Abstract
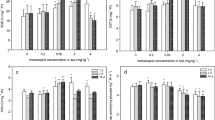
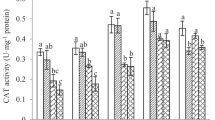
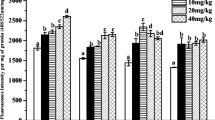
Diuron is a widely used herbicide worldwide, and its toxic effects on aquatic and amphibious organisms have received extensive concerns. However, little information is available regarding the impacts of diuron on non-target soil organism earthworm. Thus, this work investigated the toxic effects of environmentally relevant concentrations (i.e., 0.05, 0.5, and 5.0 mg/kg soil) of diuron on earthworm Eisenia fetida according to multiple biomarkers including oxidative stress, DNA damage, and histopathology. Results showed that diuron significantly induced the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and presented a dose–effect relationship (R2 > 0.6) during the first 21 days of exposure. On the seventh day, the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in E. fetida exposed to 0.05, 0.5, and 5.0 mg/kg of diuron decreased by 3.3%, 17.8%, and 37.4% with respect to the control, respectively, while the activities of catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POD), and glutathione S-transferase (GST), as well as the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) increased to varying degrees. Diuron resulted in low damage of coelomocyte DNA in E. fetida, while no tissue damage was observed on days 7 and 14. At the end of exposure period (28 d), except for ROS, all other biomarkers in the diuron-treated groups were restored to the control level. Integrated biological response (IBR) showed that ROS and GST are sensitive biomarkers to monitor the potential toxicity effect of diuron on E. fetida. The results of this study provide valuable information for risk assessment of diuron on soil ecosystem health.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aly MAS, Schröder P (2008) Effect of herbicides on glutathione S-transferases in the earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environ Sci Pollut Res 15:143–149. https://doi.org/10.1065/espr2007.02.385
Baer U, Calvet R (1999) Fate of soil applied herbicides: experimental data and prediction of dissipation kinetics. J Environ Qual 28:1765–1777. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1999.00472425002800060012x
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Bretaud S, Toutant JP, Saglio P (2000) Effects of carbofuran, diuron, and nicosulfuron on acetylcholinesterase activity in goldfish (Carassius auratus). Ecotox Environ Safe 47:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1006/eesa.2000.1954
Button M, Jenkin GRT, Bowman KJ et al (2010) DNA damage in earthworms from highly contaminated soils: Assessing resistance to arsenic toxicity by use of the comet assay. Mutat Res-Gen Tox En 696:95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2009.12.009
Calisi A, Lionetto MG, Schettino T (2009) Pollutant-induced alterations of granulocyte morphology in the earthworm Eisenia foetida. Ecotox Environ Safe 72:1369–1377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2009.03.010
Ching EWK, Siu WHL, Lam PKS et al (2001) DNA adduct formation and DNA strand breaks in green-lipped Mussels (Perna viridis) exposed to benzo[a]pyrene: dose-and time-dependent relationships. Mar Pollut Bull 42:603–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00209-5
Dogan D, Can C, Kocyigit A, Dikilitas M, Taskin A, Bilinc H (2011) Dimethoate-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in Oncorhynchus mykiss. Chemosphere 84:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.02.087
Dores EFGC, Spadotto CA, Weber OLS et al (2009) Environmental behaviour of metolachlor and diuron in a tropical soil in the central region of Brazil. Water Air Soil Poll 197:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-008-9801-1
Du L, Li G, Liu M et al (2015) Evaluation of DNA damage and antioxidant system induced by di-n-butyl phthalates exposure in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecotox Environ Safe 115:75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.01.031
Durak I, Yurtarslanl Z, Canbolat O, Akyol Ö (1993) A methodological approach to superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity assay based on inhibition of nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) reduction. Clin Chim Acta 214:103–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-8981(93)90307-P
El-Nahhal Y, Abadsa M, Affifi S (2013) Adsorption of diuron and linuron in Gaza soils. Amer J Anal Chem 4:94–99. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajac.2013.47A013
