Abstract
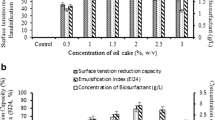
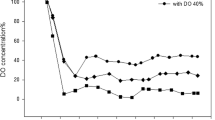
Surfactants are used in many industries such as agriculture, petrochemicals, and bioremediation. Developing using greener products leads to garnering more attention to biosurfactants. The advantages of biosurfactants compared with chemical surfactants are proper biodegradability, less toxicity, environmentally friendly, and higher efficiency. However, high production costs and low yields are important problems in the economic production of biosurfactants. As a result, optimizing and increasing the production of biosurfactants are of great importance. In this study, continuous chemostat fermentation was used to raise process time, control the process parameters, and increase the efficiency of rhamnolipid biosurfactant by Pseudomonas aeruginosa HK02. First, the best carbon source, the concentration of the minerals in the feed, and the process parameters were determined. Then, experiments were done at different flow rates to determine the washout and optimal flow rate with high yield. The best source of carbon for this strain was sunflower and soybean oil. KS 6.63 (g/L) and μmax 0.0377 (1/h) were obtained. The flow rate of 240 mL/day with a yield(p/s) of 0.88 (g/g) had the highest efficiency. The process was tested at a flow rate of 240 mL/day for 30 days. The washout flow rate was 600 mL/day. The biosurfactant production reaches 200 g/L at optimum condition. The produced biosurfactant was able to reduce the surface tension of water to 31 mN/m at 450 ppm. The results showed that the continuous fermentation process was more economical and suitable for large-scale production of rhamnolipid biosurfactants, because of high productivity, and the possibility of continuing the process for one month and more.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi H, Hamedi MM, Lotfabad TB et al (2012) Biosurfactant-producing bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa MA01 isolated from spoiled apples: physicochemical and structural characteristics of isolated biosurfactant. J Biosci Bioeng 113:211–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2011.10.002
Adu SA, Naughton PJ, Marchant R, Banat IM (2020) Microbial biosurfactants in cosmetic and personal skincare pharmaceutical formulations. J Pharm 12:1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111099
Ahmad Z, Zhang X, Imran M et al (2021) Production, functional stability, and effect of rhamnolipid biosurfactant from Klebsiella sp. on phenanthrene degradation in various medium systems. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 207:111514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111514
Alkhalaf SA, Ramadan AR, Obuekwe C et al (2021) Heavy vacuum gas oil upregulates the rhamnosyltransferases and quorum sensing cascades of rhamnolipids biosynthesis in Pseudomonas sp. Ak6u. J Mol 26:4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144122
Banat IM, Satpute SK, Cameotra SS et al (2014) Cost effective technologies and renewable substrates for biosurfactants’ production. Front Microbiol 5:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00697
Banat IM, Carboué Q, Saucedo-Castañeda G, de Jesús C-M (2021) Biosurfactants: the green generation of speciality chemicals and potential production using solid-state fermentation (SSF) technology. Bioresour Technol 320:124222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124222
Bazsefidpar S, Mokhtarani B, Panahi R, Hajfarajollah H (2019) Overproduction of rhamnolipid by fed-batch cultivation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a lab-scale fermenter under tight DO control. J Biodegrad 3:59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-018-09866-3
Bjerk TR, Severino P, Jain S et al (2021) Biosurfactants: properties and applications in drug delivery, biotechnology and ecotoxicology. J Bioeng 8:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8080115
Borah SN, Sen S, Goswami L et al (2019) Rice based distillers dried grains with solubles as a low cost substrate for the production of a novel rhamnolipid biosurfactant having anti-biofilm activity against Candida tropicalis. J Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 182:110358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110358
Bustos G, Moldes AB, Cruz JM (2007) Revalorization of hemicellulosic trimming vine shoots hydrolyzates trough continuous production of lactic acid and biosurfactants by L. pentosus. Food Eng 78:405–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.10.008
