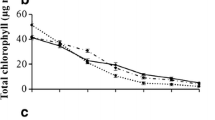
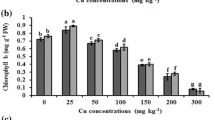
Abstract
Microalgae are sensitive bioindicators in assessing the toxic effects of heavy metals. In this regard, the effects of prolonged exposure to copper on biotechnologically important soil microalgae have not been sufficiently studied. The work aimed to study copper’s action on soil microalgae: Vischeria magna, Botrydiopsis sp., and Tetracystis sp. in a 28-day experiment with different initial cell densities (× 103 and × 106 cell/mL) using CuSO4 and Cu(CH3COO)2 as the source of copper. It was found that the toxic effect of copper depends on its concentration, initial density of algae cells in testing, and the chemical source of copper. This research revealed that Tetracystis sp. had the highest resistance to copper, which withstood copper concentrations up to 50 mg/L. Botrydiopsis sp. and V. magna were resistant to copper concentrations of 30 mg/L and 5 mg/L, respectively. Copper appeared less toxic for the test with a higher cell density (× 106 cell/mL). It was also found that the toxic effect of copper was manifested at lower concentrations in experiments with CuSO4 compared to ones using Cu(CH3COO)2. The results of this study provide a better understanding of the effects of copper on soil microalgae species and their potential for biotechnological production using heavy metal waters, bioremediation, and monitoring of algae diversity, especially in soils contaminated by heavy metals.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Ali H, Khan E, Ilahi I (2019) Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J Chem 19:6730305. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6730305
Andersen RA, Berges JA, Harrison PJ, Watanabe MM (2005) Recipes for freshwater and seawater media. In: Andersen RA (ed) Algal culturing techniques. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 429–538
ATT bioquest Inc. quest graph TM LC50 calculator (2020). http://www.aatbio.com/tools/lc50-calculator. Accessed 12 April 2022
Baścik-Remisiewicz A, Tukaj Z (2002) Toxicity of inorganic cadmium salts to the microalga Scenedesmus armatus (Chlorophyta) with respect to medium composition, pH and CO2 concentration. Acta Physiol Pl 24(1):59–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-002-0022-8
Bischoff HW, Bold HC (1963) Phycological studies IV. In: Some soil algae from enchanted rock and related algal species, University of Texas Publication, Austin
Bishop WM, Willis BE, Richardson RJ, Cope WG (2018) The presence of algae mitigates the toxicity of copper-based algaecides to a nontarget organism. Environ Toxicol Chem 37:2132–2142. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4166
Carfagna S, Lanza N, Salbitani G, Basile A, Sorbo S, Vona V (2013) Physiological and morphological responses of lead or cadmium exposed Chlorella sorokiniana 211–8K (Chlorophyceae). Springer plus 2(1):147. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-2-147
Chekroun KB, Baghour M (2013) The role of algae in phytoremediation of heavy metals: a review. J Mater Environ Sci 4(6):873–880
Csuros M, Csuros C (2002) Environmental sampling and analysis for metals. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Danouche M, Ghachtouli NE, El Arroussi HE (2021) Phycoremediation mechanisms of heavy metals using living green microalgae: physicochemical and molecular approaches for enhancing selectivity and removal capacity. Heliyon 7(7):E07609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07609
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2012) jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nature Meth 9:772. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2109
de Kuhn M, Streb C, Breiter R, Richter P, Neeße T, Häder DP (2006) Screening for unicellular algae as possible bioassay organisms for monitoring marine water samples. Water Res 40:2695–2703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.04.045
Debelius B, Forja JM, DelValls A, Lubián LM (2009) Toxicity and bioaccumulation of copper and lead in five marine microalgae. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72(5):1503–1513
Drummond AJ, Rambaut A (2007) BEAST: bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol Biol 7:214. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-7-214
Duffus JH (2002) “Heavy metals” a meaningless term? (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl Chem 74:793–807. https://doi.org/10.1351/PAC200274050793
