Abstract
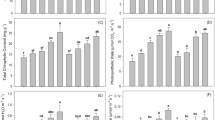
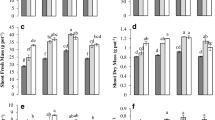
The deficiency of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) in calcareous soils of semi-arid climates is well recognized, and various green-based strategies have been employed to enhance their availability. However, the combined effects of heavy metal stress and soil calcareousness on NPK availability remain unclear. Thus, a pot experiment was conducted to assess the impact of biochar (BC), compost (Comp), and poultry manure (PM) at 1% and 2% w/w rates on NPK availability, soil characteristics, and maize performance under cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), and chromium (Cr) stress. The results demonstrated significant improvements (P ≤ 0.05) in soil properties, NPK availability, and maize growth with each amendment rate increment. Notably, the highest increases in soil pH, from 7.1 to 7.73, soil electrical conductivity (EC), from 0.32 to 0.4 dS m−1, and soil organic matter (SOM) content, from 0.79 to 1.37%, were observed with 2% BC. The highest increase in soil total nitrogen, from 0.03 to 0.08%, and extractable P, from 2.69 to 6.86 mg kg−1, occurred with 2% PM, while 2% BC led to an increase in K content, from 43.87 to 92.2 mg kg−1. Incremental rates of each amendment resulted in greater immobilization of bioavailable Cd, Pb, and Cr in the soil, leading to reduced bioaccumulation in roots and decreased translocation to shoots. The most pronounced effects were observed with 2% BC, which exhibited higher immobilization indexes for Cd (48%), Pb (53%), and Cr (51%). The effect of treatments at 2% was similar for plant height and shoot dry weight. A negative correlation was identified between NPK availability and bioavailable Cd, Pb, and Cr, indicating that organic materials reduced heavy metal stress while increasing NPK availability. BC emerged as the most effective amendment for improving NPK availability and stabilizing Cd, Pb, and Cr in the soil.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agbede TM, Oyewumi A (2022a) Benefits of biochar, poultry manure and biochar–poultry manure for improvement of soil properties and sweet potato productivity in degraded tropical agricultural soils. Resour Environ Sustain 7:100051
Agbede TM, Oyewumi A (2022b) Soil properties, sweet potato growth and yield under biochar, poultry manure and their combination in two degraded Alfisols of humid tropics. Sci Hortic 304:111331
Akbar WA, Ilyas M, Arif M, Rahim HU, Munsif F, Mudassir M, Zaheer S (2023) Biochar from on-farm feedstocks for sustainable potassium management in soils. Sustainable agriculture reviews 61: biochar to improve crop production and decrease plant stress under a changing climate, 219–229
Albert HA, Li X, Jeyakumar P, Wei L, Huang L, Huang Q, Kamran M, Shaheen SM, Hou D, Rinklebe J (2021) Influence of biochar and soil properties on soil and plant tissue concentrations of Cd and Pb: a meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 755:142582
Ali K, Arif M, Shah F, Shehzad A, Munsif F, Mian IA, Mian AA (2017) Improvement in maize (Zea mays L.) growth and quality through integrated use of biochar. Pak J Bot 49:85–94
Are KS, Adelana AO, Fademi IO, Aina OA (2017) Improving physical properties of degraded soil: potential of poultry manure and biochar. Agric Nat Resour 51:454–462
Azhar M, Ur Rehman MZ, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Naeem A, Ayub MA, Ul Haq MA, Iqbal A, Rizwan M (2019) Comparative effectiveness of different biochars and conventional organic materials on growth, photosynthesis and cadmium accumulation in cereals. Chemosphere 227:72–81
Beesley L, Marmiroli M (2011) The immobilisation and retention of soluble arsenic, cadmium and zinc by biochar. Environ Pollut 159:474–480
Benton Jones J Jr (1991) Plant tissue analysis in micronutrients. Micronutr. Agric 4:477–521
Bolan NS, Kunhikrishnan A, Choppala G, Thangarajan R, Chung J (2012) Stabilization of carbon in composts and biochars in relation to carbon sequestration and soil fertility. Sci Total Environ 424:264–270
