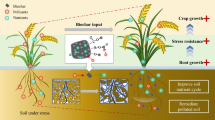
Abstract
Accumulation of Cd in the soil is a worldwide issue intimidating agricultural productivity and human health. Therefore, developing low-cost, environmentally sound, and readily available technologies is required to restore Cd-polluted agricultural soils and assure food safety. In the present field study, changes in rhizosphere soil biochemical property and Cd content of rice grains with biochar and oyster shell treatment were evaluated in two rice cultivars with contrasting Cd-accumulation potential (high = HA and low = LA). The results revealed that applied biochar and oyster shells effectively immobilized Cd. The amount of Cd extractable by DTPA and CaCl2 was reduced by 34–46% and 11–28%, respectively. Moreover, rhizosphere soil biochemical properties, including pH, MBC, and enzyme activity, were enhanced by the remarkable increases in soil pH after treatment (5.6–7.3). Applied biochar and oyster shell significantly reduced Cd uptake and accumulation in rice cultivars; a more significant reduction was observed in LA rice type with oyster shell treatment. Grain Cd concentration was reduced considerably with oyster shells in both HA (by 58%) and LA (by 70%), meeting the permissible Cd limits in rice grains. Furthermore, the reduced Cd availability and improved soil biochemical properties resulted in improved rice crop productivity. This study indicates that integrating readily available and low-cost oyster shell material with low Cd-accumulation rice cultivars could effectively reduce the transfer of soil Cd to the grain and alleviate the associated human health risks.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Abbas T, Rizwan M, Ali S, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Qayyum MF, Abbas F, Hannan F, Rinklebe J, Ok YS (2017) Effect of biochar on cadmium bioavailability and uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 140:37–47
Abd El-Azeem SAM, Ahmad M, Usman ARA, Kim K-R, Oh S-E, Lee SS, Ok YS (2013) Changes of biochemical properties and heavy metal bioavailability in soil treated with natural liming materials. Environ Earth Sci 70:3411–3420
Abollino O, Giacomino A, Malandrino M, Mentasti E (2008) Interaction of metal ions with montmorillonite and vermiculite. Appl Clay Sci 38:227–236
Ahmad M, Hashimoto Y, Moon DH, Lee SS, Ok YS (2012) Immobilization of lead in a Korean military shooting range soil using eggshell waste: An integrated mechanistic approach. J Hazard Mater 209–210:392–401
Ahn BK, Lee JH, Lee YH (2010) Impacts of oyster shell and peat treatments on soil properties in continuous watermelon cropping greenhouse plots. Korean J Soil Sci Fert 43:438–445
Alidoust D, Kawahigashi M, Yoshizawa S, Sumida H, Watanabe M (2015) Mechanism of cadmium biosorption from aqueous solutions using calcined oyster shells. J Environ Manage 150:103–110
Allison SD, Chacon SS, German DP (2014) Substrate concentration constraints on microbial decomposition. Soil Biol Biochem 79:43–49
Bhaduri D, Saha A, Desai D, Meena H (2016) Restoration of carbon and microbial activity in salt-induced soil by application of peanut shell biochar during short-term incubation study. Chemosphere 148:86–98
Bian J, Peng X-G, Wang Y, Zhang H (2016) An efficient cost-sensitive feature selection using chaos genetic algorithm for class imbalance problem. Math Probl Eng 2016:9
Bolan N, Kunhikrishnan A, Thangarajan R, Kumpiene J, Park J, Makino T, Kirkham MB, Scheckel K (2014) Remediation of heavy metal (loid) s contaminated soils–to mobilize or to immobilize? J Hazard Mater 266:141–166
Chan K, Van Zwieten L, Meszaros I, Downie A, Joseph S (2008) Using poultry litter biochars as soil amendments. Soil Res 46:437–444
Chen B, Zhou D, Zhu L (2008) Transitional adsorption and partition of nonpolar and polar aromatic contaminants by biochars of pine needles with different pyrolytic temperatures. Sci Total Environ 42:5137–5143
Chen H, Yang X, Wang P, Wang Z, Li M, Zhao F-J (2018a) Dietary cadmium intake from rice and vegetables and potential health risk: a case study in Xiangtan, southern China. Sci Total Environ 639:271–277