Chong H, Li Q (2017) Microbial production of rhamnolipids: opportunities, challenges and strategies. Microb Cell Fact 16:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-017-0753-2
Clement T, Perez M, Mouret JR et al (2011) Use of a continuous multistage bioreactor to mimic winemaking fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol 150:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.07.016
Costa JAV, Treichel H, Santos LO, Martins VG (2018) Solid-state fermentation for the production of biosurfactants and their applications. Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering. Elsevier, pp 357–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-63990-5.00016-5
da Silva AF, Banat IM, Giachini AJ, Robl D (2021) Fungal biosurfactants, from nature to biotechnological product: bioprospection, production and potential applications. J Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 44:2003–2034. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-021-02597-5
Dell’Anno F, Rastelli E, Sansone C et al (2021) Bacteria, fungi and microalgae for the bioremediation of marine sediments contaminated by petroleum hydrocarbons in the omics era. J Microorg 9:1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081695
Germer A, Tiso T, Mülle C et al (2020) crossm Exploiting the natural diversity of RhlA acyltransferases for the synthesis of the rhamnolipid precursor. Appl Env Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02317-19
Ha S, Rin S, Kim H et al (2013) Bioresource technology continuous co-fermentation of cellobiose and xylose by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioresour Technol 149:525–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.09.082
Haloi S, Sarmah S, Gogoi SB, Medhi T (2020) Characterization of Pseudomonas sp. TMB2 produced rhamnolipids for ex-situ microbial enhanced oil recovery. 3 Biotech 10:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-2094-9
Henkel M, Müller MM, Kügler JH et al (2012) Rhamnolipids as biosurfactants from renewable resources: concepts for next-generation rhamnolipid production. Process Biochem 47:1207–1219
Huang C, Li Y, Tian Y et al (2018) Rhamnolipid production of Pseudomonas aeruginosa DN1 by metabolic engineering under diverse nutritional factors. J Pet Enhanc 9:384. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7463.1000384
Ibrahim S, Khalil KA, Nabilah K et al (2020) Biosurfactant production and growth kinetics studies of the waste canola oil-degrading bacterium. J Mol 25:3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173878
Jain RM, Mody K, Mishra A, Jha B (2012) Isolation and structural characterization of biosurfactant produced by an alkaliphilic bacterium Cronobacter sakazakii isolated from oil contaminated wastewater. Carbohydr Polym 87:2320–2326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.10.065
Kim B, Eom MH, Jang H, Lee JH (2015) Optimization of the cyclic operation of a continuous biobutanol fermentation process integrated with ex-situ adsorption recovery. IFAC-PapersOnLine 28:1204–1209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2015.09.132
Makkar MRS (2002) An update on the use of unconventional substrates for biosurfactant production and their new applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:428–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-001-0924-1
Martinez S, Humery A, Groleau MC, Déziel E (2020) Quorum sensing controls both rhamnolipid and polyhydroxyalkanoate production in Burkholderia thailandensis through ScmR regulation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.01033
Müller MM, Hausmann R (2011) Regulatory and metabolic network of rhamnolipid biosynthesis: traditional and advanced engineering towards biotechnological production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:251–264
Nepomuscene J, Senn T, Gschwind P, Kohlus R (2012) Bioresource technology efficiency of Blenke cascade system for continuous bio-ethanol fermentation. Bioresour Technol 123:221–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.07.032
Olasanmi IO, Thring RW (2018) The role of biosurfactants in the continued drive for environmental sustainability. Sustain 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124817
Ozturk SS, Palsson BO (1991) Growth, metabolic and antibody production kinetics of hybridoma cell culture. Biotechnol Prog 7:481–494
Paola Chaves Martins VGM (2018) Biosurfactant production from industrial wastes with potential remove of insoluble paint. Int Biodeterior Biodeg 127:10–16
Płaza G, Achal V (2020) Biosurfactants: eco-friendly and innovative biocides against biocorrosion. Int J Mol Sci 21:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062152
