Abstract
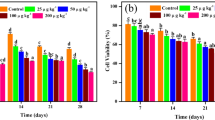
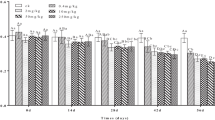
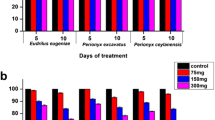
In the agricultural sector, excessive utilization of pesticides has contaminated soil at an alarming level. This leads to alteration in the structure and fertility of soil ecosystems which further results in an imbalance between flora and fauna of the soil. Earthworm is an important soil macrofauna and a key indicator species in ecotoxicological risk assessment of pesticide-contaminated soil. Neonicotinoids have become the extensively used group of pesticides in the world. As a novel neonicotinoids insecticide, clothianidin has been commonly utilized for crop protection with high biological effectiveness against different pests. The present study aimed to determine the tolerance and avoidance response of earthworms towards clothianidin (Dantotsu 50% WDG) in terms of various parameters like mortality, growth, reproduction, and enzyme activities by using an artificial soil medium. The results showed that 7 days and 14 days LC50 value of clothianidin was 16.01 and 12.00 mg/kg while EC50 value of clothianidin was 2.61 mg/kg. In growth and reproduction test, a significant decrease in body weight of earthworm was observed. Cocoon number, cocoon weight and hatchling production were also decreased significantly with an increase in concentration and exposure time. Based on growth and reproduction tests, earthworms showed tolerance potential up to 24 mg/kg till 14th day of exposure period. Different enzyme activities such as SOD, CAT, GST and POD were also carried out and significant changes were observed in dose and time-dependent manner.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. In: Packer L (ed) Methods in enzymology. Academic press, Inc., New York, pp 121–126
Blouin M, Hodson ME, Delgado EA, Baker G, Brussaard L, Butt KR, Dai J, Dendooven L, Peres G, Tondoh JE, Cluzeau D, Brun JJ (2013) A review of earthworm impact on soil function and ecosystem services. Eur J Soil Sci 64:161–182
Botías C, David A, Hill EM, Goulson D (2016) Contamination of wild plants near neonicotinoid seed-treated crops and implications for non-target insects. Sci Total Environ 566:269–278
Calabrese EJ (2005) Paradigm lost, paradigm found: the re-emergence of hormesis as a fundamental dose response model in the toxicological sciences. Environ Pollut 3:378–411
Capowiez Y, Bastardie F, Costagliola G (2006) Sublethal effects of imidacloprid on the burrowing behaviour of two earthworm species: Modifications of the 3D burrow systems in artificial cores and consequences on gas diffusion in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 38:285–293
Casida JE (2011) Neonicotinoid metabolism: compounds, substituents, pathways, enzymes, organisms and relevance. J Agric Food Chem 59:2923–2931
Chen C, Zhou QX, Liu S, Xiu ZM (2011) Acute toxicity, biochemical and gene expression responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to polycyclic musks. Chemosphere 83:1147–1154
Dabrowski JM, Shadung JM, Wepener V (2014) Prioritizing agricultural pesticides used in South Africa based on their environmental mobility and potential human health effects. Environ Int 62:31–40
Datta S, Singh J, Singh J, Singh S, Singh S (2021) Avoidance behavior of Eisenia fetida and Metaphire posthuma towards two different pesticides, acephate and atrazine. Chemosphere 278:130476
De Silva PMC, Van Gestel CA (2009a) Development of an alternative artificial soil for earthworm toxicity testing in tropical countries. Appl Soil Ecol 43:170–174
De Silva PMC, van Gestel CA (2009b) Comparative sensitivity of Eisenia andrei and Perionyx excavatus in earthworm avoidance tests using two soil types in the tropics. Chemosphere 77:1609–1613
Espinosa-Reyes G, Costilla-Salazar R, Pérez-Vázquez FJ, González-Mille DJ, Flores-Ramírez R, del Carmen C-Díaz M, Medellin-Garibay SE, Ilizaliturri-Hernández CA (2019) DNA damage in earthworms by exposure of Persistent Organic Pollutants in low basin of Coatzacoalcos River, Mexico. Sci Total Environ 65:1236–1242
Furlan L, Kreutzweiser D (2015) Alternatives to neonicotinoid insecticides for pest control: case studies in agriculture and forestry. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:135–147