Chen M, Xu P, Zeng G, Yang C, Huang D, Zhang J (2015) Bioremediation of soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, petroleum, pesticides, chlorophenols and heavy metals by composting: applications, microbes and future research needs. Biotechnol Adv 33:745–755
Chen Y, Xu J, Lv Z, Xie R, Huang L, Jiang J (2018b) Impacts of biochar and oyster shells waste on the immobilization of arsenic in highly contaminated soils. J Environ Manage 217:646–653
Cheng C-H, Lehmann J, Engelhard MH (2008) Natural oxidation of black carbon in soils: changes in molecular form and surface charge along a climosequence. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:1598–1610
Chintala R, Schumacher TE, Kumar S, Malo DD, Rice JA, Bleakley B, Chilom G, Clay DE, Julson JL, Papiernik SK, Gu ZR (2014) Molecular characterization of biochars and their influence on microbiological properties of soil. J Hazard Mater 279:244–256
Chunhabundit R (2016) Cadmium exposure and potential health risk from foods in contaminated area, Thailand. Toxicol Res 32:65–72
Clemens S, Ma JF (2016) Toxic heavy metal and metalloid accumulation in crop plants and foods. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67:489–512
Counter SA, Buchanan LH, Ortega F (2009) Neurophysiologic and neurocognitive case profiles of Andean patients with chronic environmental lead poisoning. J Toxicol Environ Health-Part A 72:1150–1159
Cruz-Paredes C, López-García Á, Rubæk GH, Hovmand MF, Sørensen P, Kjøller R (2017) Risk assessment of replacing conventional P fertilizers with biomass ash: Residual effects on plant yield, nutrition, cadmium accumulation and mycorrhizal status. Sci Total Environ 575:1168–1176
Dick WA, Cheng L, Wang P (2000) Soil acid and alkaline phosphatase activity as pH adjustment indicators. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1915–1919
El-Naggar AH, Usman ARA, Al-Omran A, Ok YS, Ahmad M, Al-Wabel MI (2015) Carbon mineralization and nutrient availability in calcareous sandy soils amended with woody waste biochar. Chemosphere 138:67–73
FAO (2012) ProdStat. Core production data base, Electronic resource under. http://faostat.fao.org/. Accessed 30 Jun 2015
Gallego SM, Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Iannone MF, Rosales EP, Zawoznik MS, Groppa MD, Benavides MP (2012) Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: Insight into regulatory mechanisms. Environ Exp Bot 83:33–46
Garrido F, Illera V, Garcia-Gonzalez M (2005) Effect of the addition of gypsum-and lime-rich industrial by-products on Cd, Cu and Pb availability and leachability in metal-spiked acid soils. Appl Geochem 20:397–408
Ghosh A, Kumar S, Manna MC, Singh AK, Sharma P, Sarkar A, Saha M, Bhattacharyya R, Misra S, Biswas SS, Biswas DR, Gautam K, Kumar RV (2019) Long-term in situ moisture conservation in horti-pasture system improves biological health of degraded land. J Environ Manage 248:109339
Gill RA, Zang L, Ali B, Farooq MA, Cui P, Yang S, Ali S, Zhou W (2015) Chromium-induced physio-chemical and ultrastructural changes in four cultivars of Brassica napus L. Chemosphere 120:154–164
Guan S, Zhang D, Zhang Z (1986) Soil enzyme and its research methods. Agricultural, Beijing 1986:274–297
Gul S, Whalen JK, Thomas BW, Sachdeva V, Deng H (2015) Physico-chemical properties and microbial responses in biochar-amended soils: mechanisms and future directions. Agr Ecosyst Environ 206:46–59
Hamid Y, Tang L, Hussain B, Usman M, Gurajala HK, Rashid MS, He Z, Yang X (2020) Efficiency of lime, biochar, Fe containing biochar and composite amendments for Cd and Pb immobilization in a co-contaminated alluvial soil. Environ Pollut 257:113609
Hamid Y, Tang L, Wang X, Hussain B, Yaseen M, Aziz MZ, Yang X (2018) Immobilization of cadmium and lead in contaminated paddy field using inorganic and organic additives. Sci Rep 8:17839
Hamid Y, Tang L, Yaseen M, Hussain B, Zehra A, Aziz MZ, Yang X (2019) Comparative efficacy of organic and inorganic amendments for cadmium and lead immobilization in contaminated soil under rice-wheat cropping system. Chemosphere 214:259–268
