Abstract
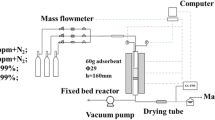
Hydrogen sulfide is an odorous gas anaerobically produced from decaying organic matter. It causes irritation when inhaled and is lethal at higher concentrations. Adsorption using activated carbon is one of the most effective methods for the removal of H2S from gas streams. The desorption of H2S from activated carbon can be facilitated using water. Due to their weak attachment affinity to H2S, the desorption energy requirements are low. In this paper, activated carbon is used to adsorb H2S from the air. The activated carbon is later regenerated using water. The effect of various parameters like temperature, pH and flowrate is studied. GC Sulfursorb Plus™ was used for this adsorption–desorption method. The H2S stream passed through the activated carbon column, where the concentration was recorded at both the influent and effluent. Desorption was conducted with water at different temperatures (10 °C, 20 °C, 40 °C, 60 °C, 80 °C and 100 °C), flowrates (10 mL/min, 20 mL/min, 50 mL/min, 100 mL/min and 150 mL/min) and pH (5, 8, 10 and 12). The temperature was maintained using a hotplate and heat tape. Whereas pH was maintained using hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide, and flowrate using a peristaltic pump. Samples were collected and analyzed for sulfide concentration. Maximum sulfide concentration (560 µg/L) was noted at pH 5. However, the maximum cumulative mass (165 µg) was observed at 100 °C. Flowrate at which maximum removal (82.5 µg) was observed at 50 mL/min. GC Sulfursorb Plus™ has a high adsorption capacity, so desorption was partially effective.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data will be made available upon request.
References
Adib F (2000) Application of unmodified activated carbon for removal of odor from wastewater treatment facilities faculty of engineering. The City University of New York, New York, p 181
Adib F, Bagreev A, Bandosz TJ (1999a) Effect of surface characteristics of wood-based activated carbons on adsorption of hydrogen sulfide. J Colloid Interface Sci 214(2):407–415. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1999.6200
Adib F, Bagreev A, Bandosz TJ (1999b) Effect of pH and surface chemistry on the mechanism of H2S removal by activated carbons. J Colloid Interface Sci 216(2):360–369. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1999.6335
Adib F, Bagreev A, Bandosz TJ (1999c) Adsorption/oxidation of hydrogen sulfide on nitrogen-containing activated carbons (world) [Research-article]. ACS Publications; Am Chem Soc https://doi.org/10.1021/la990926o
Adib F, Bagreev A, Bandosz TJ (2000a) Analysis of the relationship between H2S removal capacity and surface properties of unimpregnated activated carbons. Environ Sci Technol 34(4):686–692. https://doi.org/10.1021/es990341g
Adib F, Bagreev A, Bandosz TJ (2000b) On the possibility of water regeneration of unimpregnated activated carbons used as hydrogen sulfide adsorbents (world) [Research-article]. ACS Publications; Am Chem Soc https://doi.org/10.1021/ie990926j
Al-Degs YS, El-Barghouthi MI, El-Sheikh AH, Walker GM (2008) Effect of solution pH, ionic strength, and temperature on adsorption behavior of reactive dyes on activated carbon. Dyes Pigm 77(1):16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2007.03.001
Bagreev A, Rahman H, Bandosz TJ (2001) Thermal regeneration of a spent activated carbon previously used as hydrogen sulfide adsorbent. Carbon 39(9):1319–1326. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(00)00266-9
Bandosz TJ (2002) On the adsorption/oxidation of hydrogen sulfide on activated carbons at ambient temperatures. J Colloid Interface Sci 246(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2001.7952
Bjelopavlic, null, Newcombe, null, & Hayes, null. (1999) Adsorption of NOM onto activated carbon: effect of surface charge, ionic strength, and pore volume distribution. J Colloid Interface Sci 210(2):271–280. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1998.5975
Bunker B (2022) Construction and operation of a pilot-scale odor control device. Environmental engineering theses and graduate student research. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/envengdiss/25
Cline J D, & Richards F A (2002). Oxygenation of hydrogen sulfide in seawater at constant salinity, temperature and pH (world) [Research-article]. ACS Publications; Am Chem Soc https://doi.org/10.1021/es60032a004