Ebenezer V, Ki J-S (2013) Quantification of the sub-lethal toxicity of metals and endocrine-disrupting chemicals to the marine green microalga Tetraselmis suecica. Fish Aquat Sci 16:187–194. https://doi.org/10.5657/FAS.2013.0187
Ebenezer V, Lim WA, Ki J-S (2014) Effects of the algicides CuSO4 and NaOCl on various physiological parameters in the harmful dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides. J Appl Phycol 26:2357–2365
Expósito N, Carafa R, Kumar V, Sierra J, Schuhmacher M, Papiol GG (2021) Performance of Chlorella vulgaris exposed to heavy metal mixtures: linking measured endpoints and mechanisms. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(3):1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031037
Fettweis A, Bergen B, Hansul S, De Schamphelaere K, Smolders E (2021) Correlated Ni, Cu, and Zn sensitivities of 8 freshwater algal species and consequences for low-level metal mixture effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 40(7):2015–2025. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5034
Franklin NM, Stauber JL, Apte SC, Lim RP (2002) Effect of initial cell density on the bioavailability and toxicity of copper in microalgal bioassays. Environ Toxicol Chem 21(4):742–751. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620210409
Giordano M, Norici A, Ratti S, Raven JA (2008) Role of sulfur for algae: acquisition metabolism ecology and evolution. In: Hell R, Dahl C, Knaff D, Leustek T (eds) Sulfur metabolism in phototrophic organisms advances in photosynthesis and respiration, vol 27. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-6863-8_20
Guo H, Li T, Zhao Y, Yu X (2021) Role of copper in the enhancement of astaxanthin and lipid coaccumulation in Haematococcus pluvialis exposed to abiotic stress conditions. Bioresour Technol 335:125265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125265
Hamed SM, Selim S, Klöck G, AbdElgawad H (2017) Sensitivity of two green microalgae to copper stress: growth, oxidative and antioxidants analyses. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 144(12):19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.05.048
Heifetz PB, Förster B, Osmond CB, Giles LJ, Boynton JE (2000) Effects of acetate on facultative autotrophy in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii assessed by photosynthetic measurements and stable isotope analyses. Plant Physiol 122(4):1439–1445. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.122.4.1439
Horvatić J, Peršić V (2007) The effect of Ni2+, Co2+, Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ on the growth rate of marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum Bohlin: microplate growth inhibition test. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:494–498. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00128-007-9291-7
Hurtgen MT (2012) Geochemistry. the marine sulfur cycle, revisited. Science 337:305–306
Jeong H, Lee SJ, Kim P (2016) Procedure for adaptive laboratory evolution of microorganisms using a chemostat. J Visual Experim 115:54446. https://doi.org/10.3791/54446
Johnson HL, Stauber JL, Adams MS, Jolley DF (2007) Copper and zinc tolerance of two tropical microalgae after copper acclimation. Environ Toxicol 22(3):234–244. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20265
Kabirov RR (1995) Algotesting and algoindication. Bashkir Pedagogical University, Ufa
Kamyab H, Md Din MF, Ponraj M, Keyvanfar A, Rezania S, Taib SM, Abd Majid MZ (2016) Isolation and screening of microalgae from agro-industrial wastewater (POME) for biomass and biodiesel sources. Desalination Water Treat 57:29118–29125. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1139101
Kaplan D (2013) Absorption and adsorption of heavy metals by microalgae. In: Richmond A, Hu Q (eds) Handbook of microalgal culture: applied phycology and biotechnology, 2nd edn. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, Hoboken
Katoh K, Toh H (2010) Parallelization of the MAFFT multiple sequence alignment program. Bioinformatics 26:1899–1900. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq224
Kemer K, Mantiri DMH, Rompas RM, Rimper JR, Margyaningsih NI (2020) Transmission electron microscope analysis upon growth of lead acetate treated microalga, Dunaliella sp. AACL Bioflux 13(2):849–856
Khaneghah AM, Fakhri Y, Nematollahi A, Pirhadi M (2020) Potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in cereal-based foods: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Trends Food Sci Technol 96:30–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIFS.2019.12.007