Huang L-M, Yu G-W, Zou F-Z, Long X-X, Wu Q-T (2018) Shift of soil bacterial community and decrease of metals bioavailability after immobilization of a multi-metal contaminated acidic soil by inorganic-organic mixed amendments: a field study. Appl Soil Ecol 130:104–119
Hwidi R, TengkuIzhar TN, MohdSaad F (2018) Characterization of limestone as raw material to hydrated lime. E3S Web Confer 34:02042
Igalavithana AD, Ok YS, Niazi NK, Rizwan M, Al-Wabel MI, Usman AR, Moon DH, Lee SS (2017) Effect of corn residue biochar on the hydraulic properties of sandy loam soil. Sustainability 9:266
Janoš P, Vávrová J, Herzogová L, Pilařová V (2010) Effects of inorganic and organic amendments on the mobility (leachability) of heavy metals in contaminated soil: a sequential extraction study. Geoderma 159:335–341
Järup L, Åkesson A (2009) Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238:201–208
Jia Z, Deng J, Chen N, Shi W, Tang X, Xu H (2017) Bioremediation of cadmium-dichlorophen co-contaminated soil by spent Lentinus edodes substrate and its effects on microbial activity and biochemical properties of soil. J Soils Sediments 17:315–325
Jien S-H, Wang C-S (2013) Effects of biochar on soil properties and erosion potential in a highly weathered soil. CATENA 110:225–233
Khadem A, Raiesi F (2017) Influence of biochar on potential enzyme activities in two calcareous soils of contrasting texture. Geoderma 308:149–158
Kimetu JM, Lehmann J (2010) Stability and stabilisation of biochar and green manure in soil with different organic carbon contents. Soil Res 48:577–585
Kolb SE, Fermanich KJ, Dornbush ME (2009) Effect of charcoal quantity on microbial biomass and activity in temperate soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 73:1173–1181
Laird DA, Fleming P, Davis DD, Horton R, Wang B, Karlen DL (2010) Impact of biochar amendments on the quality of a typical Midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma 158:443–449
Lee CH, Lee D, Ali MA, Kim PJ (2008a) Effects of oyster shell on soil chemical and biological properties and cabbage productivity as a liming materials. Waste Manage 28:2702–2708
Lee HH, Kim SY, Owens VN, Park S, Kim J, Hong CO (2018) How does oyster shell immobilize cadmium? Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 74:114–120
Lee J-Y, Hong C-O, Lee C-H, Lee D-K, Kim P (2005) Dynamics of heavy metals in soil amended with oyster shell meal. Korean J Environ Agric 24:358–363
Li J, Xu Y (2015) Immobilization of Cd in paddy soil using moisture management and amendment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:5580–5586
Li N, Zare E, Huang J, Triantafilis J (2018) Mapping soil cation-exchange capacity using bayesian modeling and proximal sensors at the field scale. Soil Sci Soc Am J 82:1203–1216
Li S, Sun X, Liu Y, Li S, Zhou W, Ma Q, Zhang J (2020) Remediation of Cd-contaminated soils by GWC application, evaluated in terms of Cd immobilization, enzyme activities, and pakchoi cabbage uptake. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:9979–9986
Li Y, Tang H, Hu Y, Wang X, Ai X, Tang L, Matthew C, Cavanagh J, Qiu J (2016) Enrofloxacin at environmentally relevant concentrations enhances uptake and toxicity of cadmium in the earthworm Eisenia fetida in farm soils. J Hazard Mater 308:312–320
Liang J, Yang Z, Tang L, Zeng G, Yu M, Li X, Wu H, Qian Y, Li X, Luo Y (2017) Changes in heavy metal mobility and availability from contaminated wetland soil remediated with combined biochar-compost. Chemosphere 181:281–288
Lim JE, Ahmad M, Lee SS, Shope CL, Hashimoto Y, Kim K-R, Usman ARA, Yang JE, Ok YS (2013a) Effects of lime-based waste materials on immobilization and phytoavailability of cadmium and lead in contaminated soil. Clean—Soil Air, Water 41:1235–1241
Lim JE, Ahmad M, Lee SS, Shope CL, Hashimoto Y, Kim KR, Usman AR, Yang JE, Ok YS (2013b) Effects of lime-based waste materials on immobilization and phytoavailability of cadmium and lead in contaminated soil. Clean-Soil, Air, Water 41:1235–1241
Liu H, Xu F, Xie Y, Wang C, Zhang A, Li L, Xu H (2018) Effect of modified cocount shell biochar on availability of heavy metals and biochemical characteristics of soil in multiple heavy metals contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 645:702–709