Coppola G, Papurello D (2019) Biogas cleaning: activated carbon regeneration for H2S removal. Clean Technol 1(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol1010004
Cwalina B (2008) Biodeterioration of concrete. Arch Civil Eng Environ 4:133–140
Dubinin M M (1975) Physical adsorption of gases and vapors in micropores. In: D A Cadenhead, J F Danielli, & M D Rosenberg (Eds.), Progress in Surface and Membrane Science (Vol. 9, pp. 1–70). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-571809-7.50006-1
Dubinin MM (1989) Fundamentals of the theory of adsorption in micropores of carbon adsorbents: characteristics of their adsorption properties and microporous structures. Carbon 27(3):457–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6223(89)90078-X
Edwards S, Alharthi R, Ghaly A (2011) Removal of hydrogen sulphide from water. Am J Environ Sci 7:295–305
Feng W, Kwon S, Borguet E, Vidic R (2005) Adsorption of hydrogen sulfide onto activated carbon fibers: effect of pore structure and surface chemistry. Environ Sci Technol 39(24):9744–9749. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0507158
Ferro-García MA, Utrera-Hidalgo E, Rivera-Utrilla J, Moreno-Castilla C, Joly JP (1993) Regeneration of activated carbons exhausted with chlorophenols. Carbon 31(6):857–863. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6223(93)90185-D
Greene EA, Hubert C, Nemati M, Jenneman GE, Voordouw G (2003) Nitrite reductase activity of sulphate-reducing bacteria prevents their inhibition by nitrate-reducing, sulphide-oxidizing bacteria. Environ Microbiol 5(7):607–617. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1462-2920.2003.00446.x
Groenestijn J W van (2005). Biotechniques for air pollution control: past, present and future trends. Universidade da Coruña. https://ruc.udc.es/dspace/handle/2183/11425
Gutiérrez-Padilla Ma, G. D., Bielefeldt, A., Ovtchinnikov, S., Hernandez, M., & Silverstein, J. (2010) Biogenic sulfuric acid attack on different types of commercially produced concrete sewer pipes. Cem Concr Res 40(2):293–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2009.10.002
Hashimoto K, Miura K, Watanabe T (1982) Kinetics of thermal regeneration reaction of activated carbons used in waste water treatment. AIChE J 28(5):737–746. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690280506
Hughes MN, Centelles MN, Moore KP (2009) Making and working with hydrogen sulfide: the chemistry and generation of hydrogen sulfide in vitro and its measurement in vivo: a review. Free Radical Biol Med 47(10):1346–1353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.09.018
Kikot P, Viera M, Mignone C, Donati E (2010) Study of the effect of pH and dissolved heavy metals on the growth of sulfate-reducing bacteria by a fractional factorial design. Hydrometallurgy 104(3):494–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2010.02.026
Kim BR, Cognata MB (1990) Pac addition as a means of regenerating gac in a gac fluidized-bed reactor. Water Res 24(1):103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(90)90071-D
Kow S-H, Fahmi MR, Abidin CZA, Ong S-A, Ibrahim N (2016) Regeneration of spent activated carbon from industrial application by NaOH solution and hot water. Desalin Water Treat 57(60):29137–29142. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1168133
Loven AW et al (1973) Adsorption-desorption properties of sorbents. Chem Eng Progr 69:56
Leng C-C, Pinto NG (1996) An investigation of the mechanisms of chemical regeneration of activated carbon. Ind Eng Chem Res 35(6):2024–2031. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie950576a
Martin RJ, Ng WJ (1985) Chemical regeneration of exhausted activated carbon—II. Water Res 19(12):1527–1535. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(85)90398-7
M D Merchan and F Salvador (1994) In characterization of porous solids III. Studies in surface science and catalysis. (Edited by J Rouquerol, F Rodriguez-Reinoso, K S Sing and K K Unger), vol 87, p 391. Elsevier
Nahm SW, Shim WG, Park Y-K, Kim SC (2012) Thermal and chemical regeneration of spent activated carbon and its adsorption property for toluene. Chem Eng J 210:500–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.09.023
Neville A (1995) Chloride attack of reinforced concrete: An overview. Mater Struct 28(2):63–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02473172
Newcombe G, Donati C, Drikas M, Hayes R. (1996) Adsorption onto activated carbon: electrostatic and non-electrostatic interactions. Water supply, HERO EPA, https://hero.epa.gov/hero/index.cfm/reference/details/reference_id/7606108. Accessed on 14 Oct 2022
