0na00599a
Popa N, Visa M (2021) New hydrothermal charcoal TiO2 composite for sustainable treatment of wastewater with dyes and cadmium cations load. Mater Chem Phys 258:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123927
Pourali P, Behzad M, Arfaeinia H, Ahmadfazeli A, Afshin S, Poureshgh Y, Rashtbari Y (2020) Removal of acid blue 113 from aqueous solutions using low-cost adsorbent: adsorption isotherms, thermodynamics, kinetics and regeneration studies. Sep Sci Technol 56:3079–3091. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2020.1867583
Ramos Nieto MR, Lasagna M, Cao G, Álvarez G, Santamaria C, Rodriguez Girault ME, Bourguignon N, Giorgio ND, Ventura C, Mardirosian M, Cocca C, Núñez M (2021) Chronic exposure to low concentrations of chlorpyrifos affects normal cyclicity and histology of the uterus in female rats. Food Chem Toxicol 156:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2021.112515
Rani L, Thapa K, Kanojia N, Sharma N, Singh S, Grewal AS, Srivastav AL, Kaushal J (2020) An extensive review on the consequences of chemical pesticides on human health and environment. J Clean Prod 283:124657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124657
Rezaei Kalantary R, Barzegar G, Jorfi S (2022) Monitoring of pesticides in surface water pesticides removal efficiency in drinking water treatment plant and potential health risk to consumers using Monte Carlo simulation in Behbahan City. Iran Chemosphere 286:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131667
Rocha AC, Camacho C, Eljarrat E, Peris A, Aminot Y, Readman JW, Boti V, Nannou C, Marques A, Nunes ML, Almeida CM (2018) Bioaccumulation of persistent and emerging pollutants in wild sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Environ Res 161:354–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.11.029
Rossner A, Snyder SA, Knappe DRU (2009) Removal of emerging contaminants of concern by alternative adsorbents. Water Res 43:3787–3796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.06.009
Roy M, Ghosh S, Naskar MK (2015) Ligand-assisted soft-chemical synthesis of self-assembled different shaped mesoporous Co3O4: efficient visible light photocatalysts. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:10160–10169. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cp00649j
Sarkar B, Mandal S, Tsang YF, Vithanage M, Biswas JK, Yi H, Dou X, Ok YS (2019) Sustainable sludge management by removing emerging contaminants from urban wastewater using carbon nanotubes. Indus Munic Sludge. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-815907-1.00024-6
Scaria J, Gopinath A, Nidheesh PV (2020) A versatile strategy to eliminate emerging contaminants from the aqueous environment: heterogeneous fenton process. J Clean Prod 278:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124014
Schwantes D, Celso Gonçalves A, Conradi Junior É, Campagnolo MA, Zimmermann J (2020) Determination of CHLORPYRIFOS by GC/ECD in water and its sorption mechanism study in a RHODIC FERRALSOL. J Environ Health Sci Eng 18:149–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-020-00448-1
Sharotri N, Sharma D, Sud D (2019) Experimental and theoretical investigations of Mn-N-co-doped TiO2 photocatalyst for visible light induced degradation of organic pollutants. J Mater Res Technol 8:3995–4009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.07.008
Sharotri N, Sud D (2015) Ultrasound-assisted synthesis and characterization of visible light responsive nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanomaterials for removal of 2-Chlorophenol. Desalination Water Treat 57:8776–8788. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1026278
Sharotri N, Sud D (2017) Visible light responsive Mn-S-co-doped TiO2 photocatalyst—synthesis, characterization and mechanistic aspect of photocatalytic degradation. Sep Purif Technol 183:382–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.03.053
Sidhu GK, Singh S, Kumar V, Dhanjal DS, Datta S, Singh J (2019) Toxicity, monitoring and biodegradation of organophosphate pesticides: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 49:1135–1187. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1565554
So HL, Lin KY, Chu W (2019) Triclosan removal by heterogeneous fenton-like process: studying the kinetics and surface chemistry of Fe3O4 as catalyst. J Environ Chem Eng 7:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103432