Koller M, Saleh HM (2018) Introductory chapter: introducing heavy metals. In: Saleh H, Aglan R (eds) heavy metals. IntechOpen, London. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.74783
Kumar SD, Santhanam P, Ananth S, Devi AS, Nandakumar R, Prasath BB, Jeyanthi S, Jayalakshmi T, Ananthi P (2014) Effect of different dosages of zinc on the growth and biomass in five marine microalgae. Int J Fish Aquac 6(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.5897/IJFA2013.0393
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Lachmann SC, Mettler-Altmann T, Wacker A, Spijkerman E (2019) Nitrate or ammonium: influences of nitrogen source on the physiology of a green alga. Ecol Evol 9(3):1070–1082. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.4790
Lage OM, Soares HMVM, Vasconcelos MTSD, Parente AM, Salema R (1996) Toxicity effects of copper (II) on the marine dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae: influence of metal speciation. Eur J Phycol 31(4):341–348. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670269600651571
Levy J, Stauber JL, Jolley DF (2007) Sensitivity of marine microalgae to copper: the effect of biotic factors on copper adsorption and toxicity. Sci Total Environ 387(1–3):141–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.07.016
Li Q, Wu YY, Wu YD (2013) Effects of fluoride and chloride on the growth of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Water Sci Technol 68(3):722–727. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2013.279
Li S, Chu R, Hu D, Yin Z, Mo F, Hu T, Liu C, Zhu L (2020) Combined effects of 17β-estradiol and copper on growth, biochemical characteristics and pollutant removals of freshwater microalgae Scenedesmus dimorphus. Sci Total Environ 730:73015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138597
Liu G, Chai X, Shao Y, Hu L, Xie Q, Wu H (2011) Toxicity of copper, lead, and cadmium on the motility of two marine microalgae Isochrysis galbana and Tetraselmis chui. J Environ Sci 23(2):330–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60410-X
Lopez J, Lee L, Mackey KRM (2019) The toxicity of copper to Crocosphaera watsonii and other marine phytoplankton: a systematic review. Front Mar Sci 5:511. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2018.00511
Lukavský J, Sevdalina F, Cepák V (2003) Toxicity of metals, Al, Cd Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Ni, Pb and Zn on microalgae, using microplate bioassay 1: Chlorella kessleri, Scenedesmus quadricauda, Sc. subspicatus and Raphidocelis subcapitata (Selenastrum capricornutum). Algol Stud 110(1):127–141. https://doi.org/10.1127/1864-1318/2003/0110-0127
Magdaleno A, Vélez CG, Wenzel MT, Tell G (2014) Effects of cadmium, copper and zinc on growth of four isolated algae from a highly polluted Argentina river. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92(2):202–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1171-8
Maltsev Y, Maltseva I (2018) The influence of forest-forming tree species on diversity and spatial distribution of algae in forest litter. Folia Oecologica 45:72–81. https://doi.org/10.2478/foecol-2018-0008
Maltsev YI, Didovich SV, Maltseva IA (2017a) Seasonal changes in the communities of microorganisms and algae in the litters of tree plantations in the steppe zone. Eurasian Soil Sci 50:935–942. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229317060059
Maltsev Y, Gusev E, Maltseva I, Kulikovskiy M, Namsaraev Z, Petrushkina M, Filimonova A, Sorokin B, Golubeva A, Butaeva G, Khrushchev A, Kuzmin D (2018) Description of a new species of soil algae, Parietochloris grandis sp. nov., and study of its fatty acid profiles under different culturing conditions. Algal Res 33:358–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2018.06.008
Maltsev YI, Maltseva IA, Kulikovskiy MS, Maltseva SY, Sidorov RA (2019) Analysis of a new strain of Pseudomuriella engadinensis (Sphaeropleales, Chlorophyta) for possible use in biotechnology. Russ J Plant Physiol 66(4):609–617. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443719040083
Maltsev Y, Maltseva A, Maltseva S (2021a) Differential Zn and Mn sensitivity of microalgae species from genera Bracteacoccus and Lobosphaera. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(40):57412–57423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15981-1
