Abstract
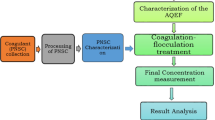
This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of plant-based coagulant extracted from Leucaena leucocephala seeds compared with alum in removing solids from aquaculture wastewater. Water-extraction method was used to extract the active ingredients from the seeds by dissolving the seeds’ powder in distilled water at 20 g/L concentration, whereas alum was dissolved directly at the same concentration. Operation parameters of jar test including dosage, rapid-mixing speed, and settling time were optimized for the water-extracted seed solution and alum to improve the removal efficiency. The optimum operation parameters for the water-extracted seed solution and alum were dosages of 240 and 320 mg/L respectively, rapid-mixing speed 150 rpm, and settling time 40 min. At the optimum operation parameters, water-extracted seed solution had removal efficiencies of 96.32%, 92.85%, and 86%, whereas alum had removal efficiencies of 99.77%, 99.92%, and 99.92% for turbidity, total suspended solids, and color, respectively. Despite the high efficiency of the water-extracted seed solution, dissolved contaminants such as NO3, PO4, COD, and true color increased owing to the presence of organic matter in the solution. With these results, L. leucocephala seeds had high potential to be used as alternative in removing solids from aquaculture wastewater. Further studies on the extraction of active ingredients should be conducted to increase the removal efficiency and avoid side effects on the contaminants dissolved in the effluent.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd Razak NH, Khairuddin N, Ismail KN, Musa M (2018) Coagulant from Leucaena leucocephala for chromium removal. In: IOP conference series: materials science and engineering. IOP Publishing, p 12025
Abidin ZZ, Ismail N, Yunus R et al (2011) A preliminary study on Jatropha curcas as coagulant in wastewater treatment. Environ Technol 32:971–977. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2010.521955
Abood MM, Nuraini N, Azhari B, Abdelmoneim AO (2017) The use of peanut and Sesame seeds as natural coagulant in the water treatment. Infrastruct Univ Kuala Lumpur Res J 5:1–10
Abu Bakar SNH, Abu Hasan H, Abdullah SRS et al (2021) A review of the production process of bacteria-based polymeric flocculants. J Water Process Eng 40:101915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.101915
Ahmad T, Ahmad K, Alam M (2016) Sustainable management of water treatment sludge through 3’R’ concept. J Clean Prod 124:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.02.073
Ahmad A, Abdullah SRS, Hasan HA et al (2021a) Plant-based versus metal-based coagulants in aquaculture wastewater treatment: effect of mass ratio and settling time. J Water Process Eng 43:102269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102269
Ahmad A, Kurniawan SB, Abdullah SRS et al (2021b) Exploring the extraction methods for plant-based coagulants and their future approaches. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151668
Ahmad A, Kurniawan SB, Abdullah SRS et al (2022a) Contaminants of emerging concern (CECs) in aquaculture effluent: insight into breeding and rearing activities, alarming impacts, regulations, performance of wastewater treatment unit and future approaches. Chemosphere 290:133319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133319
Ahmad A, Kurniawan SB, Ahmad J et al (2022b) Dosage-based application versus ratio-based approach for metal- and plant-based coagulants in wastewater treatment: merits, limitations, and applicability. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130245
Alnawajha MM, Abdullah SRS, Hasan HA et al (2022a) Effectiveness of using water-extracted Leucaena leucocephala seeds as a coagulant for turbid water treatment: effects of dosage, pH, mixing speed, mixing time, and settling time. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03233-2
Alnawajha MM, Kurniawan SB, Imron MF et al (2022b) Plant-based coagulants/flocculants: characteristics, mechanisms, and possible utilization in treating aquaculture effluent and benefiting from the recovered nutrients. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21631-x
Bhatti M, Kamboj A, Saluja AK (2013) Spectrophotometric estimation of total polysaccharides in Kalanchoe pinnatum and Kalanchoe crenata. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 5:40–41