Lu K, Yang X, Gielen G, Bolan N, Ok YS, Niazi NK, Xu S, Yuan G, Chen X, Zhang X, Liu D, Song Z, Liu X, Wang H (2017) Effect of bamboo and rice straw biochars on the mobility and redistribution of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in contaminated soil. J Environ Manage 186:285–292
Luo Y, Durenkamp M, De Nobili M, Lin Q, Brookes P (2011) Short term soil priming effects and the mineralisation of biochar following its incorporation to soils of different pH. Soil Biol Biochem 43:2304–2314
Mohamed I, Ahamadou B, Li M, Gong C, Cai P, Liang W, Huang Q (2010) Fractionation of copper and cadmium and their binding with soil organic matter in a contaminated soil amended with organic materials. J Soils Sediments 10:973–982
Moon DH, Cheong KH, Koutsospyros A, Chang Y-Y, Hyun S, Ok YS, Park J-H (2016) Assessment of waste oyster shells and coal mine drainage sludge for the stabilization of As-, Pb-, and Cu-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:2362–2370
Mounia B, Merzoug B, Chaouki B, Djaouza AA (2013) Physico-chemical characterization of limestones and sandstones in a complex geological context, examplenorth-east constantine: preliminary results. Int J Eng Technol 5:114
Mukherjee A, Lal R, Zimmerman A (2014) Effects of biochar and other amendments on the physical properties and greenhouse gas emissions of an artificially degraded soil. Sci Total Environ 487:26–36
Ok YS, Lim JE, Moon DH (2011) Stabilization of Pb and Cd contaminated soils and soil quality improvements using waste oyster shells. Environ Geochem Health 33:83–91
Ouyang L, Tang Q, Yu L, Zhang R (2014) Effects of amendment of different biochars on soil enzyme activities related to carbon mineralisation. Soil Res 52:706–716
Paranavithana G, Kawamoto K, Inoue Y, Saito T, Vithanage M, Kalpage C, Herath G (2016) Adsorption of Cd2+ and Pb2+ onto coconut shell biochar and biochar-mixed soil. Environ Earth Sci 75:1–12
Paul ALD, Chaney RL (2017) Effect of soil amendments on Cd accumulation by Spinach from a Cd-mineralized soil. J Environ Qual 46:707–713
Qu C, Shi W, Guo J, Fang B, Wang S, Giesy JP, Holm PE (2016) China’s soil pollution control: choices and challenges. Environ Sci Technol 50:13181–13183
Rehman MZU, Khalid H, Akmal F, Ali S, Rizwan M, Qayyum MF, Iqbal M, Khalid MU, Azhar M (2017) Effect of limestone, lignite and biochar applied alone and combined on cadmium uptake in wheat and rice under rotation in an effluent irrigated field. Environ Pollut 227:560–568
Rizwan M, Ali S, Abbas T, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Hannan F, Keller C, Al-Wabel MI, Ok YS (2016a) Cadmium minimization in wheat: a critical review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 130:43–53
Rizwan M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Ibrahim M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Abbas T, Ok YS (2016b) Mechanisms of biochar-mediated alleviation of toxicity of trace elements in plants: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:2230–2248
Rizwan M, Meunier J-D, Miche H, Keller C (2012) Effect of silicon on reducing cadmium toxicity in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio W.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. J Hazard Mater 209–210:326–334
Sitarz-Palczak E, Kalembkiewicz J (2012) Study of remediation of soil contamined with heavy metals by coal fly ash. J Environ Protect 3(10):11
Tefera W, Liu T, Lu L, Ge J, Webb SM, Seifu W, Tian S (2020) Micro-XRF mapping and quantitative assessment of Cd in rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 193:110245
Uchimiya M, Lima IM, Klasson KT, Wartelle LH (2010) Contaminant immobilization and nutrient release by biochar soil amendment: Roles of natural organic matter. Chemosphere 80:935–940
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) Microbial biomass measurements in forest soils: the use of the chloroform fumigation-incubation method in strongly acid soils. Soil Biol Biochem 19:697–702