Ge J, Xiao Y, Chai Y, Yan H, Wu R, Xin X, Wang D, Yu X (2018) Sub-lethal effects of six neonicotinoids on avoidance behavior and reproduction of earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 162:423–429
Goulson D (2013) An overview of the environmental risks posed by neonicotinoid insecticides. J Appl Ecol 50:977–987
Gowri S, Thangaraj R (2020) Studies on the toxic effects of agrochemical pesticide (Monocrotophos) on physiological and reproductive behavior of indigenous and exotic earthworm species. Int J Environ Health Res 30:212–225
Gu H, Yuan Y, Cai M, Wang D, Lv W (2021) Toxicity of isoprocarb to earthworms (Eisenia fetida): oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, biochemical responses and detoxification mechanisms. Environ Pollut 290:118038
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Han Y, Liu T, Wang J, Wang J, Zhang C, Zhu L (2016) Genotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by the fungicide azoxystrobin in zebrafish (Danio rerio) livers. Pestic Biochem Phys 133:13–19
Hattab S, Boughattas I, Boussetta H, Viarengo A, Banni M, Sforzini S (2015) Transcriptional expression levels and biochemical markers of oxidative stress in theearthworm Eisenia andrei after exposure to 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 122:76–82
Helling B, Sa R, Reinecke AJ (2000) Effects of the fungicide copper oxychloride on the growth and reproduction of Eisenia fetida (Oligochaeta). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 46:108–116
Hu CW, Li M, Cui YB, Li DS, Chen J, Yang LY (2010) Toxicological effects of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles in soil on earthworm Eisenia fetida. Soil Biol Biochem 42:586–591
Hund-Rinke K, Wiechering H (2001) Earthworm avoidance test for soil assessment. J Soils Sediments 1:15–20
International Organization for Standardization (2007) Soil quality-avoidance test for testing the quality of soils and effects of chemicals on behavior: test with earthworms (Eisenia fetida and Eisenia andrei). ISO 17512-1, Geneva
Jeschke P, Nauen R, Schindler M, Elbert A (2011) Overview of the status and global strategy for neonicotinoids. J Agric Food Chem 59:2897–2908
Jones A, Harrington P, Turnbull G (2014) Neonicotinoid concentrations in arable soils after seed treatment applications in preceding years. Pest Manag Sci 70:780–1784
LaCourse EJ, Hernandez-Viadel M, Jefferies JR, Svendsen C, Spurgeon DJ, Barrett J, Morgan AJ, Kille P, Brophy PM (2009) Glutathione transferase (GST) as a candidate molecular-based biomarker for soil toxin exposure in the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus. Environ Pollut 157:2459–2469
Landrum M, Cañas JE, Cobb GP, Jackson WA, Zhang B, Anderson TA (2006) Effects of perchlorate on earthworm (Eisenia fetida) survival and reproductive success. Sci Total Environ 363:237–244
Li X, Zhu L, Du Z, Li B, Wang J, Wang J, Zhu Y (2018) Mesotrione-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecol Indic 95:436–443
Liess M, Beketov M (2011) Traits and stress: keys to identify community effects of low levels of toxicants in test systems. Ecotoxicology 20:328–1340
Liu S, Zhou QX, Wang YY (2011) Ecotoxicological responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to soil contaminated with HHCB. Chemosphere 83:1080–1086
Liu T, Wang X, You X, Chen D, Li Y, Wang F (2017) Oxidative stress and gene expression of earthworm (Eisenia fetida) to clothianidin. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 142:489–496
Liu T, Zhu L, Han Y, Wang J, Wang J, Zhao Y (2014) The cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of metalaxy-M on earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Environ Toxicol Chem 33:2344–2350
Liu X, Sun Z, Chong W, Sun Z, He C (2009) Growth and stress responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida to Escherichia coli O157: H7 in an artificial soil. Microb Pathog 46:266–272
Liu Y, Zhou QX, Xie XJ, Lin DS, Dong LX (2010) Oxidative stress and DNA damage in the earthworm Eisenia fetida induced by toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene. Ecotoxicology 19:1551–1559
Lokke H, Van Gestel CAM (1998) Soil toxicity tests in risk assessment of new and existing chemicals. In: Lokke H, Gestel CAM (Eds.), Handbook of soil invertebrate toxicity tests, Wiley, Chichester, pp 3–19
