Abstract
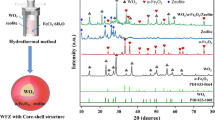
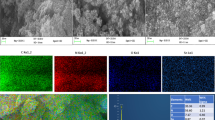
The present paper reports the photodegradation of a pharmaceutical pollutant, Levofloxacin, in an aqueous solution using two photocatalyst nanocomposites, g-C3N4/TiO2 and WO3/TiO2, under the influence of solar light and UV irradiation. These as-designed nano-heterostructures were synthesized using the hydrothermal method without organic templates or additives. The characterization results revealed that the used preparation method grants the purity of the prepared composites and gives a nanoscale character product. The effects of the weight ratio of g-C3N4/TiO2 and WO3/TiO2, the mass of the catalyst and the initial concentration of Levofloxacin on the photocatalytic activity were evaluated under UV light. Results showed that 5 mg/L of Levofloxacin with 20 mg of the prepared nanocomposite with a 5% weight ratio of g-C3N4 and WO3 allowed a quasi-total degradation of the pharmaceutical pollutant within only 30 min. The photocatalytic activities investigation of the prepared nanocomposites under sunlight irradiation showed that after 50 min of treatment, 66% of degradation is reached with WO3/TiO2 against 100% with g-C3N4/TiO2. The possible photocatalytic mechanism was thoroughly investigated, explaining the improved photocatalytic activity. This work demonstrates that the prepared nanocomposites' photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceutical pollutants is efficient, providing a friendly environmental strategy.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Elela S, El-Khateeb M (2009) Treatment of ink wastewater via heterogeneous photocatalytic oxidation. Desalin Water Treat 7:1–5. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2009.306
Abou-Elela S, El-Khateeb MA (2015) Performance evaluation of activated sludge process for treating pharmaceutical wastewater contaminated with β-lactam antibiotics. J Ind Pollut Control 31:1–5
Abu Mhady AI, Awad MA, Al-Aghah MR, El-Nahhal YZ (2019) Assessment of medical waste management in El Shifa and Al Aqsa hospitals-gaza strip. Health 11:1028–1042. https://doi.org/10.4236/health.2019.118081
Achilleos A, Hapeshi E, Xekoukoulotakis NP et al (2010) UV-A and solar photodegradation of ibuprofen and carbamazepine catalyzed by TiO2. Sep Sci Technol 45:1564–1570. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2010.487463
Alatrache A, Cortyl A, Arnoux P et al (2015) Sulfamethoxazole removal from polluted water by immobilized photocatalysis. Toxicol Environ Chem 97:32–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2014.942308
Ansari SA, Khan MM, Ansari MO, Cho MH (2015a) Gold nanoparticles-sensitized wide and narrow band gap TiO 2 for visible light applications: a comparative study. New J Chem 39:4708–4715. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ00556F
Ansari SA, Khan MM, Ansari MO, Cho MH (2015b) Silver nanoparticles and defect-induced visible light photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical performance of Ag@m-TiO2 nanocomposite. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 141:162–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2015.05.029
Antonopoulou M, Hela D, Konstantinou I (2016) Photocatalytic degradation kinetics, mechanism and ecotoxicity assessment of tramadol metabolites in aqueous TiO2 suspensions. Sci Total Environ 545–546:476–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.088
Antonopoulou M, Papadaki M, Rapti I, Konstantinou I (2023) Photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceutical amisulpride using g-C3N4 catalyst and UV-A irradiation. Catalysts 13:226. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13020226
Byberg R, Cobb J, Martin LD et al (2013) Comparison of photocatalytic degradation of dyes in relation to their structure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:3570–3581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1551-y
Cao S, Yu J (2014) g-C3N4-Based photocatalysts for hydrogen generation. J Phys Chem Lett 5:2101–2107. https://doi.org/10.1021/jz500546b
Chai B, Peng T, Mao J et al (2012) Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4)–Pt-TiO2 nanocomposite as an efficient photocatalyst for hydrogen production under visible light irradiation. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:16745–16752. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cp42484c
Chen X, Liu L, Huang F (2015) Black titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanomaterials. Chem Soc Rev 44:1861–1885. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00330F
Chong MN, Jin B, Chow CWK, Saint C (2010) Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: a review. Water Res 44:2997–3027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.02.039