Song Z, Ling P, Zang H, Li L, Wang J, Jin Y, Shao H, Zhu X, Liu F, Wang F (2015) Development, validation and influence factor analysis of a near-infrared method for the molecular weight determination of xanthan gum. Carbohydr Polym 115:582–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.08.079
Souza IPAF, Crespo LHS, Spessato L, Melo SAR, Martins AF, Cazetta AL, Almeida VC (2021) Optimization of thermal conditions of sol–gel method for synthesis of TiO2 using RSM and its influence on photodegradation of tartrazine yellow dye. J Environ Chem Eng 9:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104753
Sriprang P, Wongnawa S, Sirichote O (2014) Amorphous titanium dioxide as an adsorbent for dye polluted water and its recyclability. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 71:86–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3327-3
Sud D, Kumar J, Kaur P, Bansal P (2020) Toxicity, natural and induced degradation of chlorpyrifos. J Chil Chem Soc 65:4807–4816. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-97072020000204807
Sun J, Pan L, Tsang DCW, Zhan Y, Zhu L, Li X (2018) Organic contamination and remediation in the agricultural soils of China: a critical review. Sci Total Environ 615:724–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.271
Sun K, Li S, Yu J, Gong R, Si Y, Liu X, Chu G (2019) Cu2+-assisted laccase from trametes versicolor enhanced self-polyreaction of triclosan. Chemosphere 225:745–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.079
Taheri MA, Melika G (2015) Determination of lethal concentrations of indoxacarb in fingerling Cyprinus carpio at two temperatures. Int J Aquat Biol 3:339–345. https://doi.org/10.22034/IJAB.V3I5.113
Triwiswaraa M, Leeb CG, Kwan MJ, Parkd SJ (2020) Adsorption of triclosan from aqueous solution onto char derived from palm kernel shell. Desalination Water Treat 177:71–79. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.24872
Wan Y, Tran TM, Nguyen VT, Wang A, Wang J, Kannan K (2021) Neonicotinoids fipronil chlorpyrifos carbendazim chlorotriazines chlorophenoxy herbicides bentazon and selected pesticide transformation products in surface water and drinking water from northern Vietnam. Sci Total Environ 750:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141507
Wang F, Lu X, Peng W, Deng Y, Zhang T, Hu Y, Li X (2017) Sorption behavior of bisphenol A and triclosan by graphene: comparison with activated carbon. ACS Omega 2:5378–5384. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b00616
Wang H, Song Y, Liu W, Yao S, Zhang W (2013) Template synthesis and characterization of TiO2 nanotube arrays by the electrodeposition method. Mater Lett 93:319–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2012.11.056
Wang N, Wang J, Liu M, Ge C, Hou B, Liu N, Ning Y, Hu Y (2021) Preparation of FeS2/TiO2 nanocomposite films and study on the performance of photoelectrochemistry cathodic protection. Sci Rep 11:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-87132-y
Wang Y, Liang W (2021) Occurrence toxicity and removal methods of triclosan: a timely review. Curr Pollut Rep 7:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-021-00173-9
Wei M, Yang X, Watson P, Yang F, Liu H (2019) A cyclodextrin polymer membrane-based passive sampler for measuring triclocarban, triclosan and methyl triclosan in rivers. Sci Total Environ 648:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.151
Xia X, Peng S, Bao Y, Wang Y, Lei B, Wang Z, Huang Z, Gao Y (2018) Control of interface between anatase TiO2 nanoparticles and rutile TiO2 nanorods for efficient photocatalytic H2 generation. J Power Sour 376:11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.11.067
Xie H, Yang Y, Liu J, Kang Y, Zhang J, Hu Z, Liang S (2018) Enhanced triclosan and nutrient removal performance in vertical up-flow constructed wetlands with manganese oxides. Water Res 143:457–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.05.061
Xie X, Chen C, Wang X, Li J, Naraginti S (2019) Efficient detoxification of triclosan by a S-Ag/TiO2@g-C3N4 hybrid photocatalyst: process optimization and bio-toxicity assessment. RSC Adv 9:20439–20449. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra03279g
Yadav D, Rangabhashiyam S, Verma P, Singh P, Devi P, Kumar P, Hussain CM, Gaurav GK, Kumar KS (2021a) Environmental and health impacts of contaminants of emerging concerns recent treatment challenges and approaches. Chemosphere 272:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.12