Maltsev YI, Maltseva IA, Solonenko AN, Bren AG (2017b) Use of soil biota in the assessment of the ecological potential of urban soils. Biosyst Divers 25(4):257–262. https://doi.org/10.15421/011739
Maltsev Y, Maltseva I, Maltseva S, Kociolek JP, Kulikovskiy M (2021b) A new species of freshwater algae Nephrochlamys yushanlensis sp. Nov. (Selenastraceae, Sphaeropleales) and its lipid accumulation during nitrogen and phosphorus starvation. J Phycol 57(2):606–618. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpy.13116
Maltseva IA, Maltsev YI (2021) Diversity of cyanobacteria and algae in dependence to forest-forming tree species and properties rocks of dump. Int J Environ Sci Technol 18:545–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02868-w
Maltseva IA, Maltsev YI, Solonenko AN (2017) Soil algae of the oak groves of the steppe zone of Ukraine. Int J Algae 19(3):215–226. https://doi.org/10.1615/InterJAlgae.v19.i3.20
Matagi S, Swaiand D, Mugabe R (1998) A review of heavy metal removal mechanisms in wetlands. Afr J Trop Hydrobiol Fish 8:23–35. https://doi.org/10.4314/ajthf.v8i1.1386
Mera R, Torres E, Abalde J (2014) Sulphate, more than a nutrient, protects the microalga Chlamydomonas moewusii from cadmium toxicity. Aquat Toxicol 148:92–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.12.034
Miazek K, Iwanek W, Remacle C, Richel A, Goffin D (2015) Effect of metals, metalloids and metallic nanoparticles on microalgae growth and industrial product biosynthesis: a review. Int J Mol Sci 16(10):23929–23969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161023929
Nelson DR, Chaiboonchoe A, Fu W, Hazzouri KM, Huang Z, Jaiswal A, Daakour S, Mystikou A, Arnoux M, Sultana M, Salehi-Ashtiani K (2019) Potential for heightened sulfur-metabolic capacity in coastal subtropical microalgae. Iscience 11:450–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2018.12.035
OECD (2011) Test No. 201: Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, growth inhibition test. In: OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, section 2, OECD Publishing, Paris. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264069923-en
Pan L, Fang G, Wang Y, Wang L, Su B, Li D, Xiang B (2018) Potentially toxic element pollution levels and risk assessment of soils and sediments in the upstream river, Miyun Reservoir, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:2364. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH15112364
Perrineau MM, Zelzion E, Gross J, Price DC, Boyd J, Bhattacharya D (2014) Evolution of salt tolerance in a laboratory reared population of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ Microbiol 16:1755–1766. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12372
Phetchuay BP, Peerakietkhajorn S, Duangpan S, Buapet P (2019) Toxicity effects of copper and zinc on the photosynthetic efficiency and oxidative stress-related parameters of the green alga Chlorella vulgaris. J Fish Environ 43(2):14–26
Ramírez ME, Vélez YH, Rendón L, Alzate E (2018) Potential of microalgae in the bioremediation of water with chloride content. Braz J Biol 78(03):472–476. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.169372
Rathnayake IVN, Megharaj M, Beer M, Naidu R (2021) Medium composition affects the heavy metal tolerance of microalgae: a comparison. J Appl Phycol 33(6):3683–3695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-021-02589-8
Raven JA (2017) Chloride: essential micronutrient and multifunctional beneficial ion. J Exp Bot 68(3):359–367. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw421
Sharma J, Kumar V, Kumar SS, Malyan SK, Mathimani T, Bishnoi NR, Pugazhendhi A (2020) Microalgal consortia for municipal wastewater treatment–lipid augmentation and fatty acid profiling for biodiesel production. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 202:111638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111638
Sheikha D, Ashour L, Al-Rub FA (2008) Biosorption of zinc on immobilized green algae: equilibrium and dynamics studies. J Eng Res 5(1):20–29
Spain O, Plöhn M, Funk C (2021) The cell wall of green microalgae and its role in heavy metal removal. Physiol Pl 173(2):526–535. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13405
Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J (2008) A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML web–servers. Syst Biol 75:758–771
Stankovic S, Kalaba P, Stankovic AR (2014) Biota as toxic metal indicators. Environ Chem Lett 12:63–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-013-0430-6