Claudino CH, Kuznetsova M, Rodrigues BS et al (2020) Facile one-pot microwave-assisted synthesis of tungsten-doped BiVO4/WO3 heterojunctions with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Mater Res Bull 125:110783–110794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2020.110783
Czech B, Buda W (2015) Photocatalytic treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater using new multiwall-carbon nanotubes/TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposites. Environ Res 137:176–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2014.12.006
Duan J, Chen S, Jaroniec M, Qiao SZ (2015) Porous C3N4 nanolayers@N-graphene films as catalyst electrodes for highly efficient hydrogen evolution. ACS Nano 9:931–940. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn506701x
El-Nahhal I, El-Nahhal Y (2020) Ecological consequences of COVID-19 outbreak. J Water Sci Eng 1:1–5. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.24456.85769
El-Nahhal I, El-Nahhal Y (2021) Pesticide residues in drinking water, their potential risk to human health and removal options. J Environ Manag 299:113611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113611
El-Nahhal Y, Nir S, Margulies L, Rubin B (1999) Reduction of photodegradation and volatilization of herbicides in organo-clay formulations. Appl Clay Sci 14:105–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-1317(98)00053-2
Ferreira TLB, Garcia LMP, Gurgel GHM et al (2018) Effects of MnO2/In2O3 thin films on photocatalytic degradation 17 alpha-ethynylestradiol and methylene blue in water. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29:12278–12287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9341-4
Gong S, Sun Y, Zheng K et al (2020) Degradation of levofloxacin in aqueous solution by non-thermal plasma combined with Ag3PO4/activated carbon fibers: mechanism and degradation pathways. Sep Purif Technol 250:117264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117264
Góngora JF, Elizondo P, Hernández-Ramírez A (2017) Photocatalytic degradation of ibuprofen using TiO2 sensitized by Ru(II) polyaza complexes. Photochem Photobiol Sci 16:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00222F
Gupta VK, Jain R, Nayak A et al (2011) Removal of the hazardous dye—Tartrazine by photodegradation on titanium dioxide surface. Mater Sci Eng C 31:1062–1067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2011.03.006
He Y, Zhang L, Teng B, Fan M (2015) New application of Z-scheme Ag3PO4/g-C3N4 composite in converting CO2 to fuel. Environ Sci Technol 49:649–656. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5046309
Hou Y, Wen Z, Cui S et al (2016) Strongly coupled ternary hybrid aerogels of N-deficient porous graphitic-C3N4 nanosheets/N-doped graphene/NiFe-layered double hydroxide for solar-driven photoelectrochemical water oxidation. Nano Lett 16:2268–2277. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04496
Houas A, Lachheb H, Ksibi M et al (2001) Photocatalytic degradation pathway of methylene blue in water. Appl Catal B Environ 31:145–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(00)00276-9
Huo N, Yang S, Wei Z, Li J (2013) Synthesis of WO3 nanostructures and their ultraviolet photoresponse properties. J Mater Chem C 1:3999–4007. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tc30527a
Hussien MTM, El-Liethy MA, Abia ALK, Dakhil MA (2020) Low-cost technology for the purification of wastewater contaminated with pathogenic bacteria and heavy metals. Water Air Soil Pollut 231:400–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04766-w
Jjemba PK (2006) Excretion and ecotoxicity of pharmaceutical and personal care products in the environment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63:113–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2004.11.011
Kadiya K, Vuggili SB, Gaur UK, Sharma M (2021) Comparative photocatalytic dye and drug degradation study using efficient visible light–induced silver phosphate nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:46390–46403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10982-y
Kaewtip C, Chadpunyanun P, Boonamnuayvitaya V (2012) Effect of Co-dopants in TiO2–SiO2 thin films on the formaldehyde degradation. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:1455–1465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0957-8
Kaur A, Salunke DB, Umar A et al (2017) Visible light driven photocatalytic degradation of fluoroquinolone levofloxacin drug using Ag2O/TiO2 quantum dots: a mechanistic study and degradation pathway. New J Chem 41:12079–12090. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NJ02053H
