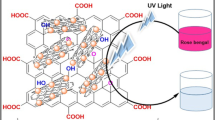
Abstract
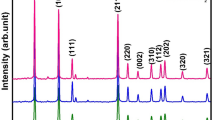
Water contamination engendered by pharmaceutical effluents and organic dyes is emerged as a serious environmental catastrophe, causing massive ecological repercussions as well as enduring risks to aquatic life and human health. Hence designing of highly efficient and robust photocatalyst with excellent intrinsic properties for the degradation of pollutants is desirable. In this research, a visible-light-responsive cerium manganese oxide (CeMnO3) perovskite nanomaterial was synthesized via facile citrate sol–gel approach to address the deterioration of tetracycline hydrochloride (TcH) antibiotic and methylene blue (MB) dye residues for the first time in aqueous media. The CeMnO3 nanostructure was characterized through XRD, XPS, FTIR, FESEM, EDS, PL, and UV–Vis spectrophotometer to disclose the catalytic functionalities, crystallographic structures, elemental interaction, structural configuration, surface morphology, and other intrinsic optical features of the material. The CeMnO3 catalyst exhibits eminent photocatalytic activity for the degradation of TcH and MB residues under visible light sources attributed to the narrow bandgap energy (2.50 eV) achieved in CeMnO3 perovskite nanomaterial. As-prepared catalysts achieved an optimum efficiency of about 89% and 95% for the photocatalytic degradation of TcH (10 mg/L) and MB (10 mg/L) for 30 mg and 25 mg catalyst dosage in 90 min, respectively. The radical scavenger test revealed that the hydroxyl radical \(\left( { \cdot {\text{OH}}} \right)\) and superoxide radicals \(\left( { \cdot {\text{O}}_{2}^{ - } } \right)\) are the chief reactive oxidizing agents in the photocatalytic degradation process. Furthermore, even after three subsequent cycles, the catalyst stays stable and demonstrates an excellent degradation efficiency, validating its potential cyclic capability and chemical stability. The current work proposes an intriguing strategy to fabricate a CeMnO3 catalyst with high-performance detoxification of TcH and MB residual compounds which are widely used and frequently reported for their contaminations in the ambient environment.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abinaya M, Govindan K, Kalpana M et al (2020) Reduction of hexavalent chromium and degradation of tetracycline using a novel indium-doped Mn2O3 nanorod photocatalyst. J Hazard Mater 397:122885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122885
Balta Z, Simsek EB (2022) Understanding the structural and photocatalytic effects of incorporation of hexagonal boron nitride whiskers into ferrite type perovskites (BiFeO3, MnFeO3) for effective removal of pharmaceuticals from real wastewater. J Alloys Compd 898:162897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162897
Bhagwan J, Sahoo A, Yadav KL, Sharma Y (2017) Nanofibers of spinel-CdMn2O4: a new and high performance material for supercapacitor and Li-ion batteries. J Alloys Compd 703:86–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.01.324
Cao J, Yang Z, Xiong W et al (2018) One-step synthesis of Co-doped UiO-66 nanoparticle with enhanced removal efficiency of tetracycline: Simultaneous adsorption and photocatalysis. Chem Eng J 353:126–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.060
Cao Z, Wang Q, Cheng H (2021) Recent advances in kaolinite-based material for photocatalysts. Chin Chem Lett 32:2617–2628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2021.01.009
Cheng C, Gao S, Zhu J et al (2020) Enhanced performance of LaFeO3 perovskite for peroxymonosulfate activation through strontium doping towards 2 4-D degradation. Chem Eng J 384:123377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123377
Chiam S-L, Pung S-Y, Yeoh F-Y (2020) Recent developments in MnO2-based photocatalysts for organic dye removal: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:5759–5778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07568-8
Deng J, Xu M, Qiu C et al (2018) Magnetic MnFe2O4 activated peroxymonosulfate processes for degradation of bisphenol a: performance, mechanism and application feasibility. Appl Surf Sci 459:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.07.198
Gao Y, Li Y, Zhang L et al (2012) Adsorption and removal of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solution by graphene oxide. J Colloid Interface Sci 368:540–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.11.015
Geetha GV, Sivakumar R, Sanjeeviraja C, Ganesh V (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye using ZnWO4 catalyst prepared by a simple co-precipitation technique. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 97:572–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05480-7
He Y, Huang Z, Ma Z et al (2019) Highly efficient photocatalytic performance and mechanism of α-ZnTcPc/g-C3N4 composites for methylene blue and tetracycline degradation under visible light irradiation. Appl Surf Sci 498:143834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143834