Yadav S, Yadav A, Bagotia N, Sharma AK, Kumar S (2021b) Adsorptive potential of modified plant-based adsorbents for sequestration of dyes and heavy metals from wastewater-a review. J Water Process Eng 42:102148
Yao S, Ma Y, Xu T, Wang Z, Lv P, Zheng J, Ma C, Yu K, Wei W, Ostrikov K, (Ken), (2021) Ti–C bonds reinforced TiO2@C nanocomposite Na-ion battery electrodes by fluidized-bed plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Carbon 171:524–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.09.023
Yen J, Donerly S, Levin ED, Linney EA (2011) Differential acetylcholinesterase inhibition of chlorpyrifos, diazinon and parathion in larval zebrafish. Neurotoxicol Teratol 33:735–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ntt.2011.10.004
Yuan D, Zhang S, Xiang Z, Liu Y, Wang Y, Zhou X, He Y, Huang W, Zhang Q (2018) Highly efficient removal of uranium from aqueous solution using a magnetic adsorbent bearing phosphine oxide ligand: a combined experimental and density functional theory study. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:9619–9627. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b04352
Zaker A, Chen Z, Zaheeruddin M, Guo J (2020) Co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and low-density polyethylene—a thermogravimetric study of thermo-kinetics and thermodynamic parameters. J Environ Chem Eng 9:1–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104554
Zeng G, Chen M, Zeng Z (2013) Risks of neonicotinoid pesticides. Science 340:1403–1403. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.340.6139.1403-a
Zhang Y, Li Y, Wang J, Wang X, Liu Y, Wang S, Kong F (2021) Interactions of chlorpyrifos degradation and Cd removal in iron-carbon-based constructed wetlands for treating synthetic farmland wastewater. Environ Manag 299:113559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113559
Zhang S, Zhang Z, Pei J, Li R, Zhang J, Cai J, Cui J (2018) A novel TiO2-SiO2 aerogel nanocomposite absorbent: preparation, characterization and photocatalytic degradation effects on automobile exhaust. Mater Res Express 5:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaaf10
Zhang Z, Li J, Luan C, Wang H, Cheng X, Fang L, Wang L, Zhao B, Ma C, Zhang H, Li C, Xu J (2019) Preparation and characterization of palladium/polypyrrole-reduced graphene oxide/foamed nickel composite electrode and its electrochemical dechlorination of triclosan. Arab J Chem 13:3963–3973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2019.04.006
Zhao H, Wang L, Kong D, Ji Y, Lu J, Yin X, Zhou Q (2019) Degradation of triclosan in peroxymonosulfate/Br- system: identification of reactive species and formation of halogenated byproducts. Chem Eng J 384:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123297
Zhou X, Xu D, Chen Y, Hu Y (2020) Enhanced degradation of triclosan in heterogeneous E-fenton process with MOF-derived hierarchical Mn/Fe@PC modified cathode. Chem Eng J 384:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123324
Zhu L, Jiang C, Panthi S, Allard SM, Sapkota AR, Sapkota A (2021) Impact of high precipitation and temperature events on the distribution of emerging contaminants in surface water in the Mid-Atlantic United States. Sci Total Environ 755:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142552
Zou L, Luo Y, Hooper M, Hu E (2006) Removal of VOCs by photocatalysis process using adsorption enhanced TiO2–SiO2 catalyst. Chem Eng Process 45:959–964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2006.01.014
Zou Z, Zhao Q, Wang Q, Zhou F (2019) Thermal stability of xanthan gum biopolymer and its application in salt-tolerant bentonite water-based mud. J Polym Eng 39:501–507. https://doi.org/10.1515/polyeng-2018-0386
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly acknowledge the SLIET chemical society for providing facilities which made this work successful. We are pleased to acknowledge the facilities provided by Panjab University, Chandigarh.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: F. ŞEN.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, A., Sud, D. Facile removal of emerging pollutants using mesoporous TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized via xanthan gum templated greener protocol. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21, 5127–5148 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05358-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05358-x