Lowe CN, Butt KR (2007) Earthworm culture, maintenance and species selection in chronic ecotoxicological studies: a critical review. Eur J Soil Biol 43:S281–S288
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lukkari T, Aatsinki M, Väisänen A, Haimi J (2005) Toxicity of copper and zinc assessed with three different earthworm tests. Appl Soil Ecol 30:133–146
OECD (1984) OECD Guideline for testing of chemicals: Earthworm, Acute Toxicity Tests. 207
OECD (2004) OECD Guideline for the testing of chemicals: Earthworm reproduction test (Eisenia fetida/Eisenia andrei). 222
Oliveira Resende AP, Santos VSV, Campos CF, Morais CRD, de Campos Júnior EO, Oliveira AMMD, Pereira BB (2018) Ecotoxicological risk assessment of contaminated soil from a complex of ceramic industries using earthworm Eisenia fetida. J Toxicol Environ Health Part A 81:1058–1065
Owagboriaye F, Dedeke G, Bamidele J, Aladesida A, Isibor P, Feyisola R, Adeleke M (2020) Biochemical response and vermiremediation assessment of three earthworm species (Alma millsoni, Eudrilus eugeniae and Libyodrilus violaceus) in soil contaminated with a glyphosate-based herbicide. Ecol Indic 108:105678
Pisa LW, Amaral-Rogers V, Belzunces LP, Bonmatin JM, Downs CA, Goulson D, Kreutzweiser DP, Krupke C, Liess M, McField M, Morrissey CA (2015) Effects of neonicotinoids and fipronil on non-target invertebrates. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:68–102
Qi S, Wang D, Zhu L, Teng M, Wang C, Xue X, Wu L (2018) Effects of a novel neonicotinoid insecticide cycloxaprid on earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:14138–14147
Reinecke SA, Reinecke AJ (2007) Biomarker response and biomass change of earthworms exposed to chlorpyrifos in microcosms. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 66:92–101
Roessink I, Merga LB, Zweers HJ, Van den Brink PJ (2013) The neonicotinoid imidacloprid shows high chronic toxicity to mayfly nymphs. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:1096–1100
Saggioro EM, do Espirito Santo DG, Júnior SFS, Hauser-Davis RA, Correia FV (2019) Lethal and sublethal effects of acetamiprid on Eisenia andrei: behavior, reproduction, cytotoxicity and oxidative stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 183:109572
Sanchez-Hernandez JC, Narvaez C, Sabat P, Martinez Mocillo S (2014) Integrated biomarker analysis of chlorpyrifos metabolism and toxicity in the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa. Sci Total Environ 490:445–3455
Satyro S, Saggioro EM, Veríssimo F, Buss DF, de Paiva MD, Oliveira A (2017) Triclocarban: UV photolysis, wastewater disinfection, and ecotoxicity assessment using molecular biomarkers. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:16077–16085
Schreck E, Geret F, Gontier L, Treilhou M (2008) Neurotoxic effect and metabolic responses induced by a mixture of six pesticides on the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa nocturna. Chemosphere 71:1832–1839
Soares C, de Sousa A, Pinto A, Azenha M, Teixeira J, Azevedo RA, Fidalgo F (2016) Effect of 24-epibrassinolide on ROS content, antioxidant system, lipid peroxidation and Ni uptake in Solanum nigrum L. under Ni stress. Environ Exp Bot 122:115–125
Song Y, Zhu LS, Wang J, Wang JH, Liu W, Xie H (2009) DNA damage and effects on antioxidative enzymes in earthworm (Eisenia foetida) induced by atrazine. Soil Biol Biochem 41:905–909
Sparks TC, Nauen R (2015) IRAC: Mode of action classification and insecticide resistance management. Pestic Biochem Phys 121:122–128
Syed Z, Alexander D, Ali J, Unrine J, Shoults-Wilson WA (2017) Chemosensory cues alter earthworm (Eisenia fetida) avoidance of lead-contaminated soil. Environ Toxicol Chem 36:999–1004
Tang H, Yan Q, Wang X, Ai X, Robin P, Matthew C, Qiu J, Li X, Li Y (2016) Earthworm (Eisenia fetida) behavioral and respiration responses to sublethal mercury concentrations in an artificial soil substrate. Appl Soil Ecol 104:48–53
Tsvetkov N, Samson-Robert O, Sood K, Patel HS, Malena DA, Gajiwala PH, Maciukiewicz P, Fournier V, Zayed A (2017) Chronic exposure to neonicotinoids reduces honey bee health near corn crops. Science 356:1395–1397