Wang C, Alidoust D, Isoda A, Li M (2017) Suppressive effects of thermal-treated oyster shells on cadmium and copper translocation in maize plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:19347–19356
Wang F, Zhang W, Miao L, Ji T, Wang Y, Zhang H, Ding Y, Zhu W (2021) The effects of vermicompost and shell powder addition on Cd bioavailability, enzyme activity and bacterial community in Cd-contaminated soil: a field study. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 215:112163
Wang M, Liu R, Lu X, Zhu Z, Wang H, Jiang L, Liu J, Wu Z (2018) Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk assessment of swine manure irrigated vegetable soils in Jiangxi Province, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 100:634–640
Wang R, Wei S, Jia P, Liu T, Hou D, Xie R, Lin Z, Ge J, Qiao Y, Chang X, Lu L, Tian S (2019) Biochar significantly alters rhizobacterial communities and reduces Cd concentration in rice grains grown on Cd-contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 676:627–638
Woldetsadik D, Drechsel P, Keraita B, Marschner B, Itanna F, Gebrekidan H (2016) Effects of biochar and alkaline amendments on cadmium immobilization, selected nutrient and cadmium concentrations of lettuce (Lactuca sativa) in two contrasting soils. Springerplus 5:397
Yang J, Yang F, Yang Y, Xing G, Deng C, Shen Y, Luo L, Li B, Yuan H (2016) A proposal of “core enzyme” bioindicator in long-term Pb-Zn ore pollution areas based on topsoil property analysis. Environ Pollut 213:760–769
Yang W-T, Zhou H, Gu J-F, Liao B-H, Peng P-Q, Zeng Q-R (2017) Effects of a combined amendment on Pb, Cd, and as availability and accumulation in rice planted in contaminated paddy soil. Soil Sediment Contam: Int J 26:70–83
Yousaf B, Liu G, Wang R, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Rizwan MS, Imtiaz M, Murtaza G, Shakoor A (2016) Investigating the potential influence of biochar and traditional organic amendments on the bioavailability and transfer of Cd in the soil–plant system. Environ Earth Sci 75:374
Yuan JH, Xu RK, Zhang H (2011) The forms of alkalis in the biochar produced from crop residues at different temperature. Bioresour Technol 102:3488–3497
Zheng J, Chen J, Pan G, Liu X, Zhang X, Li L, Bian R, Cheng K, Jinwei Z (2016) Biochar decreased microbial metabolic quotient and shifted community composition four years after a single incorporation in a slightly acid rice paddy from southwest China. Sci Total Environ 571:206–217
Zheng X, Zou M, Zhang B, Lai W, Zeng X, Chen S, Wang M, Yi X, Tao X, Lu G (2022) Remediation of Cd-, Pb-, Cu-, and Zn-contaminated soil using cow bone meal and oyster shell meal. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 229:113073
Zhou H, Zhou X, Zeng M, Liao B-H, Liu L, Yang W-T, Wu Y-M, Qiu Q-Y, Wang Y-J (2014) Effects of combined amendments on heavy metal accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) planted on contaminated paddy soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 101:226–232
Zhu H, Chen C, Xu C, Zhu Q, Huang D (2016a) Effects of soil acidification and liming on the phytoavailability of cadmium in paddy soils of central subtropical China. Environ Pollut 219:99–106
Zhu P, Liang X-X, Wang P, Wang J, Gao Y-H, Hu S-G, Huang Q, Huang R, Jiang Q, Wu S-X, Li Z-X, Ling H-T, Ying-hua X, Wu Y-N, Zou F, Yang X-F (2016b) Assessment of dietary cadmium exposure: a cross-sectional study in rural areas of south China. Food Control 62:284–290
Funding
This work was supported by the "National Natural Science Foundation of China (41877116).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wolde Tefera: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data processing, Writing- Original draft preparation; Weldemariam Seifu: Reviewing and Editing; Shengke Tian: Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Tanmoy Karak.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tefera, W., Seifu, W. & Tian, S. Coconut shell-derived biochar and oyster shell powder alter rhizosphere soil biochemical properties and Cd uptake of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 10835–10846 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04658-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04658-y