Khan SUM, Al-Shahry M, Ingler WB (2002) Efficient photochemical water splitting by a chemically modified n-TiO2. Science 297:2243–2245. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1075035
Khan MM, Ansari SA, Pradhan D et al (2014) Band gap engineered TiO2 nanoparticles for visible light induced photoelectrochemical and photocatalytic studies. J Mater Chem A 2:637–644. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA14052K
Kobkeatthawin T, Trakulmututa J, Amornsakchai T et al (2022) Identification of active species in photodegradation of aqueous imidacloprid over g-C3N4/TiO2 nanocomposites. Catalysts 12:120–135. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12020120
Krakowiak R, Musial J, Bakun P et al (2021) Titanium dioxide-based photocatalysts for degradation of emerging contaminants including pharmaceutical pollutants. Appl Sci 11:8674. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188674
Li X, Feng Y, Li M et al (2015) Smart hybrids of Zn2GeO4 nanoparticles and ultrathin g-C3N4 layers: synergistic lithium storage and excellent electrochemical performance. Adv Funct Mater 25:6858–6866. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201502938
Li W, Li T, Li G et al (2017) Electrospun H4SiW12O40/cellulose acetate composite nanofibrous membrane for photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline and methyl orange with different mechanism. Carbohydr Polym 168:153–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.03.079
Li S, Zhao J, Liu G et al (2021) Graphene oxide-grafted plasmonic Au@Ag nanoalloys with improved synergistic effects for promoting hot carrier-driven photocatalysis under visible light irradiation. Nanotechnology 32:125401–125411. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/abd128
Lin Y, Mehrvar M (2018) Photocatalytic treatment of an actual confectionery wastewater using Ag/TiO2/Fe2O3: optimization of photocatalytic reactions using surface response methodology. Catalysts 8:409–425. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8100409
Linsebigler AL, Lu G, Yates JT (1995) Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem Rev 95:735–758. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00035a013
Low W, Boonamnuayvitaya V (2013) A study of photocatalytic graphene–TiO2 synthesis via peroxo titanic acid refluxed sol. Mater Res Bull 48:2809–2816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.04.020
Luo X, Liu F, Li X et al (2013) WO3/TiO2 nanocomposites: Salt–ultrasonic assisted hydrothermal synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic activity. Mater Sci Semicond Process 16:1613–1618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2013.04.005
Ma TY, Ran J, Dai S et al (2015) Phosphorus-doped graphitic carbon nitrides grown in situ on carbon-fiber paper: flexible and reversible oxygen electrodes. Angew Chem Int Ed 54:4646–4650. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201411125
Martínez C, Canle LM, Fernández MI et al (2011) Kinetics and mechanism of aqueous degradation of carbamazepine by heterogeneous photocatalysis using nanocrystalline TiO2, ZnO and multi-walled carbon nanotubes–anatase composites. Appl Catal B Environ 102:563–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.12.039
Naraginti S, Li Y, Puma GL (2018) Photocatalytic mineralization and degradation kinetics of sulphamethoxazole and reactive red 194 over silver-zirconium co-doped titanium dioxide: reaction mechanisms and phytotoxicity assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 159:301–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.04.062
Neppolian B (2002) Solar/UV-induced photocatalytic degradation of three commercial textile dyes. J Hazard Mater 89:303–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(01)00329-6
Ong WJ, Tan LL, Ng YH et al (2016) Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4)-based photocatalysts for artificial photosynthesis and environmental remediation: are we a step closer to achieving sustainability? Chem Rev 116:7159–7329. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00075
Rajeswari J, Viswanathan B, Varadarajan TK (2007) Tungsten trioxide nanorods as supports for platinum in methanol oxidation. Mater Chem Phys 106:168–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2007.05.032
Rawal SB, Kang HJ, Won DI, Lee WI (2019) Novel ZnFe2O4/WO3, a highly efficient visible-light photocatalytic system operated by a Z-scheme mechanism. Appl Catal B Environ 256:117856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117856
Santos LHMLM, Araújo AN, Fachini A et al (2010) Ecotoxicological aspects related to the presence of pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment. J Hazard Mater 175:45–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.100
