Abstract
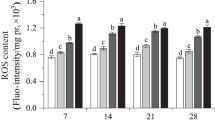
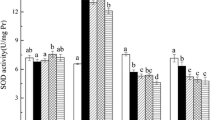
Imidacloprid, a neonicotinoid insecticide, has been used widely in agriculture worldwide. The adverse effects of imidacloprid on exposed biota have brought it increasing attention. However, knowledge about the effects of imidacloprid on antioxidant defense systems and digestive systems in the earthworm is vague and not comprehensive. In the present study, the changes in the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POD), cellulase, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and malondialdehyde (MDA) in the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to artificial soil treated with imidacloprid were examined systematically. The results showed that the activity of these biomarkers was closely related to the dose and duration of the exposure to imidacloprid. The activity of SOD was stimulated significantly at doses of 0.66 and 2 mg kg−1 imidacloprid but markedly inhibited at a dose of 4 mg kg−1 imidacloprid with prolonged exposure. The activities of CAT and POD increased irregularly at 0.2–4 mg kg−1 imidacloprid over different exposure times. The level of ROS at a dose of 2 or 4 mg kg−1 imidacloprid was significantly increased over the entire exposure period. When the concentration of imidacloprid was above 0.66 mg kg−1, the balance of the activity of the antioxidant enzymes and ROS level was interrupted. The activity of cellulase decreased significantly with prolonged exposure. At the stress of 4 mg kg−1 imidacloprid, the content of MDA was significantly increased with increasing exposure time. The results of the present study suggest that imidacloprid has a potentially harmful effect on E. fetida and may be helpful for assessment of the risk of imidacloprid to the soil ecosystem environment. However, to obtain more comprehensive toxicity data, it is necessary to investigate the effects of imidacloprid on earthworm using native soils in the future work.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bradham KD, Dayton EA, Basta NT, Schroder J, Payton M, Lanno RP (2006) Effect of soil properties on lead bioavailability and toxicity to earthworms. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:769–775
Capowiez Y, Rault M, Mazzia C, Belzunces L (2003) Earthworm behaviour as a biomarker—a case study using imidacloprid: The 7th international symposium on earthworm ecology Cardiff Wales 2002. Pedobiologia 47:542–547
Capowiez Y, Bastardie F, Costagliola G (2006) Sublethal effects of imidacloprid on the burrowing behaviour of two earthworm species: modifications of the 3D burrow systems in artificial cores and consequences on gas diffusion in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 38:285–293
Chen C, Wang YH, Zhao XP, Wang Q, Qian YZ (2014) Comparative and combined acute toxicity of butachlor, imidacloprid and chlorpyrifos on earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 100:111–115
Dittbrenner N, Moser I, Triebskorn R, Capowiez Y (2011) Assessment of short and long-term effects of imidacloprid on the burrowing behaviour of two earthworm species (Aporrectodea caliginosa and Lumbricus terrestris) by using 2D and 3D post-exposure techniques. Chemosphere 84:1349–1355
Durak I, Yurtarslanl Z, Canbolat O, Akyol Ö (1993) A methodological approach to superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity assay based on inhibition of nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) reduction. Clin Chim Acta 214:103–104
Fazeli F, Ghorbanli M, Niknam V (2007) Effect of drought on biomass, protein content, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in two sesame cultivars. Biol Plantarum 51:98–103
Felsot A, Cone W, Yu J, Ruppert J (1998) Distribution of imidacloprid in soil following subsurface drip chemigation. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 60:363–370
Fitzgerald DG, Warner KA, Lanno RP, Dixon DG (1996) Assessing the effects of modifying factors on pentachlorophenol toxicity to earthworms: applications of body residues. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:2299–2304
Garcia M, Römbke J, de Brito MT, Scheffczyk A (2008) Effects of three pesticides on the avoidance behavior of earthworms in laboratory tests performed under temperate and tropical conditions. Environ Pollut 153:450–456