Eyambe GS, Goven AJ, Fitzpatrick LC, Venables BJ, Cooper EL (1991) A non-invasive technique for sequential collection of earthworm ( Lumbricus terrestris ) leukocytes during subchronic immunotoxicity studies. Lab Anim 25:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1258/002367791780808095
Fang K, Han L, Liu Y, Fang J, Wang X, Liu T (2021) Enantioselective bioaccumulation and detoxification mechanisms of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to mandipropamid. Sci Total Environ 796:149051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149051
Finkel T (2011) Signal transduction by reactive oxygen species. J Cell Biol 194:7–15. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201102095
Fugère V, Hébert M-P, da Costa NB et al (2020) Community rescue in experimental phytoplankton communities facing severe herbicide pollution. Nat Ecol Evol 4:578–588. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-020-1134-5
Giacomazzi S, Cochet N (2004) Environmental impact of diuron transformation: a review. Chemosphere 56(11):1021–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.04.061
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Bioch 48:909–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.016
Gooddy DC, Chilton PJ, Harrison I (2002) A field study to assess the degradation and transport of diuron and its metabolites in a calcareous soil. Sci Total Environ 297:67–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00079-7
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-Transferases: The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Hou J, You G, Xu Y et al (2016) Antioxidant enzyme activities as biomarkers of fluvial biofilm to ZnO NPs ecotoxicity and the integrated biomarker responses (IBR) assessment. Ecotox Environ Safe 133:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.06.014
Jouquet P, Dauber J, Lagerlöf J, Lavelle P, Lepage M (2006) Soil invertebrates as ecosystem engineers: intended and accidental effects on soil and feedback loops. Appl Soil Ecol 32:153–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2005.07.004
Kamarudin NA, Zulkifli SZ, Azmai MNA, Abdul AFZ, Ismail A (2020) Herbicide diuron as endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) through histopathalogical analysis in gonads of javanese medaka (Oryzias javanicus, Bleeker 1854). Animals 10:525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030525
Kasozi GN, Nkedi-Kizza P, Agyin-Birikorang S, Zimmerman AR (2010) Characterization of adsorption and degradation of diuron in carbonatic and noncarbonatic soils. J Agric Food Chem 58:1055–1061. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf902792p
Kochba J, Lavee S, Spiegel-Roy P (1977) Differences in peroxidase activity and isoenzymes in embryogenic ane non-embryogenic ‘Shamouti’ orange ovular callus lines1. Plant Cell Phys 18:463–467. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a075455
Końca K, Lankoff A, Banasik A et al (2003) A cross-platform public domain PC image-analysis program for the comet assay. Mutat Res-Gen Tox En 534:15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1383-5718(02)00251-6
Lackmann C, Velki M, Seiler T-B, Hollert H (2018) Herbicides diuron and fluazifop-p-butyl affect avoidance response and multixenobiotic resistance activity in earthworm Eisenia andrei. Chemosphere 210:110–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.07.008
Łaszczyca P, Augustyniak M, Babczyńska A et al (2004) Profiles of enzymatic activity in earthworms from zinc, lead and cadmium polluted areas near Olkusz (Poland). Environ Int 30:901–910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2004.02.006
Lawler JM, Song W, Demaree SR (2003) Hindlimb unloading increases oxidative stress and disrupts antioxidant capacity in skeletal muscle. Free Radical Bio Med 35:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(03)00186-2
Li X, Zhu L, Du Z et al (2018) Mesotrione-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecol Indic 95:436–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.08.001
Li M, Ma X, Saleem M et al (2020) Biochemical response, histopathological change and DNA damage in earthworm (Eisenia fetida) exposed to sulfentrazone herbicide. Ecol Indic 115:106465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106465
Li M, Ma X, Wang Y, Saleem M, Yang Y, Zhang Q (2022) Ecotoxicity of herbicide carfentrazone-ethyl towards earthworm Eisenia fetida in soil. Comp Biochem Phys C 253:109250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2021.109250