Bremner J, Hauck R (1982) Advances in methodology for research on nitrogen transformations in soils. Nitrogen Agric Soils 22:467–502
Chng HY, Ahmed OH, Majid NMA (2016) Improving phosphorus availability, nutrient uptake and dry matter production of Zea mays L. on a tropical acid soil using poultry manure biochar and pineapple leaves compost. Expe Agric 52:447–465
Dai Y, Zheng H, Jiang Z, Xing B (2020) Combined effects of biochar properties and soil conditions on plant growth: a meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 713:136635
Iqbal A, Ali A, Fahad S, Parmar B (2016) Nitrogen source and rate management improve maize productivity of smallholders under semiarid climates. Front Plant Sci 7:1773
Khan H, Akbar WA, Shah Z, Rahim HU, Taj A, Alatalo JM (2022) Coupling phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) with inorganic phosphorus fertilizer improves mungbean (Vigna radiata) phosphorus acquisition, nitrogen fixation, and yield in alkaline-calcareous soil. Heliyon 8:e09081
Liang J, Yang Z, Tang L, Zeng G, Yu M, Li X, Wu H, Qian Y, Li X, Luo Y (2017) Changes in heavy metal mobility and availability from contaminated wetland soil remediated with combined biochar-compost. Chemosphere 181:281–288
Lima JRDS, Goes MDCCD, Hammecker C, Antonino ACD, Medeiros ÉVD, Sampaio EVDSB, Souza R (2021) Effects of poultry manure and biochar on acrisol soil properties and yield of common bean. A short-term field experiment. Agriculture 11(4):290
Medyńska-Juraszek A, Bednik M, Chohura P (2020) Assessing the influence of compost and biochar amendments on the mobility and uptake of heavy metals by green leafy vegetables. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:7861
McLean EO (1983) Soil pH and lime requirement. Methods Soil Anal Part 2 Chem Microbiol Prop 9:199–224
Naveed M, Ditta A, Ahmad M, Mustafa A, Ahmad Z, Conde-Cid M, Tahir S, Shah SAA, Abrar MM, Fahad S (2021) Processed animal manure improves morpho-physiological and biochemical characteristics of Brassica napus L. under nickel and salinity stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:45629–45645
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1996) Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. Methods Soil Anal Part 3 Chem Methods 5:961–1010
O’Connor D, Peng T, Zhang J, Tsang DC, Alessi DS, Shen Z, Bolan NS, Hou D (2018) Biochar application for the remediation of heavy metal polluted land: a review of in situ field trials. Sci Total Environ 619:815–826
Oladele SO, Ingold M, Buerkert A (2022) Impact of biochar-compost derived from thermal pyrolysis of poultry litter and woodchips on N mineralization and maize growth in contrasting tropical dryland soils. Bioresour Technol Rep 20:101225
Ozlu E, Kumar S (2018) Response of soil organic carbon, pH, electrical conductivity, and water stable aggregates to long-term annual manure and inorganic fertilizer. Soil Sci Soc Am J 82:1243–1251
Pahalvi, H. N., Rafiya, L., Rashid, S., Nisar, B., and Kamili, A. N. (2021). Chemical fertilizers and their impact on soil health. In: Microbiota and biofertilizers, vol 2, pp. 1–20. Springer
Rahim HU, Qaswar M, Wang M, Jing X, Cai X (2021) Environmental applications of reduced sulfur species and composites in transformation and detoxification of contaminants. J Environ Chem Eng 9:106696
Rahim HU, Akbar WA, Alatalo JM (2022) A comprehensive literature review on Cadmium (Cd) status in the soil environment and its immobilization by biochar-based materials. Agronomy 12:877
Rashid MS, Liu G, Yousaf B, Song Y, Ahmed R, Rehman A, Arif M, Irshad S, Cheema AI (2022) Efficacy of rice husk biochar and compost amendments on the translocation, bioavailability, and heavy metals speciation in contaminated soil: role of free radical production in maize (Zea mays L.). J Clean Prod 330:129805
Rhoades JD (1993) Electrical conductivity methods for measuring and mapping soil salinity. Adv Agron 49:201–251
Rizwan MS, Imtiaz M, Zhu J, Yousaf B, Hussain M, Ali L, Ditta A, Ihsan MZ, Huang G, Ashraf M (2021) Immobilization of Pb and Cu by organic and inorganic amendments in contaminated soil. Geoderma 385:114803