Geret F, Serafim A, Barreira L, Bebianno MJ (2002) Effect of cadmium on antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in the gills of the clam Ruditapes decussates. Biomarkers 7:242–256
Ghose T (1987) Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure Appl Chem 59:257–268
Holovská K, Lenartova V, Rosival I, Kičinková M, Majerčiaková A, Legáth J (1998) Antioxidant and detoxifying enzymes in the liver and kidney of pheasants after intoxication by herbicides MCPA and ANITEN. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 12:235–244
Jain M, Mathur G, Koul S, Sarin N (2001) Ameliorative effects of proline on salt stress-induced lipid peroxidation in cell lines of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Cell Rep 20:463–468
Jemec A, Tišler T, Drobne D, Sepčić K, Fournier D, Trebše P (2007) Comparative toxicity of imidacloprid, of its commercial liquid formulation and of diazinon to a non-target arthropod, the microcrustacean Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 68:1408–1418
Juraske R, Castells F, Vijay A, Muñoz P, Antón A (2009) Uptake and persistence of pesticides in plants: Measurements and model estimates for imidacloprid after foliar and soil application. J Hazard Mater 165:683–689
Kobori Y, Amano H (2004) Effects of agrochemicals on life-history parameters of Aphidius gifuensis Ashmead (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Appl Entomol Zool 39:255–261
Krohn J. Hellpointner E (2002) Environmental fate of imidacloprid. Pflanzenschutz Nachrichten Bayer, Special Edition, 55:1-26
Lal O, Palta R, Srivastava Y (2001) Impact of imidacloprid and carbofuran on earthworm castings in okra field. Ann Plant Prot Sci 9:137–138
Laurent FM, Rathahao E (2003) Distribution of [14C] imidacloprid in sunflowers (Helianthus annuus L.) following seed treatment. J Agric Food Chem 51:8005–8010
Lawler JM, Song W, Demaree SR (2003) Hindlimb unloading increases oxidative stress and disrupts antioxidant capacity in skeletal muscle. Free Radical Bio Med 35:9–16
Laycock I, Lenthall KM, Barratt AT, Cresswell JE (2012) Effects of imidacloprid, a neonicotinoid pesticide, on reproduction in worker bumble bees (Bombus terrestris). Ecotoxicology 21:1937–1945
Lin DS, Zhou QX, Xie XJ, Liu Y (2010) Potential biochemical and genetic toxicity of triclosan as an emerging pollutant on earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 81:1328–1333
Liu W, Zheng W, Ma Y, Liu KK (2006) Sorption and degradation of imidacloprid in soil and water. J Environ Sci Health B 41:623–634
Liu Y, Zhou QX, Xie XJ, Lin DS, Dong LX (2010) Oxidative stress and DNA damage in the earthworm Eisenia fetida induced by toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene. Ecotoxicology 19:1551–1559
Liu ZH, Dai YJ, Huang GD, Gu YY, Ni J, Wei H, Yuan S (2011) Soil microbial degradation of neonicotinoid insecticides imidacloprid, acetamiprid, thiacloprid and imidaclothiz and its effect on the persistence of bioefficacy against horsebean aphid Aphis craccivora Koch after soil application. Pest Manag Sci 67:1245–1252
Lukkari T, Taavitsainen M, Soimasuo M, Oikari A, Haimi J (2004) Biomarker responses of the earthworm Aporrectodea tuberculata to copper and zinc exposure: differences between populations with and without earlier metal exposure. Environ Pollut 129:377–386
Luo Y, Zang Y, Zhong Y, Kong ZM (1999) Toxicological study of two novel pesticides on earthworm Eisenia foetida. Chemosphere 39:2347–2356
Ma WC, Bodt J (1993) Differences in toxicity of the insecticide chlorpyrifos to six species of earthworms (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae) in standardized soil tests. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 50:864–870
Maity S, Roy S, Chaudhury S, Bhattacharya S (2008) Antioxidant responses of the earthworm Lampito mauritii exposed to Pb and Zn contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 151:1–7
Matsuda K, Buckingham SD, Kleier D, Rauh JJ, Grauso M, Sattelle DB (2001) Neonicotinoids: insecticides acting on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:573–580
Nordberg J, Arner ES (2001) Reactive oxygen species, antioxidants, and the mammalian thioredoxin system. Free Radical Bio Med 31:1287–1312