Uneme H, Konobe M, Akayama A, Yokota T, Mizuta K (2006) Discovery and development of a novel insecticide ‘clothianidin.’ Sumitomo Kagaku 2:1–14
Van Gestel CA, Koolhaas JE, Hamers T, van Hoppe M, van Roovert M, Korsman C, Reinecke SA (2009) Effects of metal pollution on earthworm communities in a contaminated floodplain area: linking biomarker, community and functional responses. Environ Pollut 157:895–903
Wang K, Pang S, Mu X, Qi S, Li D, Cui F, Wang C (2015a) Biological response of earthworm, Eisenia fetida, to five neonicotinoid insecticides. Chemosphere 132:120–126
Wang K, Mu X, Qi S, Chai T, Pang S, Yang Y, Wang C, Jiang J (2015b) Toxicity of a neonicotinoid insecticide, guadipyr, in earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 114:17–22
Wang J, Wang J, Wang G, Zhu L, Wang J (2016) DNA damage and oxidative stress induced by imidacloprid exposure in the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 144:510–517
Wang X, Zhu X, Peng Q, Wang Y, Ge J, Yang G, Wang X, Cai L, Shen W (2019) Multi-level ecotoxicological effects of imidacloprid on earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 219:923–932
Wang Y, Cang T, Zhao X, Yu R, Chen L, Wu C, Wang Q (2012) Comparative acute toxicity of twenty-four insecticides to earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 79:122–128
Xiao N, Jing B, Ge F, Liu X (2006) The fate of herbicide acetochlor and its toxicity to Eisenia fetida under laboratory conditions. Chemosphere 62:1366–1373
Xu D, Li C, Wen Y, Liu W (2013) Antioxidant defense system responses and DNA damage of earthworms exposed to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). Environ Pollut 174:121–127
Xu D, Wen Y, Wang K (2010) Effect of chiral differences of metolachlor and its (S)-isomer on their toxicity to earthworms. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1925–1931
Xu T, Dyer DG, McConnell LL, Bondarenko S, Allen R, Heinemann O (2016) Clothianidin in agricultural soils and uptake into corn pollen and canola nectar after multiyear seed treatment applications. Environ Toxicol Chem 35:311–321
Zhang Q, Zhang B, Wang C (2014) Ecotoxicological effects on the earthworm Eisenia fetida following exposure to soil contaminated with imidacloprid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:12345–12353
Zhang Q, Zhang G, Yin P, Lv Y, Yuan S, Chen J, Wei B, Wang C (2015) Toxicological effects of soil contaminated with spirotetramat to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 139:138–145
Zhang Q, Zhu L, Wang J, Xie H, Wang J, Han Y, Yang J (2013) Oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in the earthworm Eisenia fetida induced by low doses of fomesafen. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:201–208
Zhang Y, Zhang L, Feng L, Mao L, Jiang H (2017) Oxidative stress of imidaclothiz on earthworm Eisenia fetida. Comput Biochem Physiol C Toxicol 191:1–6
Zhao S, Wang Y, Duo L (2021) Biochemical toxicity, lysosomal membrane stability and DNA damage induced by graphene oxide in earthworms. Environ Pollut 269:116225
Zubrod JP, Bundschuh M, Arts G, Brühl CA, Imfeld G, Knäbel A, Payraudeau S, Rasmussen JJ, Rohr J, Scharmüller A, Smalling K (2019) Fungicides: an overlooked pesticide class? Environ Sci Technol 53:3347–3365
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Department of Botanical and Environmental Sciences, Guru Nanak Dev University Amritsar, Punjab, India for the necessary lab facilities.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
APV and JS designed the experiment. ABC performed the experiment, collected and analyzed the data. SS, JQ, RD and DA assisted in experimental work. SS gave useful suggestions for data analysis. The first draft of the manuscript was written by ABC while APV and JS read and revised the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this manuscript.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Chenxi Li.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chowdhary, A.B., Singh, J., Quadar, J. et al. Earthworm’s show tolerance and avoidance response to pesticide clothianidin: effect on antioxidant enzymes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 4245–4254 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04092-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04092-0