Nielsen PH, Raunkjær K, Hvitved-Jacobsen T (1998) Sulfide production and wastewater quality in pressure mains. Water Sci Technol 37(1):97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(97)00758-0
Notthakun S, Crittenden JC, Hand DW, Perram DL, Mullins ME (1993) Regeneration of adsorbents using heterogeneous advanced oxidation. J Environ Eng 119(4):695–714. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(1993)119:4(695)
Reese BK, Finneran DW, Mills HJ, Zhu M-X, Morse JW (2011) Examination and refinement of the determination of aqueous hydrogen sulfide by the methylene blue method. Aquat Geochem 17(4):567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-011-9128-1
Reis MA, Almeida JS, Lemos PC, Carrondo MJ (1992) Effect of hydrogen sulfide on growth of sulfate reducing bacteria. Biotechnol Bioeng 40(5):593–600. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260400506
Rivera-Utrilla J, Moreno-Castilla C, Utrera-Hidalgo E, Carrasco-Marín F (1993) Removal of tannic acid from aqueous solutions by activated carbons. Chem Eng J 52(1):37–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-9467(93)80040-U
Roncken Th, Roebers A, Hopman R, de Ligny CL, Dekker BG, Van der Laan J, Kruithof JC (1988) Activated carbon as an adsorbent for the separation of low-molecular weight alkyl halides from ground water in the production of drinking water. II. The relationship between the adsorption capacity for trichloroethene of virgin and regenerated activated carbons, and their achievement in the purification of deep-well ground water. Adsorpt Sci Technol 5(4):289–296. https://doi.org/10.1177/026361748800500404
Saeedi A, Najibi A, Mohammadi -Bardbori A, (2015) Effects of long-term exposure to hydrogen sulfide on human red blood cells. Int J Occu Environ Med 6(1):20–25. https://doi.org/10.15171/ijoem.2015.482
Salvador F, Jiménez CS (1996) A new method for regenerating activated carbon by thermal desorption with liquid water under subcritical conditions. Carbon 34(4):511–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6223(95)00211-1
Schork J M, & Fair J R (2002). Parametric analysis of thermal regeneration of adsorption beds (world). ACS Publications; American Chemical Society. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie00075a016
Sherief M, Aly Hassan A (2022) The Impact of wastewater quality and flow characteristics on H2S emissions generation: statistical correlations and an artificial neural network model. Water 14(5):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050791
Shi L, Yang K, Zhao Q, Wang H, Cui Q (2015) Characterization and mechanisms of H2S and SO2 adsorption by activated carbon. Energy Fuels 29(10):6678–6685. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b01696
Sun M, Wang X, Zhao Z, Qiu J (2022) Review of H2S selective oxidation over carbon-based materials at low temperature: from pollutant to energy storage materials. New Carbon Mater 37(4):675–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5805(22)60622-X
Tan CS, Liou DC (1988) Desorption of ethyl acetate from activated carbon by supercritical carbon dioxide. Ind Eng Chem Res 27(6):988–991. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie00078a017
USEPA (1971), Bio-Regenerated activated carbon treatment of textile dyes wastewater, water pollution control res. Ser Proi. No. 12090 DWM
USEPA R P De Filippi, V J Krukonis and R J, Robey (1980) Modell supercritical fluid regeneration of activated carbon for adsorption of pesticides. Report, EPA, Wastington, DC
Xu Q, Townsend T, Bitton G (2011) Inhibition of hydrogen sulfide generation from disposed gypsum drywall using chemical inhibitors. J Hazard Mater 191(1–3):204–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.04.063
Zuo Z, Chang J, Lu Z, Wang M, Lin Y, Zheng M, Zhu DZ, Yu T, Huang X, Liu Y (2019) Hydrogen sulfide generation and emission in urban sanitary sewer in China: what factor plays the critical role? Environ Sci: Water Res Technol 5(5):839–848. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EW00617B
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Chongqing Wang.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sherief, M., Javed, M.A., Bunker, B. et al. In-situ desorption of hydrogen sulfide from activated carbon: effect of temperature, pH and flowrate. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21, 359–370 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-04974-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-04974-x