Abstract
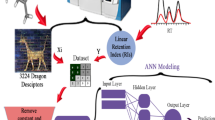
In this research, a dataset including 206 volatile organic compounds was used to develop quantitative structure–retention relationship models for predicting the retention indices of volatile organic compounds on DB-5 stationary phase. A total of 141 molecules were put in train set to build models and 65 molecules were put in test set to validate models, externally. By using stepwise-multiple linear regression, two descriptors including X1sol (solvation connectivity index chi-1) and AAC (mean information index on atomic composition) were selected to create linear and nonlinear quantitative structure–retention relationship models. Multiple linear regression, epsilon-support vector regression and deep learning-based artificial neural network were used as modeling techniques. All models were validated by calculating several statistical parameters for both train and test sets that show created models have high predictive power. R2 values for the test set of multiple linear regression, epsilon-support vector regression and deep learning-based artificial neural network models were 0.90, 0.94 and 0.94, respectively. Results show the Van der Waals interactions of molecules with methyl groups in DB-5 stationary phase and the electrostatic interactions of atoms with partial negative charge in molecules with the hydrogen atoms of phenyl groups in DB-5 stationary phase are responsible for the separation of volatile organic compounds in DB-5 stationary phase. Finally, these created models were used to predict the retention indices of 694 volatile organic compounds that had no retention index data on DB-5 stationary phase.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amos RIJ, Haddad PR, Szucs R, Dolan JW, Pohl CA (2018) Molecular modelling and prediction accuracy in quantitative structure-retention relationship calculations for chromatography. TrAC-Trends Anal Chem 105:352–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.05.019
Atkinson R, Arey J (2003) Atmospheric degradation of volatile organic compounds. Chem Rev 103:4605–4638. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr0206420
Candel A, LeDell E (2020) Deep learning with H2O. H2O.ai, Inc., California
Chang CC, Lin CJ (2011) LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol 2:1–27
Cook D (2017) Practical machine learning with H2O. O’Reilly Media, Inc., United States
Ferré J (2009) Comprehensive Chemometrics, vol 3. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Fouad MA, Tolba EH, El-Shal MA, El Kerdawy AM (2018) QSRR modeling for the chromatographic retention behavior of some β-lactam antibiotics using forward and firefly variable selection algorithms coupled with multiple linear regression. J Chromatogr A 1549:51–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.03.042
Ghavami R, Faham S (2010) QSRR models for kovátsʹ retention indices of a variety of volatile organic compounds on polar and apolar GC stationary phases using molecular connectivity indexes. Chromatographia 72:893–903. https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-010-1741-4
Ghavami R, Sepehri B (2016) QSPR/QSAR solely based on molecular surface electrostatic potentials for benzenoid hydrocarbons. J Iran Chem Soc 13:519–529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-015-0761-2
Gini G, Zanoli F, Gambab A, Raitano G, Benfenati E (2019) Could deep learning in neural networks improve the QSAR models? SAR QSAR Environ Res 30:617–642. https://doi.org/10.1080/1062936X.2019.1650827
Hessling JP (2017) Uncertainty quantification and model calibration. IntechOpen publisher, London
Hester RE, Harrison RM (1995) Volatile organic compounds in the atmosphere. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Jalali-Heravi M, Kyani A (2004) Use of computer-assisted methods for the modeling of the retention time of a variety of volatile organic compounds: a PCA-MLR-ANN approach. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 4:1328–1335. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci0342270
Kaliszan R (2007) QSRR: quantitative structure-(chromatographic) retention relationships. Chem Rev 107:3212–3246. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr068412z
Kim P (2017) MATLAB deep learning: with machine learning, neural networks and artificial intelligence. Apress, Berkeley
Li Q, Su G, Li C, Wang M, Tan L, Gao L, Wu M, Wang Q (2019) Emission profiles, ozone formation potential and health-risk assessment of volatile organic compounds in rubber footwear industries in China. J Hazard Mater 375:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.064
Luan F, Xue C, Zhang R, Zhao C, Liu M, Hu Z, Fan B (2005) Prediction of retention time of a variety of volatile organic compounds based on the heuristic method and support vector machine. Anal Chim Acta 537:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2004.12.085
