Abstract
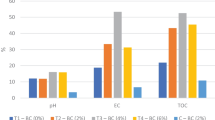
The influence of the recycling of washing agents on the removal efficiency of Cu and Zn from sewage sludge was investigated. In the recycling test, the washing agents (H3PO4, HNO3, H2SO4, citric and oxalic acids, Fenton-like reagent, and saponin) were recycled after each removal cycle and then stirred with unwashed sludge again for six cycles. When the washing agents were recycled, the Cu removal efficiency of all the washing agents, except HNO3 and saponin, was reduced. Similarly, the Zn removal efficiency of all washing agents was also diminished. The decrease in removal efficiency when recycling washing agents indicates that the capacity of the washing agents to remove Cu and Zn from the sludge was limited. During the recycling test, Cu and Zn concentrations in the sludge were compared to organic fertilizer standards in Korea and other countries. Even after recycling the washing agents six times, Cu and Zn concentrations were not only in accordance with criteria of Korea, but those other nations, depending on the washing agent. Therefore, depending on the washing agent, recycling the washing agent tested in this study six times is feasible, not only in Korea, but also in other countries. Only citric acid did not meet the minimum Korean fertilizer criteria for the sum of total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and K. This was because citric acid eliminated relatively more nutrients. This study can help determine whether the agents can be recycled to lower metal concentrations along with potential nutrient loss.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aljerf L (2018) High-efficiency extraction of bromocresol purple dye and heavy metals as chromium from industrial effluent by adsorption onto a modified surface of zeolite: Kinetics and equilibrium study. J Environ Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.07.048
Barraoui D, Blais JF, Labrecque M (2021) Cleanup of sewage sludge spiked with Cd, Cu, and Zn: Sludge quality and distribution of metals in the “soil-plant-water” system. Chemosphere 267:129223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129223
Chen WJ, Hsiao LC, Chen KKY (2008) Metal desorption from copper(II)/nickel(II)-spiked kaolin as a soil component using plant-derived saponin biosurfactant. Process Biochem 43:488–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROCBIO.2007.11.017
Geng H, Xu Y, Zheng L et al (2020) An overview of removing heavy metals from sewage sludge: Achievements and perspectives. Environ Pollut 266:115375
Gheju M, Pode R, Manea F (2011) Comparative heavy metal chemical extraction from anaerobically digested biosolids. Hydrometallurgy 108:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2011.03.006
Ghoreishi SM, Hedayati A, Ansari K (2016) Experimental investigation and optimization of supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of toxic heavy metals from solid waste using different modifiers and chelating agents. J Supercrit Fluids 117:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2016.06.012
Gong Q, Chen P, Shi R et al (2019) Health assessment of trace metal concentrations in organic fertilizer in Northern China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16061031
Hamdi H, Hechmi S, Khelil MN et al (2019) Repetitive land application of urban sewage sludge: Effect of amendment rates and soil texture on fertility and degradation parameters. CATENA 172:11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.08.015
Huang D, Hu C, Zeng G et al (2017) Combination of Fenton processes and biotreatment for wastewater treatment and soil remediation. Sci Total Environ 574:1599–1610
Kou Y, Zhao Q, Cheng Y et al (2020) Removal of heavy metals in sludge via joint EDTA-acid treatment: effects on seed germination. Sci Total Environ 707:135866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135866
Kuan YC, Lee IH, Chern JM (2010) Heavy metal extraction from PCB wastewater treatment sludge by sulfuric acid. J Hazard Mater 177:881–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.115
Liu H, Yang J, Shi Y et al (2012) Conditioning of sewage sludge by Fenton’s reagent combined with skeleton builders. Chemosphere 88:235–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.02.084
Liu Z, Li Z, Zhong H et al (2017) Recent advances in the environmental applications of biosurfactant saponins: A review. J Environ Chem Eng 5:6030–6038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.11.021
Lu Q, He ZL, Stoffella PJ (2012) Land application of Biosolids in the USA: a review. Appl Environ Soil Sci 2012:11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/201462
Ma D, Su M, Qian J, Wang Q, Meng F, Ge X, Ye Y, Song C (2020) Heavy metal removal from sewage sludge under citric acid and electroosmotic leaching processes. Sep Purif Technol 242:116822
Poulsen PHB, Al-Soud WA, Bergmark L et al (2013) Effects of fertilization with urban and agricultural organic wastes in a field trial-Prokaryotic diversity investigated by pyrosequencing. Soil Biol Biochem 57:784–793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.12.023
Pritchard DL, Penney N, McLaughlin MJ et al (2010) Land application of sewage sludge (biosolids) in Australia: Risks to the environment and food crops. Water Sci Technol 62:48–57
Roig N, Sierra J, Martí E et al (2012) Long-term amendment of Spanish soils with sewage sludge: effects on soil functioning. Agric Ecosyst Environ 158:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2012.05.016
Rumky J, Ncibi MC, Burgos-Castillo RC et al (2018) Optimization of integrated ultrasonic-Fenton system for metal removal and dewatering of anaerobically digested sludge by Box-Behnken design. Sci Total Environ 645:573–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.125
