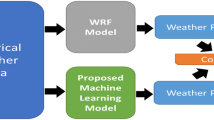
Abstract
Weather events directly affect human activities. In particular, extreme weather events with global warming, forest fires, and high air temperatures that cause drought make human life difficult. Effective and accurate weather prediction models are needed to take precautions against such climatic events. Therefore, it is essential to develop models that make precise weather predictions. Technological developments contributed significantly to developing successful deep learning-based weather prediction models. With a high success rate, this study proposed a hybrid weather prediction model based on Convolutional Neural Networks and Recurrent Neural Networks models. The proposed hybrid model was applied to the Jena dataset, which contains 14-parameter, large-scale meteorological data that were never utilized for weather prediction. The experimental results were compared with popular deep learning, machine learning, and statistical methods such as Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average, Convolution Neural Networks, Long-Short Term Memory, Multilayer Perceptron, Random Forest, Recurrent Neural Networks, and Support Vector Machine. As a result of these comparisons, the proposed hybrid model obtained the best prediction result for all metrics. For example, according to the weather prediction results for Jena, Germany, the proposed hybrid model got the results of Mean Squared Error: 0.035, Root-Mean-Squared Error: 0.189, Mean Absolute Error: 0.126, and R-Squared: 0.987.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Program codes available on request and the datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the Kaggle repository and persistent web links to dataset is below: Jena dataset: https://www.kaggle.com/mnassrib/jena-climate (Jena Climate Dataset 2016).
References
Alley RB, Emanuel KA, Zhang F (2019) Advances in weather prediction. Science 363(6425):342–344. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aav7274
Bauer P, Thorpe A, Brunet G (2015) The quiet revolution of numerical weather prediction. Nature 525(7567):47–55. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14956
Bolton T, Zanna L (2019) Applications of deep learning to ocean data inference and subgrid parameterization. J Adv Model Earth Syst 11:376–399. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018MS001472
Chattopadhyay A, Nabizadeh E, Hassanzadeh P (2020) Analog forecasting of extreme-causing weather patterns using deep learning. J Adv Model Earth Syst 12(2):e2019MS001958. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019MS001958
Cho D et al (2022) A novel ensemble learning for post-processing of NWP model’s next-day maximum air temperature forecast in summer using deep learning and statistical approaches. Weather Climate Extremes 35:100410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wace.2022.100410
Dalto M, Matuško J, Vašak M (2015) Deep neural networks for ultra-short-term wind forecasting. In: 2015 IEEE international conference on industrial technology (ICIT), 17–19 March, Seville, Spain, pp 1657–1663. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIT.2015.7125335
Dombaycı ÖA, Gölcü M (2009) Daily means ambient temperature prediction using artificial neural network method: a case study of Turkey. Renew Energy 34(4):1158–1161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2008.07.007
Fister D, et al (2023) Accurate long-term air temperature prediction with Machine Learning models and data reduction techniques. Appl Soft Comput 110118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2023.110118
Grönquist P et al (2021) Deep learning for post-processing ensemble weather forecasts. Philos Trans R Soc A 379(2194):20200092. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2020.0092
Hewage P et al (2021) Deep learning-based effective fine-grained weather forecasting model. Pattern Anal Appl 24(1):343–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-020-00898-1
Hou J et al (2022) Prediction of hourly air temperature based on CNN–LSTM. Geomatics Nat Hazards Risk 13(1):1962–1986. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2022.2102942
Hossain M, et al (2015) Forecasting the weather of Nevada: a deep learning approach. In: 2015 International joint conference neural networks (IJCNN), 12–17 July, Killarney, Ireland, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2015.7280812
Jena Climate Dataset (2016) Weather time series dataset recorded at the Weather Station of the Max Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry in Jena, Germany. https://www.kaggle.com/mnassrib/jena-climate. Accessed 20 Feb 2022
Kisi O, Shiri J (2014) Prediction of long-term monthly air temperature using geographical inputs. Int J Climatol 34(1):179–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1480-4
Li C, et al (2020) Air temperature forecasting using traditional and deep learning algorithms. In: 2020 7th International conference on information science and control engineering (ICISCE), 18–20 December, Changsha, China, pp 189–194. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICISCE50968.2020.00049