OECD (2004) Guidelines for testing of chemicals no. 222: earthworm reproduction tests (Eisenia fetida/Eisenia andrei). Organization for economic co-operation and development (OECD), Paris
Oi M (1999) Time-dependent sorption of imidacloprid in two different soils. J Agric Food Chem 47:327–332
Phillips PJ, Bode RW (2002) Concentrations of pesticides and pesticide degradates in the Croton River watershed in southeastern New York, July-September 2000. US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey
Poljšak B, Dahmane R (2012) Free radicals and extrinsic skin aging. Dermatol Res Pract Article ID 135206, 4 pages
Sardo A, Soares A (2010) Assessment of the effects of the pesticide imidacloprid on the behaviour of the aquatic oligochaete Lumbriculus variegatus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:648–656
Shalata A, Tal M (1998) The effect of salt stress on lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in the leaf of the cultivated tomato and its wild salt-tolerant relative Lycopersicon pennellii. Physiol Plant 104:169–174
Shi YJ, Shi YJ, Wang X, Lu YL, Yan SF (2007) Comparative effects of lindane and deltamethrin on mortality, growth, and cellulase activity in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Pestic Biochem Physiol 89:31–38
Song Y, Zhu LS, Wang J, Wang JH, Liu W, Xie H (2009) DNA damage and effects on antioxidative enzymes in earthworm (Eisenia foetida) induced by atrazine. Soil Biol Biochem 41:905–909
Suchail S, Guez D, Belzunces LP (2001) Discrepancy between acute and chronic toxicity induced by imidacloprid and its metabolites in Apis mellifera. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2482–2486
Sun YY, Yin Y, Zhang JF, Yu HX, Wang XR (2007) Bioaccumulation and ROS generation in liver of freshwater fish, goldfish Carassius auratus under HC Orange No. 1 exposure. Environ Toxicol 22:256–263
Sur R, Stork A (2003) Uptake, translocation and metabolism of imidacloprid in plants. B Insectol 56:35–40
Tejada M, Gómez I, Hernández T, García C (2010) Response of Eisenia fetida to the application of different organic wastes in an aluminium-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1944–1949
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M, Telser J (2007) Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:44–84
Xiang R, Wang DN (1990) The improvement of lipid peroxidation thiobarbituric acid spectrophotometry. Prog Biochem Biophys 17:241–243
Xiao NW, Jing B, Ge F, Liu XH (2006) The fate of herbicide acetochlor and its toxicity to Eisenia fetida under laboratory conditions. Chemosphere 62:1366–1373
Xu JB, Yuan XF, Lang PZ (1997) Determination of catalase activity and catalase inhibition by ultraviolet spectrophotometry. Environ Chem 16:73–76 (in chinese)
Yasmin S, D’Souza D (2007) Effect of pesticides on the reproductive output of Eisenia fetida. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:529–532
Zang Y, Zhong Y, Luo Y, Kong ZM (2000) Genotoxicity of two novel pesticides for the earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 108:271–278
Zhang BG, Li GT, Shen TS, Wang JK, Sun Z (2000) Changes in microbial biomass C, N, and P and enzyme activities in soil incubated with the earthworms Metaphire guillelmi or Eisenia fetida. Soil Biol Biochem 32:2055–2062
Zhang FQ, Wang YS, Lou ZP, Dong JD (2007) Effect of heavy metal stress on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of two mangrove plant seedlings (Kandelia candel and Bruguiera gymnorrhiza). Chemosphere 67:44–50
Zhang QM, Zhu LS, Wang J, Xie H, Wang JH, Han YN, Yang JH (2013) Oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in the earthworm Eisenia fetida induced by low doses of fomesafen. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:201–208
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41101488) and Tai-Shan Scholar Construction Foundation of Shandong Province, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Markus Hecker
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Zhang, B. & Wang, C. Ecotoxicological effects on the earthworm Eisenia fetida following exposure to soil contaminated with imidacloprid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 12345–12353 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3178-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3178-z