Ramirez D, Shaw LJ, Collins CD (2021) Oil sludge washing with surfactants and co-solvents: oil recovery from different types of oil sludges. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:5867–5879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10591-9
Rincón-Cervera MÁ, Galleguillos-Fernández R, González-Barriga V et al (2020) Fatty acid profile and bioactive compound extraction in purple viper’s bugloss seed oil extracted with green solvents. JAOCS, J Am Oil Chem Soc 97:319–327. https://doi.org/10.1002/aocs.12328
Sarubbo LA, De Luna JM, Rufino RD, Brasileiro PPF (2016) Production of a low-cost biosurfactant for application in the remediation of sea water contaminated with petroleum derivates. Chem Eng Trans 49:523–528. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1649088
Schultz J, Rosado AS (2020) Extreme environments: a source of biosurfactants for biotechnological applications. J Extrem 24:189–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-019-01151-2
Sharma S, Pandey LM (2020) Production of biosurfactant by Bacillus subtilis RSL-2 isolated from sludge and biosurfactant mediated degradation of oil. Bioresour Technol 307:123261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123261
Shay LK, Hunt HR, Wegner GH (1987) High-productivity fermentation process for cultivating industrial microorganisms. J Ind Microbiol 2:79–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569506
Sitanggang AB, Wu HS, Wang SS, Lan JCW (2010) Fermentation strategies: nutritional requirements. Ind Ferment Food Process Nutr Sources Prod Strategy 217–247
Souza EC, de Azevedo PO de S, Domínguez JM et al (2017) Influencia de la temperatura y pH en la producción de biosurfactantes, bacteriocinas y ácido láctico por Lactococcus lactis CECT-4434. CYTA J Food 15: 525–530. https://doi.org/10.1080/19476337.2017.1306806
Strandberg PE, Rauch S (2004) Mathematical models of bacteria population growth in bioreactors: formulation, phase space pictures, optimisation and control. Link¨opings Universitet, Sweden. 1–47
Thomas L, Ram H, Singh VP (2018) Inducible cellulase production from an organic solvent tolerant Bacillus sp. SV1 and evolutionary divergence of endoglucanase in different species of the genus Bacillus. Braz J Microbiol 49:429–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjm.2017.05.010
Tian W, Song J, Wang Y et al (2015) Effect of different calcium salts and methods for triggering gelation on the characteristics of microencapsulated Lactobacillus plantarum LIP-1. RSC Adv 5:73352–73362. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra13354h
Varjani S, Rakholiya P, Yong Ng H et al (2021) Bio-based rhamnolipids production and recovery from waste streams: status and perspectives. Bioresour Technol 319:124213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124213
Varrone C, Floriotis G, Heggeset TMB et al (2017) Continuous fermentation and kinetic experiments for the conversion of crude glycerol derived from second-generation biodiesel into 1, 3 propanediol and butyric acid. Biochem Eng J 128:149–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2017.09.012
Wan ZL, Wang LY, Yang XQ et al (2016) Controlled formation and stabilization of nanosized colloidal suspensions by combination of soy protein and biosurfactant stevioside as stabilizers. Food Hydrocoll 52:317–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.07.005
Winterburn JB, Russell AB, Martin PJ (2011) Integrated recirculating foam fractionation for the continuous recovery of biosurfactant from fermenters. Biochem Eng J 54:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2011.02.011
Wo M, Myszka K, Sznajdrowska A et al (2017) Isolation of rhamnolipids-producing cultures from faeces: influence of interspecies communication on the yield of rhamnolipid congeners. N Biotechnol 36:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2016.12.008
Zheng H, Fan S, Liu W, Zhang M (2020) Production and separation of pseudomonas aeruginosa rhamnolipids using coupling technology of cyclic fermentation with foam fractionation. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 148:107776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2019.107776
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Parveen Fatemeh Rupani.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Diba, F., Mokhtarani, B. & Panahi, R. Dilution rate control for overproduction of rhamnolipid in continuous fermentation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21, 371–386 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05253-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05253-5