Li C, Zhang Y, Zhao G (2019) Deep learning with long short-term memory networks for air temperature predictions. In: 2019 International conference on artificial intelligence and advanced manufacturing (AIAM), 16–18 October, Dublin, Ireland, pp 243–249. https://doi.org/10.1109/AIAM48774.2019.00056
Liu X, Yuan S, Li L (2012) Prediction of temperature time series based on wavelet transform and support vector machine. J Comput 7(8):1911–1918. https://doi.org/10.4304/jcp.7.8.1911-1918
Lynch P (2008) The origins of computer weather prediction and climate modeling. J Comput Phys 227:3431–3444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2007.02.034
Maqsood I, Khan MR, Abraham A (2004) An ensemble of neural networks for weather forecasting. Neural Comput Appl 13(2):112–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-004-0413-4
Rasp S, Pritchard MS, Gentine P (2018) Deep learning to represent subgrid processes in climate models. Proc Natl Acad Sci 115(39):9684–9689. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1810286115
Reichstein M et al (2019) Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science. Nature 566(7743):195–204. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-0912-1
Ren X et al (2021) Deep learning-based weather prediction: a survey. Big Data Res 23:100178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bdr.2020.100178
Rodrigues ER, et al. (2018) DeepDownscale: a deep learning strategy for high-resolution weather forecast. In: 2018 IEEE 14th international conference on e-Sci (e-Science), October 29 - November 1, Amsterdam, Netherlands, pp 415–422. https://doi.org/10.1109/eScience.2018.00130
Roy DS (2020) Forecasting the air temperature at a weather station using deep neural networks. Procedia Comput Sci 178:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.11.005
Salcedo-Sanz S et al (2016) Monthly prediction of air temperature in Australia and New Zealand with machine learning algorithms. Theor Appl Climatol 125:13–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1480-4
Salman AG, Kanigoro B, Heryadi Y (2015) Weather forecasting using deep learning techniques. In: 2015 International conference on advanced computer science and information systems (ICACSIS), 10–11 October, Depok, Indonesia, pp 281–285. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACSIS.2015.7415154
Schizas CN, et al (1991) Artificial neural networks in forecasting minimum temperature (weather). In: 1991 Second international conference on artificial neural networks, 18–20 November, Bournemouth, UK, pp 112–114
Schultz MG et al (2021) Can deep learning beat numerical weather prediction? Philos Trans R Soc A 379(2194):20200097. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2020.0097
Scher S (2018) Toward data-driven weather and climate forecasting: approximating a simple general circulation model with deep learning. Geophys Res Lett 45(22):12–616. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL080704
Shi X, et al (2015) Convolutional LSTM network: a machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 802–810
Tabrizi SE et al (2021) Hourly road pavement surface temperature forecasting using deep learning models. J Hydrol 603:126877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126877
Weyn JA, Durran DR, Caruana R (2019) Can machines learn to predict weather? Using deep learning to predict gridded 500-hPa geopotential height from historical weather data. J Adv Model Earth Syst 11(8):2680–2693. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019MS001705
Zaytar MA, El Amrani C (2016) Sequence to sequence weather forecasting with long short-term memory recurrent neural networks. Int J Comput Appl 143(11):7–11
Zhang J et al (2022) Prediction of remaining useful life based on bidirectional gated recurrent unit with temporal self-attention mechanism. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 221:108297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2021.108297
Zhang J et al (2023) A variational local weighted deep sub-domain adaptation network for remaining useful life prediction facing cross-domain condition. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 231:108986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2022.108986
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AU: Conceptualization, methodology, writing original draft, data analysis, and model coding. UC: Writing original draft, investigation, data analysis, data collection, and programming support. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This manuscript has not been published or presented elsewhere in part or in entirety and is not under consideration by another journal. We have read and understood your journal's policies, and we believe that neither the manuscript nor the study violates any of these.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Utku, A., Can, U. An efficient hybrid weather prediction model based on deep learning. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 11107–11120 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05092-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05092-4