Lin D, Zhou Q, Xie X, Liu Y (2010) Potential biochemical and genetic toxicity of triclosan as an emerging pollutant on earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 81:1328–1333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.08.027
Lin D, Xie X, Zhou Q, Liu Y (2012) Biochemical and genotoxic effect of triclosan on earthworms (Eisenia fetida) using contact and soil tests. Environ Toxicol 27:385–392. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20651
Liu Y, Xu Z, Wu X, Gui W, Zhu G (2010) Adsorption and desorption behavior of herbicide diuron on various Chinese cultivated soils. J Hazard Mater 178:462–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.01.105
Madhum YA, Freed VH (1987) Degradation of the herbicides bromacil, diuron and chlortoluron in soil. Chemosphere 16:1003–1011. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(87)90037-3
Mitchelmore CL, Birmelin C, Livingstone DR, Chipman JK (1998) Detection of DNA strand breaks in isolated mussel (Mytilus edulisL.) digestive gland cells using the “Comet” assay. Ecotox Environ Safe 41:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1006/eesa.1998.1666
Moon Y-S, Kim M, Hong CP, Kang JH, Jung JH (2019) Overlapping and unique toxic effects of three alternative antifouling biocides (Diuron, Irgarol 1051®, Sea-Nine 211®) on non-target marine fish. Ecotox Environ Safe 180:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.04.070
Moreira RA, Freitas JS, da Silva Pinto TJ et al (2019) Mortality, spatial avoidance and swimming behavior of bullfrog tadpoles (Lithobates catesbeianus) exposed to the herbicide diuron. Water Air Soil Pollut 230:125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4168-z
Morowati M (2000) Histochemical and histopathological study of the intestine of the earthworm (Pheretima elongata) exposed to a field dose of the herbicide glyphosate. Environmentalist 20:105–111. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006704009184
Muendo BM, Shikuku VO, Getenga ZM, Lalah JO, Wandiga SO, Rothballer M (2021) Adsorption-desorption and leaching behavior of diuron on selected Kenyan agricultural soils. Heliyon 7:e06073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06073
OECD., (1984) Test No 207: Earthworm Acute Toxicity Tests. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris
Oliveira M, Maria VL, Ahmad I et al (2009) Contamination assessment of a coastal lagoon (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal) using defence and damage biochemical indicators in gill of Liza aurata–An integrated biomarker approach. Environ Pollut 157:959–967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.10.019
Ostling O, Johanson KJ (1984) Microelectrophoretic study of radiation-induced DNA damages in individual mammalian cells. Biochem Bioph Res Co 123:291–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291X(84)90411-X
Pelosi C, Barot S, Capowiez Y, Hedde M, Vandenbulcke F (2014) Pesticides and earthworms. A Review Agron Sustain Dev 34:199–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-013-0151-z
Qi S, Wang D, Zhu L et al (2018) Effects of a novel neonicotinoid insecticide cycloxaprid on earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:14138–14147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1624-z
Rocha PRR, Faria AT, Silva GSD, Queiroz M, Silva A (2013) Half-life of diuron in soils with different physical and chemical attributes. Ciência Rural 43:1961–1966. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-84782013001100007
Rouchaud J, Neus O, Bulcke R, Cools K, Eelen H, Dekkers T (2000) Soil dissipation of diuron, chlorotoluron, simazine, propyzamide, and diflufenican herbicides after repeated applications in fruit tree orchards. Arch Environ Con Tox 39:60–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002440010080
Saint-Denis M, Narbonne JF, Arnaud C, Ribera D (2001) Biochemical responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida andrei exposed to contaminated artificial soil: effects of lead acetate. Soil Biol Biochem 33:395–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00177-2
Sanchez W, Burgeot T, Porcher J-M (2013) A novel “Integrated Biomarker Response” calculation based on reference deviation concept. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2721–2725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1359-1
Schieber M, Chandel NS (2014) ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol 24:R453–R462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.03.034
Sharma P, Jha AB, Dubey RS, Pessarakli M (2012) Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J Bot 2012:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/217037