BinAhmed S, Ayoub G, Al-Hindi M, Azizi F (2015) The effect of fast mixing conditions on the coagulation–flocculation process of highly turbid suspensions using liquid bittern coagulant. Desalin Water Treat 53:3388–3396. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.933043
Birima AH, Ahmed AT, Noor MJMM et al (2015) Application of salt extracted peanut seeds in the pretreatment of palm oil mill effluent (POME). Desalin Water Treat 55:2196–2200. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.930696
Choy SY, Prasad KMN, Wu TY, Ramanan RN (2015) A review on common vegetables and legumes as promising plant-based natural coagulants in water clarification. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:367–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0446-2
Daud NM, Sheikh Abdullah SR, Abu Hasan H (2018) Response surface methodological analysis for the optimization of acid-catalyzed transesterification biodiesel wastewater pre-treatment using coagulation–flocculation process. Process Saf Environ Prot 113:184–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.10.006
Ebeling JM, Sibrell PL, Ogden SR, Summerfelt ST (2003) Evaluation of chemical coagulation-flocculation aids for the removal of suspended solids and phosphorus from intensive recirculating aquaculture effluent discharge. Aquac Eng 29:23–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8609(03)00029-3
Ebeling JM, Ogden SR, Sibrell PL, Rishel KL (2004) Application of chemical coagulation aids for the removal of suspended solids (TSS) and phosphorus from the microscreen effluent discharge of an intensive recirculating aquaculture system. N Am J Aquac 66:198–207. https://doi.org/10.1577/a03-056.1
Ermukdakul T, Chawaloesphonsiya N, Boonchayaanant B et al (2013) Different approaches for the separation of suspended solids in aquaculture system. J Water Environ Technol 11:59–70. https://doi.org/10.2965/jwet.2013.59
Ernest E, Onyeka O, David N, Blessing O (2017) Effects of pH, dosage, temperature and mixing speed on the efficiency of water melon seed in removing the turbidity and colour of Atabong River, Awka-Ibom State, Nigeria. Int J Adv Eng Manag Sci 3:239833
Ezziddine M, Liltved H, Homme JM (2020) A method for reclaiming nutrients from aquacultural waste for use in soilless growth systems. Water Sci Technol 81:81–90. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.079
Falahi ALOA, Abdullah SRS, Hasan HA et al (2022) Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in domestic wastewater, available treatment technologies, and potential treatment using constructed wetland: a review. Process Saf Environ Prot 168:1067–1088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.10.082
Gao F, Li C, Yang Z-HH et al (2016) Continuous microalgae cultivation in aquaculture wastewater by a membrane photobioreactor for biomass production and nutrients removal. Ecol Eng 92:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.03.046
Ghernaout D, Ghernaout B (2012) Sweep flocculation as a second form of charge neutralisation—a review. Desalin Water Treat 44:15–28
Guldhe A, Ansari FA, Singh P, Bux F (2017) Heterotrophic cultivation of microalgae using aquaculture wastewater: a biorefinery concept for biomass production and nutrient remediation. Ecol Eng 99:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.11.013
Hamid SHA, Lananan F, Din WNS et al (2014) Harvesting microalgae, Chlorella sp. by bio-flocculation of Moringa oleifera seed derivatives from aquaculture wastewater phytoremediation. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 95:270–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.06.021
Hasan HA, Ezril Hafiz R, Muhamad MH et al (2020) Bioflocculant production using palm oil mill and sago mill effluent as a fermentation feedstock: characterization and mechanism of flocculation. J Environ Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.110046
Heiderscheidt E, Tesfamariam A, Pulkkinen J et al (2020) Solids management in freshwater-recirculating aquaculture systems: effectivity of inorganic and organic coagulants and the impact of operating parameters. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140398
Igwegbe CA, Onukwuli OD (2019) Removal of total dissolved solids (TDS) from aquaculture wastewater by coagulation-flocculation process using Sesamum indicum extract: effect of operating parameters and coagulation-flocculation kinetics. Pharm Chem J 6:32–45