Sim WJ, Lee JW, Lee ES et al (2011) Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater from households, livestock farms, hospitals and pharmaceutical manufactures. Chemosphere 82:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.10.026
Srivastava AK, Agnihotry SA, Deepa M (2006) Sol–gel derived tungsten oxide films with pseudocubic triclinic nanorods and nanoparticles. Thin Solid Films 515:1419–1423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2006.03.055
Subba Rao AN, Venkatarangaiah VT (2014) Metal oxide-coated anodes in wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:3197–3217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2313-6
Subramonian W, Wu TY, Chai S-P (2017) Photocatalytic degradation of industrial pulp and paper mill effluent using synthesized magnetic Fe2O3-TiO2: treatment efficiency and characterizations of reused photocatalyst. J Environ Manage 187:298–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.10.024
Tang P, Han L, Hegner FS et al (2019) Boosting photoelectrochemical water oxidation of hematite in acidic electrolytes by surface state modification. Adv Energy Mater 2019:1901836. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201901836
Tao B, Yan Z (2016) In-situ synthesis of highly efficient visible light driven stannic oxide/graphitic carbon nitride heterostructured photocatalysts. J Colloid Interface Sci 480:118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.07.009
Thomas S, Alatrache A, Pons M-N, Zahraa O (2014) Degradation of the herbicide isoproturon by a photocatalytic process. C R Chim 17:824–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2014.04.002
Trifi IM, Chaabane L, Dammak L et al (2021) Response surface methodology for boron removal by donnan dialysis: doehlert experimental design. Membranes 11:731. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11100731
Trifi B, Marzouk Trifi I, Kouass S et al (2023) Gliding arc plasma treatment of levofloxacin using experimental design approach. Clean-Soil, Air, Water 2023:2200364. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.202200364
Tseng TK, Lin YS, Chen YJ, Chu H (2010) A review of photocatalysts prepared by sol-gel method for VOCs removal. Int J Mol Sci 11:2336–2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11062336
Wang F, Zhang K (2011) Reduced graphene oxide–TiO2 nanocomposite with high photocatalystic activity for the degradation of rhodamine B. J Mol Catal A Chem 345:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2011.05.026
Yan SC, Li ZS, Zou ZG (2010) Photodegradation of rhodamine B and methyl orange over boron-doped g-C3N4 under visible light irradiation. Langmuir 26:3894–3901. https://doi.org/10.1021/la904023j
Yi J, Liao K, Zhang C et al (2015) Facile in situ preparation of graphitic-C3N4 @carbon paper as an efficient metal-free cathode for nonaqueous Li–O2 battery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:10823–10827. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b01727
Zang Y, Li L, Xu Y et al (2014) Hybridization of brookite TiO2 with g-C3N4: a visible-light-driven photocatalyst for As3+ oxidation, MO degradation and water splitting for hydrogen evolution. J Mater Chem A 2:15774–15780. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA02082K
Zhao Y, Pan K, Wei S, Zhang B (2018) Template-free hydrothermal synthesis of 3D hollow aggregate spherical structure WO3 nano-plates and photocatalytic properties. Mater Res Bull 101:280–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.01.049
Zia J, Kashyap J, Riaz U (2018) Facile synthesis of polypyrrole encapsulated V2O5 nanohybrids for visible light driven green sonophotocatalytic degradation of antibiotics. J Mol Liq 272:834–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.10.091
Zia J, Ajeer M, Riaz U (2019) Visible–light driven photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol-A using ultrasonically synthesized polypyrrole/K-birnessite nanohybrids: experimental and DFT studies. J Environ Sci 79:161–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2018.11.021
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all who assisted in contributing to this work.
Funding
The authors wish to acknowledge financial support from Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research [reference number: PRF 2019-D6P3].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Maryam Shabani.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Trifi, B., Nahdi, A., Othmani, A. et al. Photocatalytic degradation of a pharmaceutical pollutant (Levofloxacin) by two-hybrid photocatalysts g-C3N4/TiO2 and WO3/TiO2: comparative study. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21, 3747–3760 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05222-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05222-y