Hosakote Shankara A, Samuel Prabagar J, Tenzin T et al (2022) Facile synthesis of NdFeO3 perovskite for photocatalytic degradation of organic dye and antibiotic. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.10.230
Hu X, Ji Y, Wang M et al (2013) Water-soluble and biocompatible MnO@ PVP nanoparticles for MR imaging in vitro and in vivo. J Biomed Nanotechnol 9:976–984. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2013.1602
Hu Q, Yue B, Yang F et al (2019) Facile synthesis and electrochemical properties of perovskite-type CeMnO3 nanofibers. Chem Select 4: 11903–11912, Processing 64:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201903426
Hu X, Li Y, Wei X et al (2022) Preparation of double-layered Co- Ci/NiFeOOH co-catalyst for highly meliorated PEC performance in water splitting. Adv Powder Materials 1:100024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmate.2021.11.010
Jamali SS, Singh D, Tavakkoli H et al (2017) Microwave-assisted synthesis of nanostructured perovskite-type oxide with efficient photocatalytic activity against organic reactants in gaseous and aqueous phases. Mater Sci Semicond. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2017.03.012
Jeong J, Song W, Cooper WJ et al (2010) Degradation of tetracycline antibiotics: mechanisms and kinetic studies for advanced oxidation/reduction processes. Chemosphere 78:533–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.11.024
Jiang L, Yuan X, Zeng G et al (2018) Metal-free efficient photocatalyst for stable visible-light photocatalytic degradation of refractory pollutant. Appl Catal B 221:715–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.09.059
Jijoe Samuel P, Yadav S, Thinley T et al (2022) Visible light irradiation driven CO2 reduction into hydrocarbons on tri-metallic based layered double hydroxide. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.10.304
Kanhere P, Chen Z (2014) A review on visible light active perovskite-based photocatalysts. Molecules 19:19995–20022. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191219995
Kasinathan M, Thiripuranthagan S, Sivakumar A (2020) Fabrication of sphere-like Bi2MoO6/ZnO composite catalyst with strong photocatalytic behavior for the detoxification of harmful organic dyes. Opt Mater 109:110218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2020.110218
Koyuncu I, Arikan OA, Wiesner MR, Rice C (2008) Removal of hormones and antibiotics by nanofiltration membranes. J Membr Sci 309:94–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2007.10.010
Krittayavathananon A, Pettong T, Kidkhunthod P, Sawangphruk M (2017) Insight into the charge storage mechanism and capacity retention fading of MnCo2O4 used as supercapacitor electrodes. Electrochim Acta 258:1008–1015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.11.152
Kubiak A, Bielan Z, Kubacka M et al (2020) Microwave-assisted synthesis of a TiO2-CuO heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic activity against tetracycline. Appl Surf Sci 520:146344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146344
Kumar M, Jaiswal S, Sodhi KK et al (2019) Antibiotics bioremediation: perspectives on its ecotoxicity and resistance. Environ Int 124:448–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.12.065
Lan L, Kong X, Sun H et al (2019) High removal efficiency of antibiotic resistance genes in swine wastewater via nanofiltration and reverse osmosis processes. J Environ Manag 231:439–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.073
Liu W-X, Zhu X-L, Liu S-Q et al (2018) Near-infrared-driven selective photocatalytic removal of ammonia based on valence band recognition of an α-MnO2/N-doped graphene hybrid catalyst. ACS Omega 3:5537–5546. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b00161
Luo J, Li X, Ge C et al (2018) Sorption of norfloxacin, sulfamerazine and oxytetracycline by KOH-modified biochar under single and ternary systems. Biores Technol 263:385–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.05.022
Motlagh PY, Khataee A, Rad TS et al (2019) Fabrication of ZnFe-layered double hydroxides with graphene oxide for efficient visible light photocatalytic performance. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 101:186–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.04.051
Mukhtar F, Munawar T, Nadeem MS et al (2020) Multi metal oxide NiO-Fe2O3-CdO nanocomposite-synthesis, photocatalytic and antibacterial properties. Appl Phys A 126:1–14
Munawar T, Yasmeen S, Hussain F et al (2020) Synthesis of novel heterostructured ZnO-CdO-CuO nanocomposite: characterization and enhanced sunlight driven photocatalytic activity. Mater Chem Phys 249:122983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.122983
Nassar IM, Wu S, Li L, Li X (2018) Facile preparation of n-type LaFeO3 perovskite film for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting. ChemistrySelect 3:968–972. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201702997