Kadir AA, Abdullah SRS, Othman BA et al (2020) Dual function of Lemna minor and Azolla pinnata as phytoremediator for palm oil mill effluent and as feedstock. Chemosphere 259:127468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127468
Kristanda J, Sintiago KS, Kristianto H et al (2021) Optimization study of Leucaena leucocephala seed extract as natural coagulant on decolorization of aqueous congo red solutions. Arab J Sci Eng 46:6275–6286
Kristianto H, Paulina S, Muliarahayu Soetedjo JN (2018) Exploration of various indonesian indigenous plants as natural coagulants for synthetic turbid water. Int J Technol 9:464–471. https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v9i3.279
Kristianto H, Rahman H, Prasetyo S, Sugih AK (2019) Removal of congo red aqueous solution using Leucaena leucocephala seed’s extract as natural coagulant. Appl Water Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0972-2
Kumar V, Othman N, Asharuddin S (2017) Applications of natural coagulants to treat wastewater− a review. In: MATEC web of conferences. EDP Sciences, p 6016
Kurniawan SB, Abdullah SRS, Imron MF et al (2020) Challenges and opportunities of biocoagulant/bioflocculant application for drinking water and wastewater treatment and its potential for sludge recovery. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:1–33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249312
Kurniawan SB, Abdullah SRS, Imron MF et al (2021a) Potential of valuable materials recovery from aquaculture wastewater: an introduction to resource reclamation. Aquac Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.15180
Kurniawan SB, Abdullah SRS, Othman AR et al (2021b) Isolation and characterisation of bioflocculant-producing bacteria from aquaculture effluent and its performance in treating high turbid water. J Water Process Eng 42:102194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102194
Kurniawan SB, Ahmad A, Rahim NFM et al (2021c) Aquaculture in Malaysia: water-related environmental challenges and opportunities for cleaner production. Environ Technol Innov 24:101913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101913
Kurniawan SB, Ahmad A, Imron MF et al (2022a) Potential of microalgae cultivation using nutrient-rich wastewater and harvesting performance by biocoagulants/bioflocculants: mechanism, multi-conversion of biomass into valuable products, and future challenges. J Clean Prod 365:132806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132806
Kurniawan SB, Imron MF, Abdullah SRS et al (2022b) Treatment of real aquaculture effluent using bacteria-based bioflocculant produced by Serratia marcescens. J Water Process Eng 47:102708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102708
Kurniawan SB, Imron MF, Chik CENCE et al (2022c) What compound inside biocoagulants/bioflocculants is contributing the most to the coagulation and flocculation processes? Sci Total Environ 806:150902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150902
Kurniawan SB, Imron MF, Sługocki Ł et al (2022d) Assessing the effect of multiple variables on the production of bioflocculant by Serratia marcescens: flocculating activity, kinetics, toxicity, and flocculation mechanism. Sci Total Environ 836:155564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155564
Liu Z, Wei H, Li A, Yang H (2019) Enhanced coagulation of low-turbidity micro-polluted surface water: properties and optimization. J Environ Manag 233:739–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.08.101
Luo Y, Gao B, Yue Q, Li R (2018) Application of enteromorpha polysaccharides as coagulant aid in the simultaneous removal of CuO nanoparticles and Cu2+: effect of humic acid concentration. Chemosphere 204:492–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.168
Madrona GS, Branco IG, Seolin VJ et al (2012) Evaluation of extracts of Moringa oleifera Lam seeds obtained with NaCl and their effects on water treatment. Acta Sci Technol 34:289–293
Maurya S, Daverey A (2018) Evaluation of plant-based natural coagulants for municipal wastewater treatment. 3 Biotech 8:77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1103-8
Miller SM, Fugate EJ, Craver VO et al (2008) Toward understanding the efficacy and mechanism of Opuntia spp. as a natural coagulant for potential application in water treatment. Environ Sci Technol 42:4274–4279. https://doi.org/10.1021/es7025054