Saffeullah P, Nabi N, Zaman MB, Liaqat S, Siddiqi TO, Umar S (2021) Efficacy of characterized prosopis wood biochar amendments in improving growth, nitrogen use efficiency, nitrate accumulation, and mineral content in cabbage genotypes. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21:690–708
Sharma S, Tiwari S, Hasan A, Saxena V, Pandey LM (2018) Recent advances in conventional and contemporary methods for remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils. 3 Biotech 8:1–18
Soltanpour P, Schwab A (1977) A new soil test for simultaneous extraction of macro-and micro-nutrients in alkaline soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 8:195–207
Taj A, Bibi H, Akbar WA, Rahim HU, Iqbal M, Ullah S (2022) Effect of poultry manure and NPK compound fertilizer on soil physicochemical parameters, NPK availability, and uptake by spring maize (Zea mays L.) in alkaline-calcareous soil. Gesunde Pflanzen, 1–11
Tang X, Li X, Liu X, Hashmi MZ, Xu J, Brookes PC (2015) Effects of inorganic and organic amendments on the uptake of lead and trace elements by Brassica chinensis grown in an acidic red soil. Chemosphere 119:177–183
Truong THH, Marschner P (2019) Plant growth and nutrient uptake in soil amended with mixes of organic materials differing in C/N ratio and decomposition stage. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19:512–523
Ul Haq J, Sharif M, Akbar WA, Ur Rahim H, Ahmad Mian I, Ahmad S, Alatalo JM, Khan Z, Mudassir M (2022) Arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi integrated with single super phosphate improve wheat-nitrogen-phosphorus acquisition, yield, root infection activity, and spore density in alkaline-calcareous soil. Gesunde Pflanzen, 1–10
Ur Rahim H, Mian IA, Arif M, Ahmad S, Khan Z (2020) Soil fertility status as influenced by the carryover effect of biochar and summer legumes. Asian J Agric Biol 8:11–16
Ur Rahim H, Qaswar M, Uddin M, Giannini C, Herrera ML, Rea G (2021) Nano-enable materials promoting sustainability and resilience in modern agriculture. Nanomaterials 11:2068
Ur Rehman MZ, Rizwan M, Hussain A, Saqib M, Ali S, Sohail MI, Shafiq M, Hafeez F (2018) Alleviation of cadmium (Cd) toxicity and minimizing its uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum) by using organic carbon sources in Cd-spiked soil. Environ Pollut 241:557–565
Wang Z, Hassan MU, Nadeem F, Wu L, Zhang F, Li X (2020) Magnesium fertilization improves crop yield in most production systems: a meta-analysis. Front Plant Sci 10:1727
WHO G (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organization 216:303-304
Yousaf B, Liu G, Wang R, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Rizwan MS, Imtiaz M, Murtaza G, Shakoor A (2016) Investigating the potential influence of biochar and traditional organic amendments on the bioavailability and transfer of Cd in the soil–plant system. Environ Earth Sci 75:1–10
Yousaf M, Li J, Lu J, Ren T, Cong R, Fahad S, Li X (2017) Effects of fertilization on crop production and nutrient-supplying capacity under rice-oilseed rape rotation system. Sci Rep 7:1–9
Zhang J, Gao C, Zhu H, Zhong S, Yang W, Zheng J, Wu S, Shan S, Wang Z, Zhang J (2017) Mechanism and effects of biochar application on morphology and migration of heavy metals in contaminated soil. J Zhejiang a&f Univ 34:543–551
Funding
The current study didn’t receive any external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AS & MI: Supervision, Methodology, Experiment execution, Data collection, Lab and statistical analysis, HUR: Conceptualization, Investigation, Visualization, Supervision, and Discussion, Writing original draft, Review & editing. UK: Experiment execution, Data collection, WAA: Review and editing, ZA: Experiment execution, JMA: Review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Jing Chen.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saleem, A., Ur Rahim, H., Khan, U. et al. Organic materials amendments can improve NPK availability and maize growth by reducing heavy metals stress in calcareous soil. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21, 2533–2546 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05135-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05135-w