Shim M-J, Lee S-M (2021) Chemical removal of Cu and Zn from swine feces before soil application. Agriculture. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11050377
Shim MJ, Jung TY, Yoon DH et al (2020) HNO2 treatment of sludge: An alternative way of sludge usage as fertilizer. J Environ Manag 258:110016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.110016
Singh RP, Agrawal M (2008) Potential benefits and risks of land application of sewage sludge. Waste Manag 28:347–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2006.12.010
Stylianou MA, Kollia D, Haralambous KJ et al (2007) Effect of acid treatment on the removal of heavy metals from sewage sludge. Desalination 215:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2006.11.015
Suanon F, Sun Q, Dimon B et al (2016) Heavy metal removal from sludge with organic chelators: comparative study of N, N-bis(carboxymethyl) glutamic acid and citric acid. J Environ Manage 166:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.10.035
Sun TT, Liang XL, Zhu HY et al (2016) Rapid separation and identification of 31 major saponins in shizhu ginseng by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–electron spray ionization–MS/MS. J Ginseng Res 40:220–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2015.07.008
Tang J, He J, Liu T, Xin X (2017) Removal of heavy metals with sequential sludge washing techniques using saponin: optimization conditions, kinetics, removal effectiveness, binding intensity, mobility and mechanism. RSC Adv 7(53):33385–33401. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra04284a
Tang J, He J, Xin X et al (2018) Biosurfactants enhanced heavy metals removal from sludge in the electrokinetic treatment. Chem Eng J 334:2579–2592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.010
Tang J, He J, Qiu Z, Xin X (2019) Metal removal effectiveness, fractions, and binding intensity in the sludge during the multiple washing steps using the combined rhamnolipid and saponin. J Soils Sediment 19:1286–1296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2106-0
Uysal A, Celik E (2019) Removal of metals and recovery of released nutrients from municipal and industrial sludge using different biosurfactants. Desalin Water Treat 172:37–45. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.24917
Veeken AHM, Hamelers HVM (1999) Removal of heavy metals from sewage sludge by extraction with organic acids. Water Sci Technol 40:129–136. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.1999.0029
Wang X, Chen J, Yan X et al (2015) Heavy metal chemical extraction from industrial and municipal mixed sludge by ultrasound-assisted citric acid. J Ind Eng Chem 27:368–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.01.016
Wozniak DJ, Huang JYC (1982) Variables affecting metal removal from sludge. J Water Pollut Control Fed 54:1574–1580
Wu CH, Kuo CY, Lo SL (2004) Removal of metals from industrial sludge by extraction with different acids. J Environ Sci Heal-Part A Toxic/hazardous Subst Environ Eng 39:2205–2219. https://doi.org/10.1081/ESE-120039385
Wu Q, Cui Y, Li Q, Sun J (2015) Effective removal of heavy metals from industrial sludge with the aid of a biodegradable chelating ligand GLDA. J Hazard Mater 283:748–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.10.027
Xiao K, Pei K, Wang H et al (2018) Citric acid assisted Fenton-like process for enhanced dewaterability of waste activated sludge with in-situ generation of hydrogen peroxide. Water Res 140:232–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.04.051
Xu Y, Dai X (2020) Integrating multi-state and multi-phase treatment for anaerobic sludge digestion to enhance recovery of bio-energy. Sci Total Environ 698:134196
Xu Y, Lu Y, Dai X, Dong B (2017) The influence of organic-binding metals on the biogas conversion of sewage sludge. Water Res 126:329–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.09.046
Yang W, Song W, Li J, Zhang X (2020) Bioleaching of heavy metals from wastewater sludge with the aim of land application. Chemosphere 249:126134. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2020.126134
Yuan H, Zhu N, Song F (2011) Dewaterability characteristics of sludge conditioned with surfactants pretreatment by electrolysis. Bioresour Technol 102:2308–2315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.10.065
Zhu Y, Zeng G, Zhang P et al (2013) Feasibility of bioleaching combined with Fenton-like reaction to remove heavy metals from sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 142:530–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.05.070
Zingaretti D, Lombardi F, Baciocchi R (2018) Soluble organic substances extracted from compost as amendments for Fenton-like oxidation of contaminated sites. Sci Total Environ 619–620:1366–1374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.178
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2019R111A3A0106242412). I thank Ms. Yun Kyung Shim for improving the manuscript, and Ms. Hyun Joo Park for helping with the experiment. I also express my gratitude to professor Seung-Mok Lee for providing a place to experiment and some materials.
Funding
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2019R111A3A0106242412).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author has no relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shim, M.J. Recycling of washing agents for heavy metal removal from digested sewage sludge. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 11809–11820 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-04757-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-04757-4