Mohd Radzuan R, Radin Mohamed RMS, Al-Gheethi AA, Mohd Kassim AH (2017) Application of natural coagulants for wastewater treatment. Integrated Water Resources Protection (ISBN 78-967-764-99-3)
Mohd-Salleh SNA, Mohd-Zin NS, Othman N (2019) A review of wastewater treatment using natural material and its potential as aid and composite coagulant. Sains Malays 48:155–164
Mook WT, Chakrabarti MH, Aroua MK et al (2012) Removal of total ammonia nitrogen (TAN), nitrate and total organic carbon (TOC) from aquaculture wastewater using electrochemical technology: a review. Desalination 285:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.09.029
Nasir NM, Mohd Yunos FH, Wan Jusoh HH et al (2019) Advances in water and wastewater treatment harvesting of Chlorella sp microalgae using Aspergillus niger as bio-flocculant for aquaculture wastewater treatment. J Environ Manag 249:109373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109373
Omitoyin BO, Ajani EK, Okeleye OI et al (2017) Biological treatments of fish farm effluent and its reuse in the culture of nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J Aquac Res Dev. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9546.1000469
Ottinger M, Clauss K, Kuenzer C (2016) Aquaculture: relevance, distribution, impacts and spatial assessments–a review. Ocean Coast Manag 119:244–266
Sa’id S, Mohammed K, Adie DB, Okuofu CA (2016) Turbidity removal from surface water using Tamarindus indica crude pulp extract. Bayero J Pure Appl Sci 9:236–240
Saritha V, Srinivas N, Srikanth Vuppala NV (2017) Analysis and optimization of coagulation and flocculation process. Appl Water Sci 7:451–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0262-y
Tzoupanos ND, Zouboulis AI (2008) Coagulation-flocculation processes in water / wastewater treatment : the application of new generation of chemical reagents. In: 6th IASME/WSEAS international conference on heat transfer, thermal engineering and environment, pp 309–317
Wei H, Gao B, Ren J et al (2018) Coagulation/flocculation in dewatering of sludge: a review. Water Res 143:608–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.07.029
Wuang SC, Khin MC, Chua PQD, Luo YD (2016) Use of Spirulina biomass produced from treatment of aquaculture wastewater as agricultural fertilizers. Algal Res 15:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.02.009
Yin CY (2010) Emerging usage of plant-based coagulants for water and wastewater treatment. Process Biochem 45(9):1437–1444
Zhang X, Hu J, Spanjers H, Van Lier JB (2014) Performance of inorganic coagulants in treatment of backwash waters from a brackish aquaculture recirculation system and digestibility of salty sludge. Aquac Eng 61:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaeng.2014.05.005
Zhao YQ, Babatunde AO, Hu YS et al (2011) Pilot field-scale demonstration of a novel alum sludge-based constructed wetland system for enhanced wastewater treatment. Process Biochem 46:278–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2010.08.023
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Long Term Research Grant Scheme (LRGS/1/2018/USM/01/1/1) (LRGS/2018/USM-UKM/EWS/01) granted by Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia for funding this research project.
Funding
Long Term Research Grant Scheme (LRGS/1/2018/USM/01/1/1) (LRGS/2018/USM-UKM/EWS/01) granted by Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MMA: Investigation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, Visualization, SBK: Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review and Editing, Data Curation, Visualization, SRSA: Supervision, Funding Acquisition, Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Writing—Review and Editing, HAH: Supervision, Funding Acquisition, Visualization, ARO: Supervision, Funding Acquisition, Visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies involving human or animal subjects.
Availability of data and materials
Upon request.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Lifeng Yin.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alnawajha, M.M., Kurniawan, S.B., Abdullah, S.R.S. et al. Performance of water-extracted Leucaena leucocephala seeds as coagulant and alum in treating aquaculture effluent: effect of dosage, rapid mixing speed, and settling time. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 9981–9994 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04682-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04682-y