Ravindra YS, Puttaiah SH, Yadav S, Prabagar JS (2020) Evaluation of polymeric g-C3N4 contained nonhierarchical ZnV2O6 composite for energy-efficient LED assisted photocatalytic mineralization of organic pollutant. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 31:16806–16818. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04235-4
Saeed M, Muneer M, Akram N et al (2019) Synthesis and characterization of silver loaded alumina and evaluation of its photocatalytic activity on photodegradation of methylene blue dye. Chem Eng Res Des 148:218–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2019.06.020
Salehi K, Shahmoradi B, Bahmani A et al (2016) Optimization of reactive black 5 degradation using hydrothermally synthesized NiO/TiO2 nanocomposite under natural sunlight irradiation. Desalin Water Treat 57:25256–25266. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1149890
Shah LR, Ali B, Zhu H et al (2009) Detailed study on the role of oxygen vacancies in structural, magnetic and transport behavior of magnetic insulator: Co-CeO2. J Phy Cond Matter 21:486004. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/21/48/486004
Soltani T, Entezari MH (2013a) Solar photocatalytic degradation of RB5 by ferrite bismuth nanoparticles synthesized via ultrasound. Ultrason Sonochem 20:1245–1253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2013.01.012
Soltani T, Entezari MH (2013b) Sono-synthesis of bismuth ferrite nanoparticles with high photocatalytic activity in degradation of Rhodamine B under solar light irradiation. Chem Eng J 223:145–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.02.124
Sousa JM, Macedo G, Pedrosa M et al (2017) Ozonation and UV254 nm radiation for the removal of microorganisms and antibiotic resistance genes from urban wastewater. J Hazard Mater 323:434–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.03.096
Suwannaruang T, Kidkhunthod P, Butburee T et al (2021) Facile synthesis of cooperative mesoporous-assembled CexSr1-xFexTi1-xO3 perovskite catalysts for enhancement beta-lactam antibiotic photodegradation under visible light irradiation. Surf Interfaces 23:101013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2021.101013
Tenzin T, Yashas SR, Anilkumar KM, Shivaraju HP (2021) UV–LED driven photodegradation of organic dye and antibiotic using strontium titanate nanostructures. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 32:21093–21105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06609-8
Thinley T, Yadav S, Samuel Prabagar J et al (2022) Facile synthesis of MnTiO3/Ag/gC3N4 nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline antibiotic and synthesis of ammonia. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.10.232
Vattikuti SVP, Reddy PAK, NagaJyothi PC et al (2018) Hydrothermally synthesized Na2Ti3O7 nanotube-V2O5 heterostructures with improved visible photocatalytic degradation and hydrogen evolution-Its photocorrosion suppression. J Alloy Compd 740:574–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.12.371
Wang S, Lin S, Zhang D et al (2017) Controlling charge transfer in quantum-size titania for photocatalytic applications. Appl Catal B 215:85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.05.043
Wang X, Jiang L, Li K et al (2020) Fabrication of novel Z-scheme SrTiO3/MnFe2O4 system with double-response activity for simultaneous microwave-induced and photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline and mechanism insight. Chem Eng J 400:125981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125981
Wang T, Dissanayake PD, Sun M et al (2021) Adsorption and visible-light photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants by functionalized biochar: role of iodine doping and reactive species. Environ Res 197:111026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111026
Wu J, Fang X, Zhu Y et al (2020a) Well-designed TiO2@ UiO-66-NH2 nanocomposite with superior photocatalytic activity for tetracycline under restricted space. Energy Fuels 34:12911–12917. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c02485
Wu S, Hu H, Lin Y et al (2020b) Visible light photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline over TiO2. Chem Eng J 382:122842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122842
Xie F, Wang J, Li Y et al (2019) One-step synthesis of hierarchical SnO2/TiO2 composite hollow microspheres as an efficient scattering layer for dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim Acta 296:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electracta.2018.10.194
Yadav S, Jijoe Samuel P, Thinley T et al (2022) Hybrid ZnFe2O4/Ag2S nanocomposite for enhanced photocatalytic and bacterial activity towards targeted superbugs. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.10.305