Majchrzak T, Wojnowski W, Lubinska-Szczygeł M, Różańska A, Namieśnik J, Dymerski T (2018) PTR-MS and GC-MS as complementary techniques for analysis of volatiles: a tutorial review. Anal Chim Acta 1035:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.06.056
Moolayil J (2019) Learn Keras for deep neural networks. Jojo Moolayil, Berkeley
Olsen E, Nielsen F (2001) Predicting vapour pressures of organic compounds from their chemical structure for classification according to the VOC directive and risk assessment in general. Molecules 6:370–389. https://doi.org/10.3390/60400370
Ramadan A, Yassin MF, Alshammari BZ (2019) Health risk assessment associated with volatile organic compounds in a parking garage. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:2549–2564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1641-y
Sarkhosh M, Ghasemi JB, Ayati M (2012) A quantitative structure- property relationship of gas chromatographic/mass spectrometric retention data of 85 volatile organic compounds as air pollutant materials by multivariate methods. Chem Cent J 6:S4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-153X-6-S2-S4
Roy K, Ambure P, Aher RB (2017) How important is to detect systematic error in predictions and understand statistical applicability domain of QSAR models? Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 162:44–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2017.01.010
Sepehri B, Ghavami R (2018) Towards in-silico design of new HSP90 inhibitors: molecular docking and 3D-QSAR CoMFA studies of tetrahydropyrido [4, 3-d] pyrimidine derivatives as HSP90 inhibitors. Med Chem 14:439–450. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573406414666180321151029
Shen X, Zhao Y, Chen Z, Huang D (2013) Heterogeneous reactions of volatile organic compounds in the atmosphere. Atmos Environ 68:297–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.11.027
Skoczylas M, Bocian S, Buszewski B (2020) Quantitative structure-retention relationships of amino acids on the amino acid- and peptide-silica stationary phases for liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1609:460514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460514
Smola AJ, SchöLkopf B (2004) A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat Comput 14:199–222
Song C, Liu B, Dai Q, Li H, Mao H (2019) Temperature dependence and source apportionment of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) at an urban site on the north China plain. Atmos Environ 207:167–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.03.030
Suzuki N, Nakaoka H, Nakayama Y, Takaya K, Tsumura K, Hanazato M, Tanaka S, Matsushita K, Iwayama R, Mori C (2020) Changes in the concentration of volatile organic compounds and aldehydes in newly constructed houses over time. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:333–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02503-3
Todeschini R, Consonni V (2009) Molecular descriptors for chemoinformatics. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co, KGaA, Weinheim
Vapnik VN (1998) Statistical learning theory. Wiley
Xu J, Wang L, Liang G, Wang L, Shen X (2011) A general quantitative structure-property relationship treatment for dielectric constants of polymers. Polym Eng Sci 51:2408–2416. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.22016
Xu X, van Stee LLP, Williams J, Beens J, Adahchour M, Vreuls RJJ, Brinkman UAT, Lelieveld J (2003) Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography (GC×GC) measurements of volatile organic compounds in the atmosphere. Atmos Chem Phys 3:665–682. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-3-665-2003
Zhang X, Gao B, Creamer AE, Cao C, Li Y (2017) Adsorption of VOCs onto engineered carbon materials: a review. J Hazard Mater 338:102–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.05.013
Zhang Z, Li G (2010) A review of advances and new developments in the analysis of biological volatile organic compounds. Microchem J 95:127–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2009.12.017
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Funding
This research has been supported by University of Kurdistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: S. Hussain.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sepehri, B., Ghavami, R., Farahbakhsh, S. et al. Machine learning-based quantitative structure–retention relationship models for predicting the retention indices of volatile organic pollutants. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 1457–1466 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03271-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03271-9