Shi Z, Tang Z, Wang C (2017) A brief review and evaluation of earthworm biomarkers in soil pollution assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:13284–13294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8784-0
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4827(88)90265-0
Soares C, de Sousa A, Pinto A et al (2016) Effect of 24-epibrassinolide on ROS content, antioxidant system, lipid peroxidation and Ni uptake in Solanum nigrum L. under Ni stress. Environ Exp Bo 122:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2015.09.010
Song Y, Zhu LS, Wang J, Wang JH, Liu W, Xie H (2009) DNA damage and effects on antioxidative enzymes in earthworm (Eisenia foetida) induced by atrazine. Soil Biol Biochem 41:905–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.09.009
Song P, Gao J, Li X et al (2019) Phthalate induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Environ Int 129:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.04.074
Van Bruggen AHC, He MM, Shin K et al (2018) Environmental and health effects of the herbicide glyphosate. Sci Total Environ 616–617:255–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.309
Velki M, Di Paolo C, Nelles J, Seiler TB, Hollert H (2017) Diuron and diazinon alter the behavior of zebrafish embryos and larvae in the absence of acute toxicity. Chemosphere 180:65–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.04.017
Wang K, Pang S, Mu X et al (2015) Biological response of earthworm, Eisenia fetida, to five neonicotinoid insecticides. Chemosphere 132:120–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.002
Wang X, Martínez MA, Wu Q et al (2016) Fipronil insecticide toxicology: oxidative stress and metabolism. Crit Rev Toxicol 46:876–899. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408444.2016.1223014
Wang C, Zhang Q, Wang F, Liang W (2017) Toxicological effects of dimethomorph on soil enzymatic activity and soil earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 169:316–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.090
Wang C, Harwood JD, Zhang Q (2018) Oxidative stress and DNA damage in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) exposed to the herbicide mesotrione. Chemosphere 193:1080–1086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.148
Xiang R, Wang DN (1990) The improvement of lipid peroxidation thiobarbituric acid spectrophotometry. Prog Biochem Biophys 17:241–242
Xu J, Yuan X, Lang P (1997) The determination of enzymic activity and its inhibition on catalase by ultraviolet spectrophotometry. Environ Chem 16:73–76
Yang Y, Xiao Y, Chang Y, Cui Y, Klobučar G, Li M (2018) Intestinal damage, neurotoxicity and biochemical responses caused by tris (2-chloroethyl) phosphate and tricresyl phosphate on earthworm. Ecotox Environ Safe 158:78–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.04.012
Yao X, Zhang F, Qiao Z et al (2020) Toxicity of thifluzamide in earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Ecotox Environ Safe 188:109880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109880
Zhang Q, Zhu L, Wang J et al (2013) Oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in the earthworm Eisenia fetida induced by low doses of fomesafen. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:201–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0962-5
Zhang Q, Zhang B, Wang C (2014) Ecotoxicological effects on the earthworm Eisenia fetida following exposure to soil contaminated with imidacloprid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:12345–12353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3178-z
Zhang Q, Zhang G, Yin P et al (2015) Toxicological effects of soil contaminated with spirotetramat to the earthworm Eiseniafetida. Chemosphere 139:138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.05.091
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the support of the project from Natural Science Foundation (ZR2016CM11) and Primary Research & Development Plan (2017GSF21112) of Shandong Province, China. We thank three anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions on our manuscript. We also thank Ms. Mu Yalin (a member of our laboratory) for her assistance in paper revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Jing Chen.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, Y., Ma, X. et al. Ecotoxicity of herbicide diuron on the earthworm Eisenia fetida: oxidative stress, histopathology, and DNA damage. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 6175–6184 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04348-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04348-9