Yashas SR, Shivaraju HP, Thinley T et al (2020) Facile synthesis of SnO2 2D nanoflakes for ultrasound-assisted photodegradation of tetracycline hydrochloride. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:2593–2604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02636-w
Yashas SR, Shivaraju HP, McKay G et al (2021a) Designing bi-functional silver delafossite bridged graphene oxide interfaces: Insights into synthesis, characterization, photocatalysis and bactericidal efficiency. Chem Eng J 426:131729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131729
Yashas SR, Shivaraju HP, Pema G et al (2021b) Sonochemical synthesis of graphitic carbon nitride-manganese oxide interfaces for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:4778–4789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131729
Yi H, Xu J, Tang X et al (2018) Novel synthesis of Pd-CeMnO3 perovskite based on unique ultrasonic intervention from combination of Sol-Gel and impregnation method for low temperature efficient oxidation of benzene vapour. Ultrason Sonochem 48:418–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.06.009
Yi H, Miao L, Xu J et al (2021) Palladium particles supported on porous CeMnO3 perovskite for catalytic oxidation of benzene. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 623:126687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126687
Yuan X, Qu S, Huang X et al (2021) Design of core-shelled g-C3N4@ ZIF-8 photocatalyst with enhanced tetracycline adsorption for boosting photocatalytic degradation. Chem Eng J 416:129148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129148
Zhang S, Zhao Y, Diaz-Somoano M et al (2018) Synergistic mercury removal over the CeMnO3 perovskite structure oxide as a selective catalytic reduction catalyst from coal combustion flue gas. Energy Fuels 32:11785–11795. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b02518
Zhang D, Lv S, Luo Z (2020a) A study on the photocatalytic degradation performance of a [KNbO3] 0.9-[BaNi 0.5 Nb 0.5 O 3- δ] 0.1 perovskite. RSC Adv 10:1275–1280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129148
Zhang Q, Jiang L, Wang J et al (2020b) Photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline antibiotics using three-dimensional network structure perylene diimide supramolecular organic photocatalyst under visible-light irradiation. Appl Catalysis B Environ 277:119122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119122
Zhang Y, Zhou J, Chen J et al (2020c) Rapid degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride by heterogeneous photocatalysis coupling persulfate oxidation with MIL-53 (Fe) under visible light irradiation. J Hazard Mater 392:122315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122315
Zhang M, Sun W, Lv H, Zhang Z-H (2021a) Syntheses and applications of perovskite-based photocatalysts in light-driven organic reactions. Curr Opinion Green Sustain Chem 27:100390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2020.100390
Zhang W, Ma Y, Zhu X et al (2021b) Fabrication of Ag decorated g-C3N4/LaFeO3 Z-scheme heterojunction as highly efficient visible-light photocatalyst for degradation of methylene blue and tetracycline hydrochloride. J Alloys Compd 864:158914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.158914
Zhang L, Ma P, Dai L et al (2022) Removal of pollutants via synergy of adsorption and photocatalysis over MXene-based nanocomposites. Chem Eng J Adv 10:100285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceja.2022.100285
Zhu Z, Wan S, Lu Q et al (2022) A highly efficient perovskite oxides composite as a functional catalyst for tetracycline degradation. Separation Purification Technol 281:119893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119893
Acknowledgements
Hosakote Shankara Anusha: Investigation; Data curation; Methodology; Visualization; Writing—Original Draft. Jijoe Samuel P, Yadav Sneha, Thinley Tenzin, Wantala Kitirote; Kotermane Mallikarjunappa Anilkumar: Visualization; Review & Editing. Harikaranahalli Puttaiah Shivaraju: Conceptualization; Supervision; Writing—review & editing; Visualization.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Many ideas on the paper are suggested by LZ to support the work, LX contributed to model establishing and paper writing, PH analyzed the data, and MJ reviewed the work and modified the article. In general, all authors cooperated as much as possible during all the progress of the research.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any competing interests in the manuscript.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Anusha, H.S., Yadav, S., Tenzin, T. et al. Improved CeMnO3 perovskite framework for visible-light-aided degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride antibiotic residue and methylene blue dye. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 13519–13534 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04742-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04742-3