Stauber JL, Florence TM (1987) Mechanism of toxicity of ionic copper and copper complexes to algae. Mar Biol 94(4):511–519
Sun XM, Ren LJ, Zhao QY, Ji XJ, Huang H (2018) Microalgae for the production of lipid and carotenoids: a review with focus on stress regulation and adaptation. Biotechnol Biofuels 11:272. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-018-1275-9
Suratno S, Puspitasari R, Purbonegoro T, Mansur D (2015) Copper and cadmium toxicity to marine phytoplankton, Chaetoceros gracilis and Isochrysis sp. Indones J Chem 15(2):172–178. https://doi.org/10.22146/ijc.21211
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Mol Clinic Environ Toxicol 101:133–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6
Trzcińska M, Pawlik-Skowrońska B (2008) Soil algal communities inhabiting zinc and lead mine spoils. J Appl Phycol 20:341–348
Tsai KP (2016) Management of target algae by using copper-based algaecides: effects of algal cell density and sensitivity to copper. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2926-8
Viana SM, Rocha O (2005) The toxicity of copper sulphate and atrazine to the diatom Aulacoseira Granulata (Ehrenberg) simmons. Acta Limnol Bras 17:291–300
Violante A, Cozzolino V, Perelomov L, Caporale AG, Pigna M (2010) Mobility and bioavailability of heavy metals and metalloids in soil environments. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 10(3):268–292. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162010000100005
Wang H, Sathasivam R, Ki JS (2017) Physiological effects of copper on the freshwater alga Closterium ehrenbergii Meneghini (Conjugatophyceae) and its potential use in toxicity assessments. Algae 32:131–137. https://doi.org/10.4490/algae.2017.32.5.24
Wang H, Ebenezer V, Ki JS (2018) Photosynthetic and biochemical responses of the freshwater green algae Closterium ehrenbergii Meneghini (Conjugatophyceae) exposed to the metal coppers and its implication for toxicity testing. J Microbiol 56:426–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-018-8081-8
Yap CK, Ismail A, Omar H, Tan SG (2004) Toxicities and tolerances of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in a primary producer (Isochrysis galbana) and in a primary consumer (Perna viridis). Environ Int 29(8):1097–1104. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00141-7
Zada S, Raza S, Khan S, Iqbal A, Kai Z, Ahmad A, Ullah M, Kakar M, Fu P, Dong H, Xueji Z (2022) Microalgal and cyanobacterial strains used for the bio sorption of copper ions from soil and wastewater and their relative study. J Indust Eng Chem 105:463–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2021.10.003
Zaghloul A, Saber M, Gadow S, Awad F (2020) Biological indicators for pollution detection in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Bull Natl Res Cent 44:127. https://doi.org/10.1186/S42269-020-00385-X
Zamani-Ahmadmahmoodi R, Malekabadi MB, Rahimi R, Johari SA (2020) Aquatic pollution caused by mercury, lead, and cadmium affects cell growth and pigment content of marine microalga Nannochloropsis oculata. Environ Monit Assess 192:330. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10661-020-8222-5
Zimmermann J, Jahn R, Gemeinholzer B (2011) Barcoding diatoms: evaluation of the V4 subregion on the 18S rRNA gene, including new primers and protocols. Org Divers Evol 11:173–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13127-011-0050-6
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Funding
This publication is based on research carried out with financial support by Russian Science Foundation (project number 20-74-10076). Morphological descriptions of algal strains were maintained within the state assignment of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (theme No. 122042700045-3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.M contributed to conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, writing the original draft; S.M contributed to data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, visualization, writing original draft; M.K contributed to conceptualization, methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Rangabhashiyam.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Maltsev, Y., Maltseva, S. & Kulikovskiy, M. Toxic effect of copper on soil microalgae: experimental data and critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 10903–10920 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-04766-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-04766-3